Anatomy Unit 2 Practice Test
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 2 Practice Test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
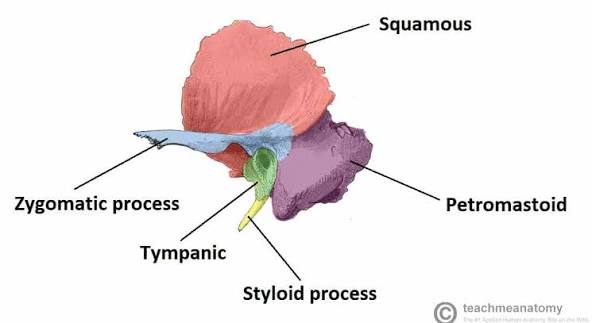
which bone contains the mastoid, squamous, tympanic and petrous regions?
temporal bone
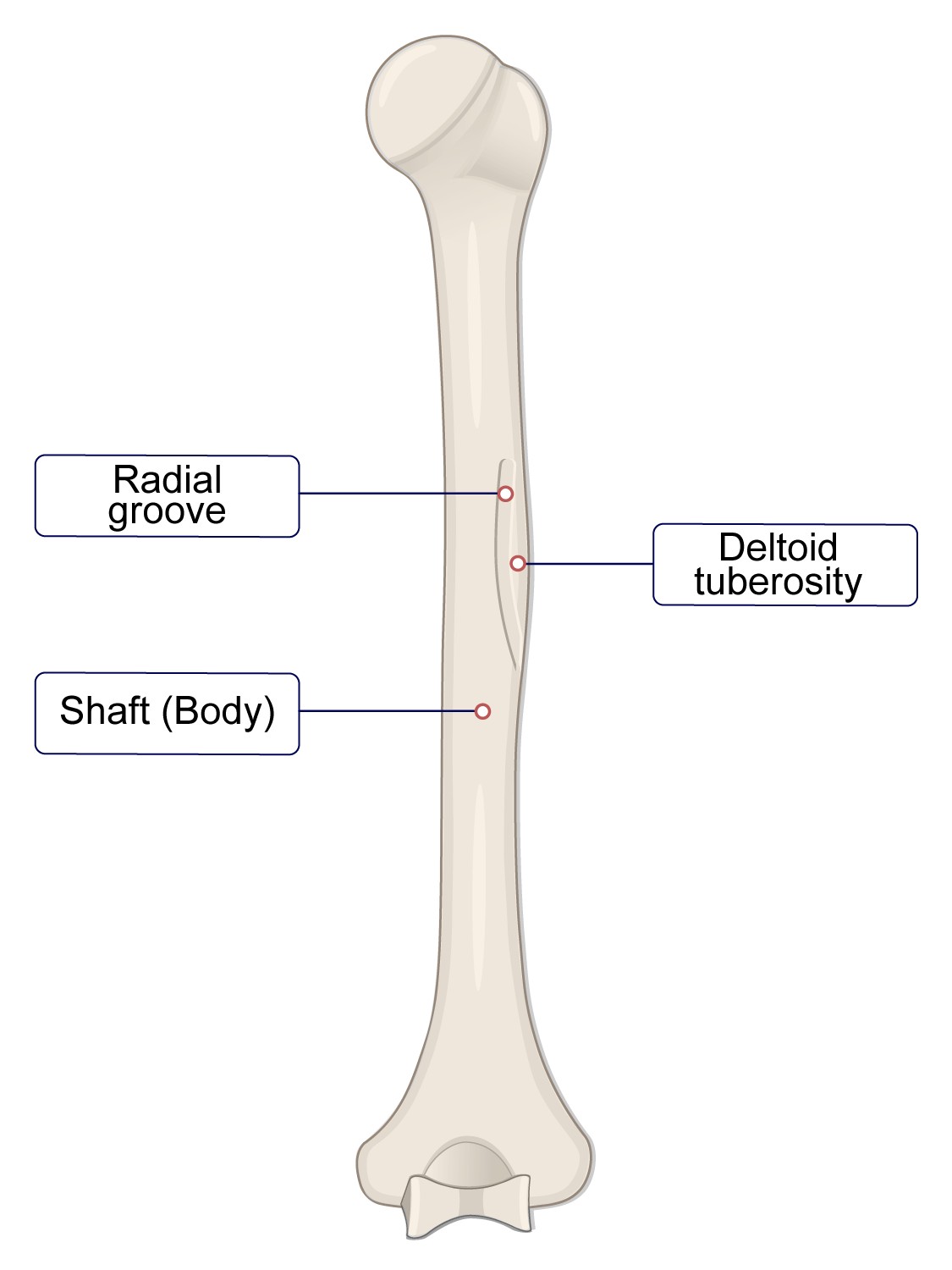
What type of joint is a suture?
synarthrosis/fibrous joint
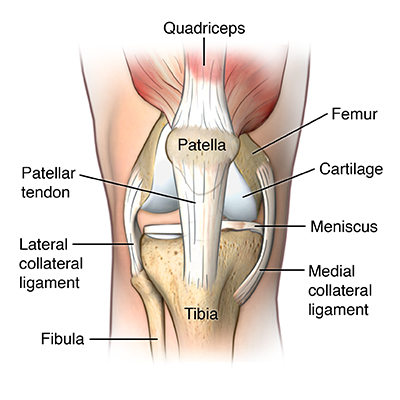
the tibial tuberosity is the attachment site for the
patellar ligament
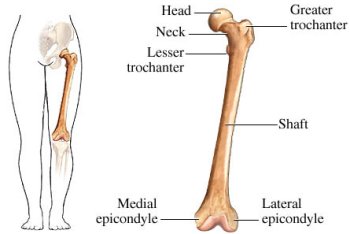
which bone marking is a large, blunt projection only the femur?
Trochanter
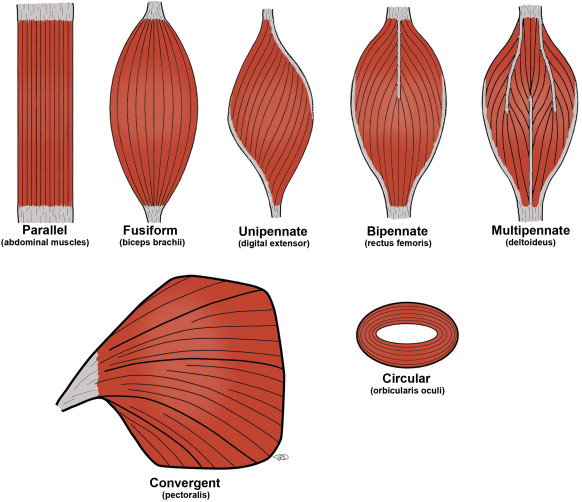
Which fascicle arrangement produces the greatest tension?
pennate
The ball-and-socket joint of the upper limb is the:
Glenohumeral
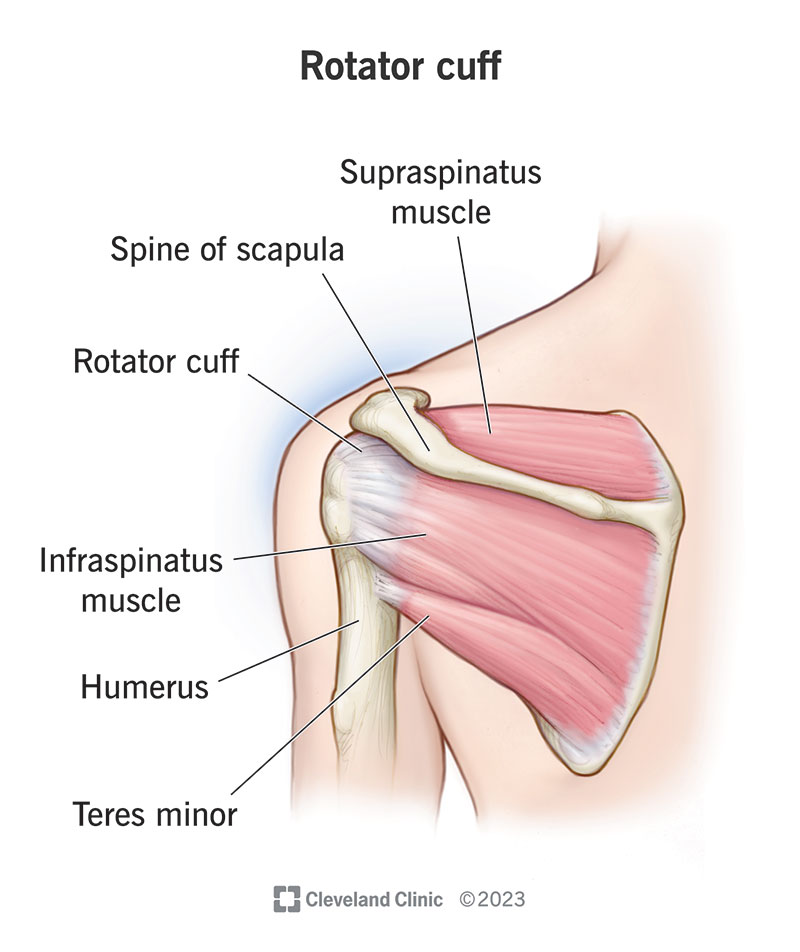
The primary stabilizers of the shoulder joint are the:
Rotator cuff
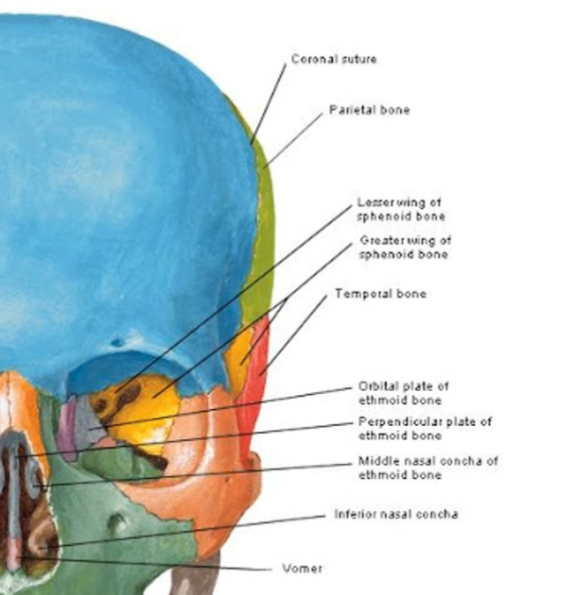
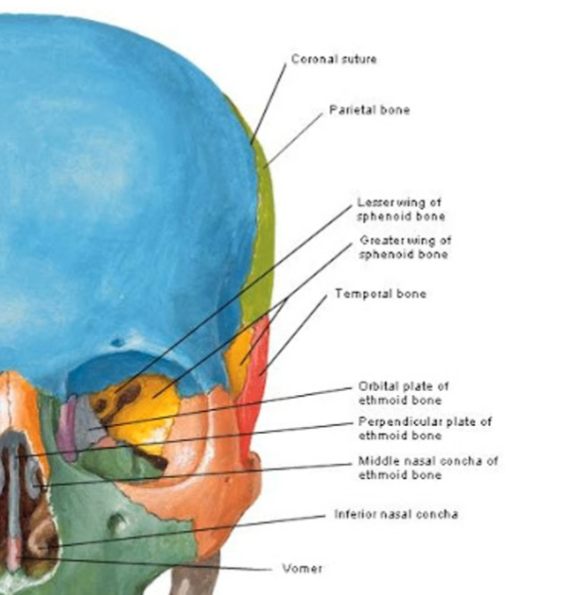
Which bone forms most of the orbital floor?
maxilla
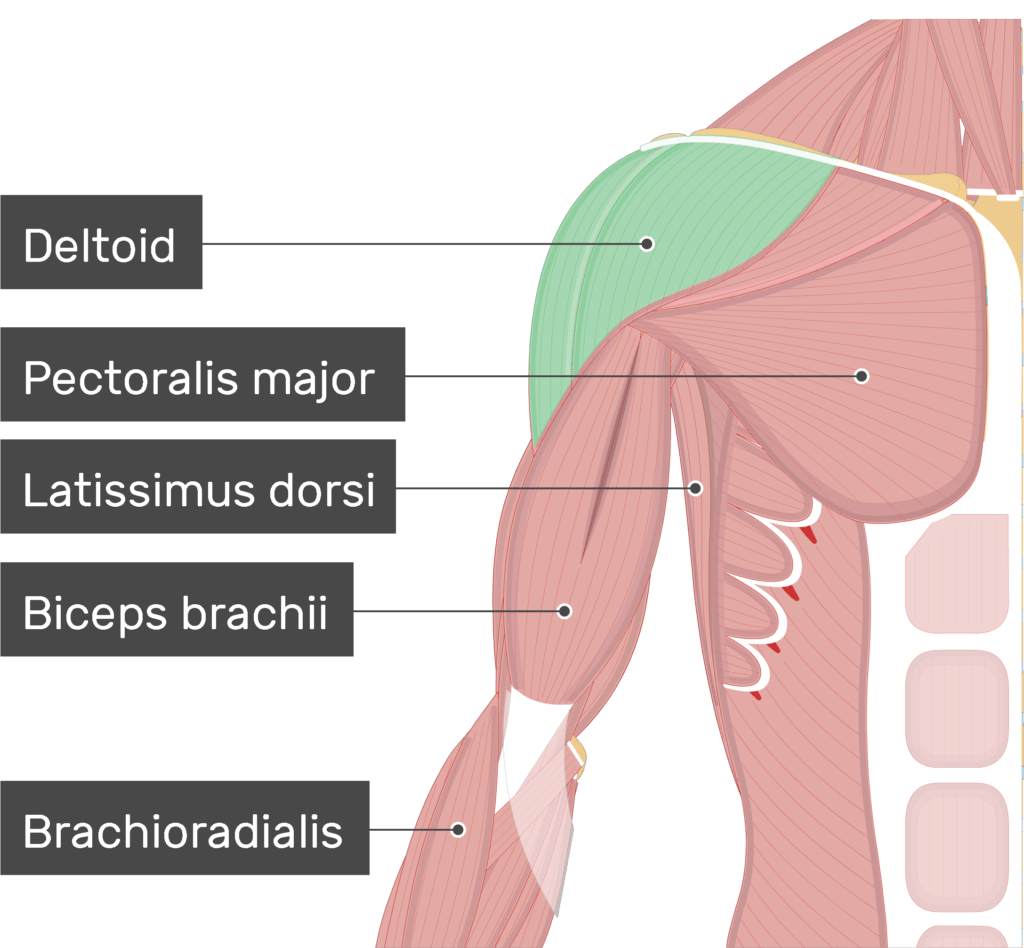
Which muscle is multipennate?
deltoid
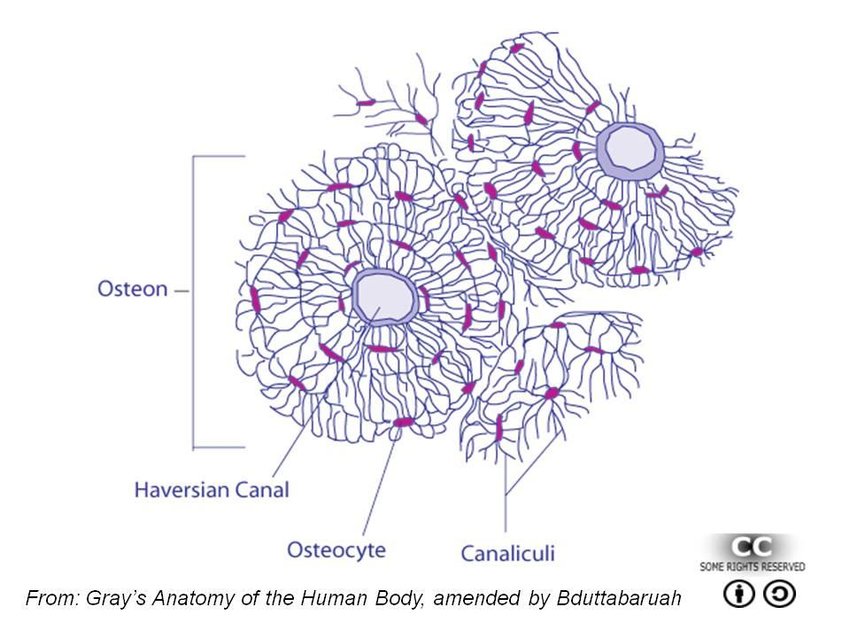
what is an osteocyte
a bone cell, formed when an osteoblast becomes embedded in the matrix it has secreted.
Difference between synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis, diarthrosis.
Synarthrosis joints are immovable, amphiarthrosis joints allow for slight movement, and diarthrosis joints are freely movable.
List the 7 orbit bones.
frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, lacrimal, maxilla, palatine, and zygomatic
Explain the roles of synovial fluid
lubricates joints, absorbs shock, transports nutrients and oxygen to avascular cartilage,
Compare spongy vs compact bone.
Compact bone is dense, strong, and located on the outer layer of bones, while spongy bone is porous, lighter, and found in the interior. Spongy bone houses red bone marrow for blood cell production.
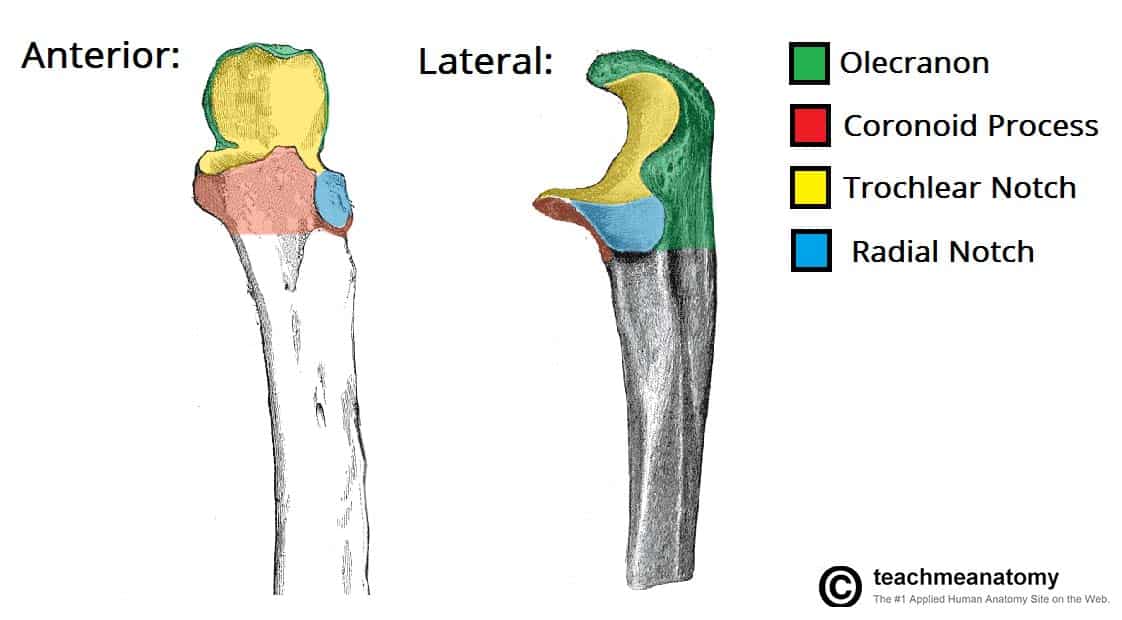
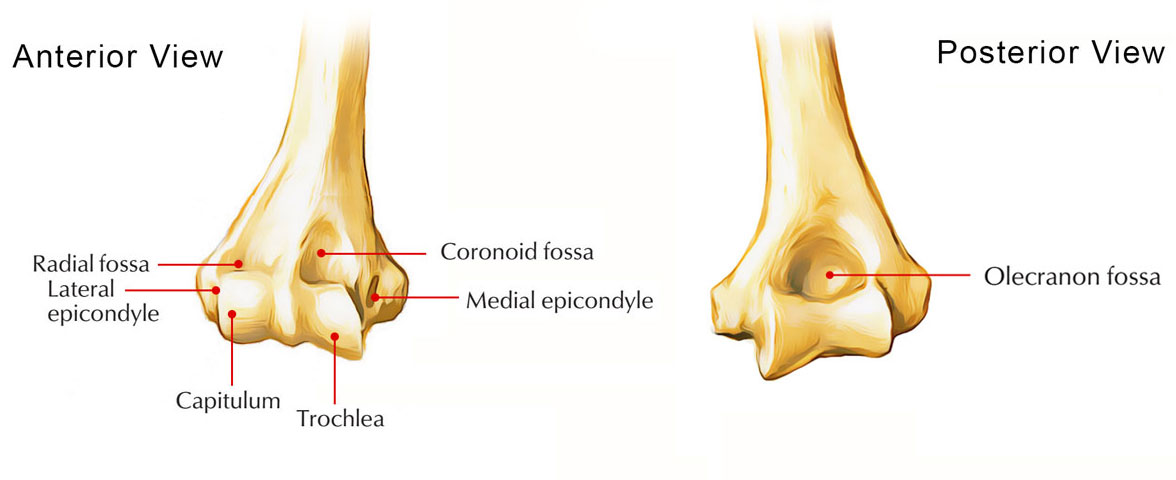
Trochlear notch
a large, C-shaped depression on the proximal ulna bone in the forearm that articulates with the trochlea of the humerus to form the hinge of the elbow joint
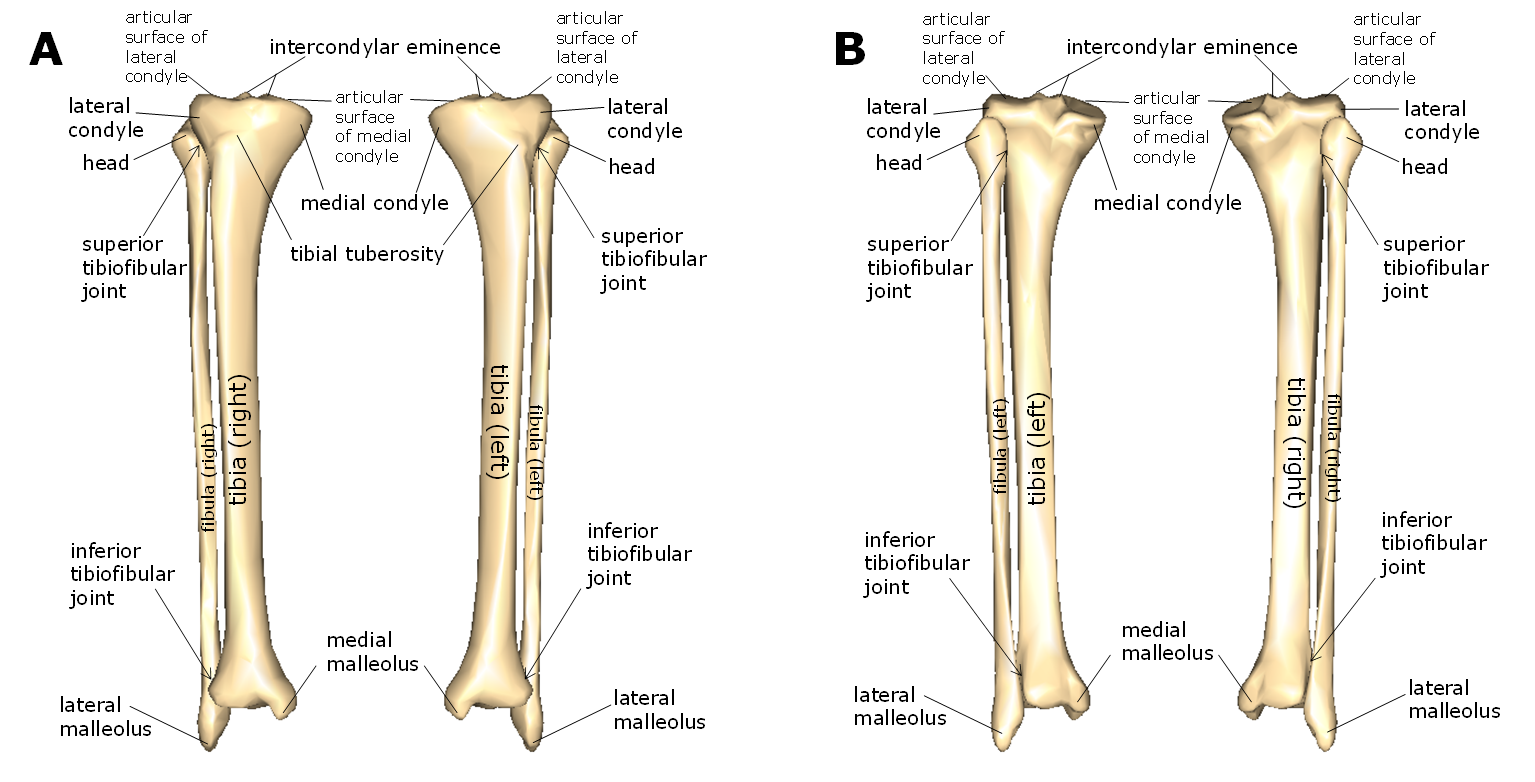
Name the lateral lower leg bone.
the fibula
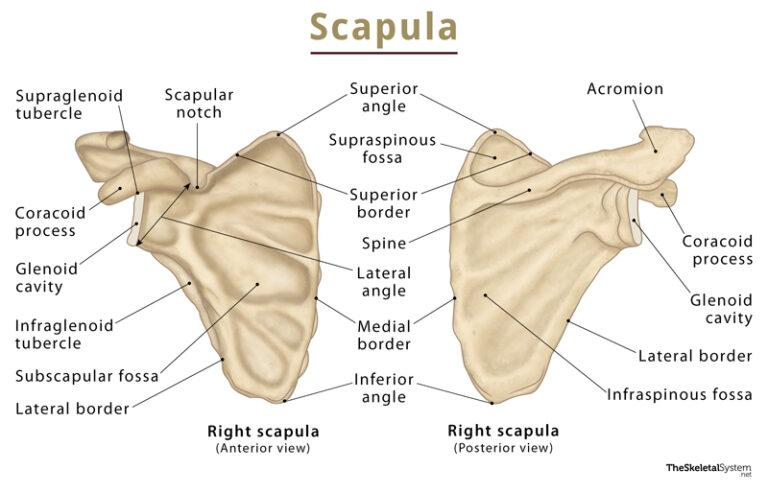
What is the glenoid cavity?
socket on the scapula (shoulder blade) that forms the "socket" of the shoulder's ball-and-socket joint
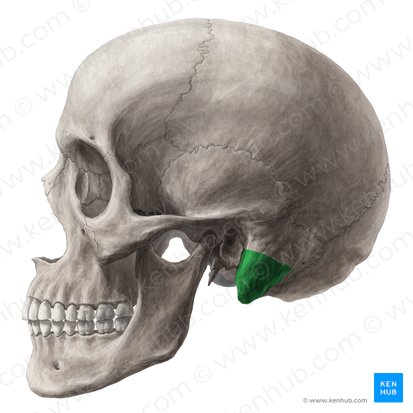
Identify the mastoid process.
a bony, cone-shaped prominence located at the base of the skull, just behind the ear.
Name the medial lower leg bone.
tibia
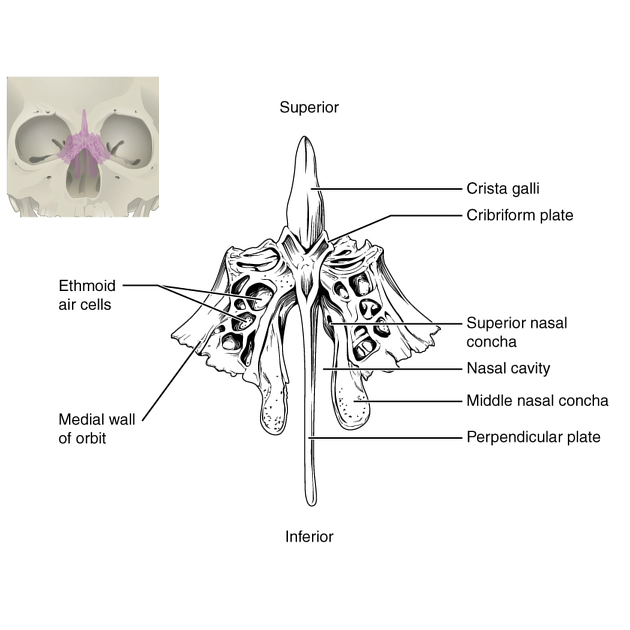
Name the bone with cribriform plate
ethmoid bone. This is a spongy, unpaired bone located between the eyes that forms part of the skull's base, the nasal cavity, and the orbits
Name the socket of the hip.
Name the socket of the hip
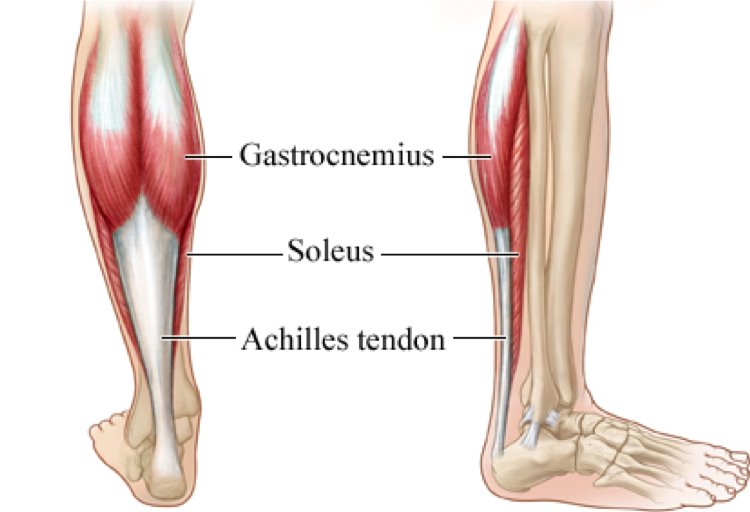
Name the primary plantar flexor muscle.
he soleus, which is the deep muscle of the calf
Femur head points (medially or laterally)
Medially.
Olecranon fossa is on (posterior/anterior).
Posterior of humerus
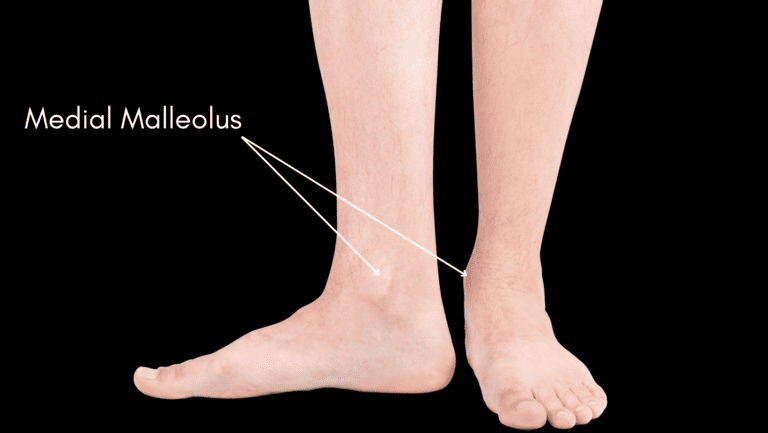
Medial malleolus belongs to which bone?
tibia
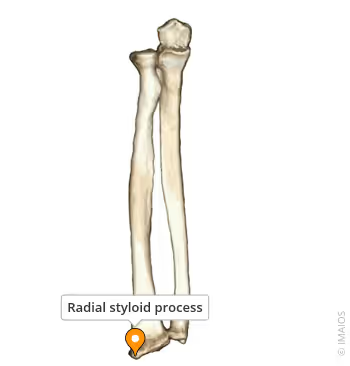
Radius styloid is lateral or medial?
lateral
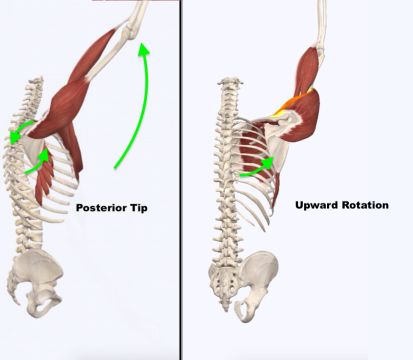
Serratus anterior action.
Protracts scapula.
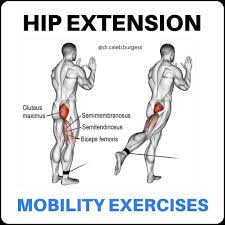
Gluteus maximus action
Hip extension.
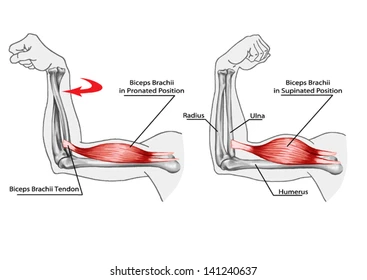
Biceps brachii action.
Elbow flexion & supination.
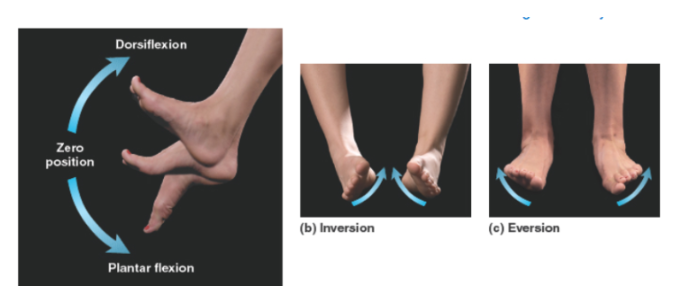
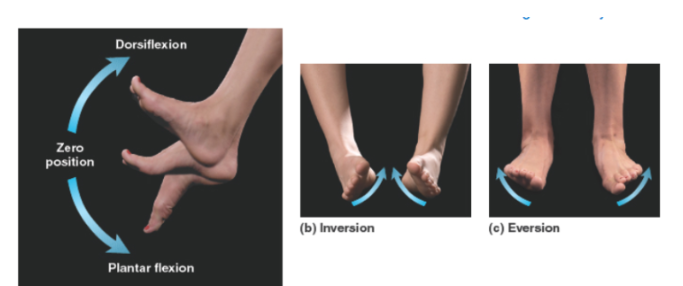
Tibialis anterior action.
Dorsiflexion.
. Gastrocnemius action.
Plantar flexion.
Triceps brachii action
Elbow extension.
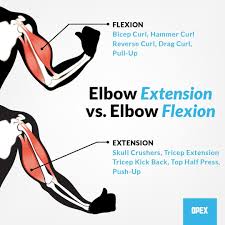
Deltoid action.
Shoulder abduction.
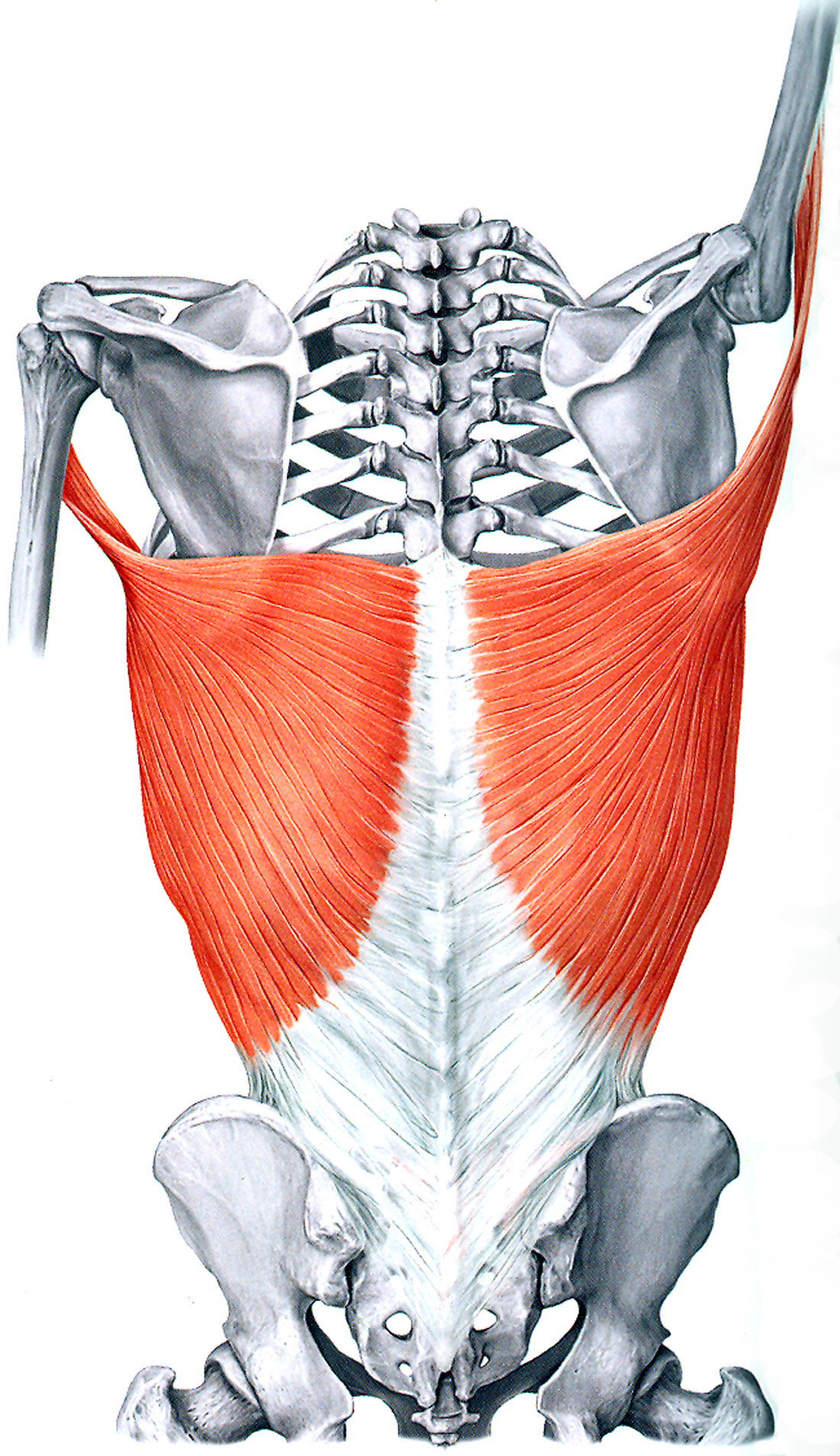
38 Latissimus dorsi action.
Shoulder extension/adduction.
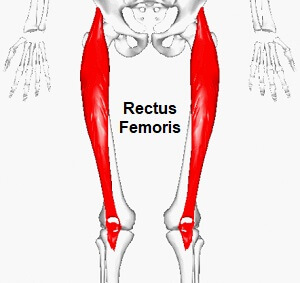
39. Rectus femoris action
Knee extension & hip flexion
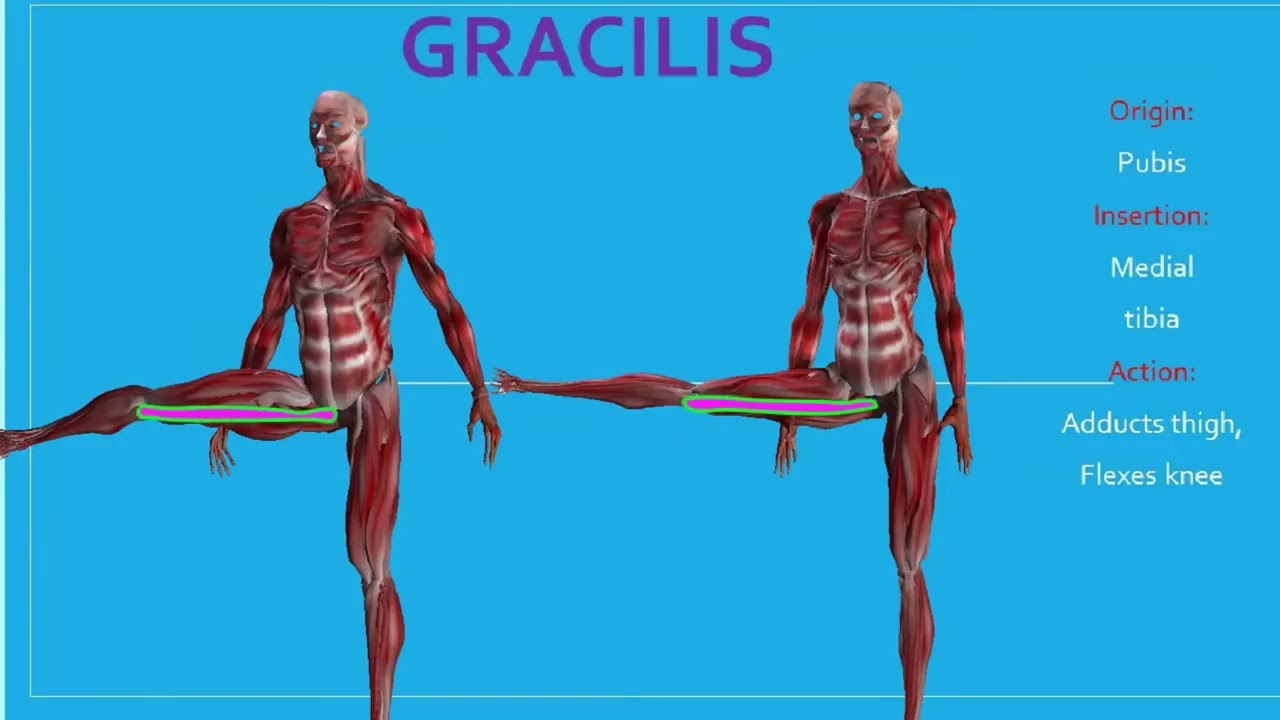
40. Gracilis action.
Hip adduction.
41. Turning sole inward.
. Inversion.
42. Lifting shoulders upward.
Elevation
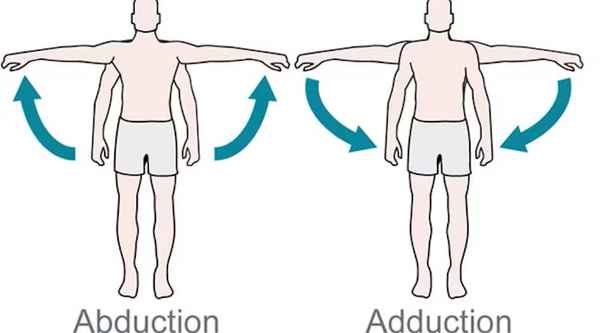
43. Moving arm away from midline.
Abduction.
44. Bending knee.
Flexion
45. Thumb to fingertips movement
Opposition.
46. Define condyle.
Rounded articular surface.
47. Define foramen.
Hole for nerves/vessels.
48. Define fossa
Shallow depression.
49. Define spine (bone marking).
Sharp slender projection.
50. Define tuberosity
Large rough projection.