Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
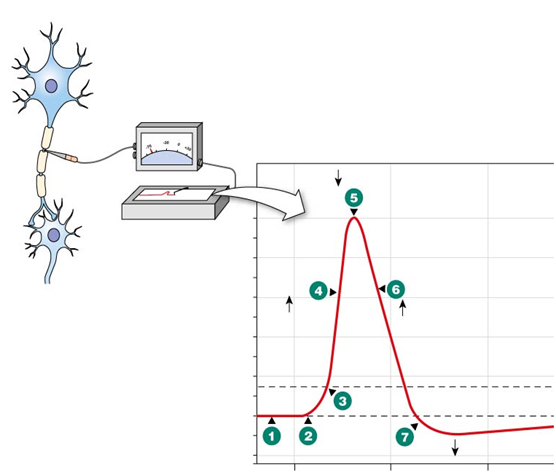
At which number (1-7) is membrane potential most positive?
Number 5
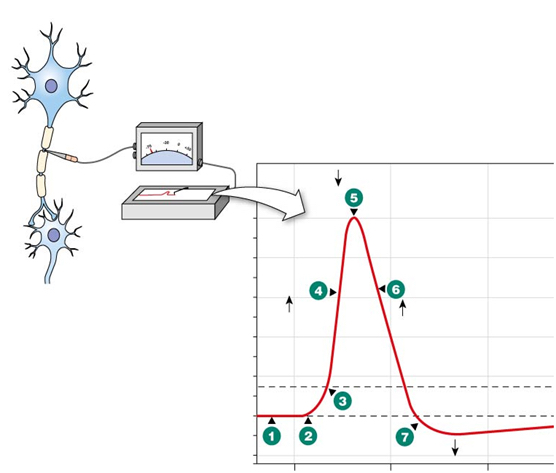
At which number (1-7) is this neuron most permeable to Na+?
(Pass through it)
Number 4
The membrane potential at which enough voltage-gated Na+ channels open to cause positive feedback is called the
Threshold
When you apply lidocaine or TTX to the axon of a neuron, its ability to fire an action potential is __________
because it binds to and blocks ________
Eliminated
Voltage-gated sodium channels
The time interval when a neuron requires a stronger than normal stimulus to fire an action potential because some voltage-gated Na+ channels are inactivated and some voltage-gated K+ channels are open is called
The Relative Refractory Period
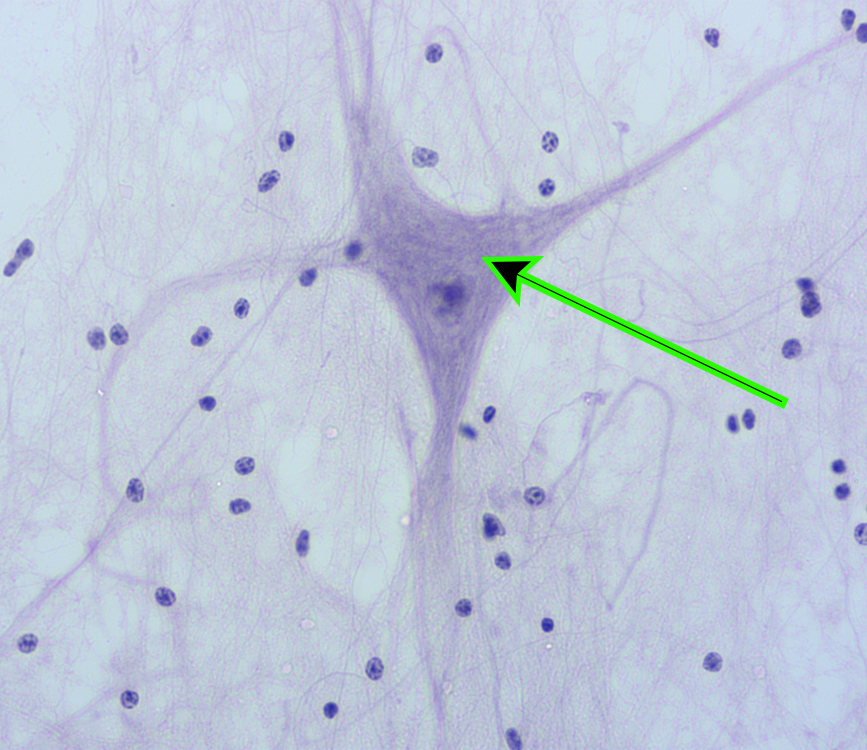
ID specific cell at the end of the pointer:
Multipolar Neuron
The EEG wave that is most readily recorded from the frontal lobes of a patient who is engaging in mental activity with thier eyes open is called the
Beta Wave
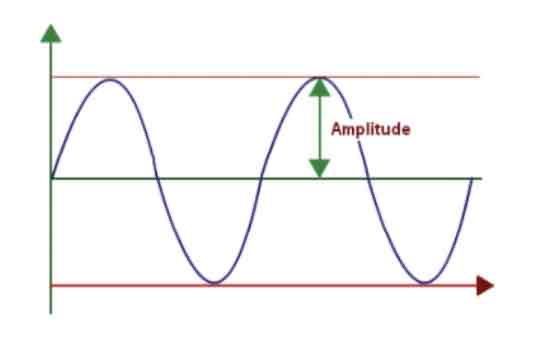
The height of a wave, or more specifically, the vertical distance between the peak of a wave and the point of equilibrium is called the
Amplitude
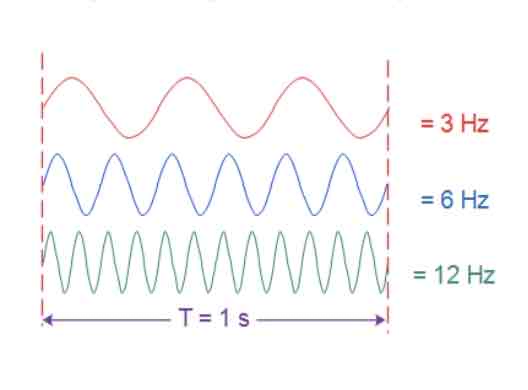
The number of waves that are generated or pass a certain point each second is called the
Frequency
The EEG wave that is most readily recorded from the sweep posteriorly across the cerebral cortex and are common during sleep in adults but are frequently observed in infants who are awake
Delta Wave
• EEG of subjects in _____ sleep is characterized by prominent delta waves (with low frequency and high amplitude)
• Deepest sleep occurs during the first two sleep cycles of the night
• Growth hormone released during _____sleep
Non-REM (NREM)
What happens to the ability of an axon to conduct an action potential when you apply TTX
No action potential occurs
Where is TTX obtained from?
Puffer fish
What two factors increase the nerve conduction speed?
Diameter and Myelination
What generates the gradient for Na and K in a living cell?
Na+ / K+ pumps
Did the amplitude (height) of the AP change as the stimulus was increased ?
No
What happens to the RMP as the extra cellular K+ is increased? Does it become more positive or more negative or stays the same ?
More Positive
State the law or rule that describes this property? PhysioEX 3
Falls under the all or none law.
Define Action Potential
A rapid , all or none. self regenerating reversal of membrane voltage that is conducted throughout the membrane of the cell.
Define Resting Membrane Potential?
The relatively stable voltage across them membrane of a cell at rest. Typically, the space just inside a cell is approximately 70 mV more negative than the space just outside the cell.
What is Depolarization?
Membrane potential becomes more positive (even above 0 mV).
Not as Important or didn’t cover in class
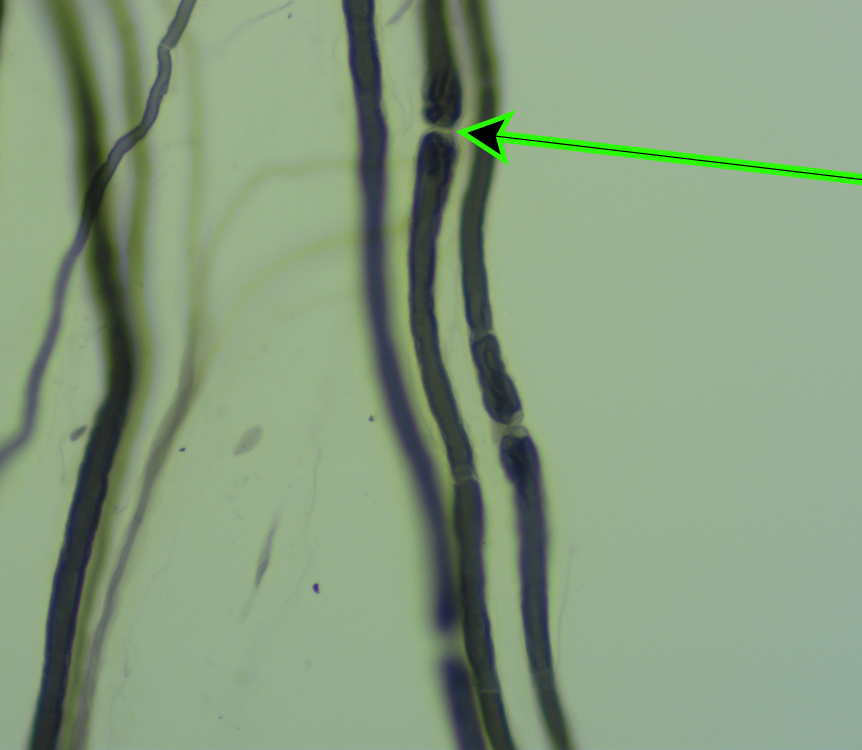
specific structure (light) at the end of the pointer.
Node of Ranvier
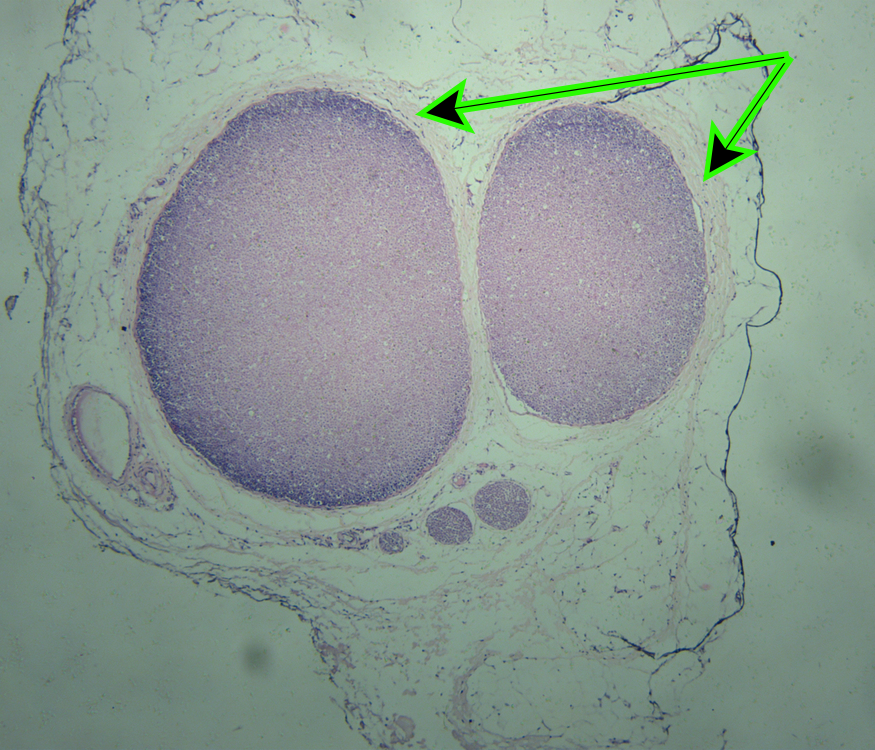
Identify the connective tissue sheath at the end of both pointers:
Perineurium
What does the acronym EEG stand for?
ELECTRO- ENCE- PHALOGRAM
The EEG wave that is most readily recorded from the parietal and occipital lobes of a patient when they are awake and relaxed with thier eyes closed is called the
Alpha Wave
•EEG of subjects in ____sleep is similar to waking EEG (looks similar to alpha wave)
• Metabolic activity and energy consumption similar to waking state but voluntary control of skeletal muscles inhibited
• Dreams occur during ______ sleep
(REM) Rapid Eye Movement
The EEG wave that is most readily recorded from the begin temporal and occipital lobes. Common in newborns but in adults, may indicate severe emotional stress.
Theta Waves
What is the Relative refractory period?
The time during which it is possible but more difficult (i.e. it requires a stronger, more depolarizing stimulus) to initiate an action potential in an excitable cell (i.e. a neuron). This lasts from the end of the absolute refractory period until the end of the hyperpolarizing undershoot, when the membrane potential has return to resting membrane potential.
What is the Refractory Period
The time during which it is impossible to initiate an action potential in an excitable cell (i.e. a neuron). This lasts from the time the action potential begins until several milliseconds after the action potential begins.