Comprehensive Overview of Cranial Nerves in Relation to Mandibular and Tongue Functionality
1/259
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
260 Terms
preganglionic fibers innervating glands and smooth muscle usually emerge from the brain and synpase where?
parasympathetic ganglion outside the CNS and near the target organs
post ganglionic fibers innervating glands and smooth muscle supply as far down as the
abdomen, and other glands
pain fibers and reflex fibers carry
visceral sensation
somatic sensory fibers
afferent
fibers carrying general sensation
somatic sensory afferent
fibers that carry touch, pressure and temperature are:
a. somatic
b. efferent
c. afferent
d.visceral
a. somatic
c. afferent
cranial nerve 1
olfactory nerve
nerve that carries a sense of smell
CN 1
origin of CN1
olfactory area in the roof of the nasal cavity through the top of nasal septum and medial wll of superior concha
CN1 fibers pass vertically through the ___________________ of the ethmoid to reach the olfactory bulb
cribiform plate
true or false: CN1 is only a sensory nerve
true
loss of function of _______________ leads to anosmia
CN1
loss of smell
anosmia
CN 2
optic nerve
nerve that carries a sense of vision
optic nerve (CN2)
nerve that is considered a direct extension of the brain because it is surrounded by all three layers of meninges
optic nerve
origin of optic nerve
retina
optic nerve enters/ exits the skull through what?
optic canal
point at which the right and left optic nerve join in the cranial cavity
optic chiasm
true or false: the optic chiasm sits above the pituitary gland
true
the dura of the optic nerves continues as the ___________ of the eye
sclera
the pupillary light reflex is
afferent (sensory)
the pupillary light reflex leads to __________________ of the pupils in response to light
constriction
the _______________ limb of the pupillary light reflex is conveyd through the optic nerve
afferent
a pituitary adenoma might lead to what?
vision loss
a patient presents with loss of peripheral vision, what might you expect to be the diagnosis?
a pituitary adenoma
CN 3
oculomotor
what nerves constitute motor supply for the eye muscles?
oculomotor, trochlear and abducens
eye muscles can be __________ or ___________
intraocular or extraocular
elevator muscle of the upper eyelid
levator palpebrae superioris muscle
which nerves exit the superior orbital fissure?
CN 2, 3, 4, 6
optic
oculomotor
trochlear
abducens
what nerves pass through the cavernous sinus?
CN II, III, IV, V-1, V-2, VI
and postganglionic sympathetic fibers en route to the orbit all pass thru the cavernous sinus. Only CN VI is "free-floating". Cavernous portion of internal carotid artery is also here.
important dural venous sinus that cranial nerves can pass through
cavernous sinus
an infection in veins in the face can lead to
cavernous sinus thrombosis
a patient is experiencing complications secondary to a dental infection, the patient reports lid ptosis and opthalmoplegia as their symptoms. what might be the cause?
cavernous sinus thrombosis
signs of CST
opthalmoplegia and lid ptsosis
lid ptosis
eyelid drooping
paralysis of eye muscles
opthalmoplegia
can happen secondary to a dental infection, or infection on the skin and is lift threatening
CST
nerve that originates from the mid brain pierces the dura, and runs on the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus
oculomotor nerve
Somatic motor nerve for the 4/6 extraocular eye muscles
oculomotor
how does CN3 enter the orbit?
superior orbital fissure
eye muscles supplied by CN 3
superior, inferior and medial rectus and inferior oblique (extraocular eye muscles), and levator palpebrae superioris
what muscles can you expect to recieve a somatic motor innervation via the oculomotor nerve?
a. superior rectus
b. inferior rectus
c. lateral rectus
d. superior oblique
e. lateral oblique
f. medial rectus
g. levator palpebrae superioris
h. inferior oblique
a. superior rectus
b. inferior rectus
d. superior oblique
f. medial rectus
g. levator palpebrae superioris
nerve that supplies visceral motor innervation to the ciliary muscles and spinchter muscles of the eye
CN 3
visceral motor innervation through the cilliary ganglion to buldge the lens or constrict the pupil is _________________________
parasympathetic
through what ganglion does the oculomotor work to buldge the lens or constrict the pupils?
ciliary ganglion
you would expect near vision and bright light accomodation to occur through what fibers?
a. parasympathetic, somatic
b. sympathetic, visceral
c. parasympathetic, visceral
d. sympathetic, somatic
c. parasympathetic, visceral
muscle that buldges the lens
ciliary muscle
muscle that constricts the pupil
sphincter pupillae
the _______________ ____________ limb of the puillary reflex is conveyed through the oculomotor nerve
visceral efferent
parasympathetics of the eye are conveyed through what nerve?
CN 3
cranial nerve 4
trochlear nerve
where does the trochlear nerve originate?
midbrain
nerve that supplies somatic motor innervation to the superior oblique muscle
trochlear nerve (CNIV)
cranial nerve 6
abducens nerve
origin of CN VI
pontomedullary junction
nerve that supplies somatic motor innervation to the lateral rectus muscle
CNVI
cranial nerve 5
trigeminal nerve
CNV-1
opthalamic nerve
CNV-2
maxillary nerve
CNV-3
mandibular nerve
the motor root of the trigmenial is eclusive to the ___________________ divison
mandibular
nerve that is chief sensory supply to the face, oral cavity, nasal cavity, teeth and dura of the cranial cavity
trigeminal nerve
nerve that supplies somatic motor innervation to the muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric, tensor veli palatini, and tensor tympani muscles
mandibular division of trigmeninal nerve
anesthesia
numbeness
paresthesia
tingling
a patient presents with anesthesia of the right side of their face and you feel a hard mass presenting around their submandibular gland area. what nerve is causing the numbness of the face?
CNV
a condition that presents as a sudden onset of sharp severe pain spontaneously or through a sensory trigger like eating/ shaving
trigeminal neuralgia
true or false: you can have trigeminal neuraliga in the absence of a pathological condition
true
true or false: trigeminal neuralgia affects the motor distribution of the trigeminal nerve
false
it affects the sensory distribution
in what condition, will a patient present with a one inch fiber sign with paroxymal lightning like jabs?
trigeminal neuraliga
the afferent limb of the corneal reflex is supplied by what nerve?
opthalmic division of trigmeninal
blinking in response to air being blown into your eye is supplied by what nerve fibers?
afferent limb of the opthalmic division of the CNV
condition of reactivation of the latent herpes zoster virus in regions along the trigeminal nerve
trigeminal herpes zoster
a patient presents with swelling along regions of the face with painful eruptions and vesicles. you suspect this is a reactivation of latent herpes zoster. what nerve might be affected?
trigeminal nerve
lesions affecting the motor function of the mandibular division of CNV will result in deviation of mouth opening or mandibular protrusion towards the ____________________ side
ipsilateral
why will a lesion to the mandibular division result in a deviation of mouth opening to the ipsilateral side?
imbalanced action of only one lateral ptyergoid muscle
the opthalmic nerve is purely
sensory
where does the opthalmic nerve exit the cranium?
superior orbital fissure
nerve that supplies sensory to the forehead, superior eyelid, cornea, upper conjunctiva, mucosa of the anterosuperior nasal cavity, frontal and ethmoidal sinuses, anterior and supratentorial dura and skin over dorsum of nose
opthalmic division of CNV
the lacrimal nerve is a branch of ......
opthalmic nerve of CNV
the frontal nerve is a branch of .....
opthalmic nerve of CNV
the nasociliary nerve is a branch of......
opthalmic division CNV
main branches off the opthalmic nerve
1. lacrimal nerve
2. frontal nerve
3. nasociliary nerve
what branches off the lacrimal nerve to connect the zygomatic nerve?
communicating branch from zygomatic nerve
the supratrochlear nerve and supraorbital nerve branch off of ....
the frontal nerve of the opthalmic division
the ganglionic branches of ciliary ganglion, long and short ciliary nerves, anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerves and infratrochlear nervers branch off of ......
nasociliary nerve
what are all the nerves that branch off the opthalmic nerve?
1. lacrimal nerve
- communicating branch from zygomatic nerve
2. frontal nerve
- supratrochlear nerve
-supraorbital nerve
3. nasociliary nerve
- ganglionic branches of ciliary ganglion
-long and short ciliary ganglino
-anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerves
-infratrochlear nerve
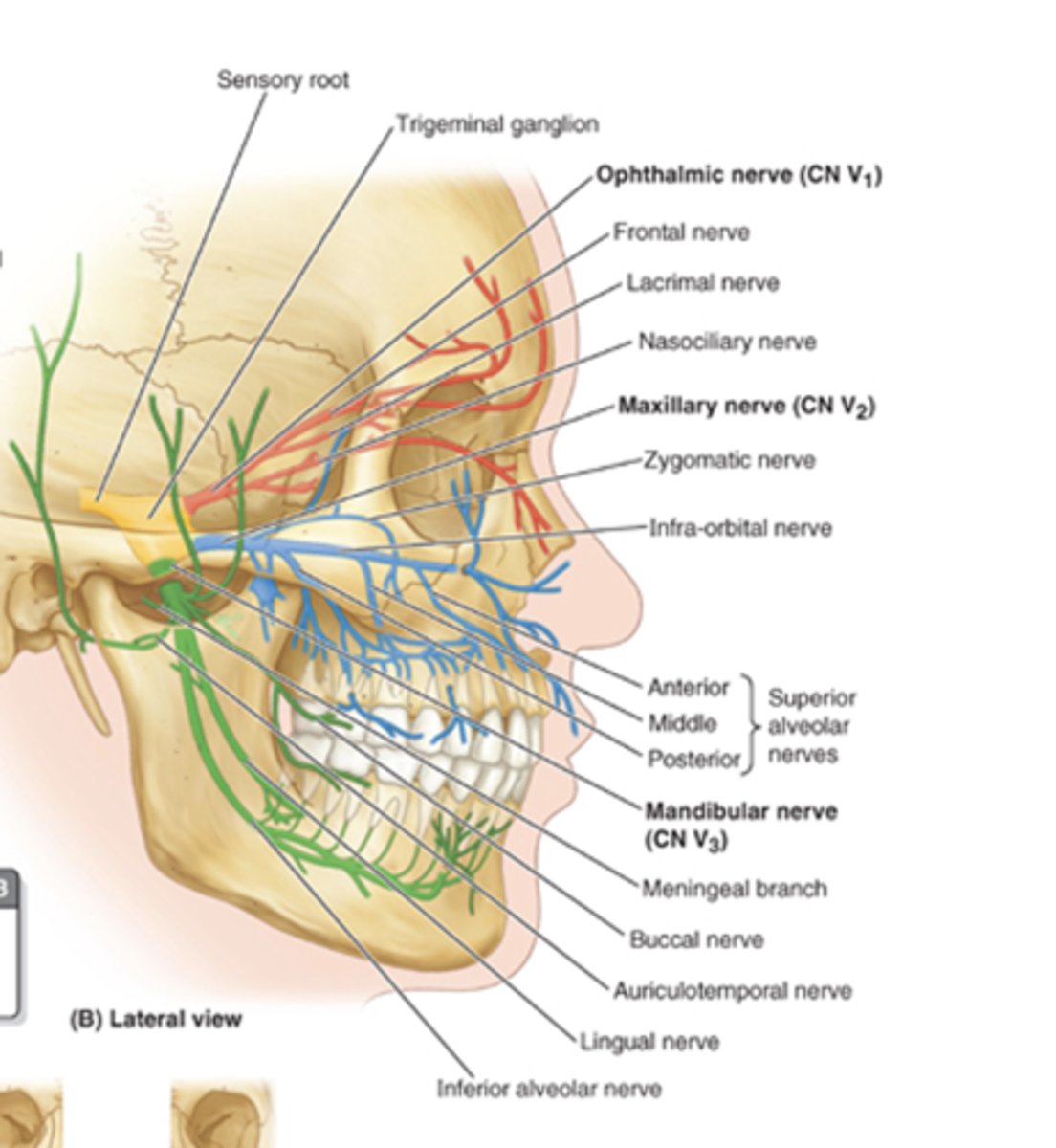
what nerves of the trigeminal are purely sensory?
opthalmic and maxillary nerve
where does the maxillary nerve exit the skull?
foramen rotundum
nerve that continues anteriorly in the infraorbital groove in the floor of the orbit, into the infraorbital canal and emerges onto the face beneath the orbit from the infraorbital foramen
maxillary nerve of opthalmic division
nerve that supplies the dura of anterior part of middle cranial fossa, mucosa of posteroinferior nasal cavity, maxillary sinus, maxillary teeth, apalte, skin of lateral nose, inferior eyelid and superior lip
maxillary nerve
what are the main branches that come off the maxillary nerve?
1. zygomatic nerve
2. ganglionic branches of ptyergopalatine ganglion
3. posterior superior alveolar nerve
4. infraorbital nerve
5. greater palatine nerve
6. lesser palatine nerves
7. nasopalatine nerve
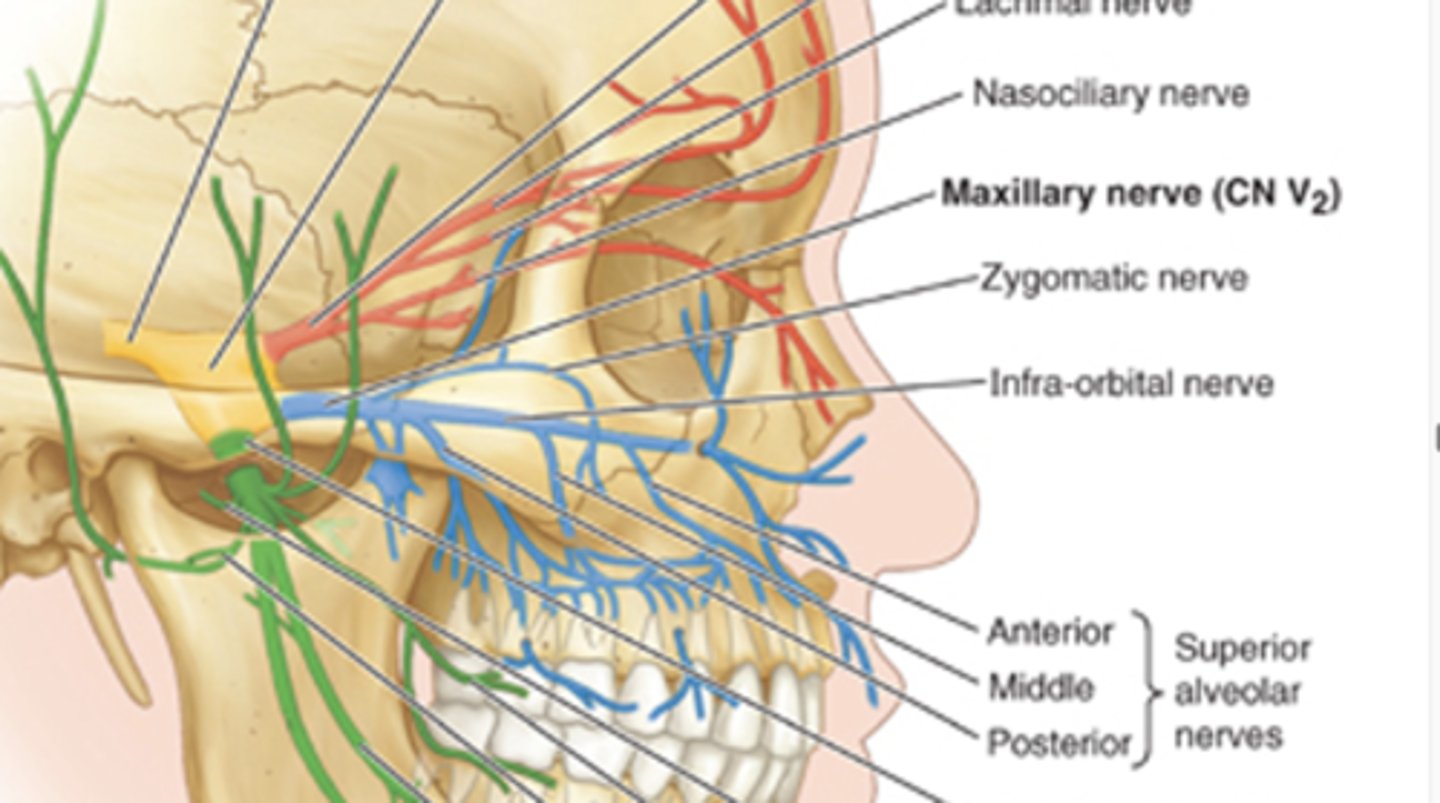
branches of the zygomatic nerve
1. zygomaticotemporal branch
2. zygomaticofacial brnach
3. communicating branch to lacrimal nerve
true or false: the zygomatic nerve descends off the CNVII
false
what nerve supplies sensory to the pulp, bone and buccal mucoperiosteum of molar maxillary teeth?
posterior superior alveolar nerve
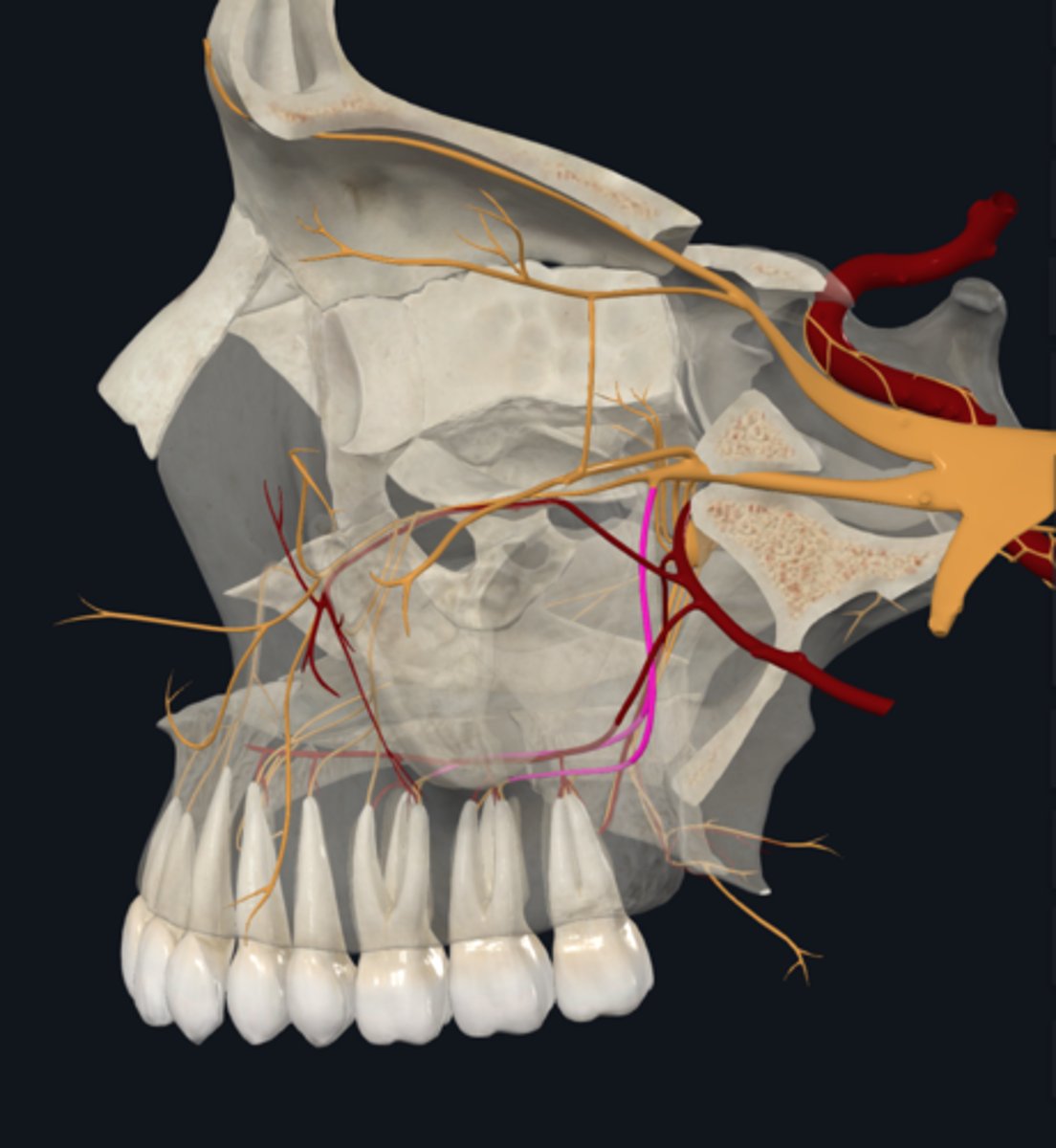
the anterior and middle superior alveolar nerves branch off the
infraorbital nerve
sensory supply to the pulp, bone and buccal mucoperiosteum of anterior teeth and premolars
anterior and middle superior alveolar nerve
if present, the middle superior alveolar nerve will supply what additional root?
mesiobuccal root of first molar and premolars