T5 - IE5 - Gastroenterology - Lam - Portal Hypertension & Complications of the Liver
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
Cirrhosis is the _______ ______ of any chronic liver disease
- end stage (of any chronic liver disease)
Cirrhosis is the end stage of any __________ __________ ________
- (of any) chronic liver disease
Cirrhosis is characterized histologically by __________ _________ surrounded by _______ tissue
- regenerative nodules
- fibrous (tissue)
Cirrhosis example figure
Clinical Types of Cirrhosis
Compensated
Decompensated
Cirrhosis - Burden of Disease: a ________ ______ of morbidity and mortality in the United States
- leading cause (of morbidity and mortality)
Early readmission increase clinical / economic burden in such patients
Cirrhosis - Burden of Disease: Early readmission increase ________ / __________ burden in such patients
- clinical / economic
Stages and substages of cirrhosis chart
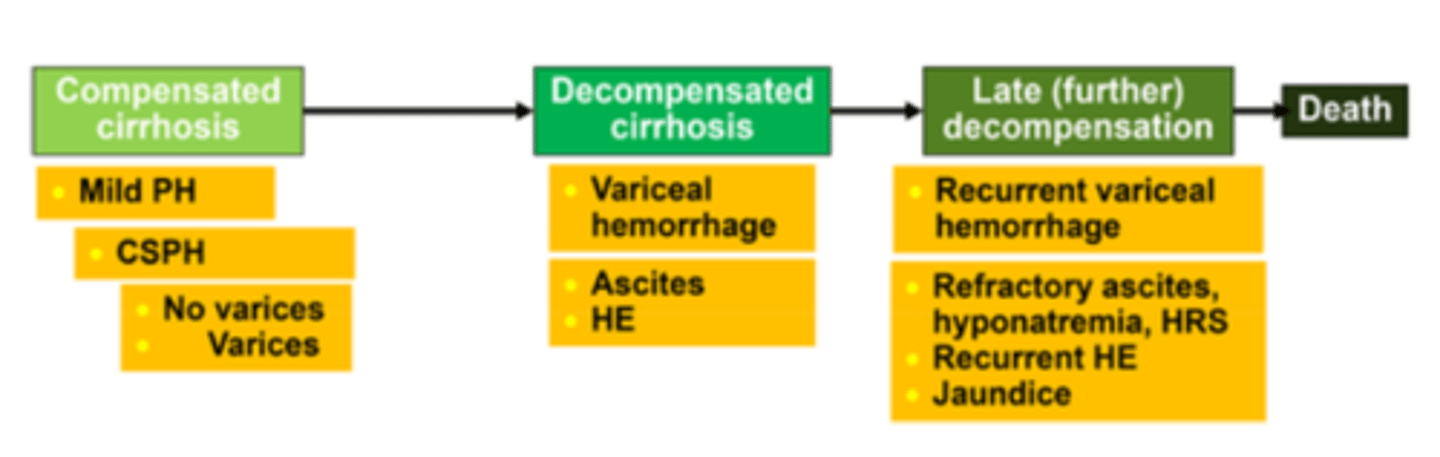
Compensated cirrhosis substages
mild portal hypertension (PH)
clinically significant portal hypertension (CSPH)
No varices
Varices
Decompensated cirrhosis substages
variceal hemorrhage
ascites
hepatic encephalopathy
HE
hepatic encephalopathy
Late (further) decompensation substages
recurrent variceal hemorrhage
refractory ascites, hyponatremia, hepatorenal syndrome (HRS)
recurrent hepatic encephalopathy
jaundice
HRS
hepatorenal syndrome
Complications of cirrhosis pathway chart
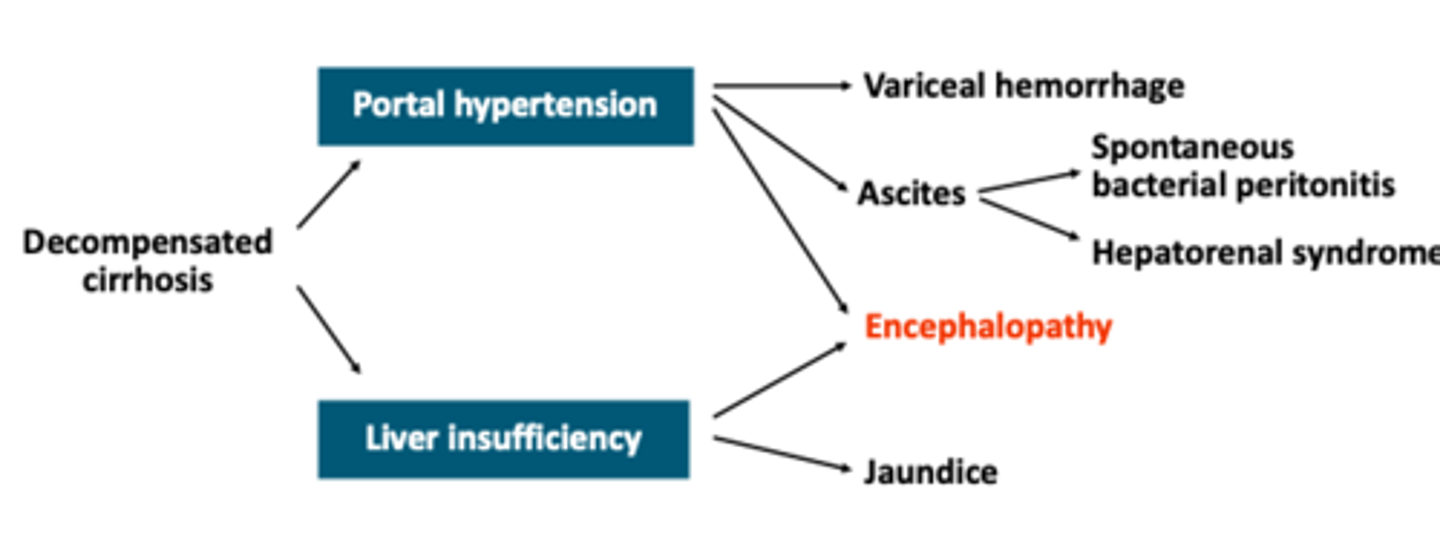
Clinical presentation of liver disease
weakness, tiredness, malaise
N/V, abdominal discomfort and pain
anorexia, weight loss (common with acute and chronic liver disease)
jaundice or dark urine
sudden and massive bleeding, with or without shock on presentation
edema and abdominal swelling (ascites); splenomegaly
Clinical presentation of liver disease: _________ _____ is common with chronic and acute liver disease
- weight loss (is common)
Portal hypertension - epidemiology: Portal hypertension (HTN) is a frequent manifestation of ______ ________
- (frequent manifestation of) liver cirrhosis
Portal hypertension - epidemiology: 2016 liver cirrhosis accounted for ~40,545 deaths, making it the _____ leading cause of US deaths
Western countries: ________ and _____ cirrhosis are the leading causes of portal HTN & esophageal varices
- 10th (leading cause of US deaths)
- alcoholic
- viral (cirrhosis)
Portal hypertension - epidemiology in western countries: alcoholic and viral cirrhosis are the leading causes of ____________ ____ and ___________ ______
- (leading causes of) portal HTN
- esophageal varices
Portal hypertension - epidemiology: males make up more than _____% of patients with chronic liver disease and cirrhosis
- 60(% of patients with chronic liver disease and cirrhosis)
Portal HTN: _________ pressures in the portal venous system, a major vein that _______ to the liver that ___ ___ mm Hg
- elevated (pressures)
- leads (to the liver)
- ≥ 10 (mm Hg)
Decompensated portal hypertension ≥ 12 mm Hg
Portal hypertension: elevated pressures in the ______ _______ system, a major that vein that leads to the _______ that is ≥ 10 mm Hg
Decompensated portal hypertension: ____ ____ mm Hg
- portal venous (system)
- (vein that leads to the) liver
- ≥ 12 (mm Hg)
Portal hypertension is an increase in the pressure within the portal vein caused by ___-________, ______-_______ or ________-_______ factors
- pre-hepatic
- intra-hepatic
- post-hepatic (factors)
Results in increase in pressure (HVPG ≥ 10 mm Hg), results in increase in portal venous flow, or hepatic resistance
Portal hypertension: results in __________ in pressure (HVPG ≥ 10 mm Hg), results in increase in _______ _______ ______, or hepatic _________
- increase (in pressure)
- (increase in) portal venous flow
- (hepatic) resistance
This causes the development of varices across the esophagus and stomach to get around the blockage
Portal hypertension: due to increased in pressure, portal venous flow and hepatic reisstance
Results in development of _______ across the esophagus and stomach to get around the __________
- (development of) varices
- (to get around the) blockage
Portal Hypertension Anatomy
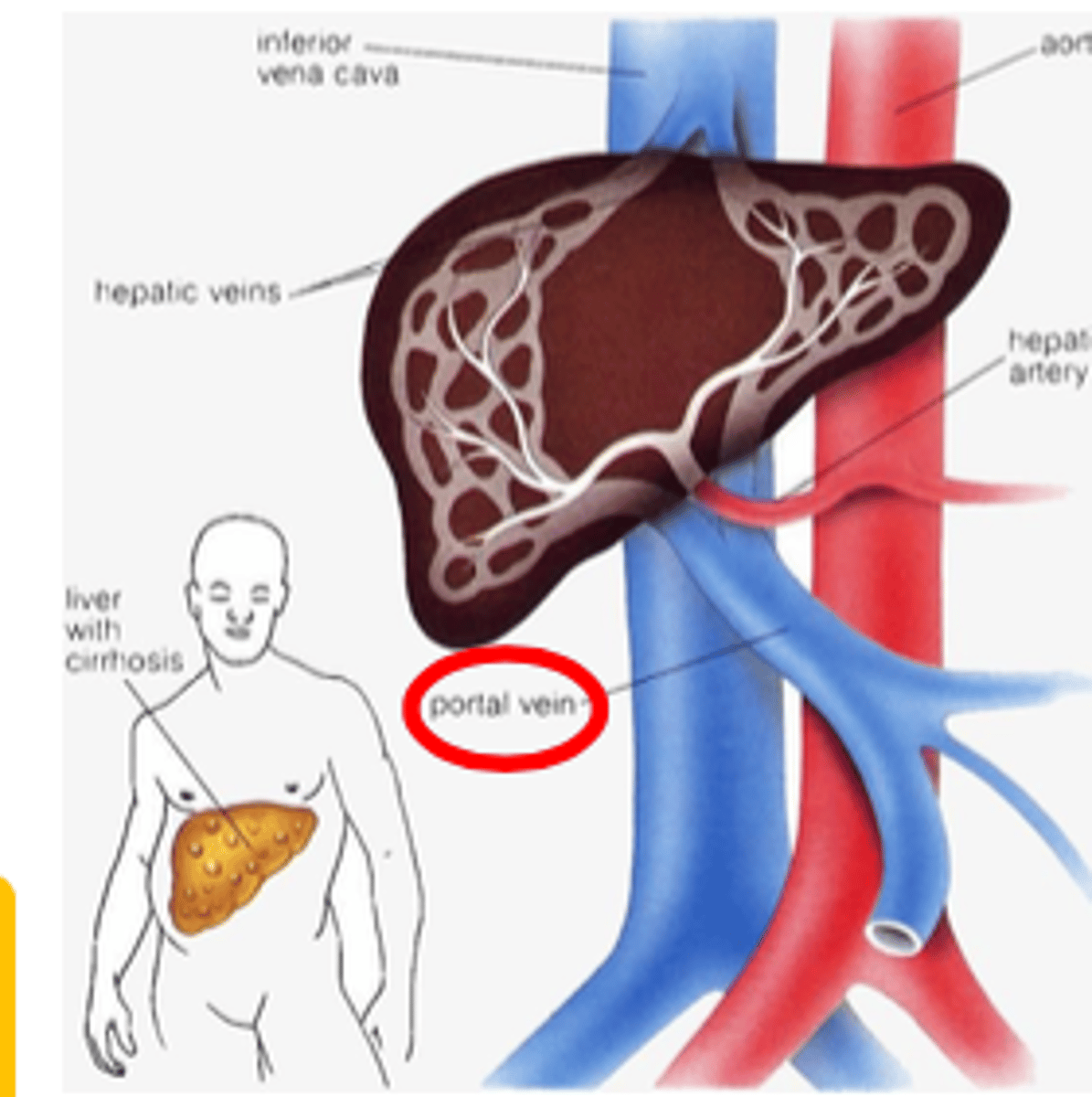
Portal hypertension causes
pre-hepatic (obstruction)
- portal vein thrombosis
- chronic pancreatitis
intra-hepatic (intrinsic)
- liver cirrhosis [most common]
post-hepatic (structural)
- Budd-chiari syndrome
- venous occlusive disease
- cardiac-related (e.g., right heart failure or constrictive [occlusive pericarditis])
Portal hypertension: pre-hepatic causes are usually due to ___________
- (usually due to) obstruction
Portal hypertension: pre-hepatic causes
portal vein thrombosis
chronic pancreatitis
Portal hypertension - intra-hepatic is usually ___________
- (usually) intrinsic
Portal hypertension - intra-hepatic: _________ ___________ is the most common cause of portal HTN
- liver cirrhosis (is the most common cause)
Portal hypertension - intra-hepatic causes
liver cirrhosis (the most common)
Portal hypertension - post-hepatic is due to a _________ cause
- structural (cause)
Portal hypertension - post-hepatic (structural) causes
Budd-Chiari syndrome
Venous occlusive disease
Cardiac-related
(e.g., right heart failure or constrictive [occlusive pericarditis])
Portal-hypertension: intra-hepatic causes compose of ___ ___% of the cases with ___________ being the most common
- ≥ 70(% of the cases)
- cirrhosis (being the most common)
Portal hypertension - intra-hepatic: Causes of Cirrhosis
alcohol (most common)
chronic HBV, HCV
autoimmune hepatitis
PBC (primary biliary cirrhosis)
PSC (primary sclerosingitis)
NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis)
Biliary atresia: occurs in children
Cryptogenic / idiopathic: 20% of all diagnoses
Portal hypertension - intra-hepatic: other causes than cirrhosis
schistosomiasis: occurs world-wide
genetic causes
- Wilson disease
- hemochromatosis
- α1-antitrypsin deficiency
- congenital hepatic fibrosis
Pharmacological treatments & management of portal hypertension figure
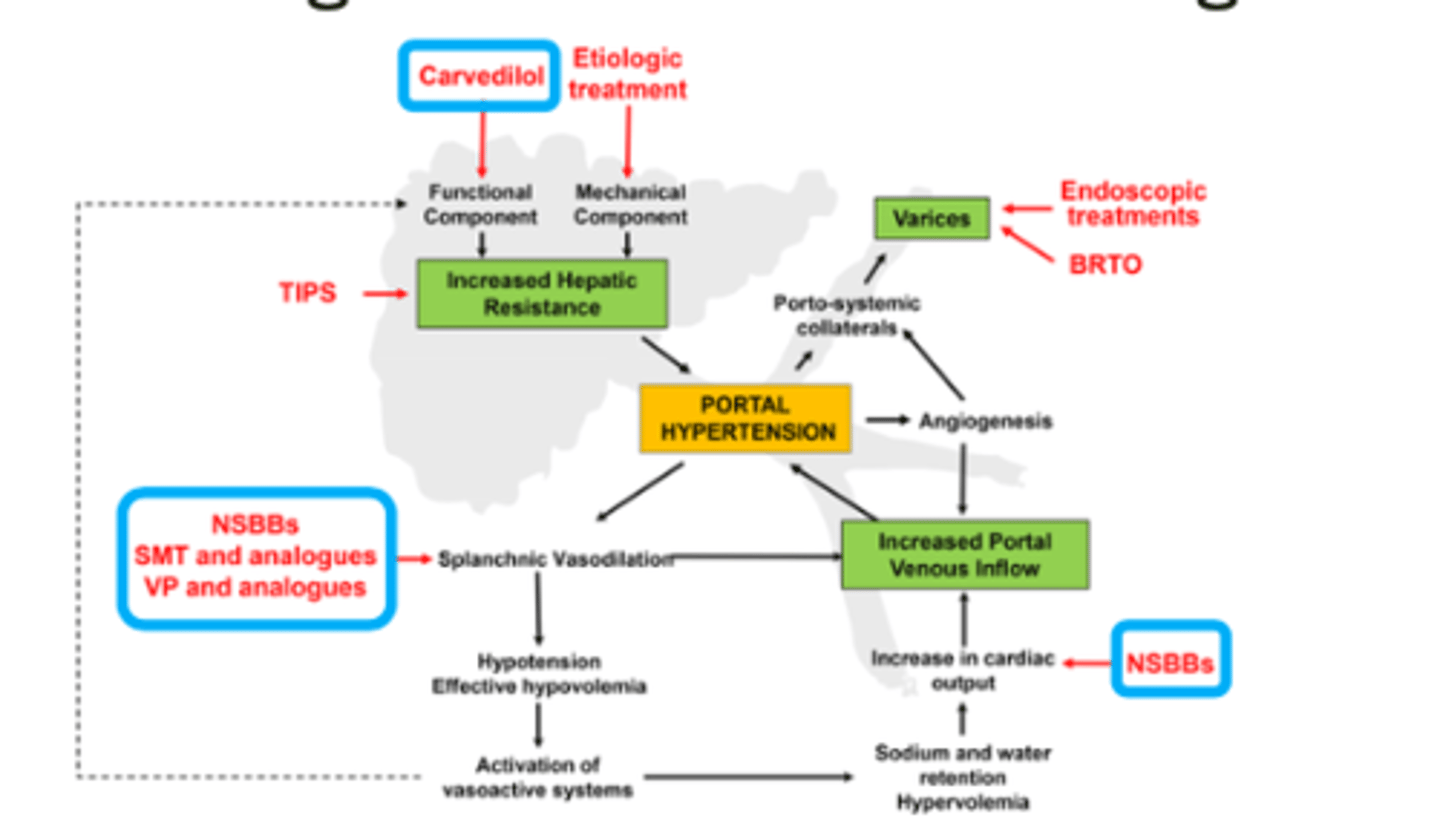
Portal hypertension - pharmacological treatments: β-blockers
propranolol (INDERAL)
nadolol (CORGARD)
carvedilol (COREG)
propranolol
INDERAL
nadolol
CORGARD
carvedilol
COREG
Portal hypertension - pharmacological treatments: β-blockers adverse effects
light-headedness
fatigue
hypotension
bradyarhythmia
hyperglycemia
ED
Portal hypertension - pharmacological treatments: β-blockers contraindications
asthma
diabetes with frequent or severe hypoglycemia
peripheral vascular disease
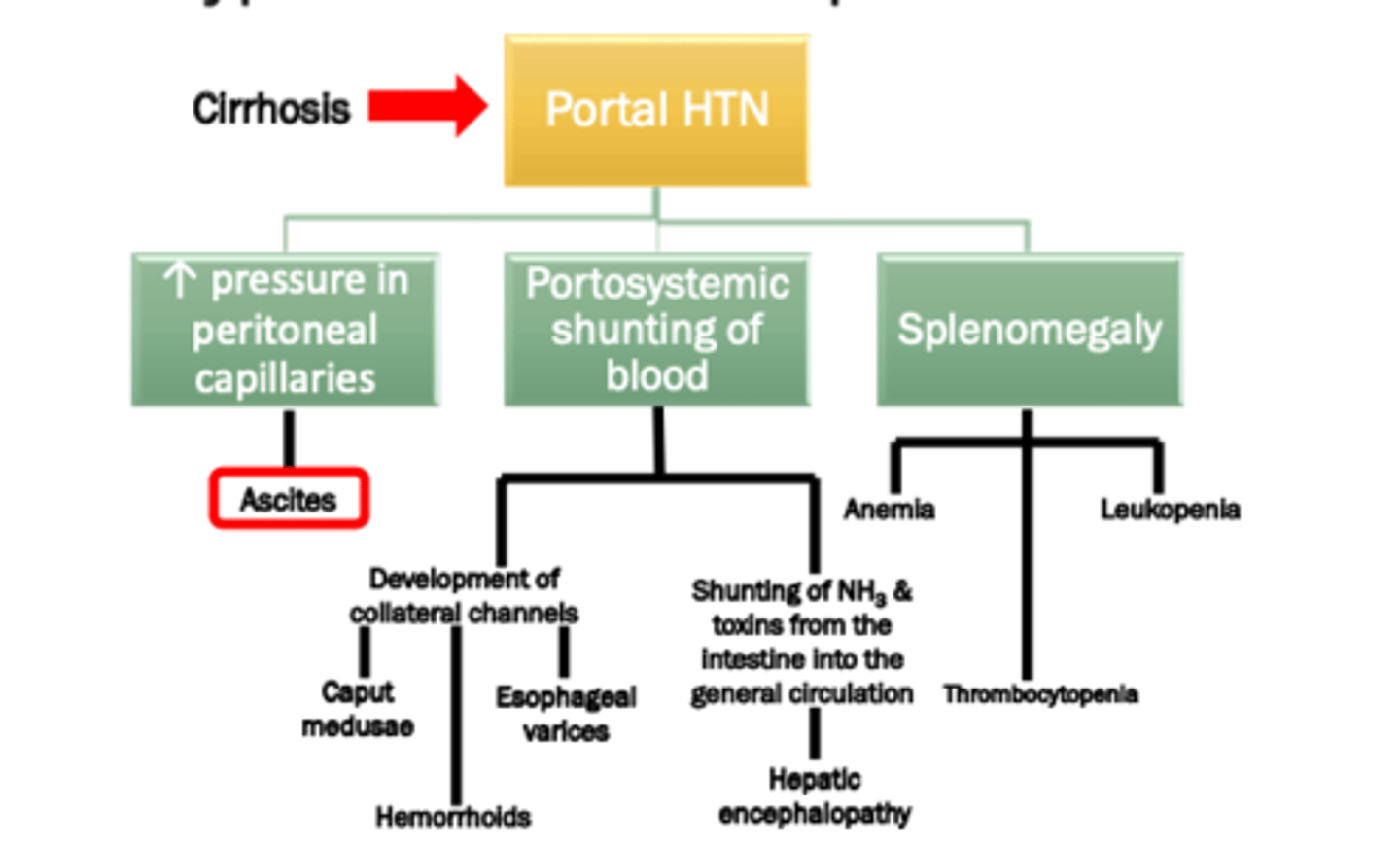
Portal Hypertension Complications Algorithm
increase pressure in peritoneal capillaries
portosystemic shunting of blood
splenomegaly
Ascites is caused by ______________ from decreased _________ __________
- hypoalbuminemia
- (from decreased) protein synthesis
This causes increase in capillary permeability and volume overload, which leads fluids escaping to vascular space and accumulating in peritoneal space (cavity)
Ascites is caused by hypoalbuminemia from decreased protein synthesis
This causes increase in ____________ ________ and volume _________
- (increase in) capillary permeability
- (volume) overload
Which allows fluid to escape vascular space and accumulate in peritoneal space
Ascites causes increase in capillary permeability and volume overload, which allows fluid to __________ the _______ space and _________ in peritoneal cavity
- escape
- vascular (space)
- accumulate (in peritoneal cavity)
Ascites results in the increased _________ _______ in the abdominal ________
- (increased) hydrostatic pressure
- (abdominal) circulation
Fluid is pushed into the peritoneal space ("third spacing")
Ascites: fluid is used into the _________ space (______ _______)
Sinusoidal pressure > _______ _______ pressure
- peritoneal (space)
- "third spacing"
- (sinusoidal pressure >) colloid oncotic (pressure)
Ascites is induced by ____________ ________ and ______
- physiologic stress
- fluids
Ascites figure
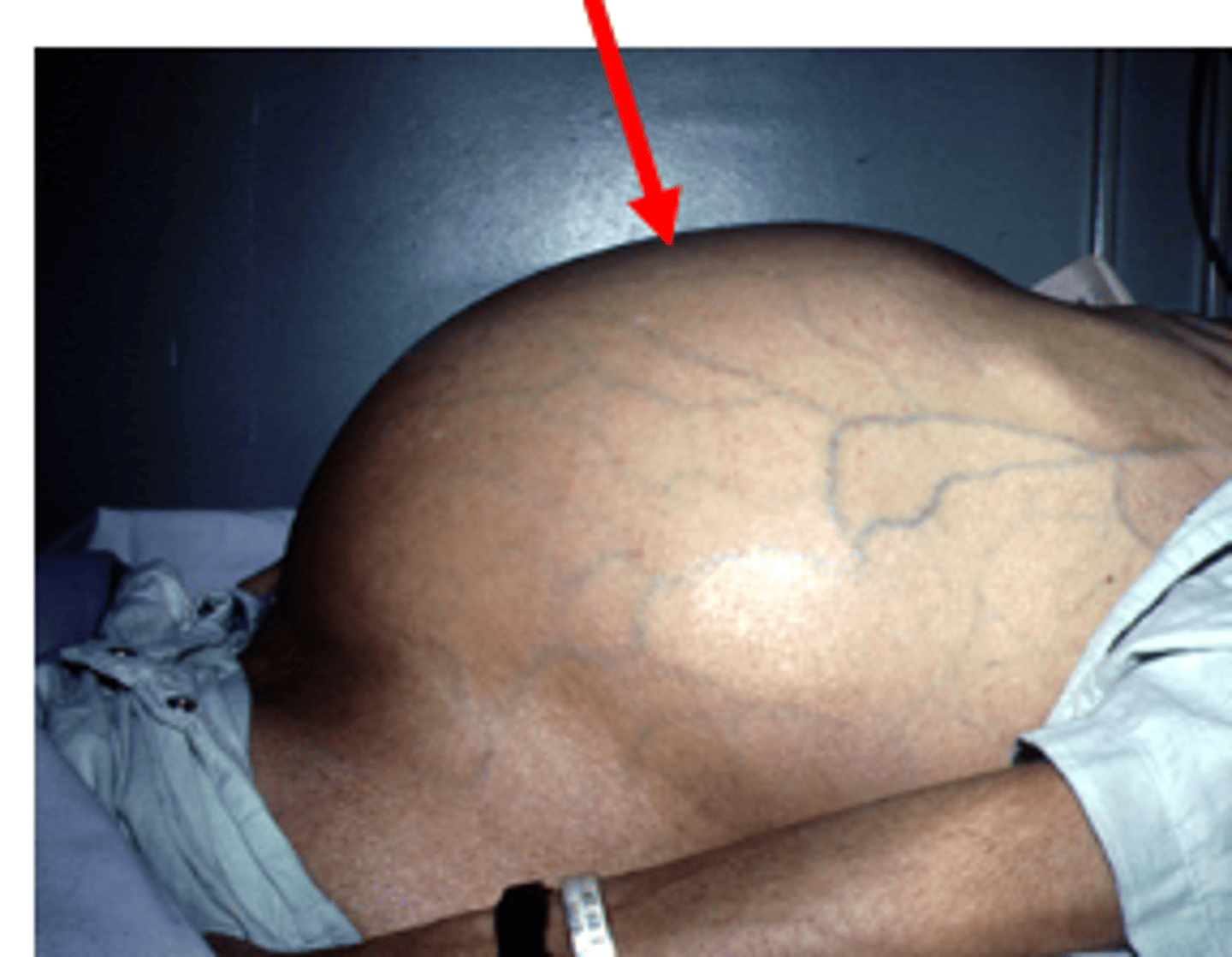
Ascites complications
spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
hepatorenal syndrome
Ascites pharmacologic therapy
Diuretics
colloids
Ascites management
sodium / water restriction
large volume paracentesis
peritoneal-venous shunt
Ascites approach: perform ___________, drain the _______ fluids from abdomen into __________
- pericentesis
- excess (fluids)
- (into) vacutainers
Ascites approach: administer _______ (with or without ________)
- diuretics
- (with or without) albumin
Ascites approach: administer _________ to increase the ________ pressure inside the veins and vascular spaces
- (administer) albumin
- (increase the) colloid (pressure)
Causes water to go back into vascular spaces and veins
Ascites approach: administering albumin causes water to go back into the ________ ______ and ______
- vascular spaces
- veins
Ascites approach: monitor _____ _____ and _______
- vital signs
- electrolytes
Ascites pharmacological treatments
spironolactone
furosemide
spironolactone + furosemide (preferred treatment approach)
Ascites pharmacological treatments: spironolocatone is ______ for ascites
- DOC (for ascites)
DOC = drug of choice
Onset of effect: 3-5 days before maximal natriuresis achieved; titrate dose Q3-5 days
Ascites pharmacological treatments: spironolocatone onset of effect ___-___ days before maximal natriuresis achieved, titrate dose ____-____ days
- 3-5 (days)
- (titrate dose) 3-5 (days)
Dose-limiting side effects: acute renal failure
Ascites pharmacological treatments: spironolocatone dose-limiting side effects
acute renal failure
monitor:
- hyperkalemia
- gynecomastia
for spironolactone
Ascites pharmacological treatments: spironolocatone monitor
hyperkalemia
gynecomastia
Ascites pharmacological treatments: furosemide is ____ _______ for ascites as monotherapy
- NOT effective (for ascites as monotherapy)
Ascites pharmacological treatments: spironolactone:furosemide ratio
100mg:40 mg
Ascites pharmacological treatments: ___________ + __________ is the preferred treatment approach
- spironolactone (+) furosemide
Ascites pharmacological treatments: furosemide monitoring
BP
UOP
electrolytes
SCr / BUN
DOC
drug of choice
Ascites treatment: albumin ____ use with large volume ____________
- PRN (use)
- (large volume) paracentesis
> 5 liters removed
Ascites treatment: albumin MOA
expands effective plasma volume and may improve effect of vasopressors (by binding vasoconstrictions and increasing central blood volume)
Ascites monitoring parameters
daily weights (should be losing ~500 mL/day)
electrolytes
SCr / BUN
peripheral edema
Spironolactone
ALDACTONE
Spironolactone (ALDACTONE) is preferred as ________ treatment of ascites
- initial (treatment of ascites)
Furosemide
LASIX
Furosemide (LASIX): IV to PO
IV = 50% of PO dose
Routes: PO, IVP, IV infusion NOT effective as monotherapy for ascites
Albumin infusion rate rate for ascites
1 mL/min
STOP infusion if patient is hypotensive
Ascites - non-pharmacological treatment
Low sodium diet
Fluid restriction
Paracentesis ("tap")
TIPS: transjugular intrahaptic portosystemic shunt
TIPS
transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
Ascites - non-pharmacological treatment: low sodium diet
< 2 gms of sodium / day
Ascites - non-pharmacological treatment: fluid restriction
< 1000 mL/day
only for symptomatic dilutional hyponatremia (Na+ < 130 mEq/L + ascites and/or edema)
Paracentesis ("tap"): treatment option for ______ volume and _______ ascites
- large (volume)
- refractor (ascites)
Typically Q2-4 weeks in refractory
Paracentesis: has _______ risk of complications; ______ and ______ _______ than conventional diuretic therapy
- lower (risk of complications)
- faster
- more effective (than conventional diuretic therapy)
Paracentesis: larger volume (> 5 liters) tap should be accompanied by _________ to decrease complications
- (accompanied by) albumin
Ascites - non-pharmacological treatment: TIPS - prevent ascites in ________ patients; associated with decreased ___-_________- of ascitic fluid compared to large volume taps
- refractory (patients)
- re-accumulation (of ascitic fluid)
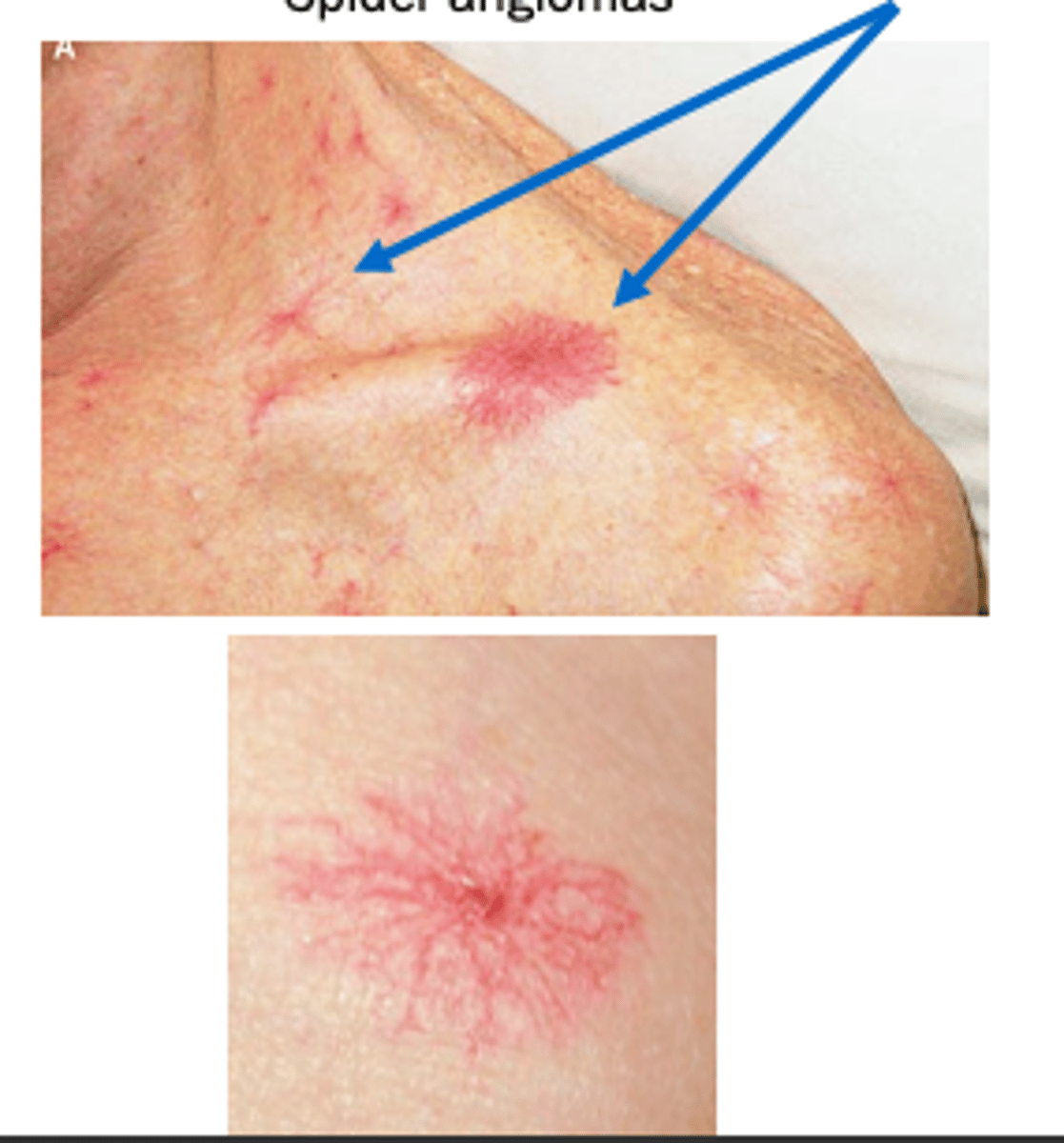
Portal hypertension complications - spider angioma: red ________ with peripherally ___________ out arteries
- (red) macules
- branching (out arteries)
Macules = body of the spider
Arteries = spider legs
Portal hypertension complications - spider angioma: develop because the liver is primarily responsible for ________________ estrogen
Estrogen can cause _________ _________
- metabolizing (estrogen)
- (can cause) spider angiomas
If there are more than 5 of these, there may be something wrong especially if patient is at risk of liver failure
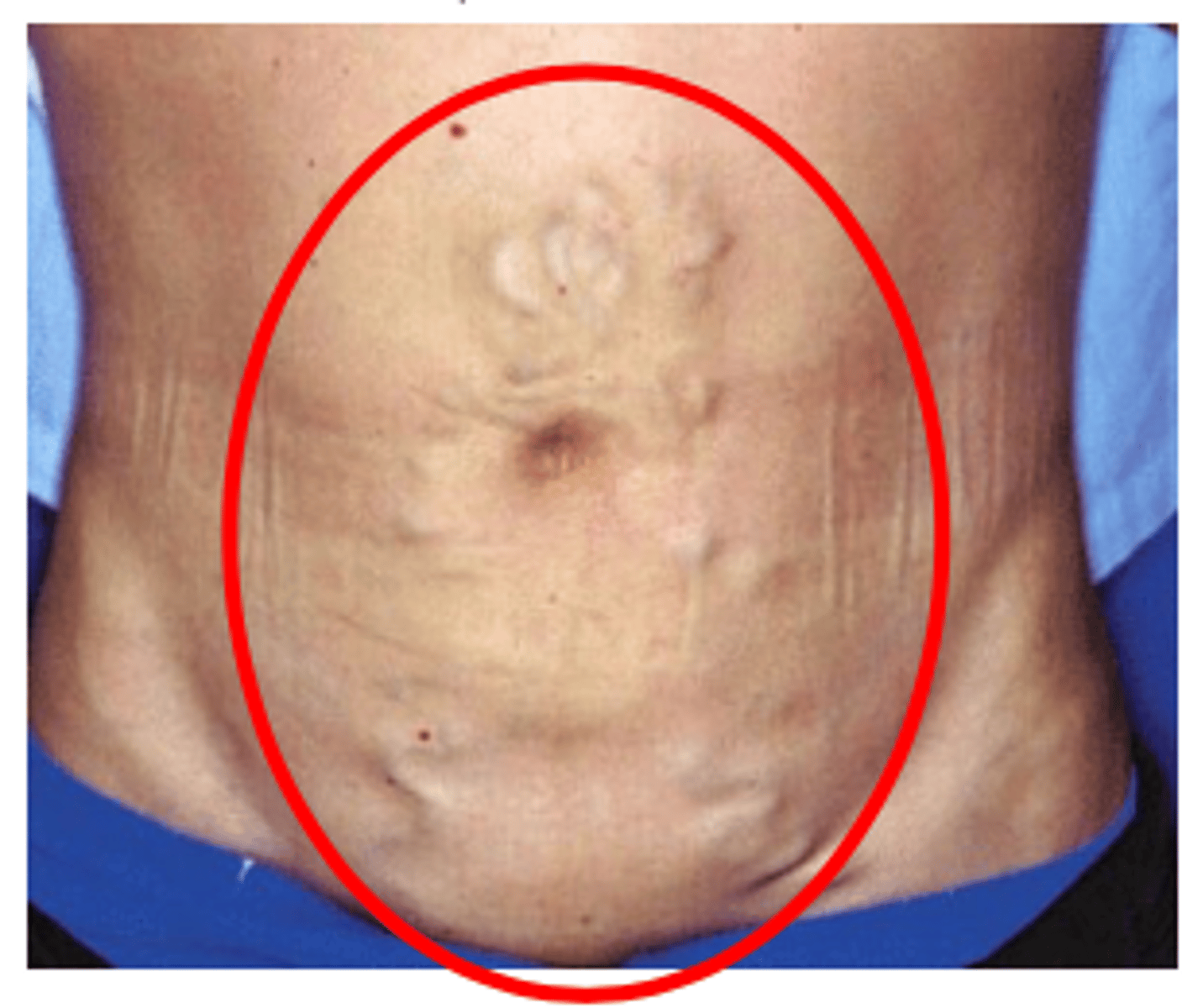
Portal hypertension complications - caput Medusa: tortuous, dilated _________ _________ and another _______ of portal hypertension
- dilated (umbilical vessels)
- sign (of portal hypertension)
Spider angiomas figure
Caput medusae figure
Variceal bleeding: splanchnic system drains venous blood from the _____ _______ to the _______
- (from the) GI tract
- (to the) liver
Portal HTN causes resistance to drainage -> superficial vessels (varices) develop to handle overload
Variceal bleeding: splanchnic system drains venous blood from the GI tract to the liver
Portal HTN causes ___________ to drainage -> superficial vessels (varices) ___________ to handle overload
- resistance (to drainage)
- develop (to handle overload)
Varices are weak & easily damaged, which causes GI bleeding
Portal HTN causes resistance to drainage -> superficial vessels (varices) develop to handle overload
Variceal bleeding: splanchnic system drains venous blood from the GI tract to the liver
___________ ____________ causes resistance to drainage -> ______________ ____________ (___________) develop to handle overload
- portal hypertension
- superficial vessels (varices)
Variceal bleeding: Portal HTN causes resistance to drainage -> superficial vessels (varices) develop to handle overload
Varices are _____ & easily __________, which causes _____ __________
- weak
- (easily) damaged
- GI bleeding
Management of acute variceal bleeding - goals: ________ bleeding, _________ rebreeding and avoid acute complications such as ______
- control (bleeding)
- prevent (rebreeding)
- SBP
SBP = spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Management of acute variceal bleeding - stabilize blood volume: to ____________ stability and Hgb ___ g/dL
- hemodynamic (stability)
- 8 (g/dL)
Management of acute variceal bleeding
stabilize blood vlume
- hemodynamic stability
- Hgb ~ 8 g/dL
Airway management
fluid resuscitation
Management of acute variceal bleeding - pharmacological therapy
octreotide (SANDOSTATIN)