biogeochem: Phosphorous cycle
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what is the biggest reservoir for P
sediments
what is the residence time for P in sediments
super slow, 1.82×108
describe the phosphorus cycle
weathering (and mining) pulls P from sediments. goes to crops, internally cycles with plants and soils, runs off into water ways, cycles through ocean waters, gets buried in sediments to be brought up again
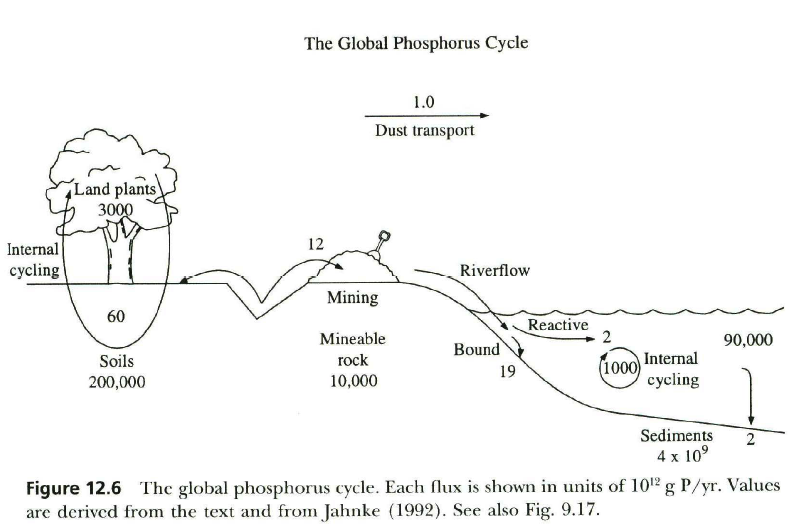
how as the P cycle been altered by humans
through mining and fertilizer. 4x increase!
Is P easily available, why or why not?
P is easily immobilized by chemical reactions. Binding removes P from bio-available pools. Although total P in soils can be large, only a small fraction is available to biota. Microbes are important in transforming organic P to inorganic and mobilizing chemically fixed P to more bio-available forms
what binds to materials and depends on what
Ca, Mg, Fe, Al
apatite, hydroxylapatite, fluorapatite
chemical P fixation is pH-dependent
how is P exported from terrestrial ecosystems
runoff
how is P returned to terrestrial ecosystems
new ways - guano is one
does P have a gaseous phase?
No significant gaseous phase
how is aquatic productivity limited by P
P is absorbed by plants, algae, and some bacteria. assimilatory reactions, not dissimilatory
what is an example of too much P
HABs in Lake Erie
What action was taken to address HABs in Lake Erie
binational agreement to reduce P by 40%
2012 Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement
what did Ohio do to address high P
fertilizer and manure ban
dredging limits
wastewater treatment rules
what is challenging about reducing P
Can regulate waste water treatment, but CANT regulation nonpoint sources so you have to get creative and try to regulate fertilizer composition and application
Michigan Domestic Action Plan
Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development (MDARD)
Supports conservation practice implementation with additional state funding for the Western Lake Erie Basin
Formally tracks progress using the Great Lakes Watershed Management System
Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE)
Administers Point Source Permit Program
Monitors tributary nutrient loads
Supports watershed management planning and implementation
Michigan Department of Natural Resources (DNR)
Assesses and monitors fish and wildlife populations and habitats
Protects and restores wetlands
Priority watersheds: River Raisin and Upper Maumee River and had 4 key wwtp permit limited