KNES 505 Midterm 2
1/379
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
380 Terms
Given the heterogenous nature of concussion, what kind of approach is warranted to treat concussions?
Interdisciplinary approach including a variety of health care professionals
Who is included in a collaborative team approach to treat concussions and optimize care?
Sport medicine physicians
Physiotherapists
Family physicians
Physician specialists
Psychologists
Athletic therapists
Neurologists
Neuropsychologists
Other health care professionals
What is physiotherapy?
Treatment to restore, maintain, & make the most of a patient's mobility, fx, & wellbeing
What does physiotherapy incorporate?
Physical rehab
Injury prevention
Health & fitness
Physiotherapists get you involved in your own recovery.
How are physiotherapists an integral part of the interdisciplinary team?
They possess a unique skillset that can inform recognition of concussions on the field of play, inform differential diagnosis of concussions, early management, re-evaluation & rehabilitation of physical ramifications of concussions across the continuum of care in the clinic & facilitate return to sport & school
What does the precise role of the physiotherapist depend on?
Locations
Expertise & competency that the physiotherapist has in each context (specializations)
What ensures a coordinated & comprehensive approach to care?
Working collaboratively w the treating physician & other health care professionals
What is the vital first step in developing a relationship w a patient?
Structured history
Gain a clear understanding of the injury, the level of risk for persistent symptoms, & to develop a hypothesis driven examination
What must be thoroughly investigated in terms of hx?
Patient's past medical, social, & prior concussions hx
What are the principal goals when understanding the current concussion?
The mechanism of injury, the initial & ongoing symptom presentation, what medical mgmt has been recommended, & any risk or prognostic factors that may contribute to a prolonged recovery
What is the emerging research of physiotherapy mgmt for dizziness post-concussion?
Positive outcomes of the cervical spine & vestibular/balance systems
Participants who received an individualized multimodal cervical & vestibular physiotherapy mgmt were how much more likely to be medically cleared to return to sport by 8 weeks than those treated w the control intervention?
3.91 times
(95% CI 1.34 to 11.34)
What are some of the causes of dizziness?
Underlying migraine/tension headaches
Cervical issues
Vestibular impairments
CNS/autonomic impairments
Psychogenic
Vascular/CBF challenges
Medication complications
More than 1 cause & multiple diff subcategories
What is the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR)?
Responsible for maintaining stable vision during head motion
Important in sport settings
Can be impaired following concussions
What is peripheral vestibular hypofx?
Relative imbalance of input from peripheral vestibular apparatus leads to relative excessive input to intact side of vestibular nucleus results in vertigo & imbalance
10% show peripheral vestibular hypofunction (trauma to labryth)
What is the head thrust test (HTT)?
Slight nod
Unpredictable
Small amount of rotation only
Neg: eyes stay on the target (GOOD)
Pos: corrective saccade observed toward the side of the thrust (eyes move with head, then correct)
What does the HTT assess?
Eye tracking w head movement
What is dynamic visual acuity (DVA)?
Slight nod
ETDRS chart
Metronome set at 2 Hz
20 degrees rotation
13 feet from the target
Static visual acuity: lowest line read w head still
DVA: lowest line read w head moving
What is the Hallpike-Dix test?
Patient long sitting
Head rotated 45 degrees
Examiner assists to bring head & trunk into supine position with head handing at 30 degrees
head in line with tested canal = feel vertigo
only 1-3 treatments
for BPDP (crystals dislodged into semicircular canals)
What does the Hallpike-Dix test assess for?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
What can be predictors of PPCS?
Positive tests for dizziness/neck pain/ocular motor fx
What is the #1 symptom reported after concussion?
Headaches
How many patients experience headaches post concussion?
25-90%
What is the lifetime prevalence post-traumatic headache (PTH)?
4.7% in men & 2.4% in women
How many ppl experience persisting PTH following concussion?
15-75%
How many ppl w headaches still experience headaches at 4 yrs post-injury?
Up to 20%
What are the 6 types of heaches?
Cervicogenic
ANS/tension
Migraine
Occipital neuralgia
Ocular
Medication overuse (rebound)
What is a cervicogenic headache?
Often associated w neck tension, neck pain, & a pulling/whiplash feeling (damage radiating up neck)
Most often felt in posterior portion of the head
may present in MRIs (bulging/herniation)
What is an ANS/tension headche?
Can be associated w imbalance of sympathetic & parasympathetic innervations (band around head)
Often felt as a band around the head & can be linked w challenges in neurovascular coupling
may be due to blood flow in the head
What is a migraine?
Typically presents as an extreme, stabbing pain on 1 side of the head (or the other), generally near the top of the head
Often seen in individuals who have a predisposition to (or family history) of migraines
Can occur w & w/out 'aura' (warning sign of migraine such as seeing spots/flashing lights)
What is an occipital neuralgia headache?
Often an undiagnosed cause of head & neck pain that can occur from whiplash &/or concussion
Can have severe stabbing pain in the greater occipital nerve region (back side of head)
Can be diagnosed & treated w an occipital nerve block
What is an ocular headache?
Often felt as a pounding, pulsing or throbbing pain behind the eye
Can be associated w sensitivity to light, noise &/or odours
related to hypertension/ANS headaches
What is a medication overuse (rebound) headache?
Typically caused by patients taking too many analgesic medications
As medication wears off, the headache pain increases & this may be unrelated to the concussion
If suspected, medication detoxification should occur
What links most headaches?
Neurovascular coupling
In terms of involvement of cervical spine in headaches, what types of symptoms may be experienced?
Neck pain
Cervicogenic headaches
Cervicogenic dizziness
In terms of involvement of cervical spine in headaches, what may be the source of pain/dysfx?
Joint
Myofascial
Nerve
Sensorimotor
Neuromotor control
Higher centres
Psychological distress
What does a typical ax of the cervical spine include?
Biomech exam
Cervical flexor/extensor endurance test
Cervical flexion rotation test
Joint position error
Head & neck position sense
Head perturbation test
Craniocervical flexion test
How is sensorimotor control assesed?
Cervical proprioception
Postural control
Eye movement control
How is cervical proprioception assessed?
Joint position sense
Cervical movement accuracy
How is postural control assessed?
Standing balance
Dynamic & fx'al movement
What are 3 tests for the pos prediction rule - facet joint mediated pain?
Manual spinal exam (MSE)
Palpation - segmental tenderness (PST)
Extension rotation test
What is included in a multifaceted ax?
Symptoms
Neurological screen
Cognition
Cervical spine
Vision
Balance/vestibular
Exertion
What are 9 tests that measure cervical, vestibular, dynamic balance w tasks of divided attention?
Cervical flexor endurance
Cervical flexion rotation test
Cervical rotation side flexion test
Head perturbation test
Clinical DVA
Computerized DVA
Fx'al gait ax
Walk while talk test
What are the 5 R's for concussion mgmt?
Rest
Rehab
Refer
Recovery
Return to sport
What do multifaceted ax's lead to?
Targeted treatment in a multidisciplinary collaborative setting
What does the evidence say for concussion mgmt?
Multimodal approach
Manual therapy & exercise
Specific exercises
Sensorimotor
What is vestibular rehab?
Canalith repositioning maneuvers (mechanical problem)
Habituation exercises (desensitize the brain with specific movements)
Gaze stability retraining (vestibulooccular reflex training)
Static & dynamic balance retraining
Substitution
What does progressions for concussion mgmt consider?
Repeated exposures
Deliberate practice
Context specific
What did Kathryn Schneider describe the progressions for concussion mgmt as?
Plain background
Busy visual environment (plaid/polka dots, TV screen, crowds)
Distracted environment (carry on conversation, problem solving)
Alter afferent input (eyes closed, unsteady ground, smaller base of support)
Combinational
What does the 2023 CISG say about dizziness, neck pain, &/or headaches?
Cervicovestibular rehab for individuals who have sustained an SRC & reports symptoms for longer than 10 days
Vestibular rehab, active rehab, & collaborative care for adolescents with persisting symptoms following SRC
What are intrinsic risk factors for concussions?
Previous concussion
Pre-existing symptoms
Player weight
Sex
Age
Neuromuscular control
What are extrinsic risk factors for concussions?
Psycho-social
Sport
Session type
Equipment
Rules of the game
Level of play
Position
What do physiotherapists focus on?
Not only on the evidence around sensitivity & specificity of diagnostic concussion tests, but also on the best evidence around assessment & targeted treatment of the relevant domains that may be impaired
What is the physiotherapy community a major part of?
The catalyst for a paradigm shift in our conceptual & practical framework of concussion mgmt, in all its complexity
What are the conclusions of current research comparing strict rest vs usual care following a concussion?
Strict rest offers no benefits over current usual care
Symptoms lasted longer for individuals following strict rest as compared to usual care for all 10 days post injury
What was a limitation for current research comparing strict rest vs usual care following a concussion in adolescents?
Adolescents' symptom reporting may be influenced by restricting activity (limiting screen time)
In 1783, what did Alexander Monro say about the brain?
The brain was enclosed in a non-expandable case of bone
The substance of the brain was nearly incompressible
The volume of the blood in the cranial cavity was therefore constant or nearly constant
A continuous outflow of venous blood from the cranial cavity was required to make room for the continuous incoming arterial blood
What are the measurements of CSF, blood, & brain parenchyma volume?
CSF: 150 mL (10%)
replaced every 8hrs
Blood: 150 mL (10%)
can change most rapidly
Brain parenchyma: 1400 mL (80%)
What are ventilatory thresholds?
2 points during exercise where the rate of ventilation increases significantly
What happens to the ventilatory thresholds post-concussion?
Decreases
What is 1 of the main factors contributing to symptom exacerbation during submaximal exercise post concussion?
Initial increase in CBF during mild to moderate exercise intensity and then decreases during moderate to heavy exercise intensity
decreases later due to hyperventilation = vasoconstriction
Why are symptoms exacerbated during exercise post concussion?
The amount of incompressible fluid in the skull increases during initial exercise to reduce the amount of space available to make symptoms worse
What is the effect of moderate-vigorous physical activity on concussion?
Can exacerbate symptoms and delay recovery
more time spent in MVPA during the first 3 days following concussion diagnosis is associated with a greater time to medical clearance to RTP
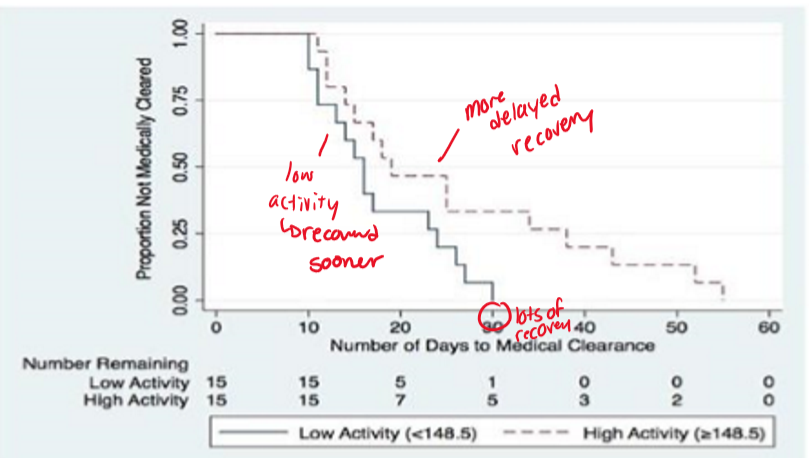
What does the concussion exercise curve recommend?
Too little & too much exercise delays recovery
Like Goldilocks, there is an ideal sweet spot
What is the proposed mechanism for PPCS?
Concussion-induced mechanical changes coupled w neurometabolic alterations can affect fx'al cerebral circulation & combined w post-TBI autonomic dysfx
Cerebral autoregulation & CBF are disturbed post-concussion, potentially explaining why symptoms reappear or worsen
What do the alterations to neurovascular coupling following SRC reveal?
More nutrients and resources are required to accomplish the same task prior to injury
greater increase in PCAv and total activation indicating more nutrients are required to accomplish the same task
Why is CBF an important issue in adolescents?
Abnormal CBF is reported for weeks after injury despite reported resolution of resting symptoms
What is the cause of abnormal regulation of CBF?
Altered autonomic nervous system (ANS) fx &/or altered carbon dioxide regulation post-concussion
What is one of the primary regulations of CBF
CO2 tension in the blood
Where is the control center for the primary ANS?
In the brainstem
may be damaged in concussion, particularly with rotational force applied to the upper cervical spine
What happens in concussed athletes with altered ANS balance vs controls?
Higher HR during steady-state exercise
What causes altered autonomic regulation after TBI?
Changes in the autonomic centers in the brain &/or an uncoupling of the connections b/w the central ANS, the arterial baroreceptors, & the heart
Proportional to TBI severity & improves during recovery
What does emerging data suggest about how exercise improves brain fx?
Via favorable effects on brain neuroplasticity as early as 6-8 weeks of exercise
What is the mechanism of exercise improving brain fx?
May not involve exercise influence on cerebrovascular disease risk, but rather improved neuronal fx
What are the effects of exercise on the brain?
Cognitively protective & is associated w greater levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is involved in neuron repair after injury, greater hippocampal volume, & improved spatial memory (energy metabolism, synaptic fx & plasticity, neurotransmitter modulation)
Improved regulation of CBF
Angiogenesis & vascular health
Neurogenesis & cell survival
Pros of exercise with concussion
Moderate aerobic exercise (60% of maximum HR performed for 150min/wk) is cognitively protective and is associated with greater levels of brain- derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is involved in neuron repair after injury, as well as greater hippocampal volume and improved spatial memory.
Another salutary effect of regular exercise is improved regulation of CBF.
What is the relationship between concussions & deconditioning?
Physical deconditioning of the cardiovascular system due to prolonged rest is common post concussion
Deconditioning is associated w reduced CBF, whereas exercise training has beneficial effects on CBF control, which may relate to restoration of autonomic balance &/or sensitization of the autoregulatory system to gradual increases in systemic BP w controlled exercise.
What is the Buffalo Concussion Treadmill/Bike Test (BCTT/BCBT) based off of?
Balke cardiac treadmill test that requires a gradual increase in workload safe for patients w cardiac & orthopedic problems
The HR and BP recorded at the threshold of symptom exacerbation become the basis for the individualized exercise prescription for patients with PPCS.
How does the BCTT work?
Starting speed is ~ 5 km/h at 0% incline for the 1st minute (adjust for height & activity levels)
Incline increased by 1% at minute 2 & by 1% each minute while maintaining the same speed until the max incline (15%) is reached or the patient cannot continue
Once max incline is reached, speed increases ~ 0.5 km/h
Rating of perceived exertion (RPE, Borg Scale) & symptoms are assessed every minute
HR by HR monitor & BP by automated cuff (not mandatory) are measured at every stage
What are the contraindications of the BCTT/BCBT?
Same as the contraindications of a cardiac stress test
History: unwilling to exercise, increased risk for cardiopulmonary disease, beta blocker use, major depression, does not understand English
Physical exam: focal neurologic deficit, significant/minor balance deficit, visual deficit, orthopedic injury, BP > 140/90, BMI > 30
Symptoms increase by >2pt (skip a phase) and don’t do test if rated between 7-10
What parts of the BCTT/BCBT become the basis for the individualized exercise prescription for patients w PPCS?
HR & BP recorded at the threshold of symptom exacerbation
When is the BCTT/BCBT stopped?
When there is a 2 point increase in overall condition
dont do test between 7-10
What are other cut-off criteria for the BCTT/BCBT?
RPE > 18 on Borg (6-20) Scale
HR > 180 BPM
Voluntary exhaustion
How does the BCBT work?
Starting speed is 60 rpm & resistance is increased every 2 minutes based on the patient's mass
When is the individual not allowed to begin the BCTT/CCCT?
When their overall condition is at least a 7/10
Stop: >2pt increase from the pre-exercise baseline symptoms level or HR reaches 90% of HRmax
What has the BCTT also been adapted to?
A physiologically informed cycle ergometer protocol (Calgary Concussion Cycle Test - CCCT)
What is the starting wattage for females & males?
F: 0.11 times body weight (kg)
M: 0.14 times body weight (kg)
What do the BCTT/BCBT/CCCT help determine?
If symptoms present following concussion are physiological in nature
Why is buffalo concussion bike test not accurate?
Does not match treadmill
“takes longer to reach physiological steady state on cycle ergo vs. treadmill” - stage on treadmill = 1min, on cycle each stage = 2min
doesn’t take longer
>VT1 = won’t reach steady state
USE Calgary Concussion Cycle Test and Calgary Adapted aRm Ergometer
What symptoms are we expecting and want an increase in following exertion testing?
feeling slowed down
fatigue/low energy
How has exercise been used as treatment for other conditions in the past?
Passive cycling was used in the ICU w/in the first 72 hours
Severe TBI
What was the effect of passive cycling on rehab periods?
Improved patient outcomes
Reduced hospital stay times
Helped patients get back to as good a life as possible & as soon as possible
What are the cardiovascular effects of exercise?
Decreased HR
Increased SV
Antioxidants
Which systems does exercise benefit?
All systems & aspects
What is the progression of concussion mgmt?
1. Concussion injury
1.1. Pre-existing factors
2. Neurometabolic cascade
2.1. Pre-existing factors
3. Deficits/ dysfx
4. Assess & manage:
4.1 Symptoms
4.2 Motor
4.3 Cognitive
4.4 Vestibular/occular
4.5. Other
5. Recovery
5.1. Non-recovery.
Why do we want to engineer treatment?
To move people from the non-recovery group to the recovery group
Similar to observations w severe TBIs, what is the effect of exercise as treatment in patients w PPCS?
Positive recovery trajectories
What exercise treatments lead to the best outcomes?
Prescribed exercise thresholds based upon individualized symptom thresholds
What do prescribed exercise threshold programs utilize?
BCTT or CCCT
What are the exercise prescriptions?
20 mins/day
Once/day
6-7 days/week
80-90% of the threshold HR RESERVE