AP European History "Must Knows"
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
Greek and Roman texts
were classical works of philosophy, science, and literature from antiquity that were rediscovered during the Renaissance, such as Aristotle's Politics, which influenced early modern political thought.

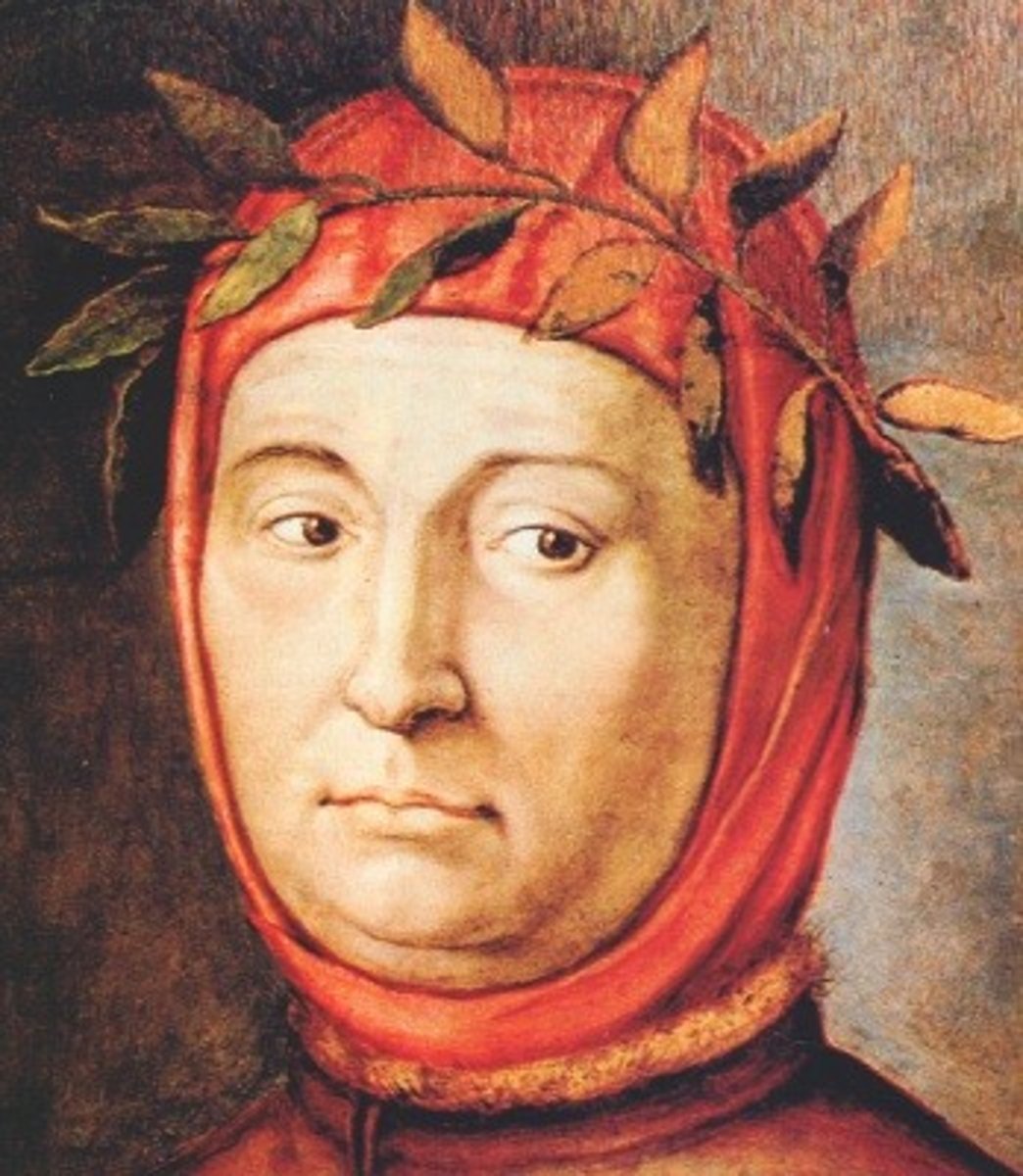
Petrarch
was a 14th-century Italian scholar who is considered the "Father of Humanism" for reviving classical literature, exemplified by his rediscovery and promotion of Cicero's letters.

Catholic Church
was the dominant religious and political institution in medieval and early modern Europe, exemplified by its role in the Inquisition to suppress heresy.

Printing press
invented by Johannes Gutenberg around 1440, revolutionized the spread of information, as seen in the mass production of the Gutenberg Bible.
Erasmus
Christian humanist who criticized Church corruption and emphasized inner piety, notably in his work In Praise of Folly.

Henry VIII
English king who broke with the Catholic Church and created the Church of England to annul his marriage to Catherine of Aragon.

Elizabeth I
Protestant queen of England who stabilized the nation through the Elizabethan Religious Settlement and defeated the Spanish Armada in 1588.

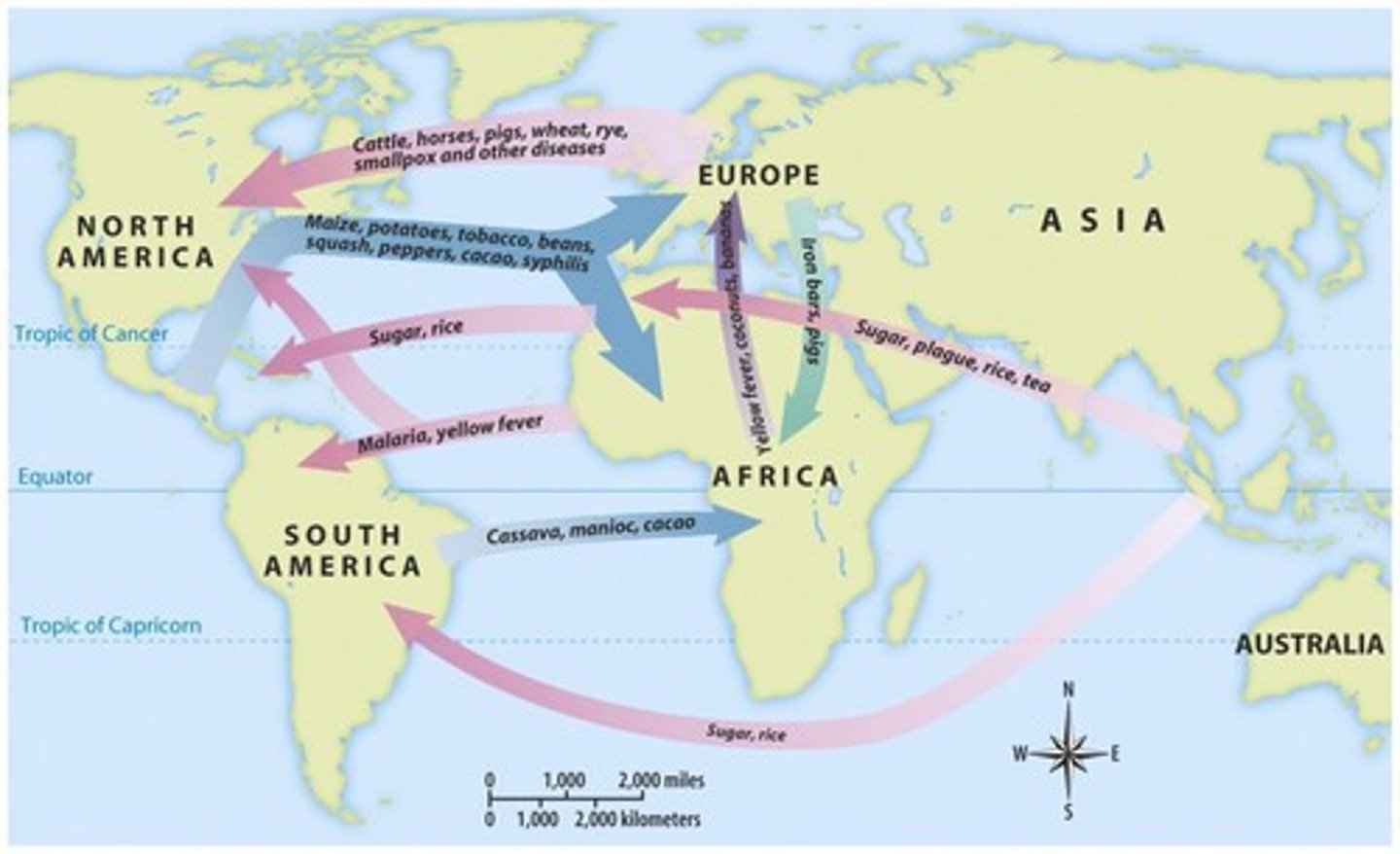
Columbian Exchange
the global transfer of plants, animals, and diseases following 1492, such as the introduction of potatoes to Europe from the Americas.
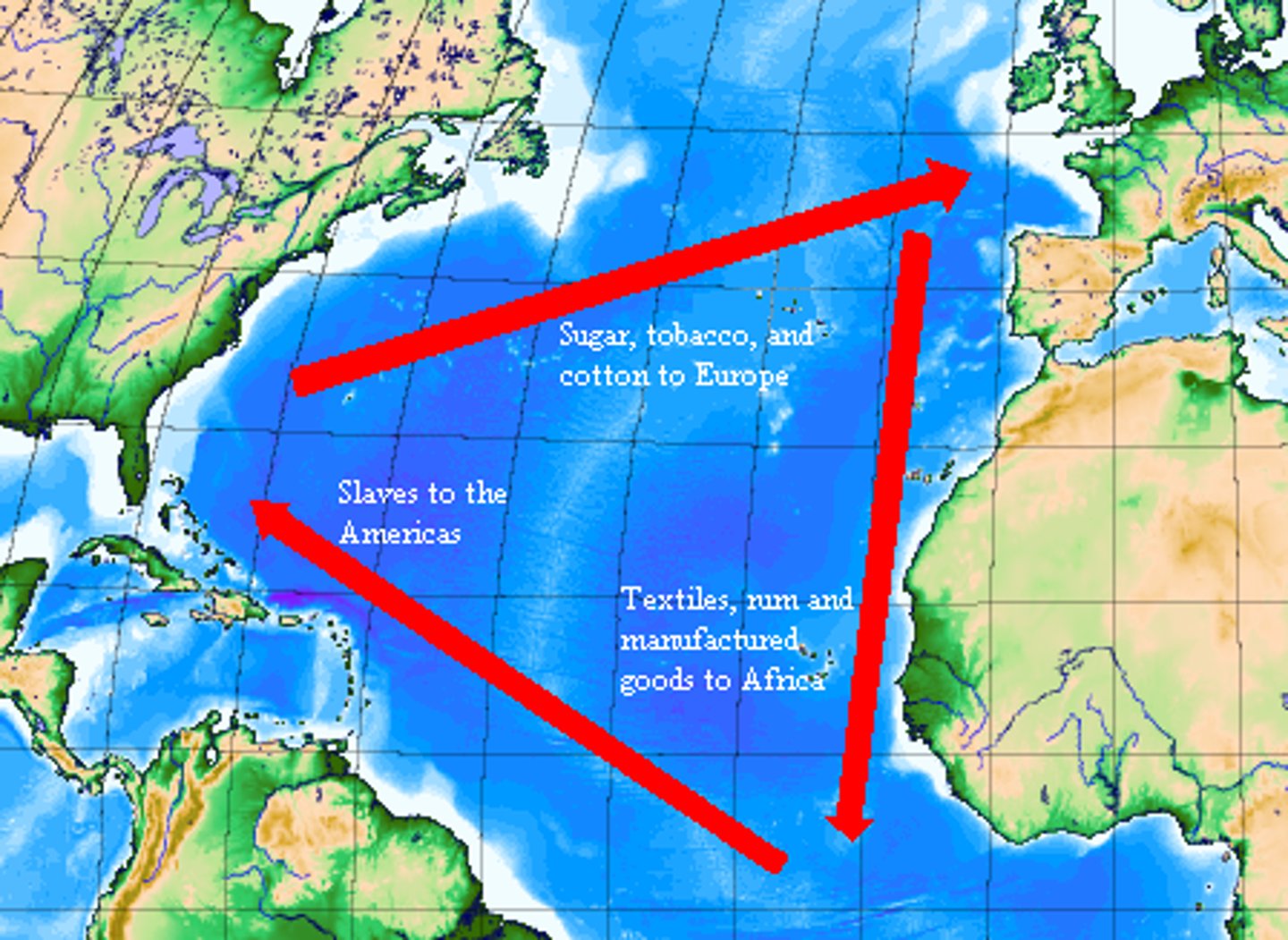
Transatlantic slave-labor
forcibly transported Africans to the Americas to work on plantations, exemplified by the sugar plantations in the Caribbean.
Martin Luther
German monk who sparked the Protestant Reformation by posting his 95 Theses against Church indulgences in 1517.

John Calvin
Protestant reformer who promoted predestination and a theocratic society, as seen in the establishment of Calvinist Geneva.

Anabaptists
radical reformers who believed in adult baptism and separation from state churches, exemplified by the Munster Rebellion in 1534.

Reformation
religious movement in the 16th century challenging Catholic authority, leading to the rise of Protestant denominations like Lutheranism in Germany.

Edict of Nantes
1598 decree by Henry IV of France granting religious tolerance to Huguenots, ending the French Wars of Religion.

Peace of Westphalia
1648 treaty that ended the Thirty Years' War and established the principle of state sovereignty in Europe.

Jesuits
Catholic religious order founded by Ignatius of Loyola that led the Counter-Reformation through education, like founding schools across Europe.

Council of Trent
Catholic council (1545-1563) that reformed Church doctrine and practices in response to the Protestant Reformation, affirming traditional teachings and banning indulgence abuse.
Mannerism
artistic style characterized by elongated figures and unusual perspectives, as seen in El Greco's The Burial of the Count of Orgaz.

Baroque
dramatic and ornate artistic style used to promote religious and royal power, exemplified by Bernini's Ecstasy of Saint Teresa.

English Civil War
(1642-1651) was a conflict between Royalists and Parliamentarians over governance, resulting in the execution of King Charles I.

Glorious Revolution
1688 was the nonviolent overthrow of James II of England and the establishment of a constitutional monarchy under William and Mary.

Agricultural Revolution
18th century improved farming efficiency through innovations like Jethro Tull's seed drill, increasing food production.
putting-out system
pre-industrial production method where merchants outsourced textile work to rural households, particularly in the English wool industry.

Dutch Republic
17th-century commercial and naval power known for religious tolerance and economic innovation, as seen in the Amsterdam stock exchange.
Poland's partition
late 18th century involved the division of Polish territory among Russia, Prussia, and Austria, erasing it from the map by 1795.
Battle of Vienna (1683)
1683 when European forces, led by Polish King Jan Sobieski, stopped the Ottoman Empire's advance into Central Europe.

Louis XIV
absolute monarch of France who centralized power and built the Palace of Versailles to glorify his rule and control the nobility.

Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Louis XIV's finance minister who strengthened the French economy through mercantilist policies, including state-supported industries like textiles.

Peter I of Russia
modernized and expanded Russia by westernizing its military and building a new capital at St. Petersburg.

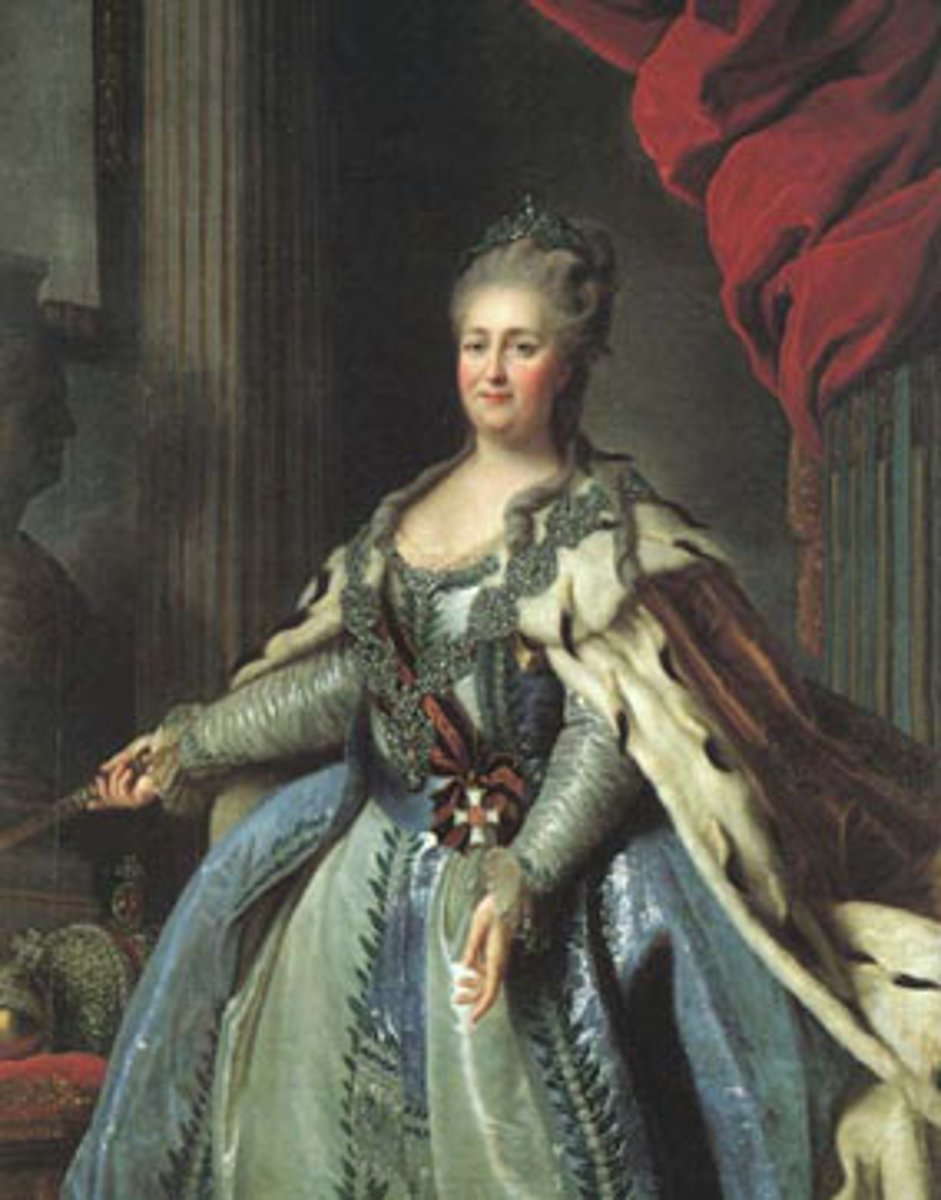
Catherine II of Russia
Enlightened Absolutist who expanded Russian territory and corresponded with Voltaire, promoting education and limited reform.

Scientific Revolution
period of major advances in science during the 16th and 17th centuries, including the heliocentric theory by Copernicus.

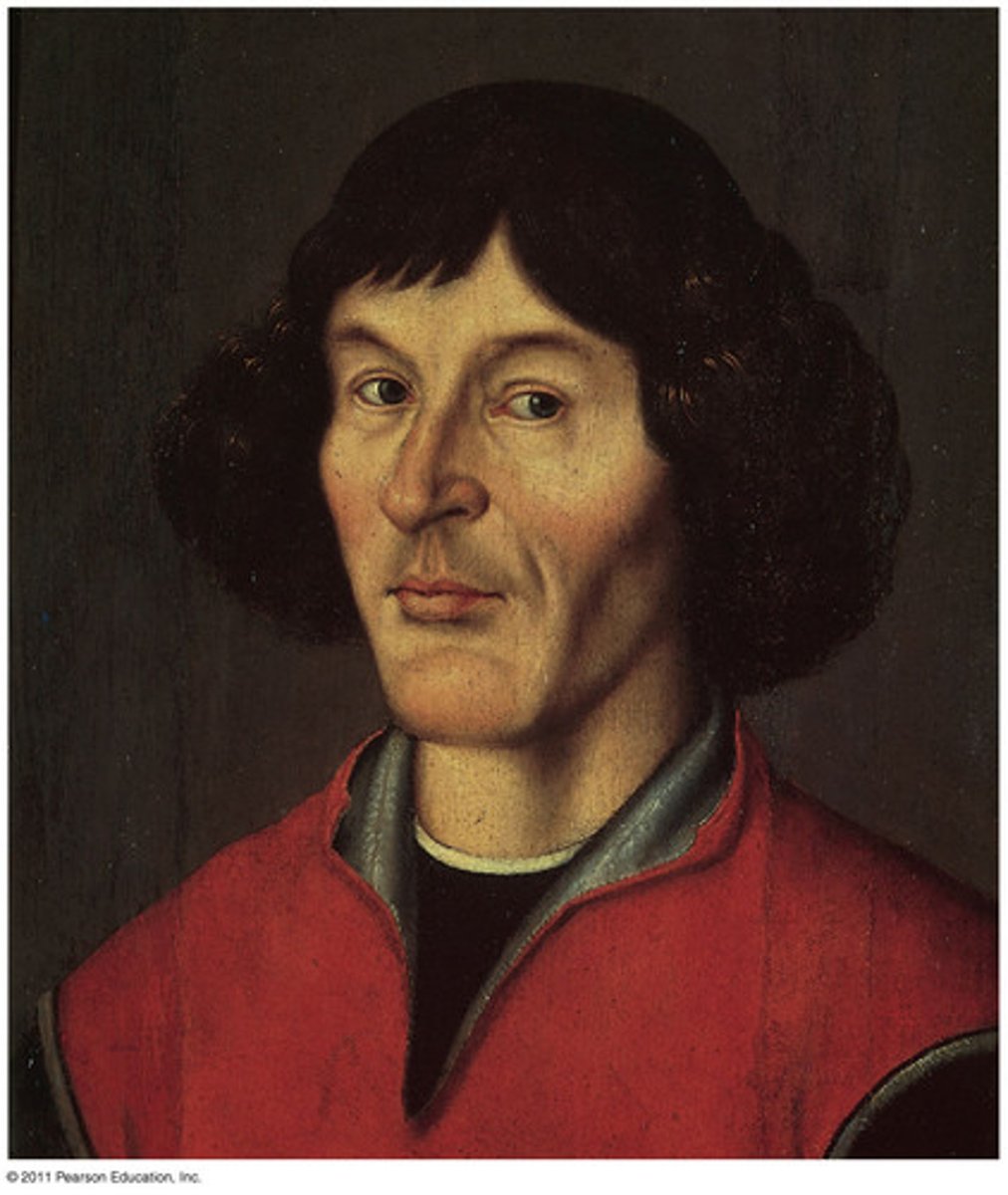
Copernicus
Renaissance astronomer who proposed the heliocentric model of the solar system in On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres (1543).

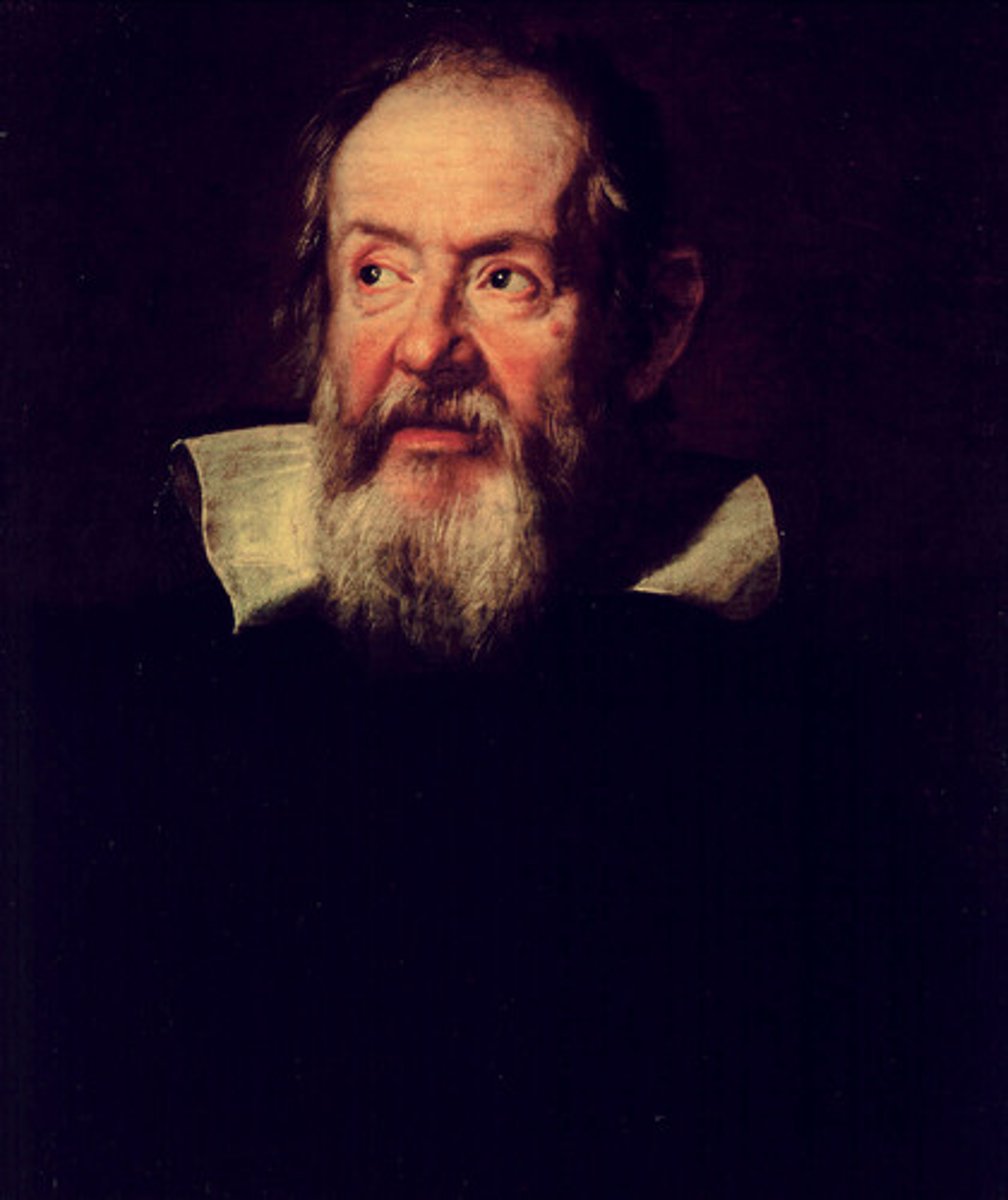
Galileo
Italian scientist who supported heliocentrism and improved the telescope, leading to his trial by the Inquisition in 1633.

Isaac Newton
English physicist who formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation in his Principia Mathematica (1687).

William Harvey
English physician who discovered the circulation of blood through the body, challenging traditional views of anatomy.
Galen
Greek physician whose inaccurate theories about human anatomy dominated medicine until the Scientific Revolution, such as his belief in four bodily humors.

Francis Bacon
English philosopher who developed the scientific method based on empirical observation, as outlined in Novum Organum.

Rene Descartes
French philosopher emphasized deductive reasoning and rationalism, famously stating "I think, therefore I am" in Discourse on Method.

Voltaire
French Enlightenment writer who criticized religious intolerance and absolute monarchy, as in his novel Candide.

Denis Diderot
chief editor of the Encyclopédie, which spread Enlightenment ideas on science, politics, and philosophy across Europe.

John Locke
English philosopher who argued that government must protect natural rights—life, liberty, and property—in Two Treatises of Government.

Jean-Jacques Rousseau
French philosopher believed in the general will and popular sovereignty, as explained in The Social Contract (1762).

Enlightenment Salons
gatherings hosted mostly by upper-class women where intellectuals discussed ideas, such as those organized by Madame Geoffrin in Paris.

Adam Smith
Scottish economist who promoted free-market capitalism in The Wealth of Nations (1776), advocating for the "invisible hand" of the economy.

Physiocrat
Enlightenment economists who believed land and agriculture were the true sources of wealth, like François Quesnay's Tableau Économique.

Enlightenment
18th-century intellectual movement emphasizing reason, individualism, and secularism, influencing reforms like Frederick the Great's legal code.

Neoclassicism
18th-century artistic style inspired by classical antiquity, exemplified by Jacques-Louis David's painting Oath of the Horatii.

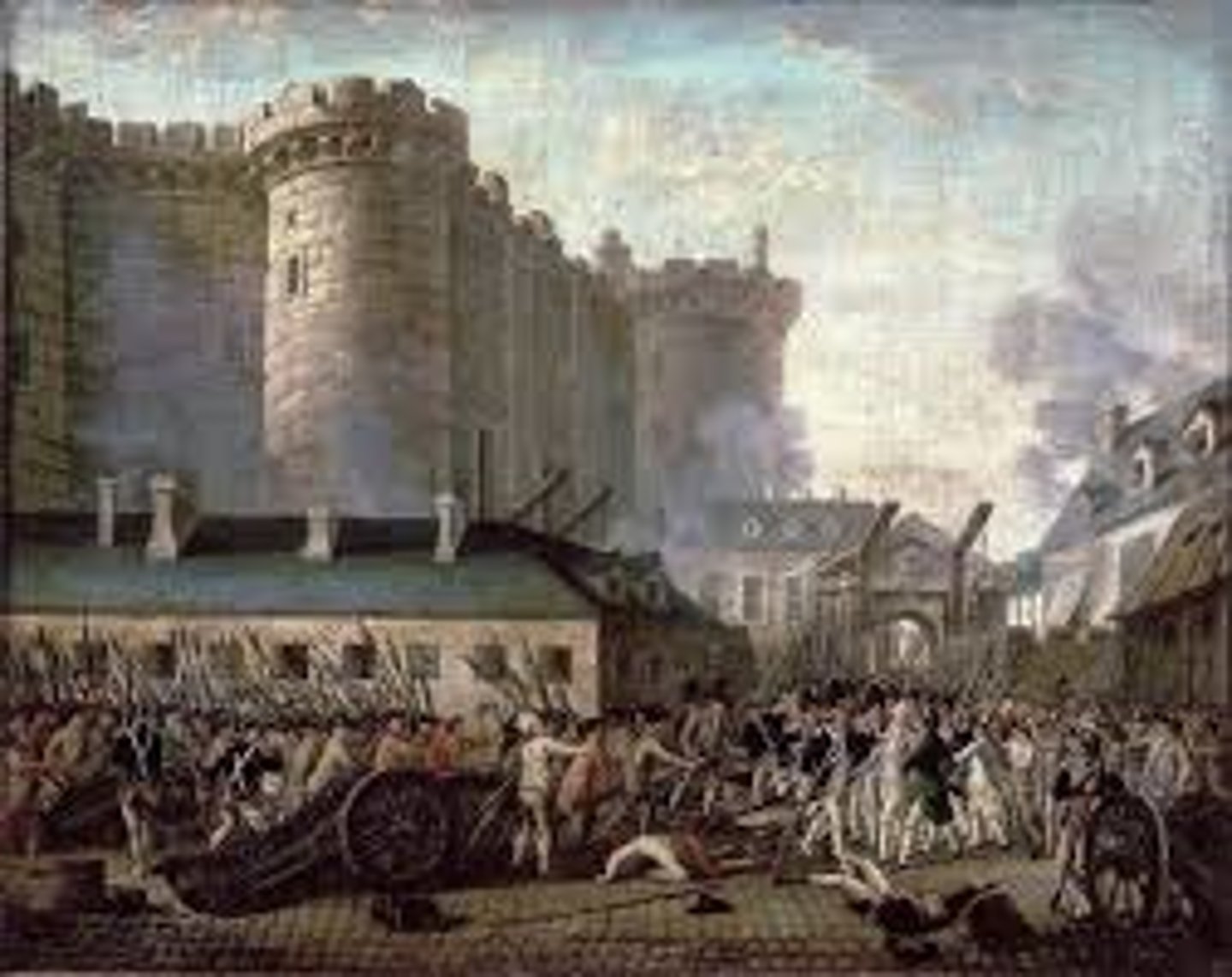
French Revolution
political and social uprising (1789-1799) that overthrew the monarchy and led to radical changes, starting with the storming of the Bastille.

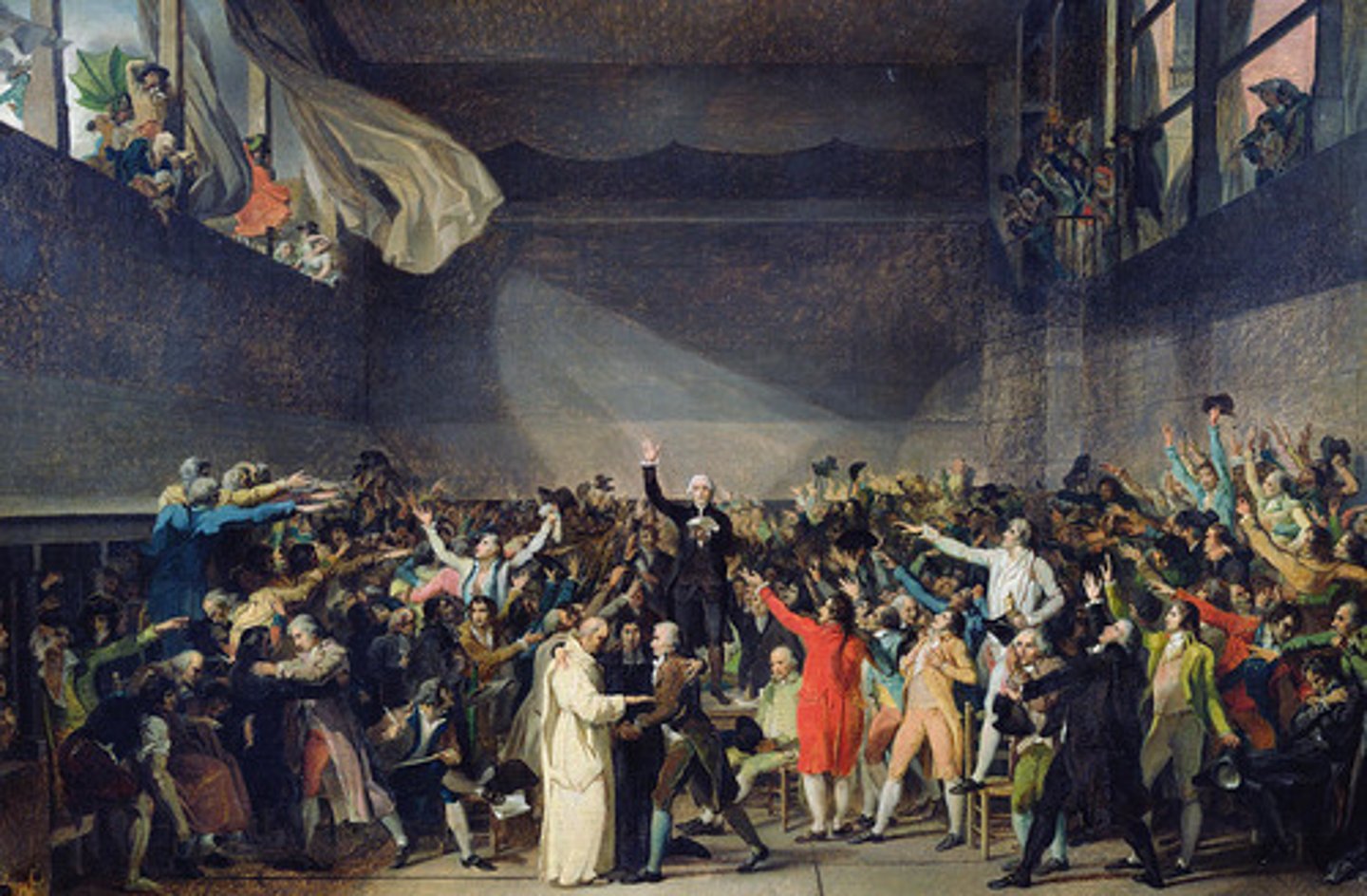
Liberal phase of French Revolution
phase (1789-1792) of the French Revolution established a constitutional monarchy and passed the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen.

Moderate phase of French Revolution
phase sought to reform the monarchy and society without complete upheaval, exemplified by the creation of the National Assembly and civil reforms before the radicalization of 1793.

Louis XVI
last absolute monarch of France whose failure to address economic crises and resistance to reform led to his execution during the French Revolution in 1793.

Maximilien Robespierre
led the radical Jacobins during the Reign of Terror and authorized mass executions by guillotine, including the execution of Queen Marie Antoinette.

Toussaint L'Ouverture
was a former slave who led the successful Haitian Revolution against French colonial rule, establishing the first Black republic in 1804.

Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte rose to power during the French Revolution and expanded his empire across Europe before being defeated at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.

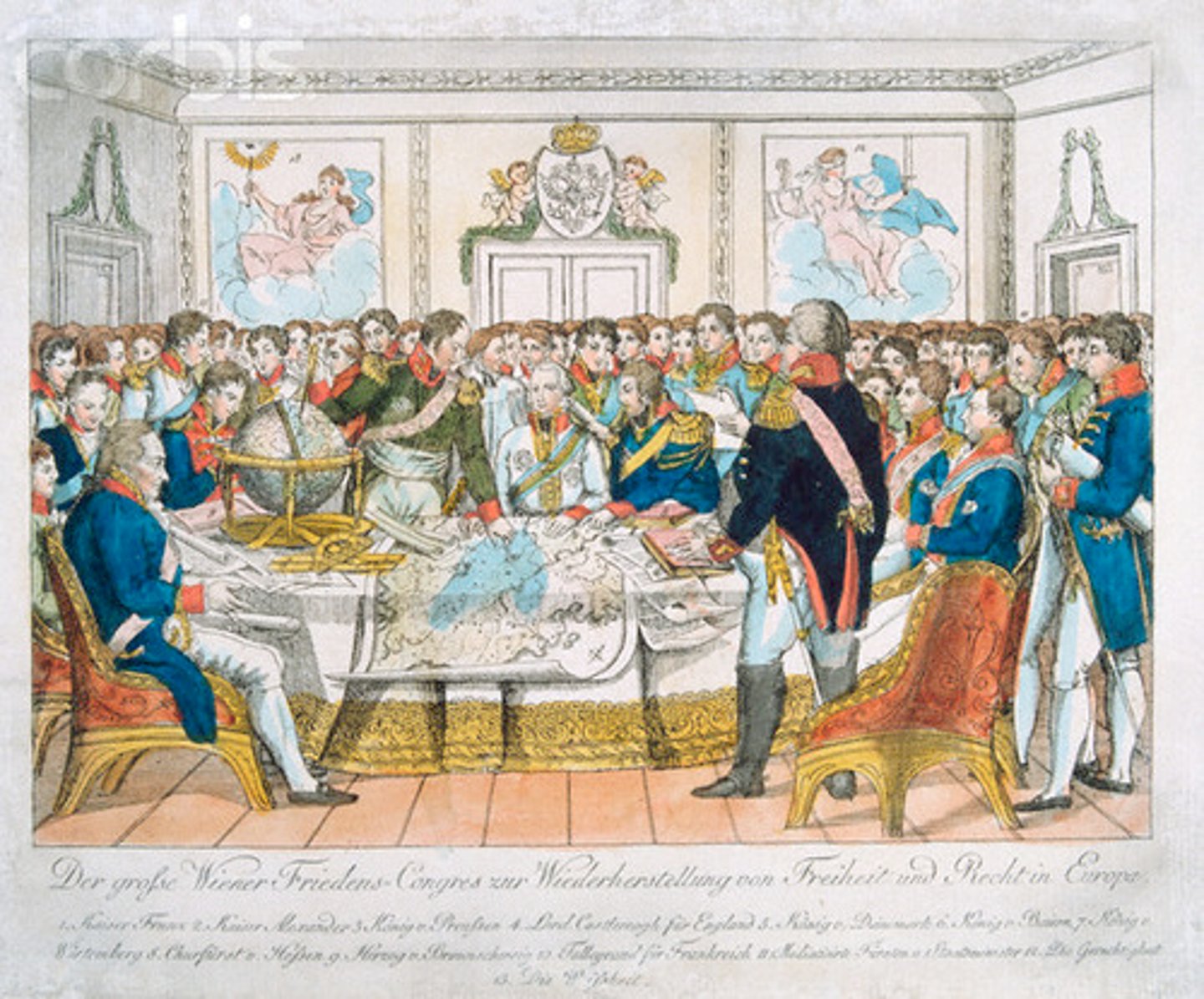
Congress of Vienna
(1814-1815) was a diplomatic meeting to restore balance and monarchies after Napoleon's fall, leading to the restoration of Bourbon rule in France.

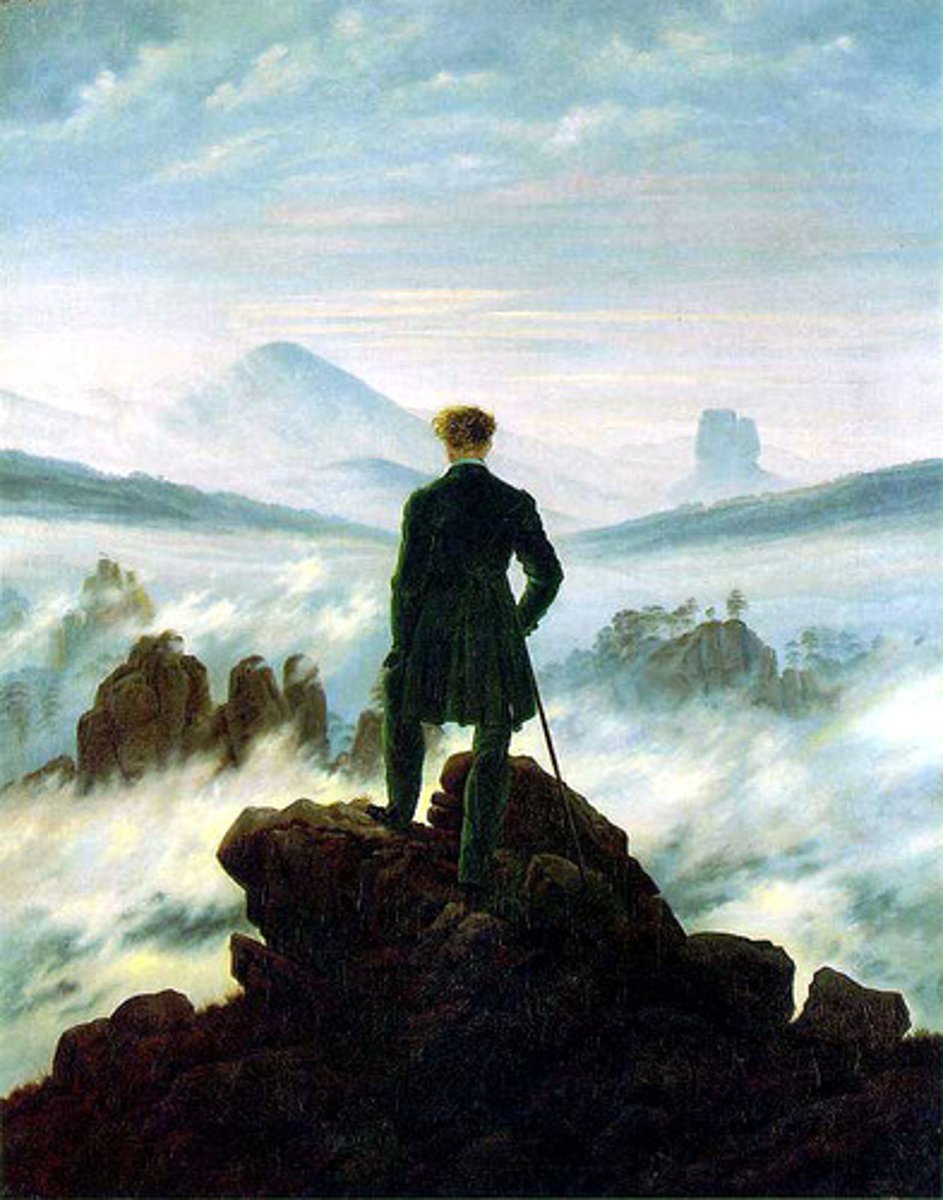
Romanticism
cultural movement emphasizing emotion and nature as seen in Francisco Goya's painting The Third of May 1808, depicting resistance to Napoleon's troops and Caspar Friedrich's Wanderer Above the Sea of Fog.

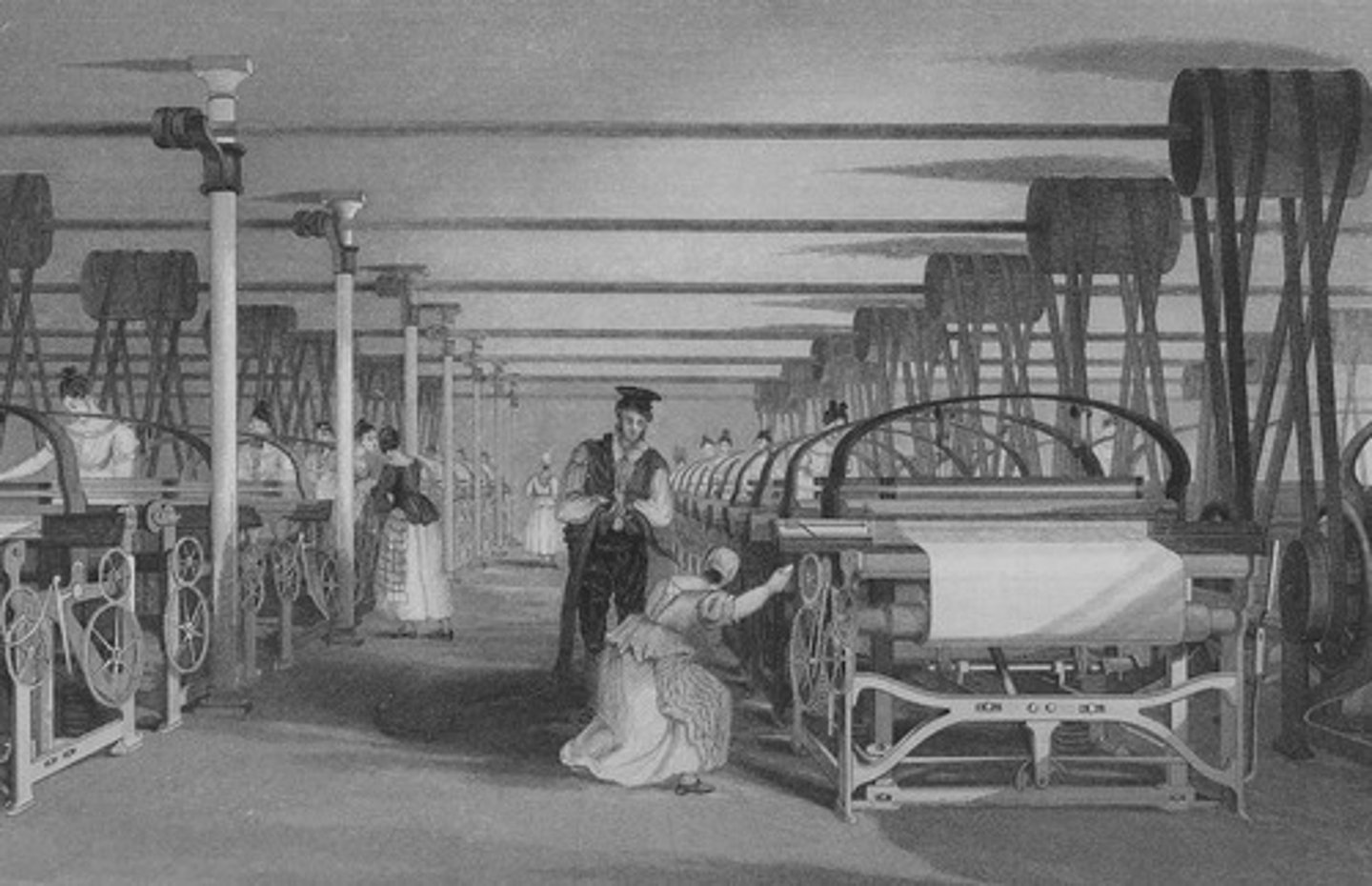
1st Wave of Industrialization
(late 18th-early 19th century) focused on textiles, steam power, and coal in Britain, such as the creation of the spinning jenny.

2nd Wave of Industrialization
(late 19th century) featured steel, electricity, and chemicals, exemplified by Germany's development of the Siemens electrical company.

consumerism
emerged as mass production allowed more people to buy goods like department store products in late 19th-century Paris.

Prussia
German state known for its strong military and leadership in unifying Germany under Otto von Bismarck in 1871.
class consciousness
the awareness of social class and shared interests, as seen in 19th-century labor movements like Chartism in Britain.

Bourgeoisie
middle-class capitalists who owned the means of production, such as factory owners during the Industrial Revolution.

Proletariat
working-class laborers who did not own property, like textile factory workers in Manchester during the 1800s.

Concert of Europe
system of alliances to maintain post-Napoleonic peace, such as the Holy Alliance between Russia, Austria, and Prussia.
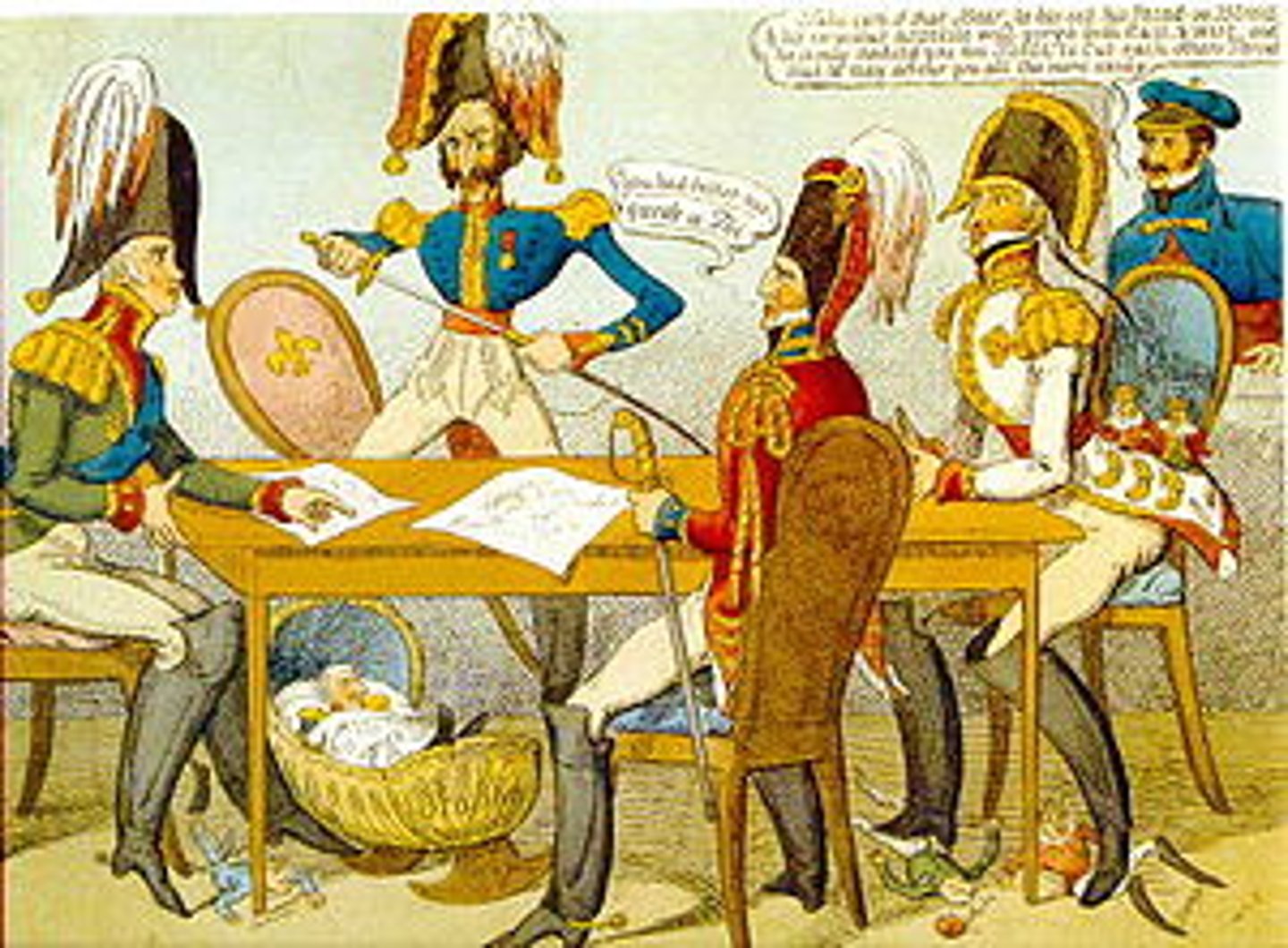

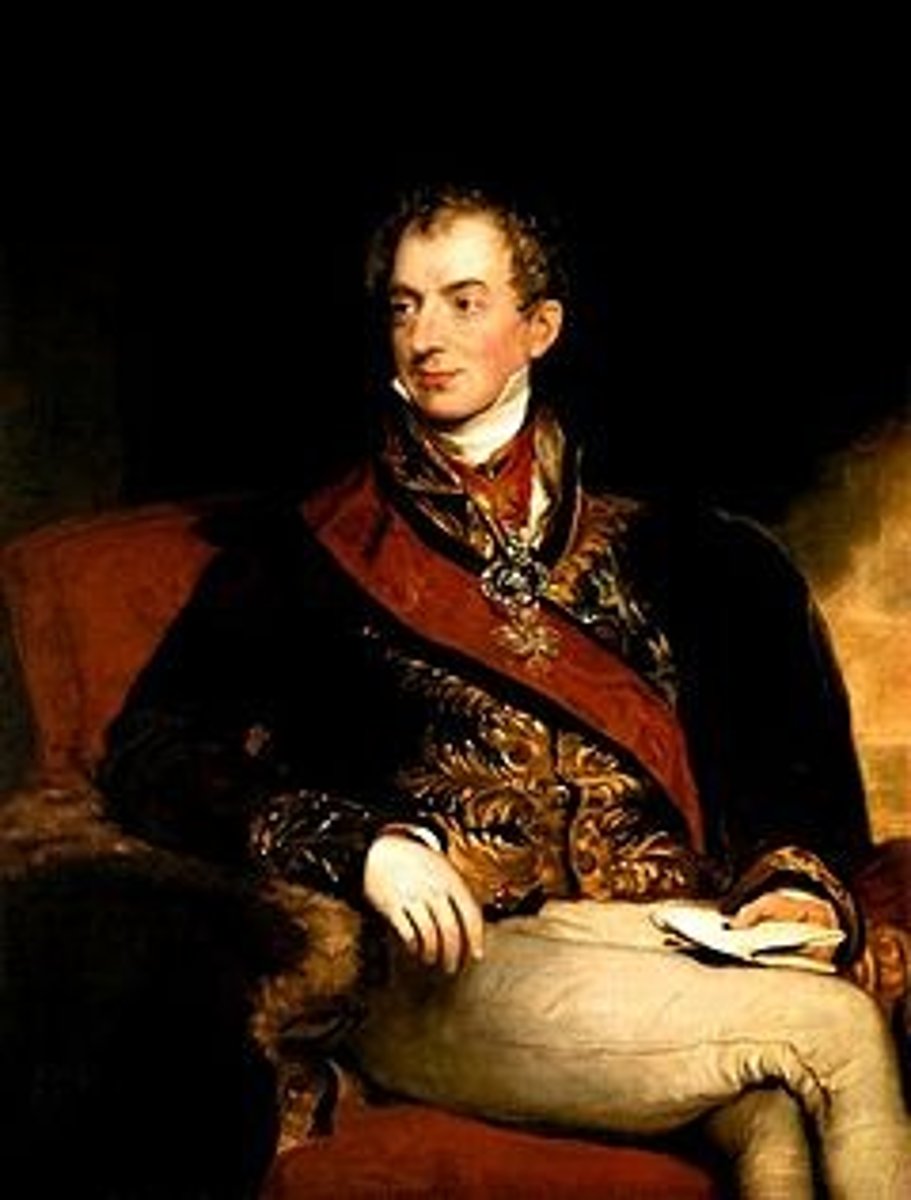
Klemens von Metternich
Austrian diplomat who dominated the Congress of Vienna and advocated conservative order, censorship, and suppression of liberal revolts.

Conservatism
promoted tradition and monarchy after 1815, exemplified by Edmund Burke's support for gradual change and opposition to the French Revolution.

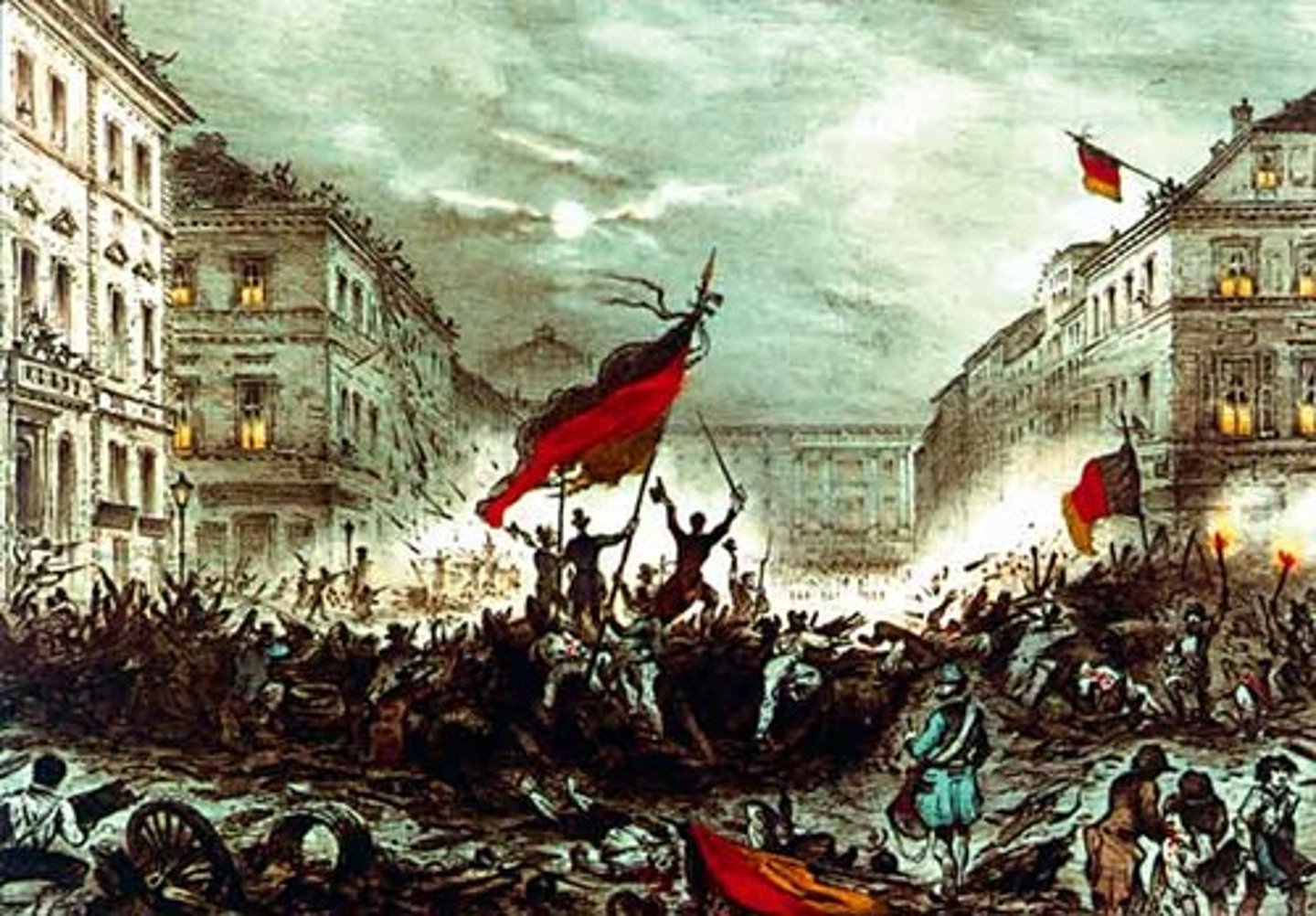
Revolutions of 1848
liberal and nationalist uprisings across Europe demanding constitutions and rights, like the failed revolt in the Austrian Empire.

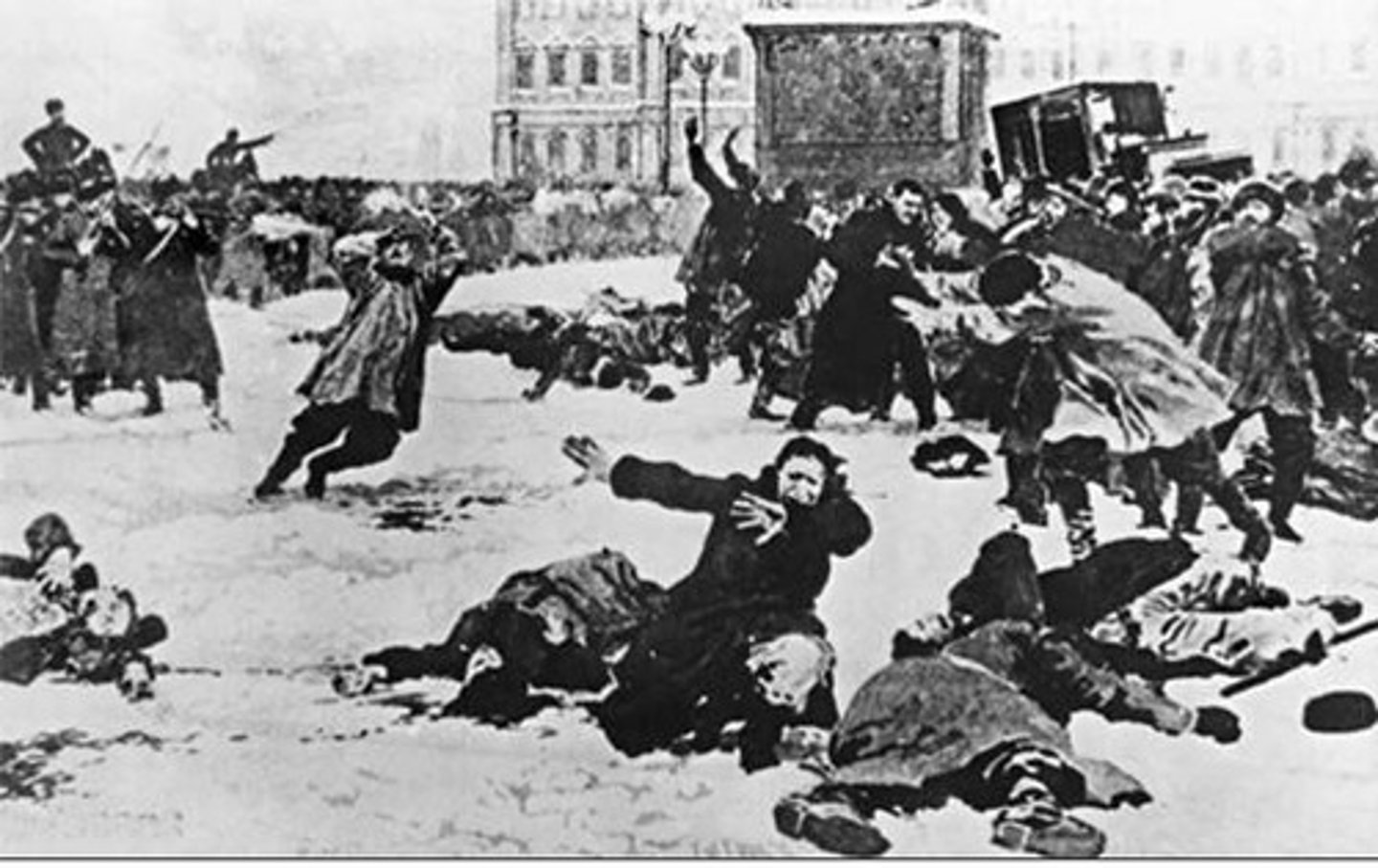
Russian Revolution (1905)
wave of political unrest sparked by Bloody Sunday, forcing Tsar Nicholas II to issue the October Manifesto.

Liberals
sought constitutional government, civil liberties, and economic freedom, as shown by support for the 1830 July Revolution in France.

Radicals
pushed for broader democratic reforms, including universal suffrage, as seen in the demands of the 1848 Chartist movement in Britain.

Socialists
aimed for social and economic equality through collective ownership, as promoted by figures like Karl Marx and early trade unions.
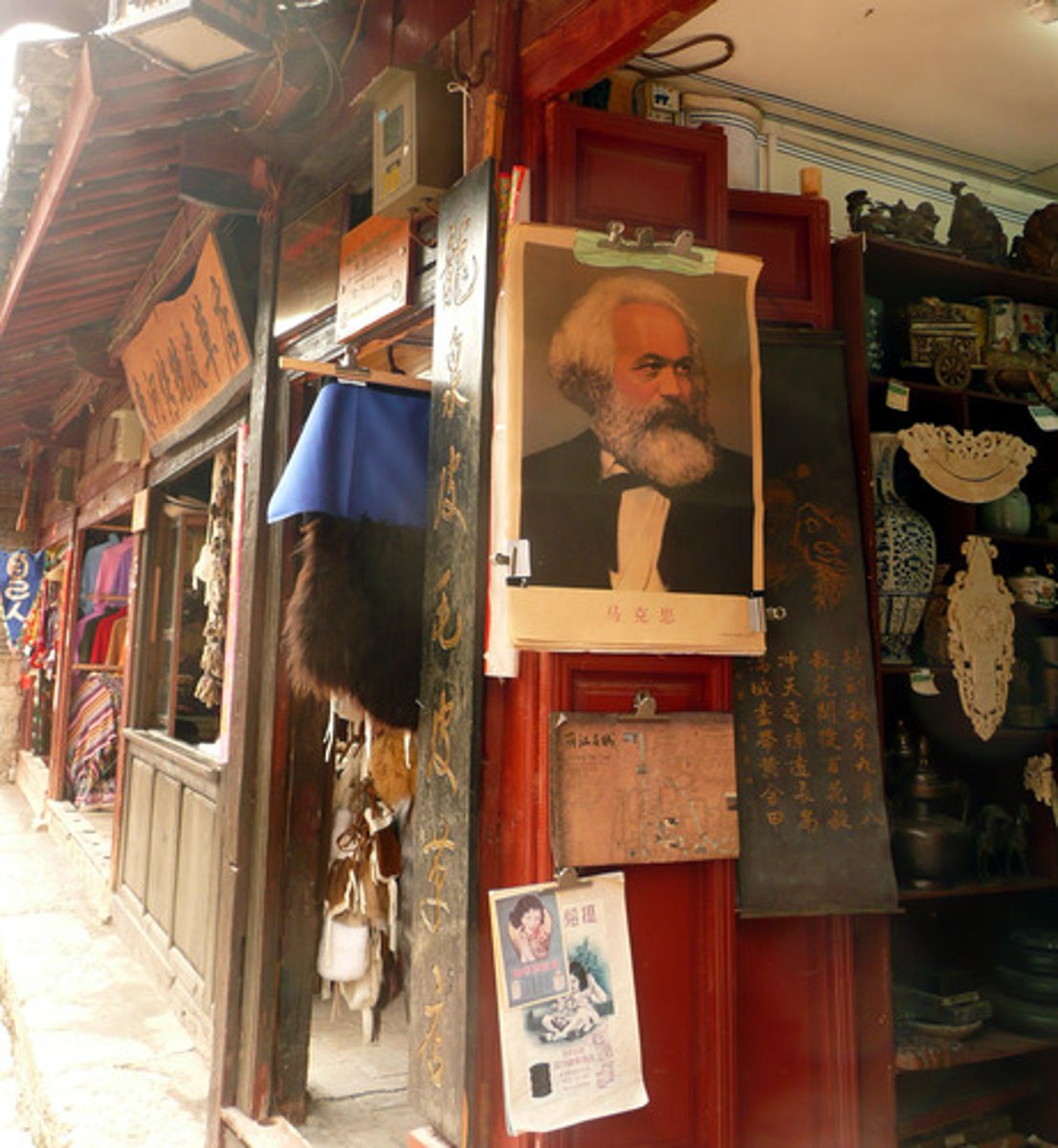

Marxists
Ideas of class struggle and revolution, outlined in The Communist Manifesto (1848) with Friedrich Engels.

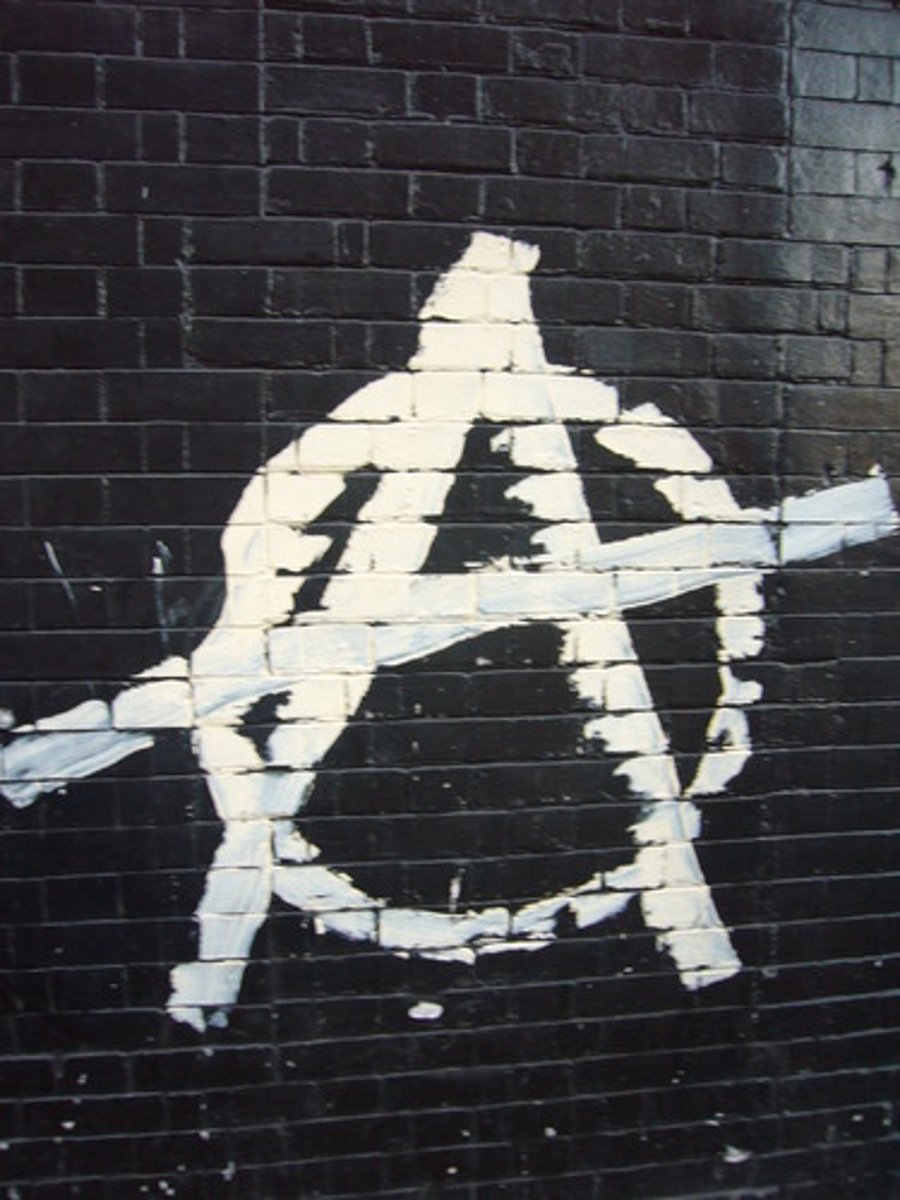
Anarchists
opposed all forms of government, sometimes using violence, like the assassination of Tsar Alexander II in 1881 by a Russian anarchist group.

Feminists
19th century advocated for women's rights, like Mary Wollstonecraft in A Vindication of the Rights of Woman (1792).

Zionism
nationalist movement to establish a Jewish homeland, founded by Theodor Herzl and later leading to the Balfour Declaration in 1917.

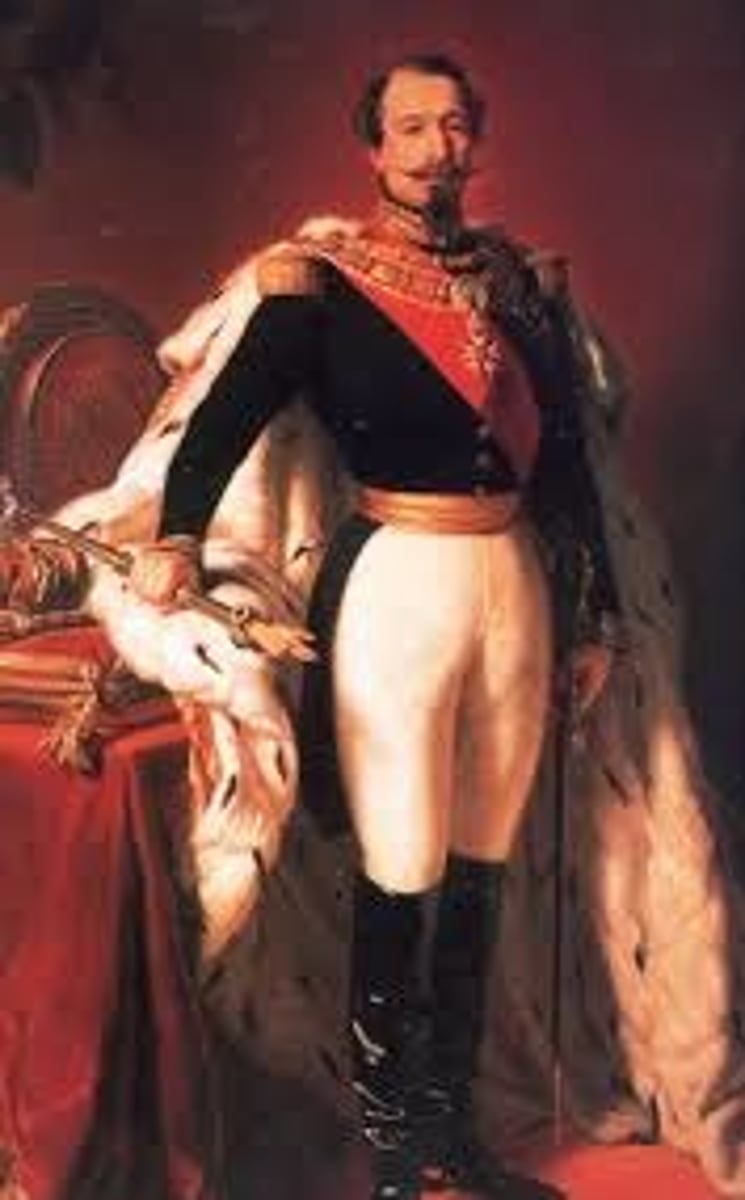
Napoleon III
ruler of the Second French Empire who modernized Paris and lost power after the Franco-Prussian War in 1870.

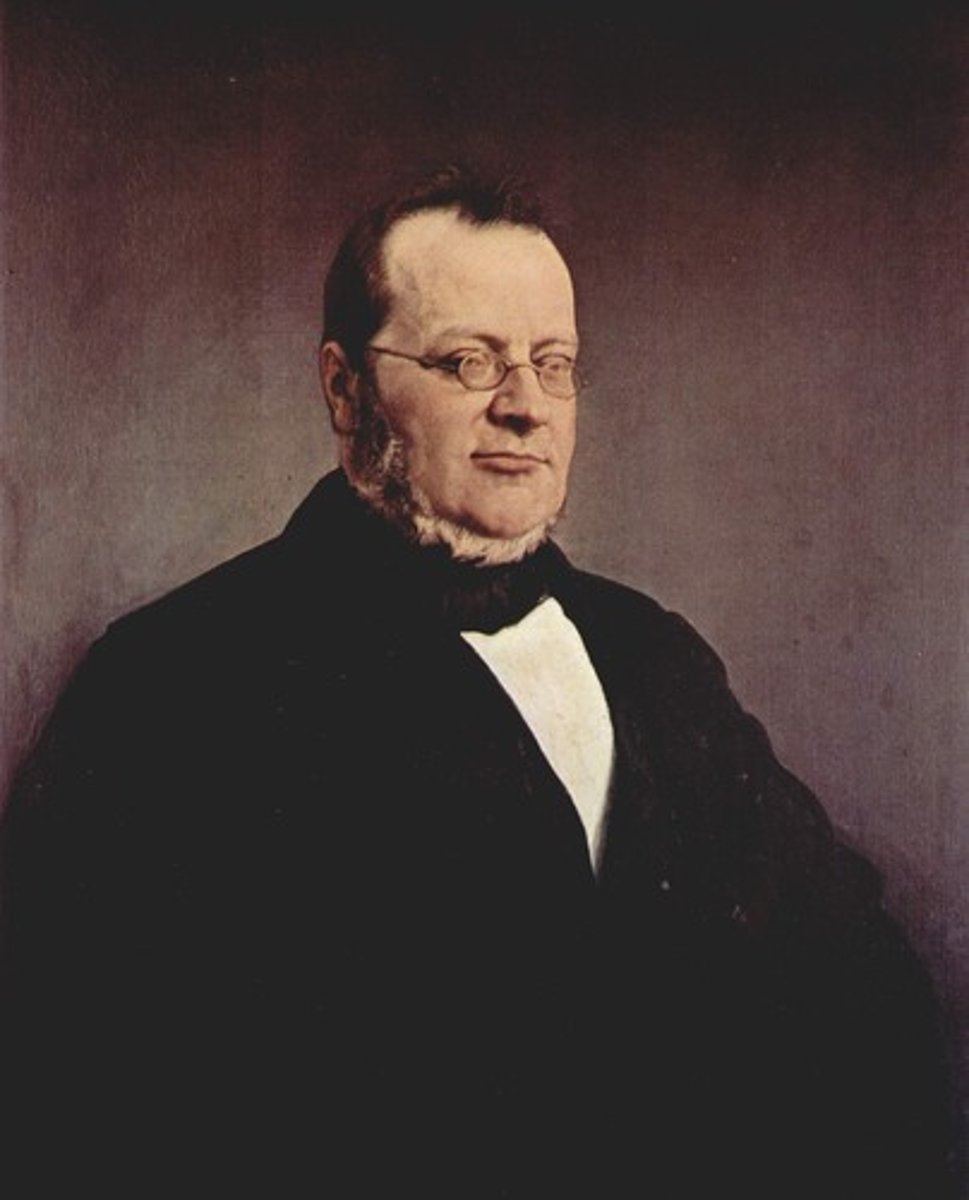
Camilo Cavour
prime minister of Piedmont-Sardinia who used diplomacy and alliances to unify northern Italy, especially through an alliance with France in 1859.

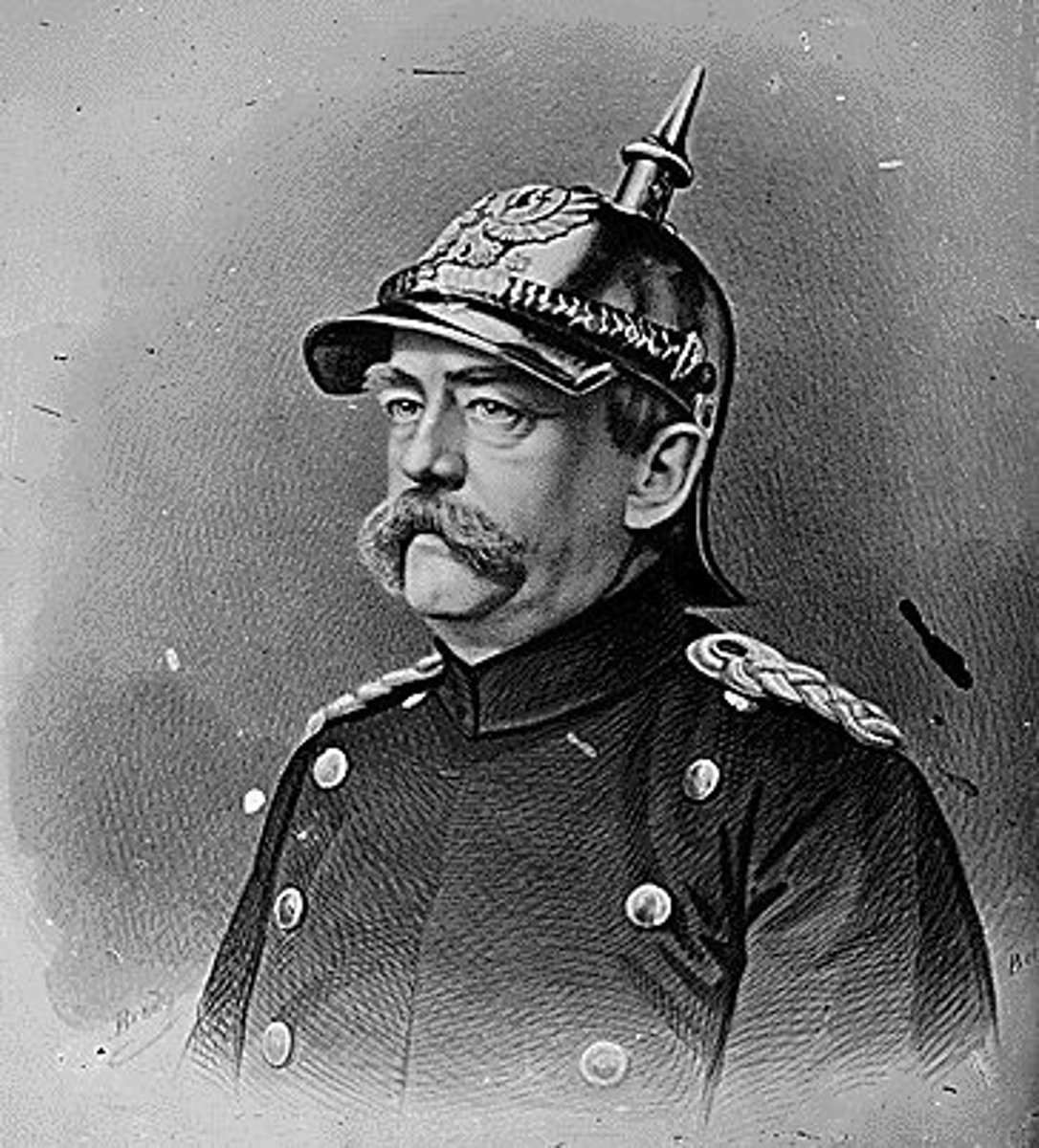
Otto von Bismarck
Prussian chancellor who unified Germany through wars and diplomacy, culminating in the 1871 proclamation of the German Empire at Versailles.

Crimean War
(1853-1856) was a conflict between Russia and an alliance of Britain, France, and the Ottoman Empire over influence in the Black Sea, with Florence Nightingale gaining fame for her nursing work.
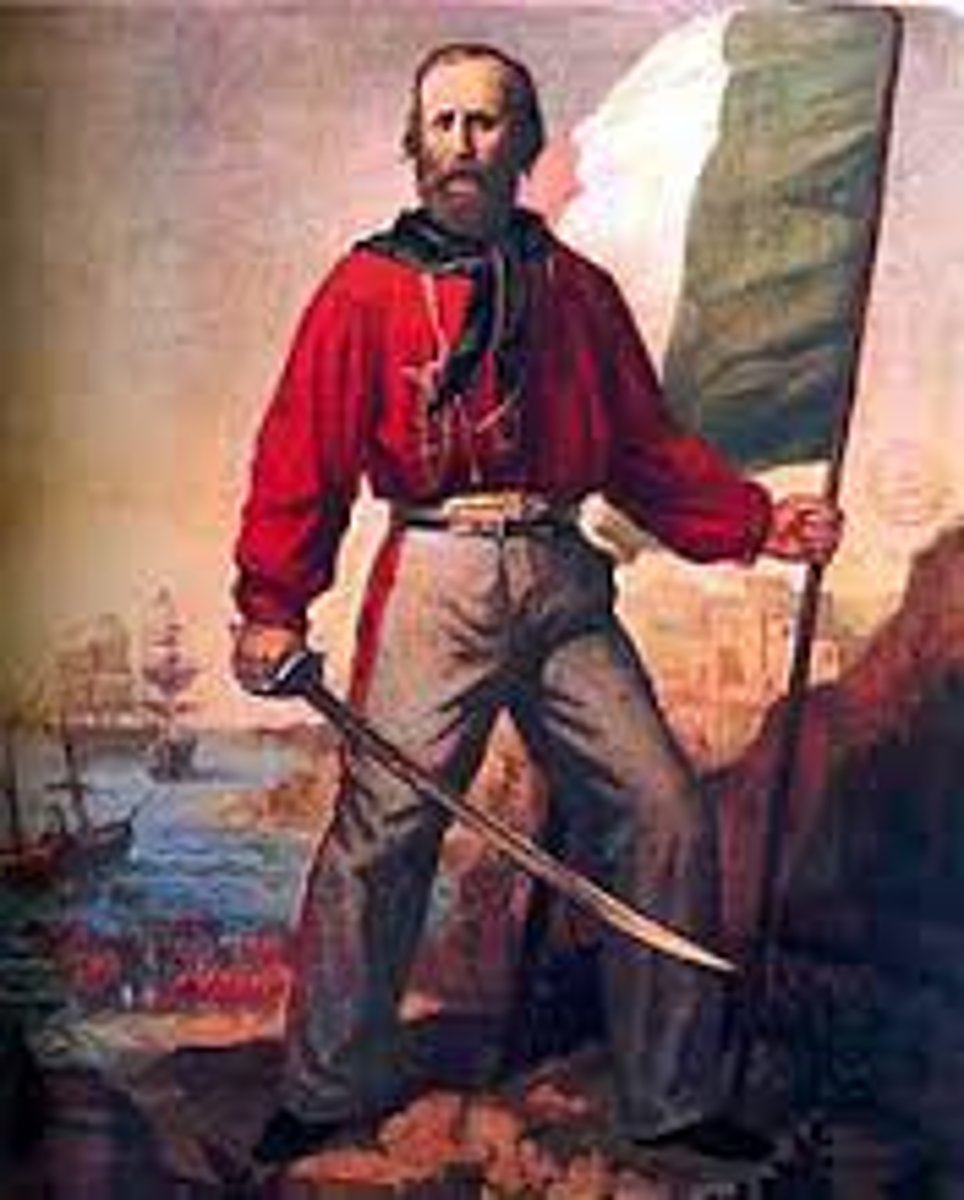
Guiseppe Garibaldi
Italian nationalist who led the Red Shirts to conquer southern Italy, which he later handed over to King Victor Emmanuel II in 1860.

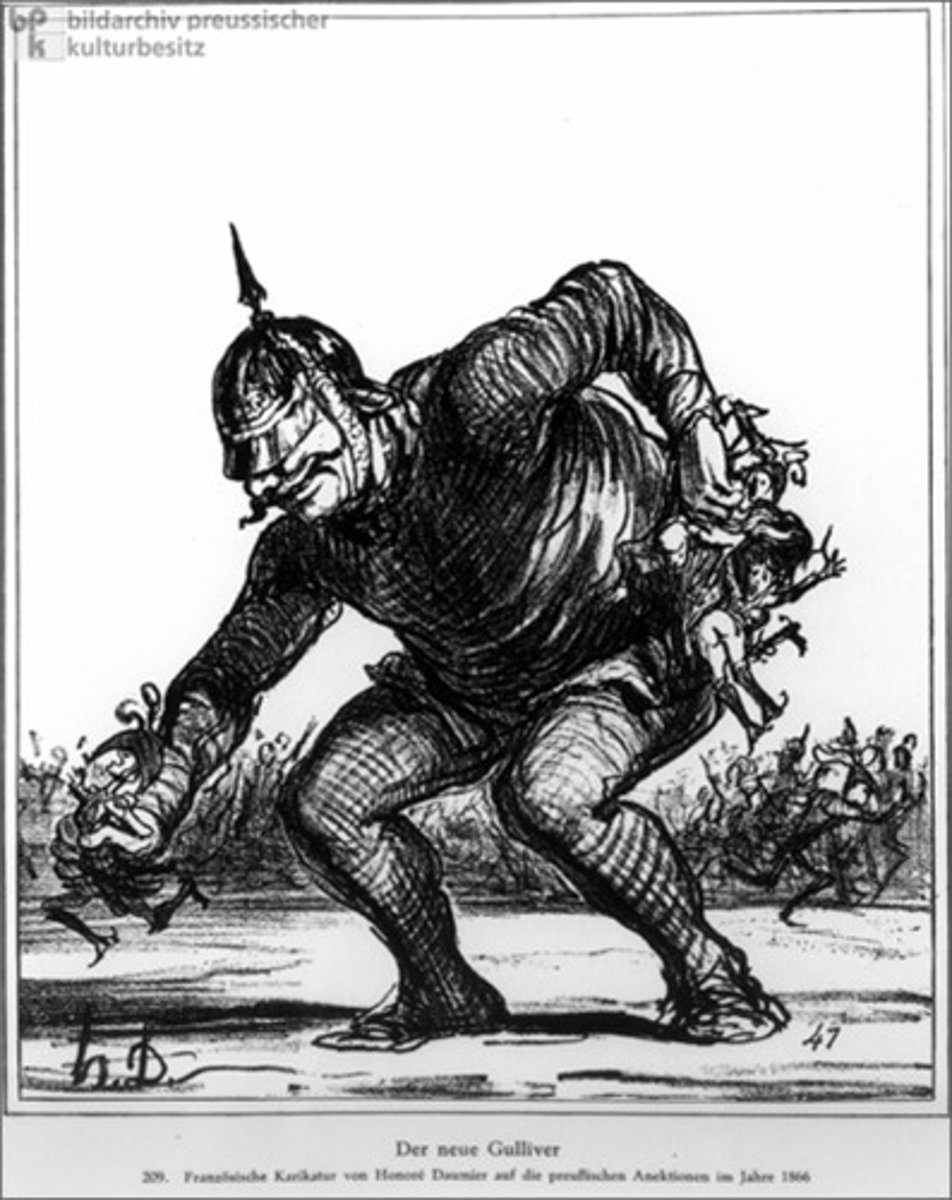
Realpolitik
based on practical goals rather than ideals, as used by Bismarck in manipulating the Ems Dispatch to provoke the Franco-Prussian War.

Charles Darwin
developed the theory of natural selection in On the Origin of Species (1859), challenging traditional beliefs about creation.

Positivism
founded by Auguste Comte, emphasized the use of scientific methods to understand society, influencing the rise of sociology in the 19th century.

Sigmund Freud
psychologist who founded psychoanalysis and introduced concepts like the unconscious mind and the Oedipus complex.

Albert Einstein
revolutionized physics with his theory of relativity, published in 1905, challenging Newtonian mechanics.

Imperialism
19th-century expansion of European empires into Africa and Asia, such as Britain's colonization of India.

Impressionism
art movement focused on light and everyday scenes, exemplified by Claude Monet's Impression, Sunrise (1872).

Post-Impressionism
built on Impressionism with more structure and emotion, as seen in Vincent van Gogh's Starry Night (1889).

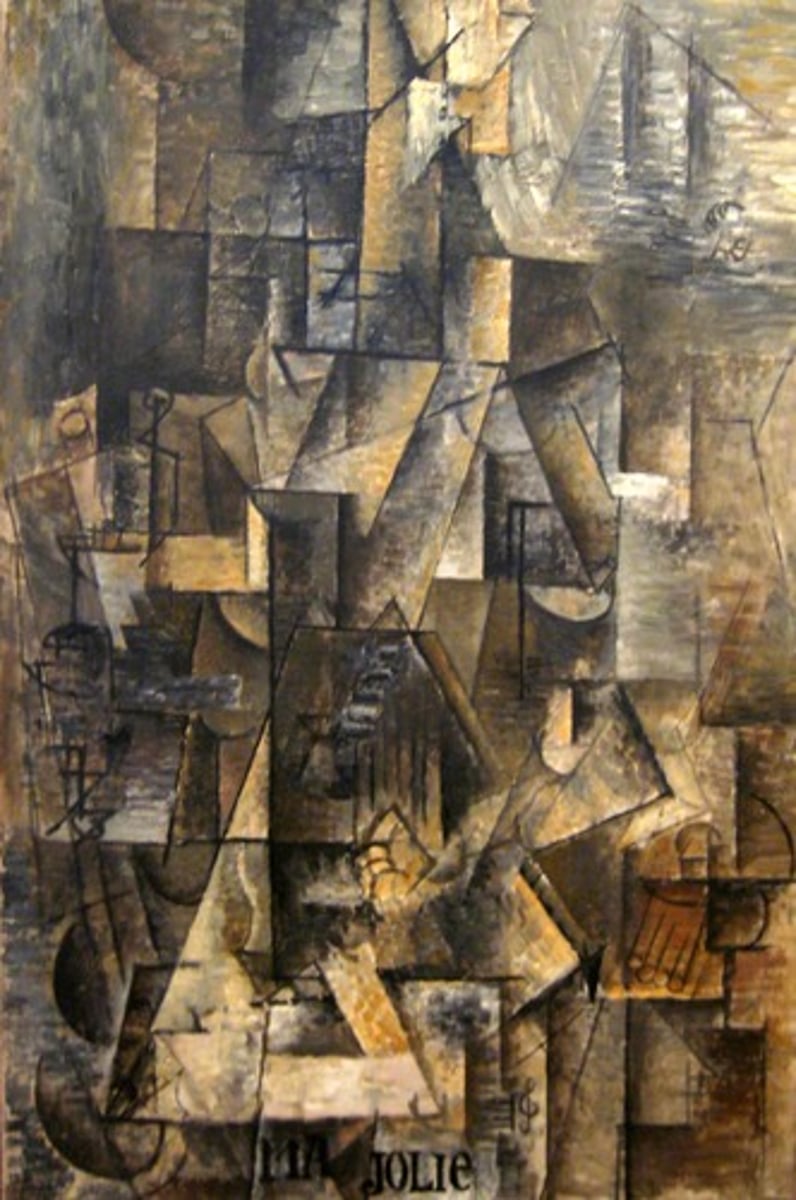
Cubism
modern art movement using geometric shapes and multiple perspectives, pioneered by Pablo Picasso in Les Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907).

WWI
(1914-1918) was a global conflict sparked by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and marked by trench warfare and mass casualties.
Bolshevik Revolution
1917 overthrew the Russian Provisional Government, leading to communist rule under Lenin.

Marxist-Leninist theory
idea of a vanguard party to lead a proletarian revolution, applied during the Russian Revolution.

Provisional Government
Government in Russia replaced the tsar in March 1917 but failed to exit WWI, leading to its overthrow by the Bolsheviks.
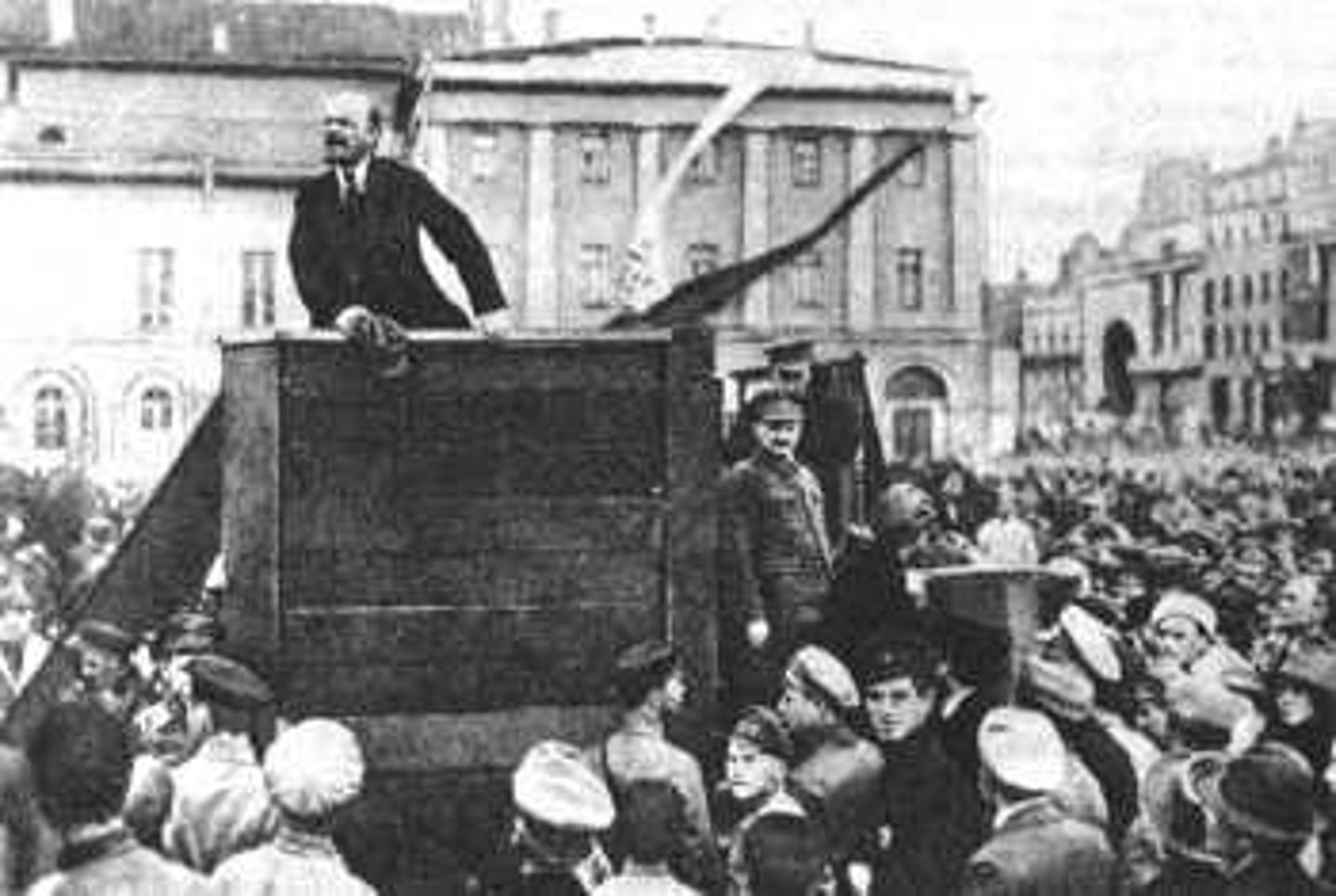

Lenin
led the Bolsheviks in the 1917 revolution and established a communist state through policies like the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk.

New Economic Policy
(1921) allowed limited capitalism to revive the Soviet economy after the Russian Civil War.

Treaty of Versailles
(1919) ended WWI by imposing harsh penalties on Germany, including war guilt and reparations.

Woodrow Wilson
U.S. president who proposed the Fourteen Points and helped form the League of Nations after WWI.

League of Nations
international organization formed after WWI to maintain peace, but it failed to prevent WWII.

Weimar Republic
Germany's democratic government after WWI, marked by hyperinflation and political instability in the 1920s.

USSR
established in 1922 as a communist federation of republics, led first by Lenin and then by Stalin.