Topic 2 - Organisation
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Principles of Organisation
Cells - Basic building unit of life
Tissue - Group of cells with a similar function.
Organs - Similar tissues performing specific functions.
Organ systems - Organs work together to form an organism.
Mouth
Mechanical digestion by teeth; salivary glands secrete amylase which breaks starch into maltose.
Oesophagus
Food travels to stomach
Stomach
Churns and pummels food.
Pepsin digests proteins (works best in acidic conditions, pH ~2).
Hydrochloric acid kills bacteria.
Small Intestine
Bile (made in liver, stored in gall bladder):
Neutralises stomach acid. Emulsifies fats for easier digestion. Produces enzymes
Large Intestine
Absorbs excess water.
Rectum & Anus
Stores faeces → excretion.
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speeds up a chemical reaction, without being used up itself. Enzymes help to break down food because they catalyse chemical reactions.
Lock and Key Method
Enzymes have an active site and substrate that binds together.
Substrate fits into active site (of enzyme)
Shape of active site is unique to substrate,
Active site and substrate bind together to break the bonds within substrate
Effect of Temperature on Enzymes
Increased temperature → more kinetic energy → faster reactions (up to the optimum temperature).
Beyond optimum, bonds break → enzyme loses shape → denaturation. Denatured enzymes → substrate can't bind → reaction stops.
Effect of pH on Enzymes
Too low/high → bonds break → enzyme denatures. Denatured active site → substrate can’t bind → reaction stops.
Amylase
Produced by: Salivary glands, Pancreas, Small intestine;
Substrate: Starch; Product: Maltose.
Protease
Produced by: Stomach, Pancreas, Small intestine;
Substrate: Protein; Product: Amino acids.
Lipase
Produced by: Pancreas, Small intestine;
Substrate: Lipids; Product: Glycerol + fatty acids.
Enzyme Practical
1. Add 2 cm³ of starch solution and 2 cm³ of amylase solution into separate boiling tubes.
2. Place both tubes in a water bath at 20 °C for 5 minutes.
3. Mix the starch and amylase solutions together.
4. Every 30 seconds, test the mixture with iodine on a spotting tile until the iodine no longer changes colour.
5. Repeat the experiment at 25 °C, 35 °C, and 45 °C.
Key Question: Why did the student leave both tubes in the water bath for 5 minutes in step 2? -
To get both solutions to the same temperature
Food tests
Grind food with pestle and mortar.
Add water, then stir to dissolve the food
Filter solution using filter paper.
Benedict's Test
Tests for: Sugars (e.g., glucose, maltose).
Steps:
Prepare food sample in a test tube
Add Benedict's solution to test tube using pipette.
Heat in 25°C water bath for 5 mins.
Positive result: From Blue to Green or Yellow or Brick-red (depending on sugar concentration).
Iodine Test
Tests for: Starch in foods like rice, pasta, potatoes.
Steps:
Prepare food sample.
Add iodine solution directly.
Positive result: Brown/orange → Blue-black.
Biuret Test
Tests for: Proteins in foods like meat, cheese.
Steps:
Prepare food sample.
Add Biuret solution (mix of potassium hydroxide + copper(II) sulfate).
Positive result: Blue → Purple.
Sudan III Test
Tests for: Lipids in foods like olive oil, milk.
Steps:
Prepare food sample.
Add Sudan III solution.
Shake gently.
Positive result: Red layer on top.
Heart
Organ that pumps blood around the body via a double circulatory system.
Right Ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs for oxygen
Left Ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood around the body, where oxygen is used up
Oxygenated blood from lungs to body cells:
Blood travels through the pulmonary vein
Blood enters left atrium
Blood enters the left ventricle
Blood leaves the heart through the aorta then to body
Deoxygenated blood from body cells to lungs:
Blood travels through the vena cava
Blood enters right atrium
Blood enters the right ventricle
Blood leaves the heart through the pulmonary artery then to lungs
Vessels travel
Vessel | Blood Type | From —> To | Mnemonic |
Vena Cava | Deoxygenated | Body —> Right Atrium | "Vicious Cats Dance But Run Aggressively." |
Pulmonary Artery | Deoxygenated | Right ventricle —> Lungs | "Penguins And Ducks Race Very Loudly." |
Pulmonary Vein | Oxygenated | Lungs —> Left atrium | "Purple Vampires Often Love Lemon Apples." |
Aorta | Oxygenated | Left Ventricle —> Body | "Always Observe Little Vulnerable Birds." |
Pacemaker (Natural)
Group of cells in right atrium that controls heartbeat.
Pacemaker (Artificial)
Electrical device fitted to control irregular heartbeat.
Artery
Thick walls, narrow lumen
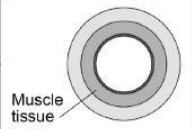
Artery Function
Carries high-pressure oxygenated blood around body’s organ
Vein
Thin walls, large lumen(hole),
valves(prevents backflow of blood).
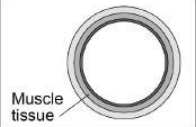
Vein Function
Return low pressure deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart
Capillary
One cell thick; allows exchange of substances with tissues.
Lungs
Trachea → Bronchi → Bronchioles → Alveoli ➔ Air Pathway: "The Best Battles Are Amazing."
Air enters through the trachea (big tube), splits into two bronchi (one to each lung), branches into smaller bronchioles, and finally reaches the alveoli (tiny air sacs for gas exchange).
Alveoli adaptations
Adaptation | Explanation |
Large surface area | More space for oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse quickly. |
Thin walls | Short diffusion distance, making gas exchange faster and more efficient. |
Moist | Gases dissolve easily, helping diffusion across alveolar walls. |
Good blood supply | Maintains a steep concentration gradient for faster diffusion of gases. |
Red Blood Cells
Transport oxygen around the body.
Biconcave shape for large surface area; no nucleus to maximise space.
White Blood Cells
Defend body against pathogens; have a nucleus.
Platelets
Forms blood clot at wound. - Prevent excessive bleeding and entry of pathogens.
Plasma
Carries blood cells, nutrients, CO₂, urea, hormones, heat around body
Coronary Heart Disease
Build-up of fatty material in coronary arteries → reduced oxygen → heart attacks.
Statins
Drugs that lower LDL ('bad') cholesterol by:
Inhibiting its production in the liver
Reducing fatty build-up in arteries
Lowering the risk of coronary heart disease.
Statins advantages
Lower risk of heart attacks, strokes, and CHD.
May prevent other diseases.
Increase HDL cholesterol levels
Statins disadvantages
Must be taken regularly over a long period.
Takes time to become effective.
Possible side effects: muscle and joint pain, kidney problems
Stents
Small tubes inserted into arteries to widen them and allow blood flow.
Stents advantages
Quickly restore blood flow to the heart muscle.
Effective at reducing the risk of heart attacks.
Long-lasting solution.
Procedure is relatively simple and minimally invasive
Stents disadvantages
Risk of blood clots (thrombosis) forming around the stent.
Risk of infection during the procedure.
Potential damage to the blood vessel during insertion
Weak Immune System
Higher risk of infection and illness.
Cancer
Uncontrolled cell division forming tumours.
Benign Tumour
Non-cancerous; grows in one place and doesn’t invade other tissues.
Malignant Tumour
Cells divide uncontrollably, invade nearby tissues, and spread via the bloodstream to form secondary tumours.
Cancer Risk Factors
Lifestyle: Smoking (lung cancer), obesity (bowel, kidney), alcohol.
Environment: UV radiation (skin cancer).
Infections: HPV (linked to cervical cancer).
Genetic: Inherited faulty genes (e.g. BRCA in breast cancer).
Epidermal Tissue (Plant)
Covers plant surfaces; protects; secretes waxy cuticle to reduce water loss.
Palisade Mesophyll
Packed with chloroplasts → main site of photosynthesis
Spongy Mesophyll
Loosely packed cells for gas exchange; air spaces increase diffusion.
Xylem
Transports water and minerals from roots to leaves (one-way).
Phloem
Transports sugars from leaves to rest of the plant (two-way, translocation).
Meristem
Found in root/shoot tips; cells divide by mitosis for growth.
Leaf Adaptation
Flat shape: Increases surface area for light absorption.
Thin: Short diffusion path for gases.
Large surface area: Maximises light capture.
Root Hair Cells
Long projections: Increase surface area.
Thin cell walls: Short diffusion path.
Many mitochondria: Provide energy for active transport of mineral ions.
Absorb water by osmosis and minerals by active transport.
Xylem
Made of dead cells forming hollow tubes.
Strengthened with lignin for support.
Carries water and minerals upwards from roots to leaves.
Movement is one-way.
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from leaf surfaces, mainly through stomata.
Creates a pull (transpiration stream) that draws water up through xylem.
Factors Increasing Transpiration
High light, temperature, wind; low humidity.
work
Stomata
Stomata: Allow CO₂ in for photosynthesis and O₂ out; water vapour also escapes.
Guard Cells
pen in light (absorb water, become turgid) and close in dark or drought (flaccid), helping to reduce water loss
Phloem
Living cells with sieve plates; transports sugars; uses energy (active transport).
Translocation
Movement of sugars from leaves to other parts of plant.