PSYCH 101 Exam
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
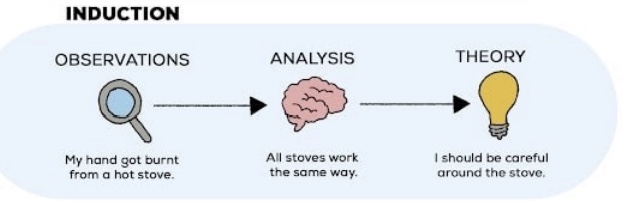
inductive reasoning
uses specific and limited observations to draw general conclusions
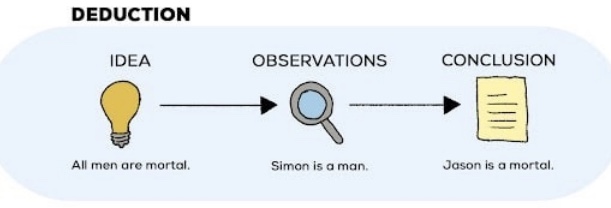
deductive reasoning
uses a general principle or premise as grounds to draw specific conclusions
falsifiability
ability to be shown as false
e.g. “all swans are white” can be proven false with a black swan
pseudoscience
a claim that is presented as scientific but does not adhere to the standards and methods of science
e.g. astrology, numerology, conspiracy theories
introspection
a reflective looking inward; an examination of one’s own thoughts and feelings
empiricism
knowledge is based on one own’s (sensory) experiences
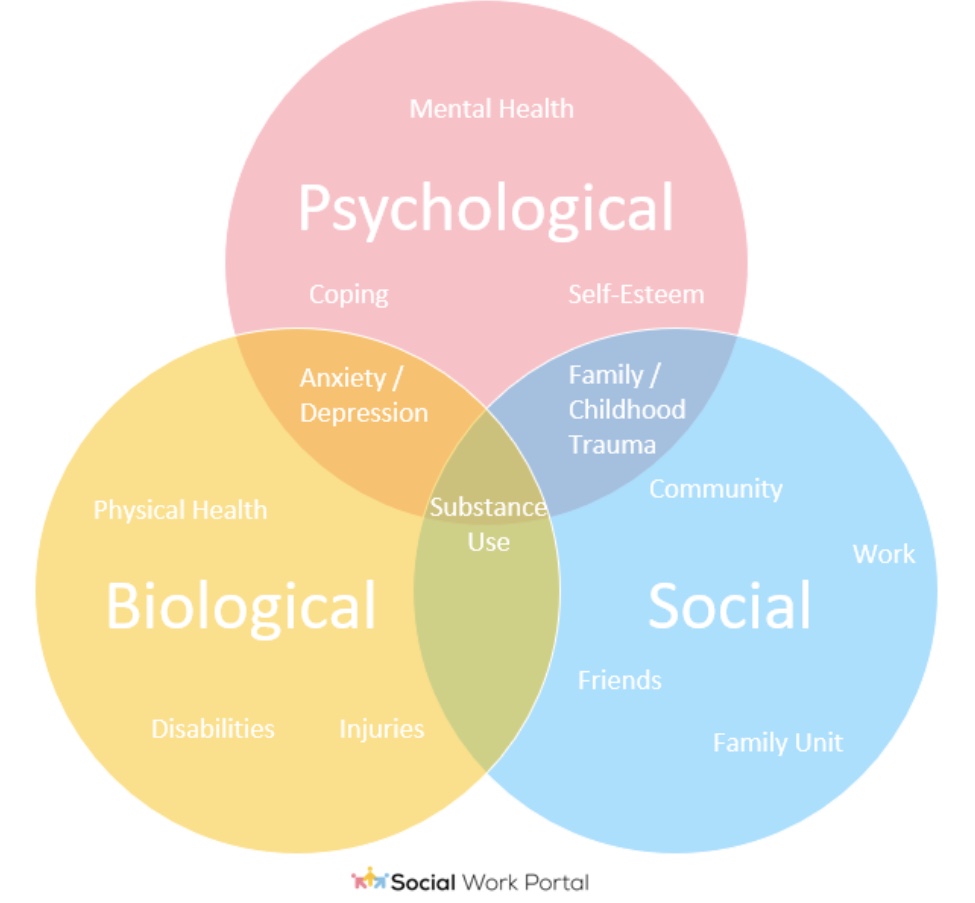
bio-psycho-social model
health and illness are determined by a dynamic interaction between biological, psychological, and social factors
W.E.I.R.D
Western
Educated
Industrialized
Rich
Democratic
a specific demographic that dominates behavioral science research
ethics
protects clients from harm and uphold their privacy, dignity, and well-being
hypothesis vs theory
hypothesis = tentative explanation that can be tested by further investigation
theory = a well-supported explanation of observations
independent variable
manipulated
not influenced by other variables/results
predictor
dependent variable
measured
affected by changes in IV
outcome
operational definition
defining variables in terms of how we plan to measure them
null vs alternative hypothesis
null = no significant relationship between the IV and DV (data does NOT support the hypothesis)
alternative = there is a significant relationship between the IV and DV (data supports the hypothesis)
reliability vs validity
reliability = measurement provides consistent results
validity = measurement assesses what it’s supposed to measure
sample
subset of a population recruited to participate in research
simple random sampling
data collected from a random subset of a population to draw conclusions about the whole population.
descriptive design
snapshot of current patterns of behavior (e.g., case study)
correlational design
investigating relationships between naturally occurring variables
no manipulation of IV (due to practical/ethical reasons)
can evaluate a larger range of variable
time and efficiency
experimental design
intended to see if one variable causes another
must have at least one experimental group, control group, IV, ID, and random assignment
random assignment
allows researchers to assume that all groups are comparable at the beginning of a study
randomly placing participants into an experimental group or a control group
prevents bias
case study
intensive, in-depth study of a person or group
often used to explore rare conditions or experiences
not generalizable to other people or contexts
confound
extraneous variables that vary along with the main variables of interest
provide an alternative explanation for our results
natural experiment
“Quasi-experimental” design that uses a naturally-occurring event to provide scientific information
useful when random assignment is unfeasible or unethical
correlation coefficient (R)
statistical measure of the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
ranges from -1 to 1.
cross-sectional vs longitudinal
cross-sectional = multiple age groups examined at one time point
goal: examine relationship between age and DV
longitudinal = same group of participants examined over multiple time points
goal: examine how participants change over time
heritability
a measure of how well differences in people's genes account for differences in their traits (from 0 to 1)
higher heritability = characteristic more influenced by genetics
estimates phenotype, not genotype
twin studies
monozygotic (MZ) twins = 100% of genetics in common
dizygotic (DZ) twins = ~50% of genetics in common
if MZ twins are more similar than DZ twins on a certain characteristic, then genetics plays a strong role
concordance rate
degree of similarity among pairs of family members
if concordance rate is higher for MZ than DZ twins, this suggests trait is partly genetic
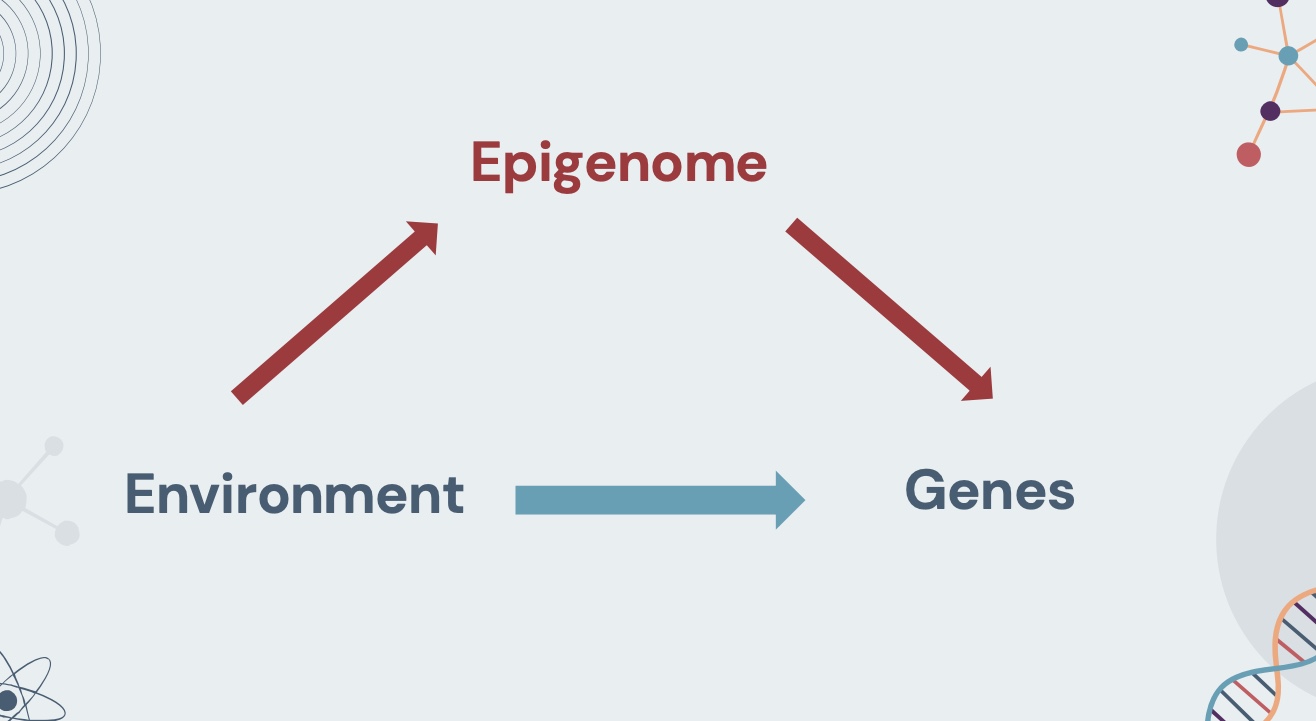
epigenome
chemical compounds that tell the genome what to do
social determinants of health
non-medical factors that influence a person’s health and wellbeing
heavily influenced by race and class
can influence gene expression

culture
explicit & documented (e.g., what is taught in school, who can get married)
implicit (e.g., unspoken norms for social interactions)
structural (e.g., resources available, prejudice, oppression)
central nervous system
brain and spinal chord
peripheral nervous system
nerves extending from spinal chord
sympathetic vs. parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic = “fight or flight” response to stress/danger
parasympathetic = relaxes body after periods of stress/danger
neurons
cells of the brain and nervous system
responsible for receiving sensory input from environment and relaying electrical signals to the body
dendrite
the structure on neurons that allow the cell to receive signals from other neurons
axon
long and single nerve-cell process that conducts impulses away from the cell body.
myelin sheath
allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells
synapse
junction between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron
action potential
electric signals sent down the axon
neurotransmitters
chemical signals released by the action potentials that travel across synapses
brainstem
connects brain to spinal cord
regulates breathing, blood flow, heart rate, reflexes
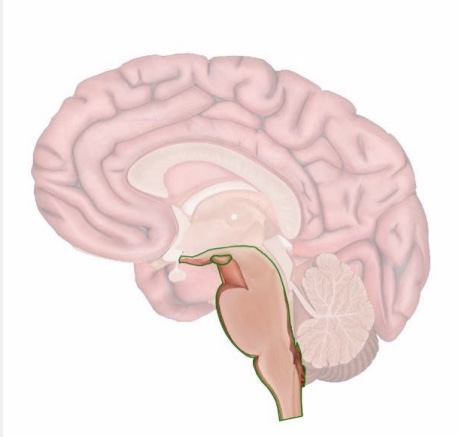
cerebellum
coordination of muscle movements (e.g., posture, balance, and speech)
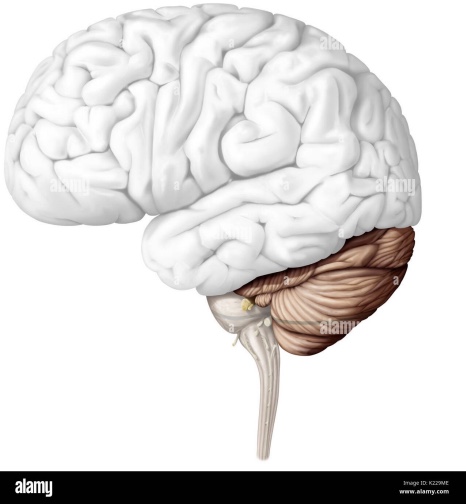
cerebrum
major lobes of the brain
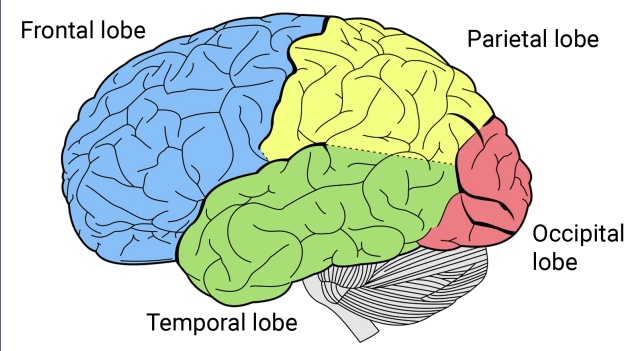
occipital lobe
located at the back of the cerebrum, is the house of the visual area of the brain
‘A’
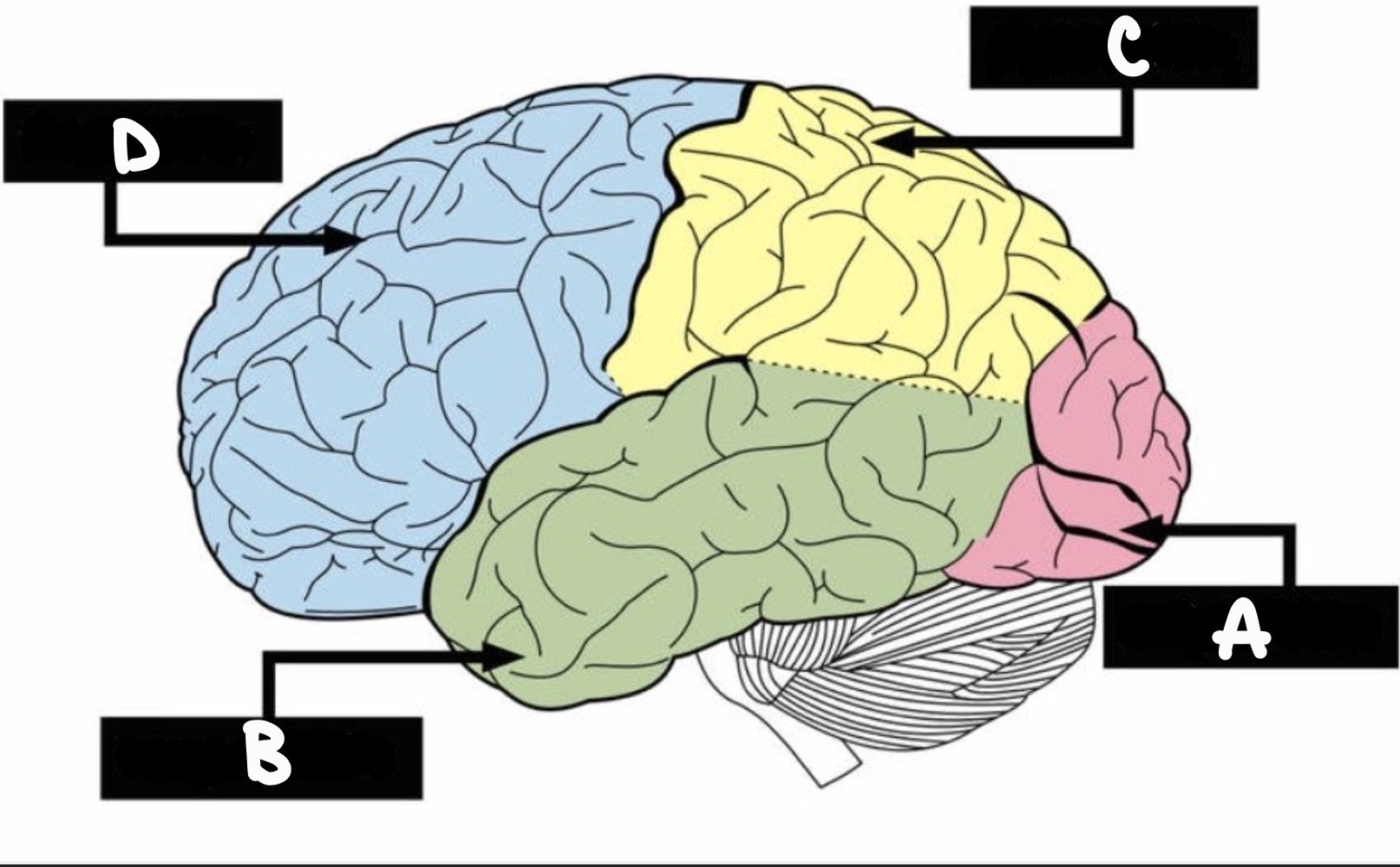
temporal lobe
underside, where sounds and smells are processed
‘B’
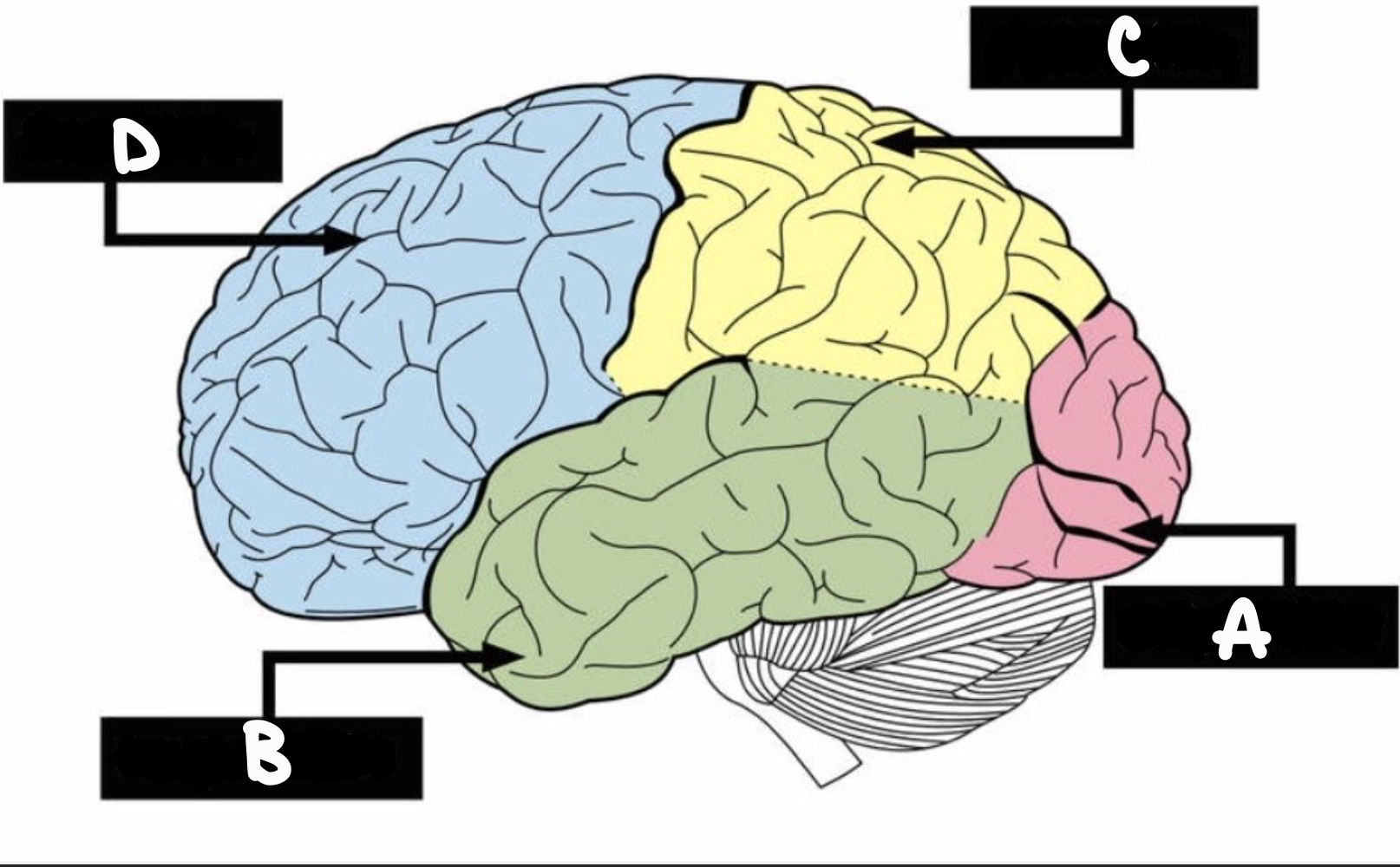
parietal lobe
upper back, where touch and taste are processed
‘C’
frontal lobe
forward; planning and organizing tasks, problem-solving and decision-making, working memory and attention, and impulse control
‘D'
limbic system
a collection of highly specialized neural structures that sit at the top of the brain stem, which are involved in regulating our emotions
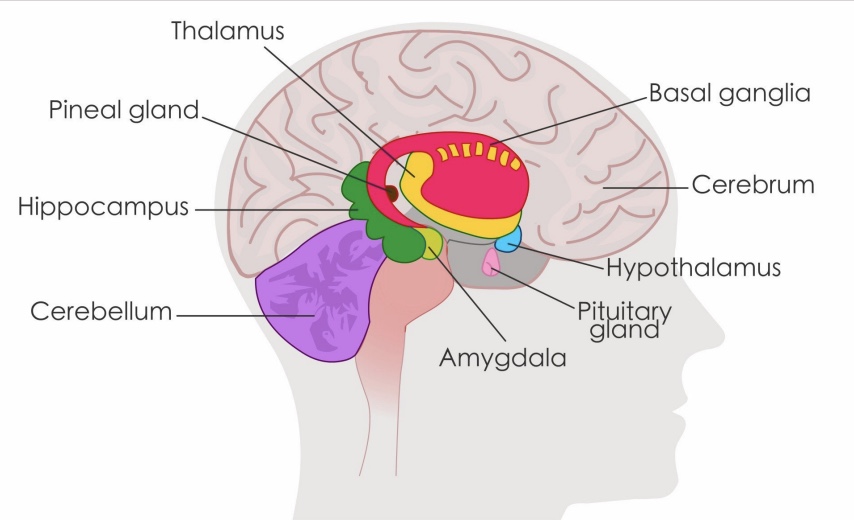
white vs. grey matter
white matter: bundles of myelinated axons
grey matter: neuron cell bodies and dendrites

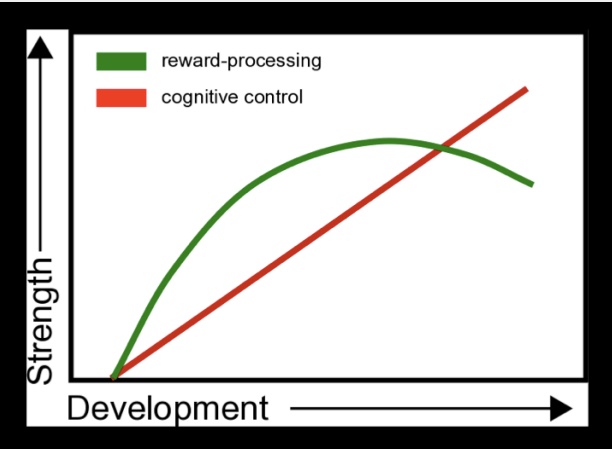
dual systems model
limbic regions develop earlier than prefrontal regions
explains higher risk taking/impulses in adolescence
wernicke’s area vs broca’s area
wernicke’s area = responsible for language comprehension (understanding spoken and written language)
broca’s area = responsible for language production (speaking and writing)
corpus callosum
bundle of fibers connecting two hemispheres of the brain
structural plasticity vs functional plasticity
structural = physical changes in the brain structure (e.g. synaptogenesis and synaptic pruning)
functional = brain’s ability to shift functions from damaged areas to healthy ones
synaptogenesis
formation of synaptic connections
synaptic pruning
elimination of unused synaptic connections (“use it or lose it”)
sensitive period
window of time when the brain is most receptive to certain stimuli and experiences
experience-expectant processes vs experience-dependent processes
experience-expectant:
brain functions expected to develop properly for normal functioning
“critical or sensitive periods” for development
e.g. vision, face processing, language development
experience-dependent:
new synaptic connections formed based on unique interactions with environment
require learning & reinforcement
e.g. sports, playing an instrument
perceptual narrowing
developmental process during which the brain uses environmental experiences to shape perceptual abilities
sensation
receiving raw stimuli from the environment
transduction
conversion of one form of energy to another
perception
interpretation of experiences
absolute threshold
minimum level of stimulation a person can detect 50% of the time
measured with signal detection
bottom-up vs. top-down processing
bottom-up processing = starting with the individual stimulus to build perception
top-down processing = using prior knowledge and context to interpret new information
multi-modal perception
integrating information from multiple senses
subliminal messaging
using hidden words or images to influence people’s thoughts and behaviors without their conscious awareness
often used in advertising
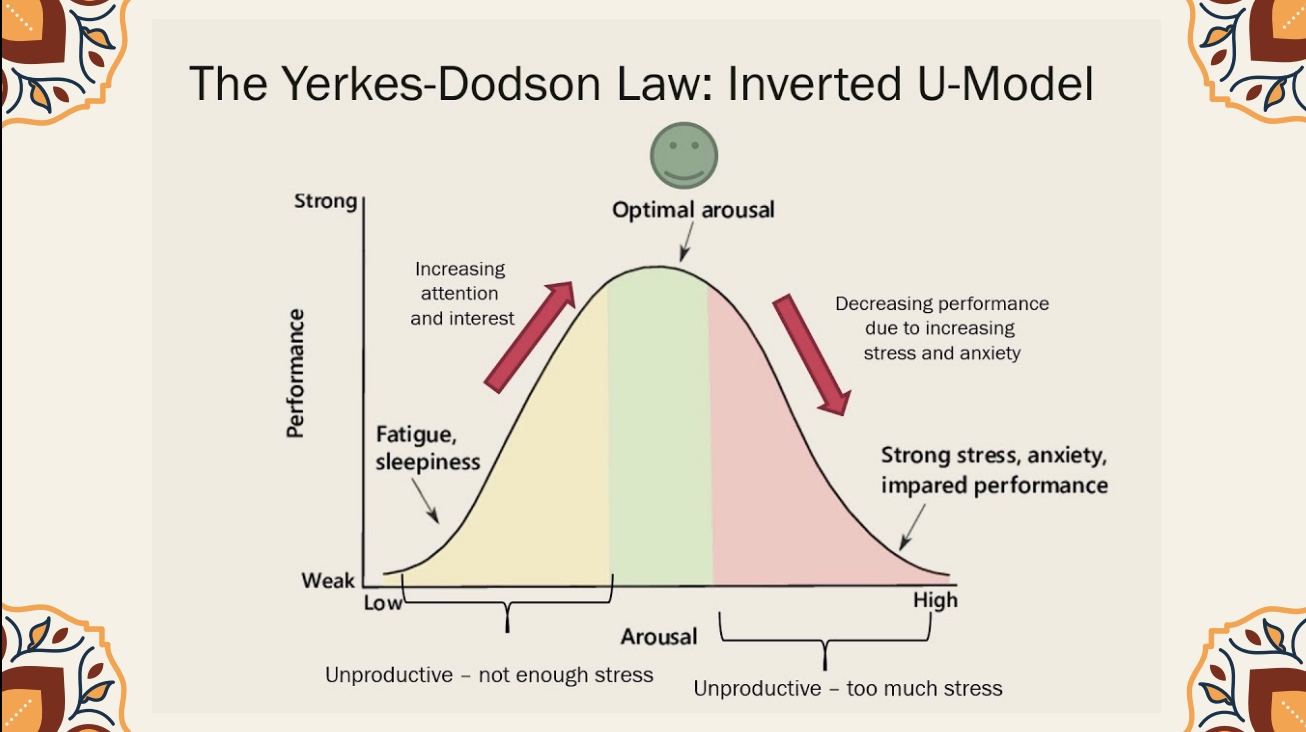
Yerkes-Dodson Law
performance improves with increasing stress up to an optimal point, but then declines if stress becomes too high or is too low
allostatic load
“wear and tear” on the body as a result of repeated or chronic stress
trier social stress test
experimental procedure designed to induce psychological stress in laboratory settings