Econ Test 2
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Where is consumer surplus?
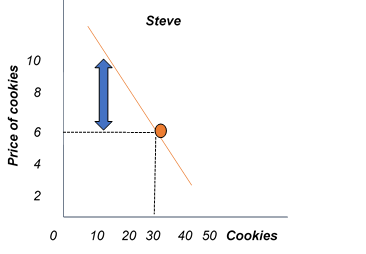
How do you calculate what consumers are willing and able to pay?
consumer surplus + cost
What is producer surplus?
The difference between the benefit (value) the seller receives minus the (marginal) cost to produce the amount sold
Where is producer surplus?
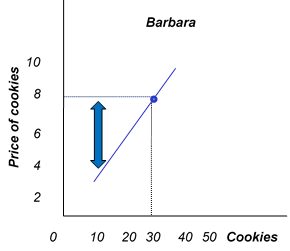
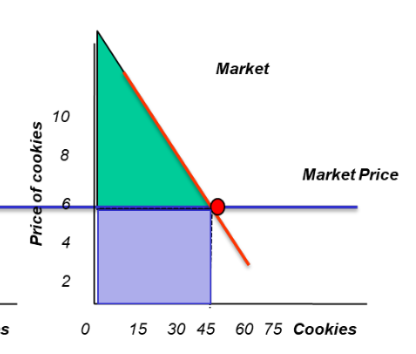
How do you calculate market total revenue/value?
producer surplus + cost
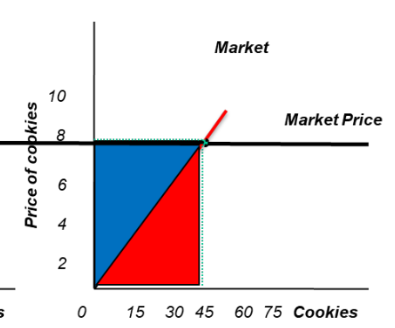
Where does allocative efficiency occur?
Equilibrium
What does underproduction look like?
A production amount below the allocative efficiency quantity
INEFFICIENT
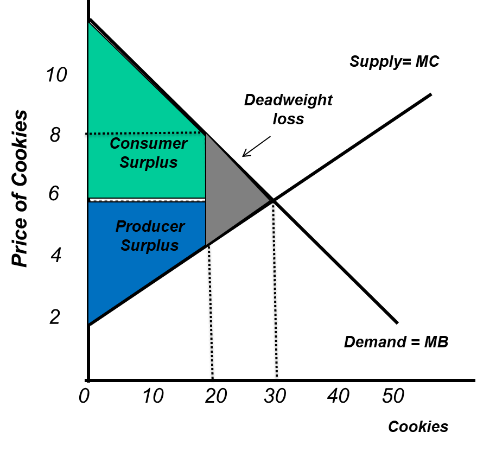
What does overproduction look like?
A production amount above the allocative efficiency
INEFFICIENCT
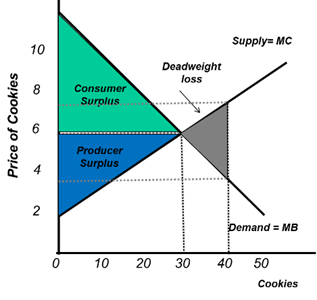
What is Utilitarianism?
Maximizing society's total utility or happiness by equating everyone's marginal utilities
If the market outcome (equilibrium) is not in society’s best interest, who can intervene to promote societal interest?
The government
What is a price ceiling?
A limit on how high a price to charge for a product or service
What is a price floor?
A limit on how low a price to charge for a goood or service
What is a perfectly regulated market?
Where no one can influence the market price in a market with so many buyers and sellers
True or False: A price ceiling set above the equilibrium price is ineffective since the equilibrium price is already below the legal maximum of the price ceiling.
True
What do the effects of a price ceiling look like on a market?
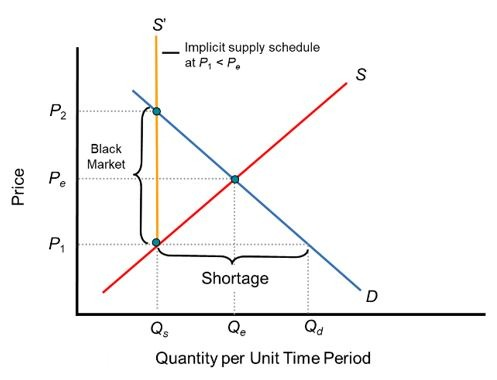
What is a black market?
The exchange of a good or service at a price above or below the government-imposed price control.
What is search activity?
The time and effort (cost) it takes to complete a transaction with another market participant
What do the effects of a price floor look like in a market?
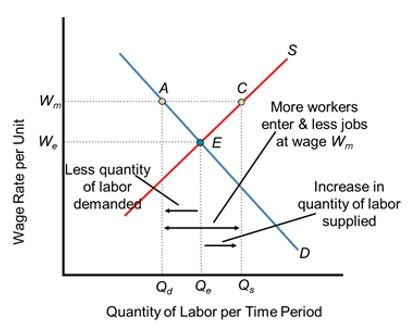
A surplus in the labor market is also known as…
Unemployment
A price floor leads to…
Overproduction/surplus
Above equilibrium price
A price ceiling leads to…
Underproduction/shortage
Below equilibrium price
What is the tax law?
It does not matter who initially receives the tax imposition. Regardless if the government places a tax on buyers or sellers, the tax incidence (burden) is the same
What happens to the curves when the government imposes a tax?
They shift left
What is a subsidy?
Financial aid or cash grants are given to suppliers or demanders of a good or service by the government
What is a quota?
A limit or restriction in quantity supplied of a good or service
What is an externality?
A cost of benefit affecting a third party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.
is someone outside the marketplace
not a direct buyer or seller but receive a benefit or pay cost
What is an example of a negative externality?
Pollution
What is the difference between social and private cost?
External cost
What is marginal private cost (MC)?
The opportunity cost of producing or consuming one more unit of a good or service
What is marginal external cost?
The additional cost to someone other than the buyer or seller for producing or consuming one more unit of a good or service
What is marginal social cost (MSC)?
The additional cost to society for producing or consuming one more unit of a good or service.
What is the formula for marginal social cost (MSC)?
MSC = MC + Marginal external cost
What is a Pigovian tax?
A tax on a market outcome that causes a negative externality
How do you calculate the tax amount?
Pe - Pm
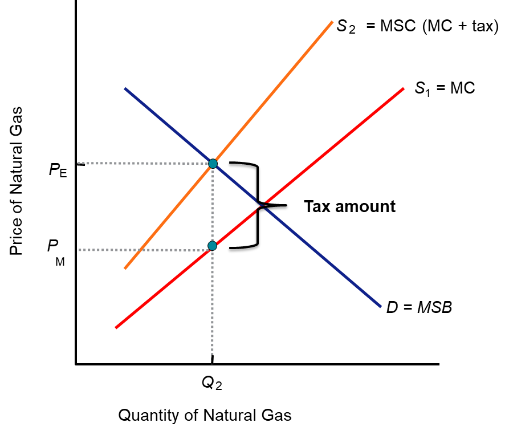
What is the Coase theorem?
The efficient allocation of an outcome with negative externalities
What is marginal private benefit (MB)?
The additional benefit from producing or consuming one more unit of a good or service
What is marginal external benefit?
The additional benefit to someone other than the buyer or seller for producing or consuming one more unit of a good or service
What is marginal social benefit (MSB)?
The additional benefit to society for producing or consuming one more unit of a good or service
What is the formula for marginal social benefit (MSB)?
MSB = MB + Marginal external benefit
What is an example of a positive externality?
Vaccines or education
Can goods have both a positive and negative externality?
Yes; Hershey chocolate example
What is a rival good?
A good consumed by one person prevents the consumption of that same good by another
consumed only once
What is an excludable good?
Preventing someone who has not paid for a good from consuming it
What is a free ride?
People who benefit from a good, but do not pay for it
causes the market to underproduce public goods (represents market failure)
What is a common good?
A good that is both rival and nonexcludable
What is tragedy of commons?
Self-interested individuals overconsume or deplete a good or resource contrary to societal interest
Is the free rider problem worse for common goods or public goods?
Common goods
What is consumer optimum?
Maximizing the happiness or satisfaction from consuming a bundle of goods and services subject to income and prices
utility-maximizing choice
can change if price, preferences, or income changes
How do you calculate relative price?
the price of one good divided by the price of another good
is also the slope
What does a change in price do?
It changes the affordability quantity of that good and changes the slope of the budget line
What is real income?
A household’s income expressed as the quantity of goods that the household can afford to buy
maximum quantity you can buy
What does a change in income do?
A change in income brings a parallel shift to the budget line
slope does not change
What are preferences?
They determine the benefits or satisfaction a person receives consuming a good or service
What is a utility?
A benefit or satisfaction from consuming a good or service
What is total utility?
The total benefit a person gets from the consumption of goods.
more consumption means more utility
What is marginal utility?
The change in total utility due to a one-unit change in the quantity of a good or service consumed
What is the marginal utility formula?
change in total utility/change in # of units consumed
Where total utility is maximized…
marginal utility equals zero
What is diminishing marginal utility?
The principle that as more of any good or service is consumed, its extra benefit declines
What is consumer efficiency?
When consumers maximize their utility, they are using resources efficiently
What is a nonrival good?
a good consumed by more than one person prevents the consumption of that same good by another
public goods are nonrival and nonexcludable
What is a nonexcludable good?
cannnot prevent someone who has not paid for a good by consuming it
common goods are rival and nonexcludable
All economic questions are about…
how to deal with scarcity
What is the difference between microeconomic vs. macroeconomic
Micro is the study of individual decisions; whereas, macro is the study of the economy as a whole.
micro ex: pollution or crime on a sector
macro ex: inflation or taxes
What is opportunity cost?
The highest-valued, next best alternative given up (sacrificed) to attain something or satisfy a want.
What is positive economics?
a statement, doesn’t have to be true
‘What is’
May be wrong, but has to be able to be tested
What is normative economics?
personal opinion
‘What ought to be’
What we hope you will apply
What are the four factors of production?
Land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
What do the four factors of production earn?
Land earns rent
Labor earns wages
Capital earns interest
Entrepreneurship earns profit
What are the assumptions for a PPC?
Resources are fully employed
Production is for a specific time
Resources are fixed for the time
Technology does not change over time
Points inside the PPC represent…
inefficiency
Points outside the PPC represent…
an unattainable point
What is comparative advantage?
Producing a good or service at a lower relative opportunity cost
helps determine specialization
can only occur for one good
What is absolute advantage?
Producing a greater quantity of goods or services than competitors, using the same amount of resources
focuses on productivity
can occur for both goods
What does the per-worked-production function represent?
illustrate economic growth for the entire macroeconomy.
What’s the formula for Q (Real GDP per capita?
Q = A*F(K,L,N,H)
What’s the formula for New GDP?
Old * (1+growth rate)^N

How do you calculate how long it will take to double?
70 / Growth Rate
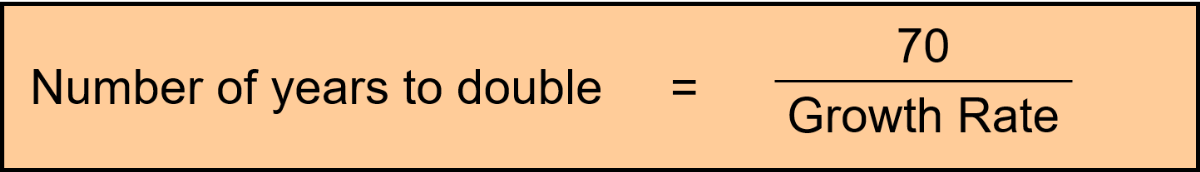
What is the law of demand?
There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
ex: when price increases, demand decreases
What is the substitution effect?
When the price of a good/service increases, the consumer is motivated to buy less of the good
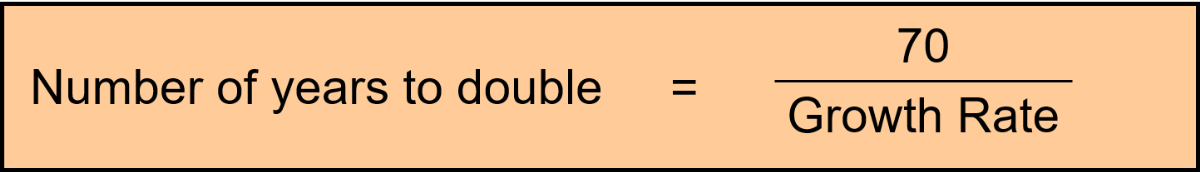
What is the income effect?
If the price of a good or service increases, purchasing power decreases and the consumer’s overall buying power decreases
What are the factors (determinants) that shift demand?
Income
Tastes and preferences
The price of related goods in consumption
Taxes and subsidies on consumption
Expectations
Market size (buyers)
If your income increases, what happens to demand?
You will demand more normal goods, and less inferior goods
What happens to demand for a complement?
When one’s price goes up, the demand of the other complement decreases.
ex: When the price of peanut butter rises, a peanut butter and jelly sandwich is now more expensive. Thus, you would demand less jelly.
What happens to demand for a substitute?
There is a direct relationship between the two substitutes.
When one’s price goes up, the demand for the other substitute goes up.
ex: if the price of Pepsi increases, then the demand for Coke increases because Coke is now the relatively cheaper good
Increases in taxes do what to demand?
Decrease
Increase in subsidies do what to demand?
Increase
What is the law of supply?
There is a direct relationship between price and quality supplied.
ex: when price increases, quantity supplied increases
What are the factors (determinants) that shift the supply curve?
Cost of inputs
The price of related goods in production
Technology and productivity
Taxes and subsidies on production
Price expectation
Number of firms
If the cost of inputs increases, what happens to supply?
The supply decreases
If the price of a complementary good increases, what happens to supply?
Increases (direct relationship)
ex: If the price of beef increases due to an increase in demand for beef, then the supply of leather increases because it is a byproduct of more beef produced.
If the price of a substitute good increases, what happens to supply?
Decreases (indirect)
ex: a farmer produces either corn or wheat but not both. When the demand for corn increases, a farmer's profit from growing corn increases.
How do technology improvements effect supply?
Increase supply
Increases in taxes do what to supply?
Decrease
Increase in subsidies do what to supply?
Increase
If the number of firms increases, what happens to supply?
Increases
All economic questions are about…
How to deal with scarcity
What is microeconomics?
The study of individual decisions
ex: pollution
What is macroeconomics?
The study of the economy as a whole
ex: taxes
What are maximizers?
People who behave rationally to maximize their happiness or some goal