Cranium
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
How many cranium bones are there?
8 cranium bones
How many facial bones are there?
14 facial bones
How many hyoid bones?
1
How many auditory ossicles?
6
How many bones of the vertebral column
26
How many ribs are there?
24 ribs
How many total bones of the axial skeleton?
80 bones
Parietal bone
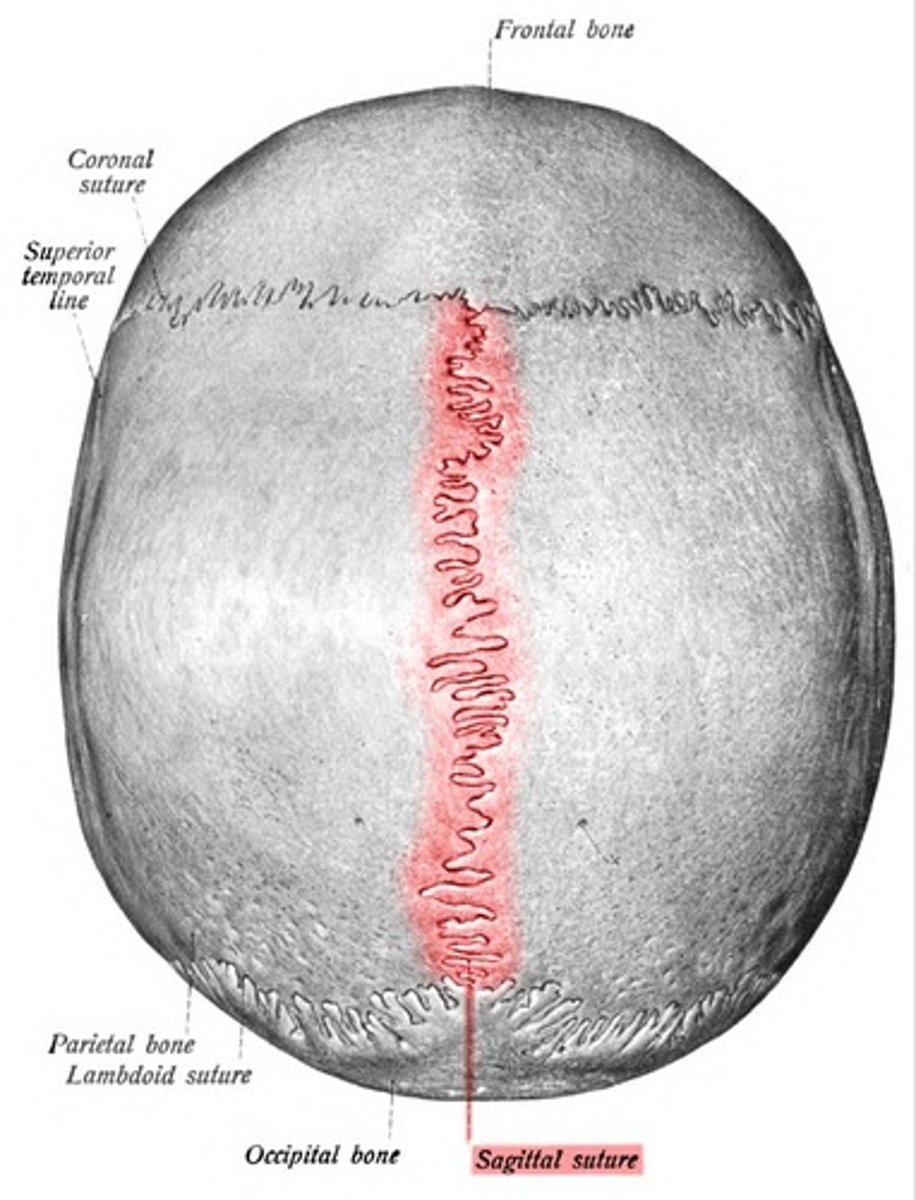
Separated from each other by the sagittal suture, the frontal bone by the coronal suture
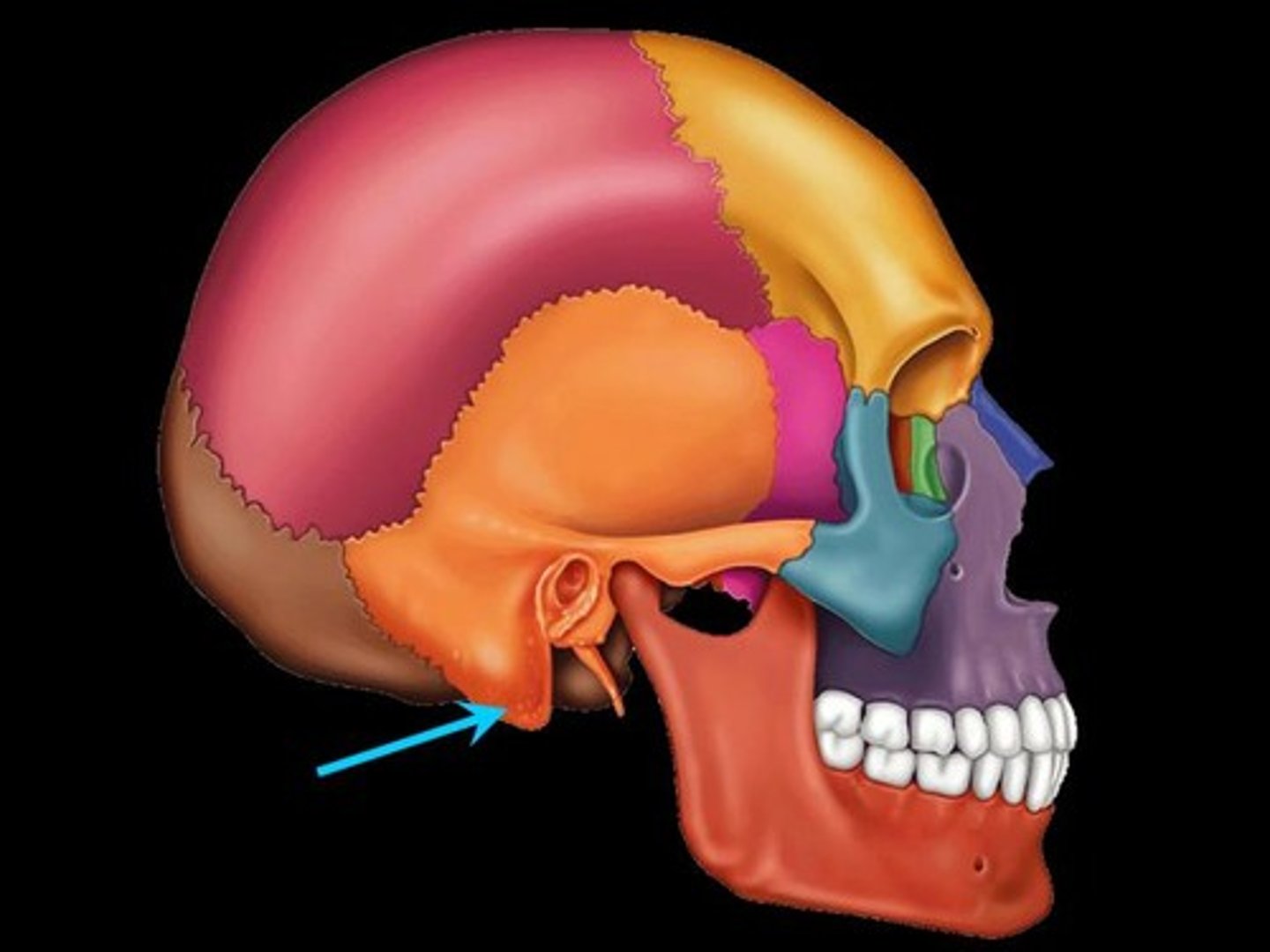
temporal bone
squamous part of temporal bone
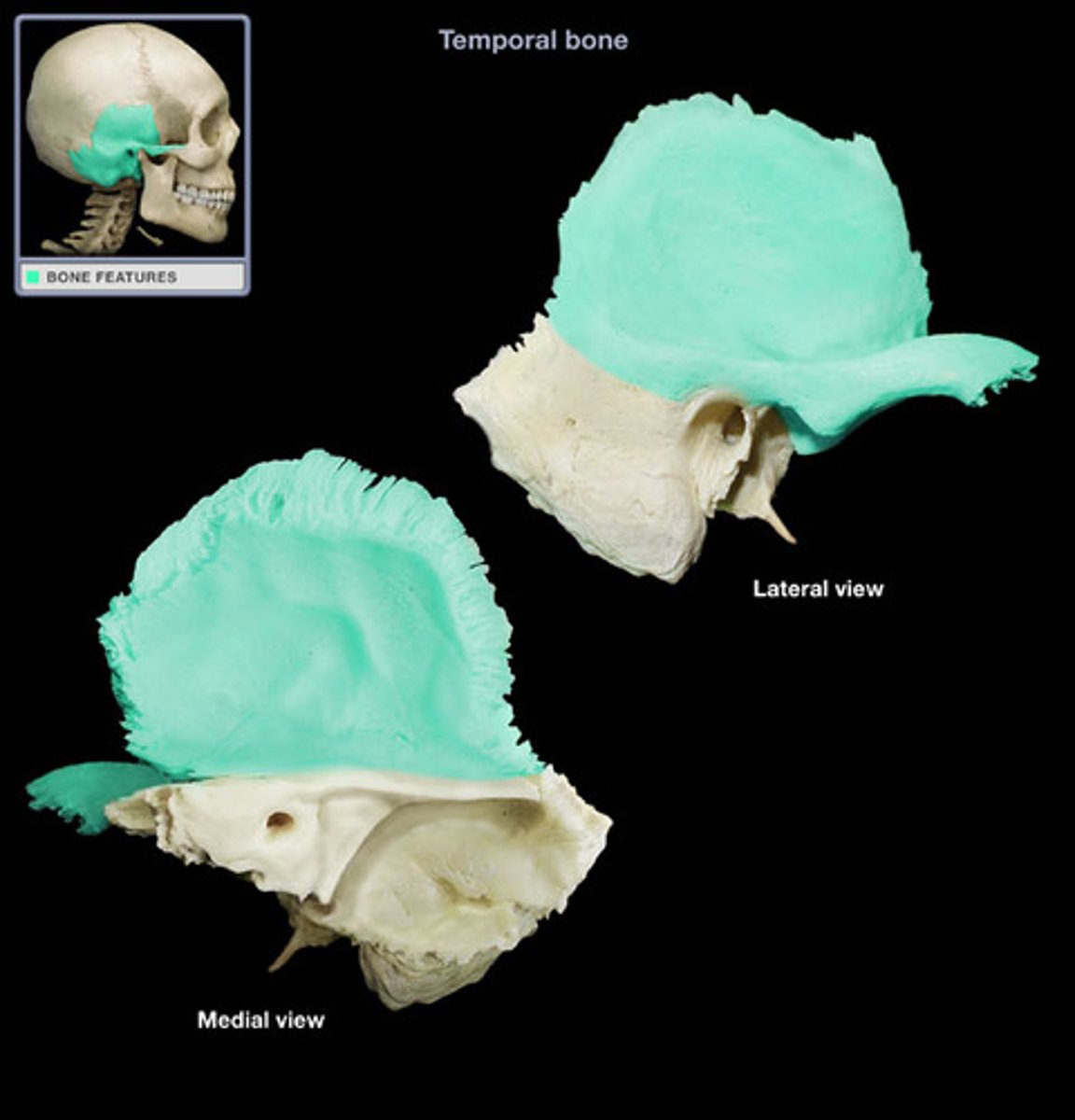
petrous part of temporal bone
mastoid process
Rounded projection attachment site for many neck muscles
external (acoustic) auditory meatus
directs sound into ear
occipital bone (skull)
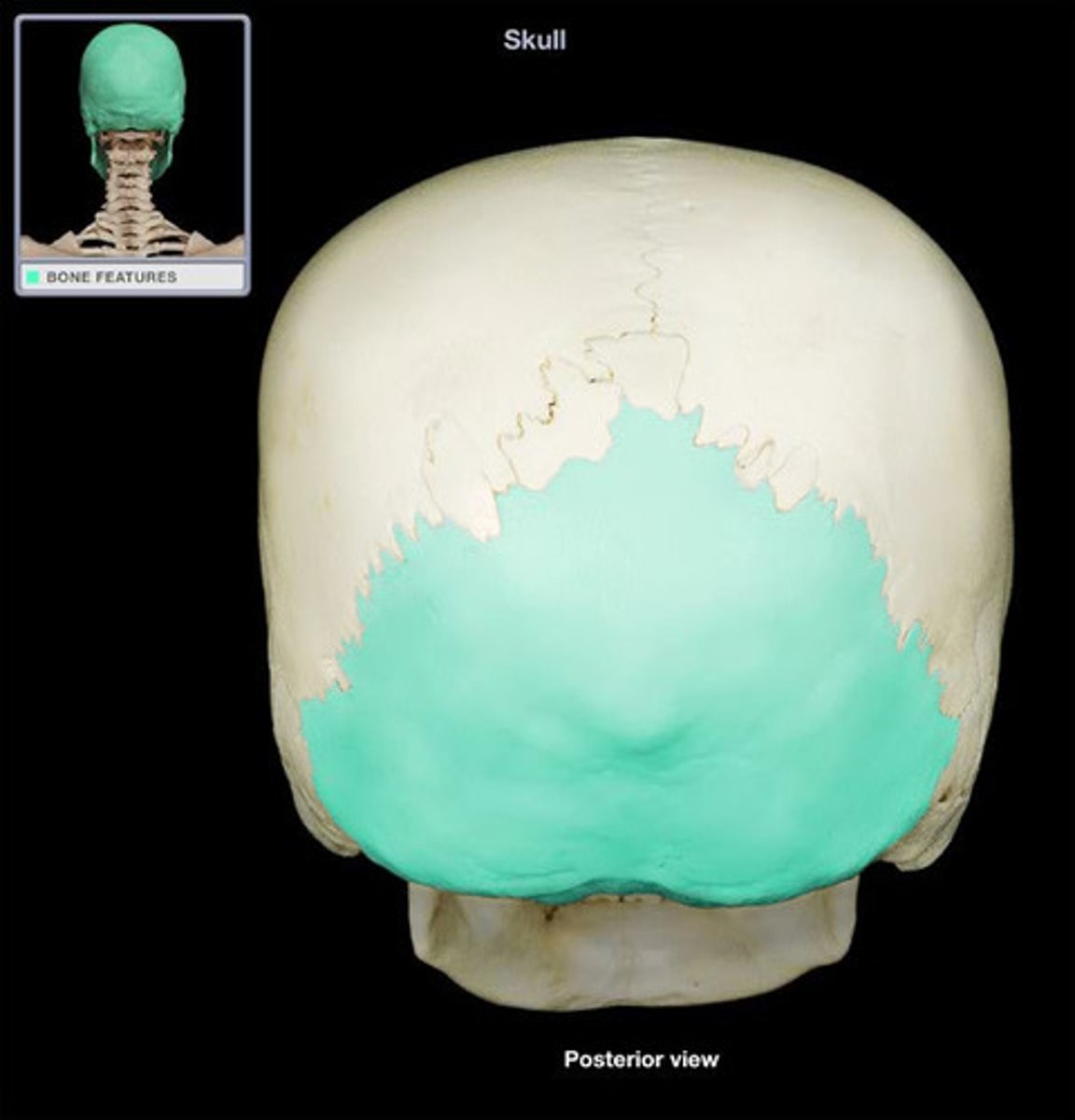
foramen magnum
Medulla oblongata of brain connects with spinal cord through this hole
frontal bone
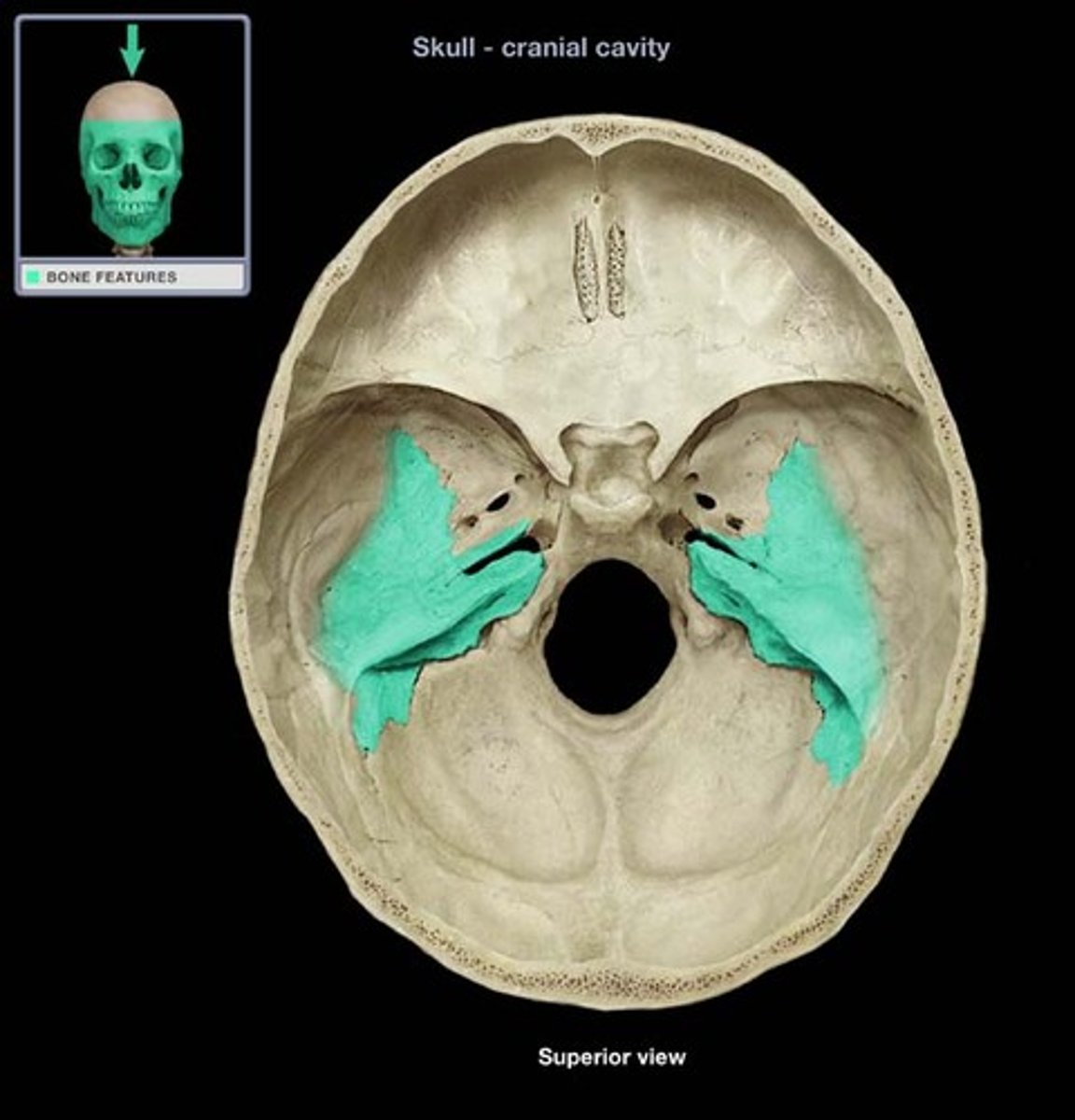
sphenoid bone
Middle part of the base of the skull. Greater and lesser wings articulate and hold together other cranial bones, such as frontal, occipital, parietal and ethmoid.
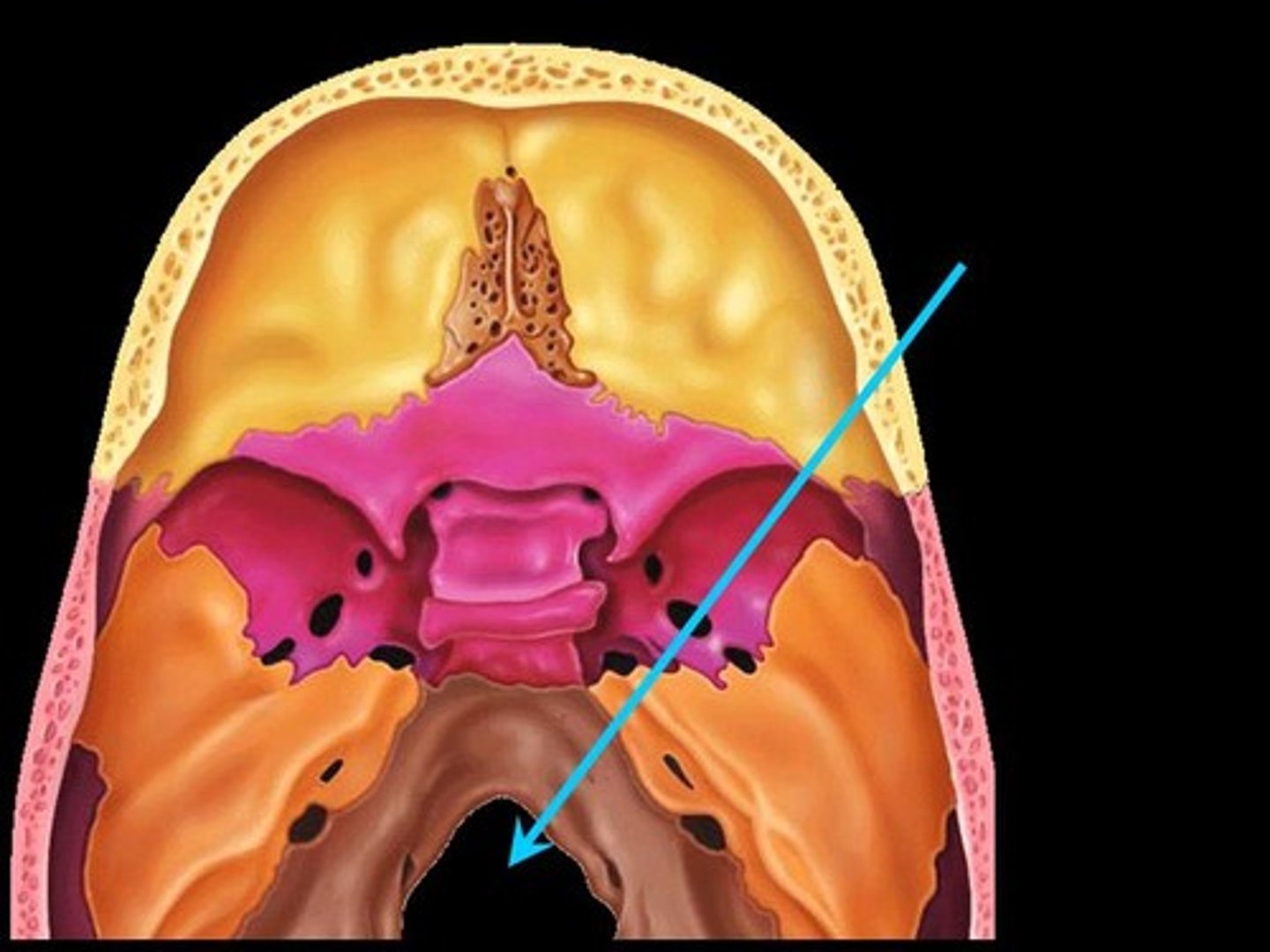
ethmoid bone
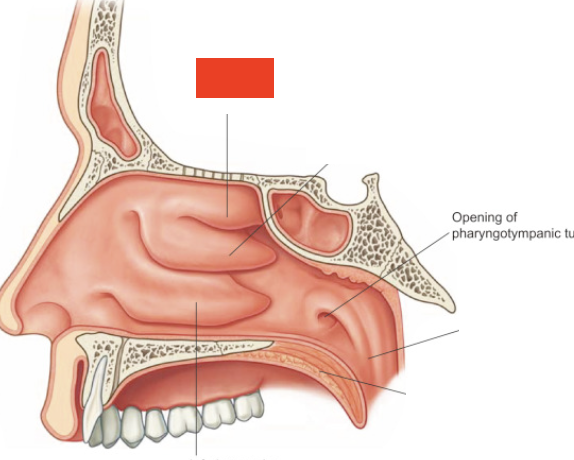
Supporting structure of the nasal cavity positioned in the anterior part of the cranial floor between the orbits
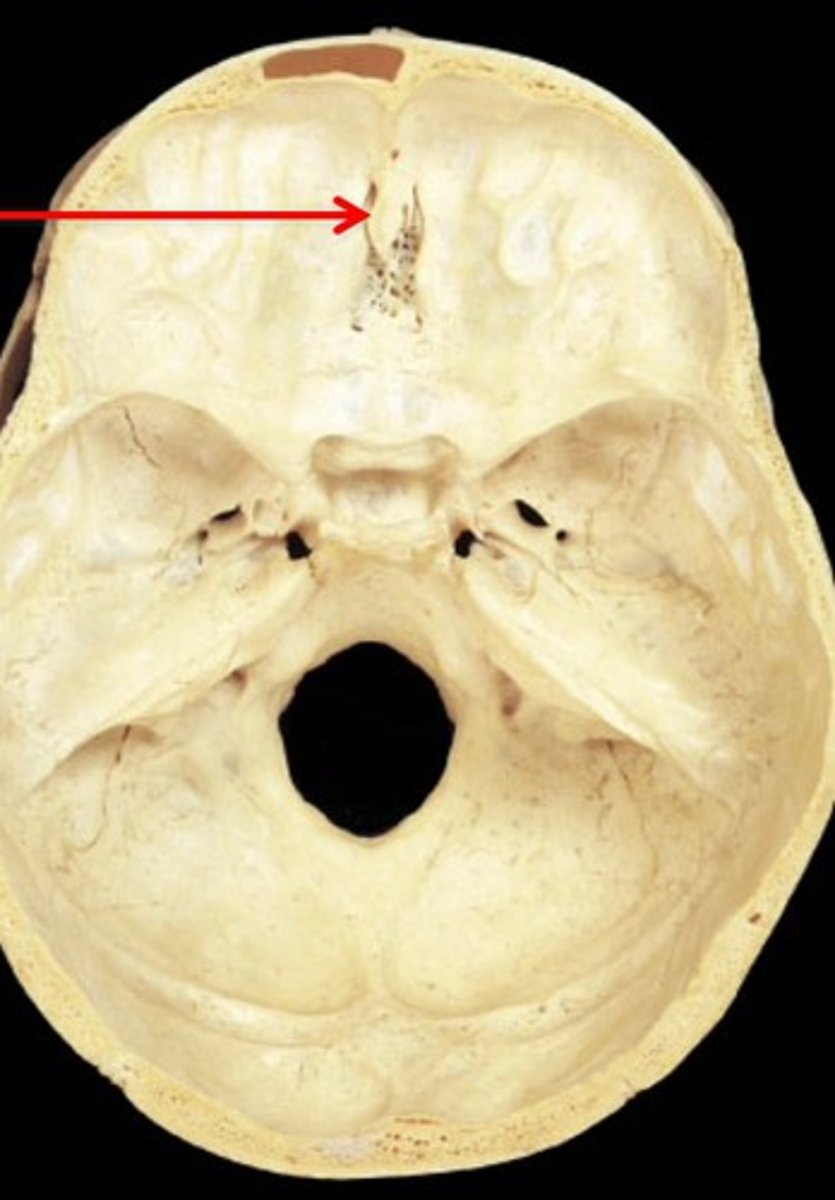
Crista Gali
the point - an attachment ridge for membranes of the brain
supraorbital margin
frontal squama
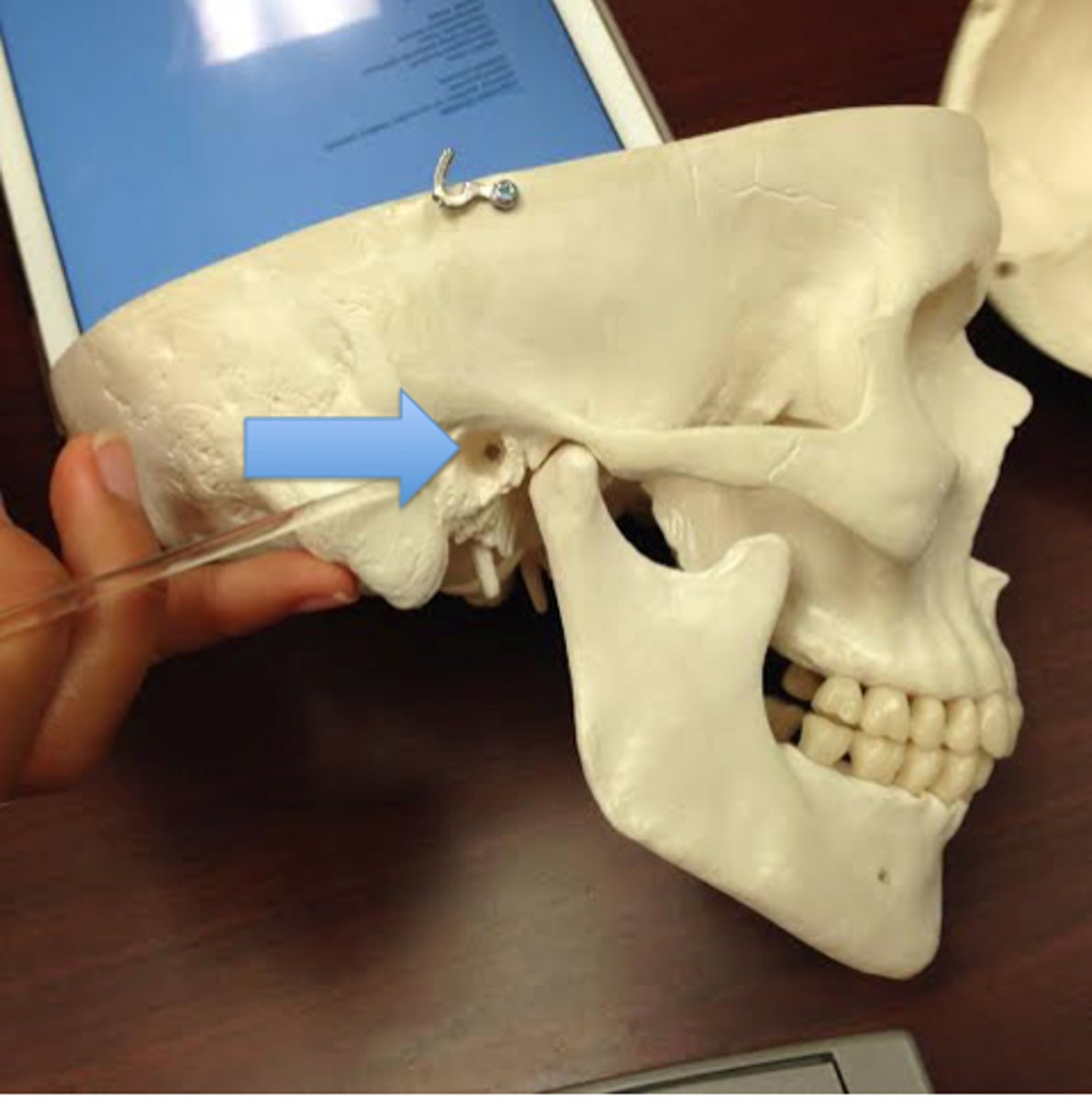
supraorbital foramen
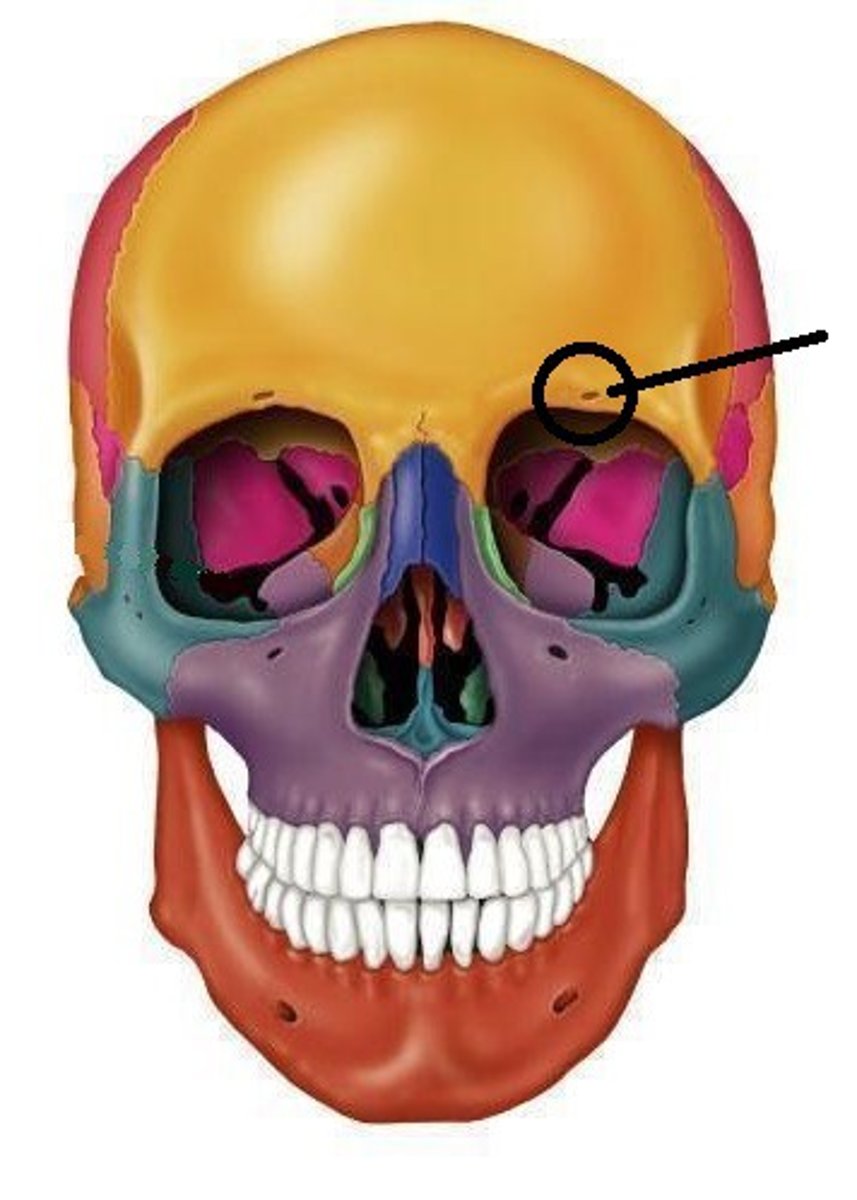
infraorbital foramen
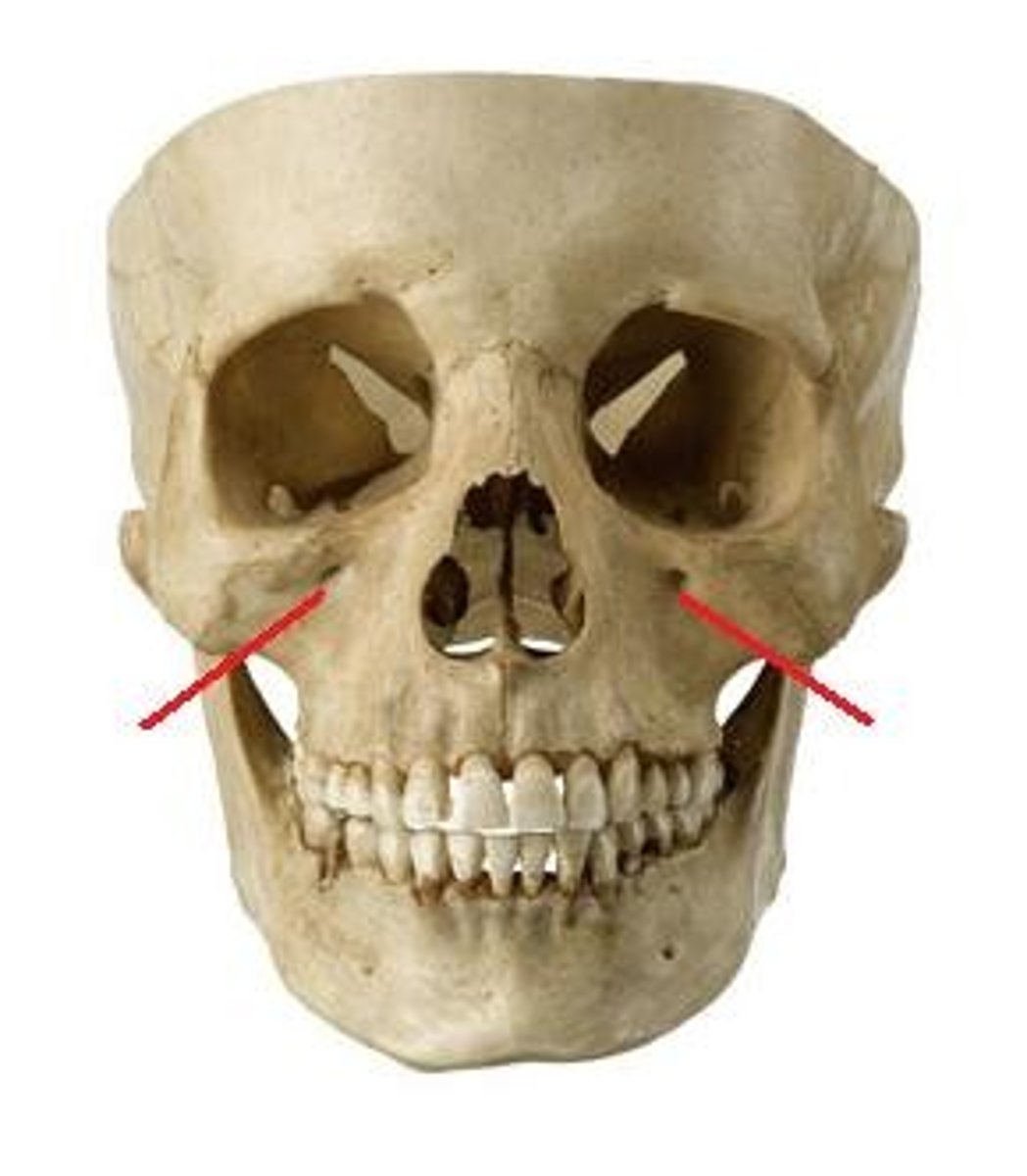
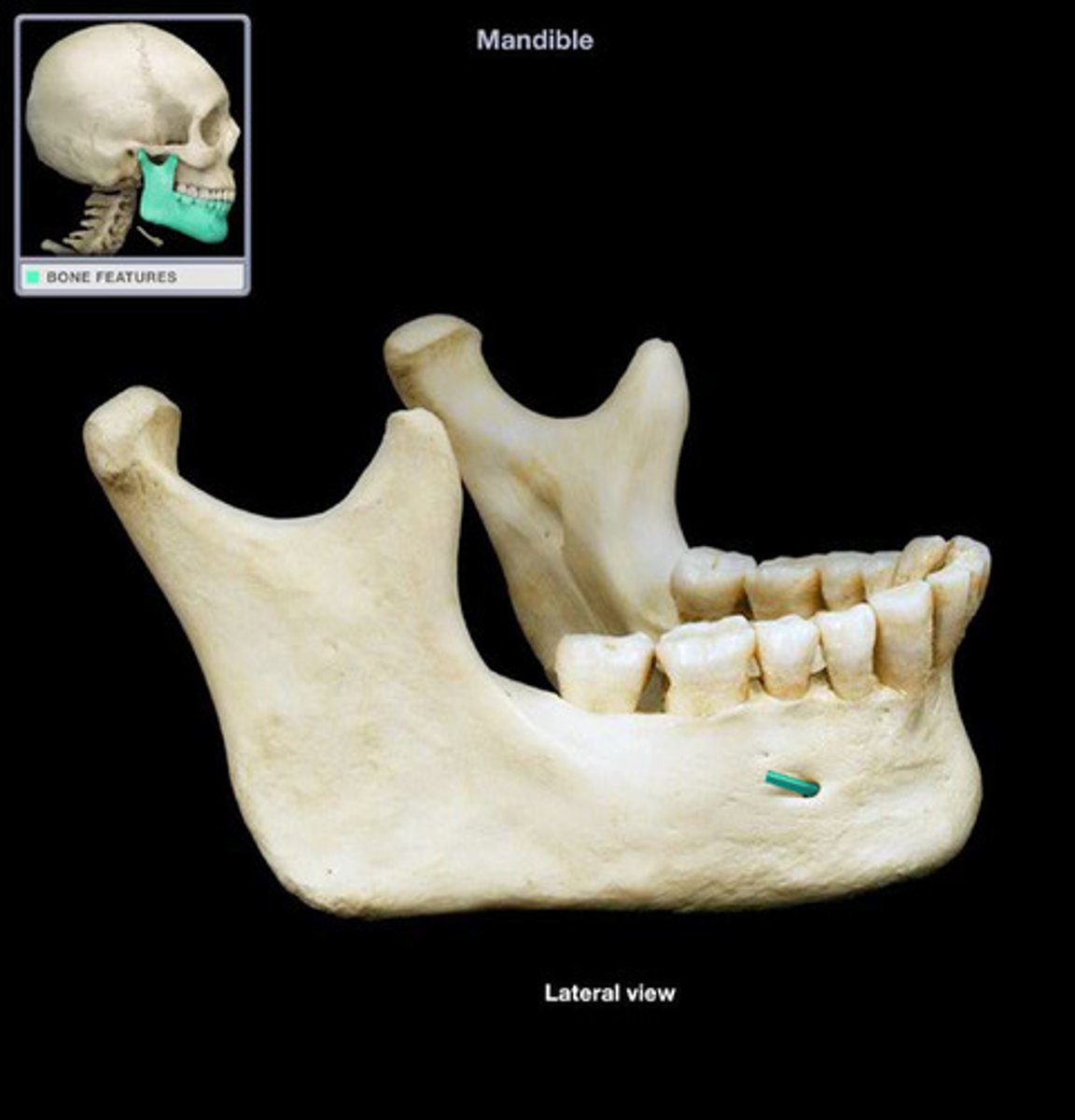
mental foramen
Saggital Suture (Skull)
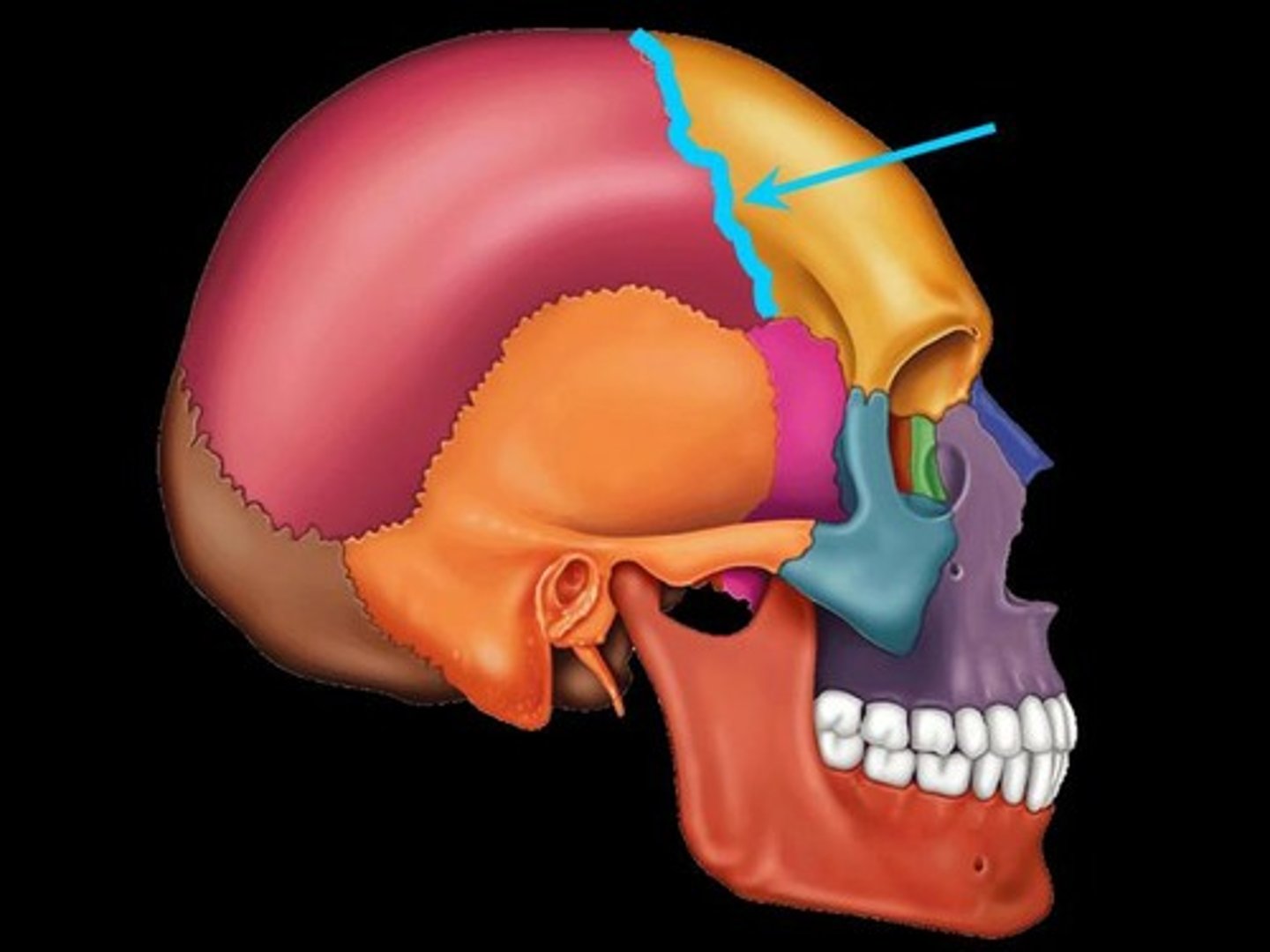
Coronal suture
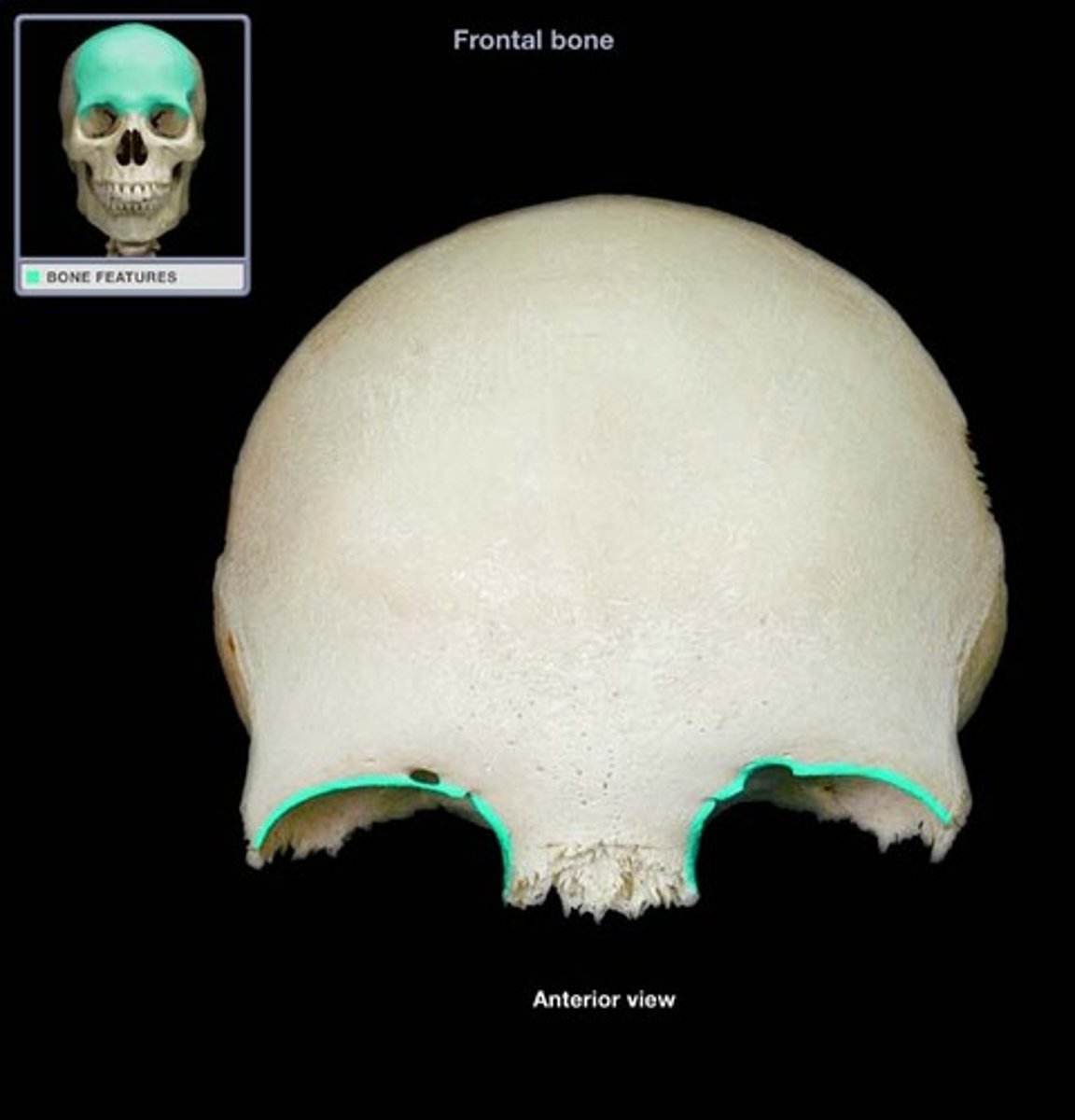
lambdoid suture
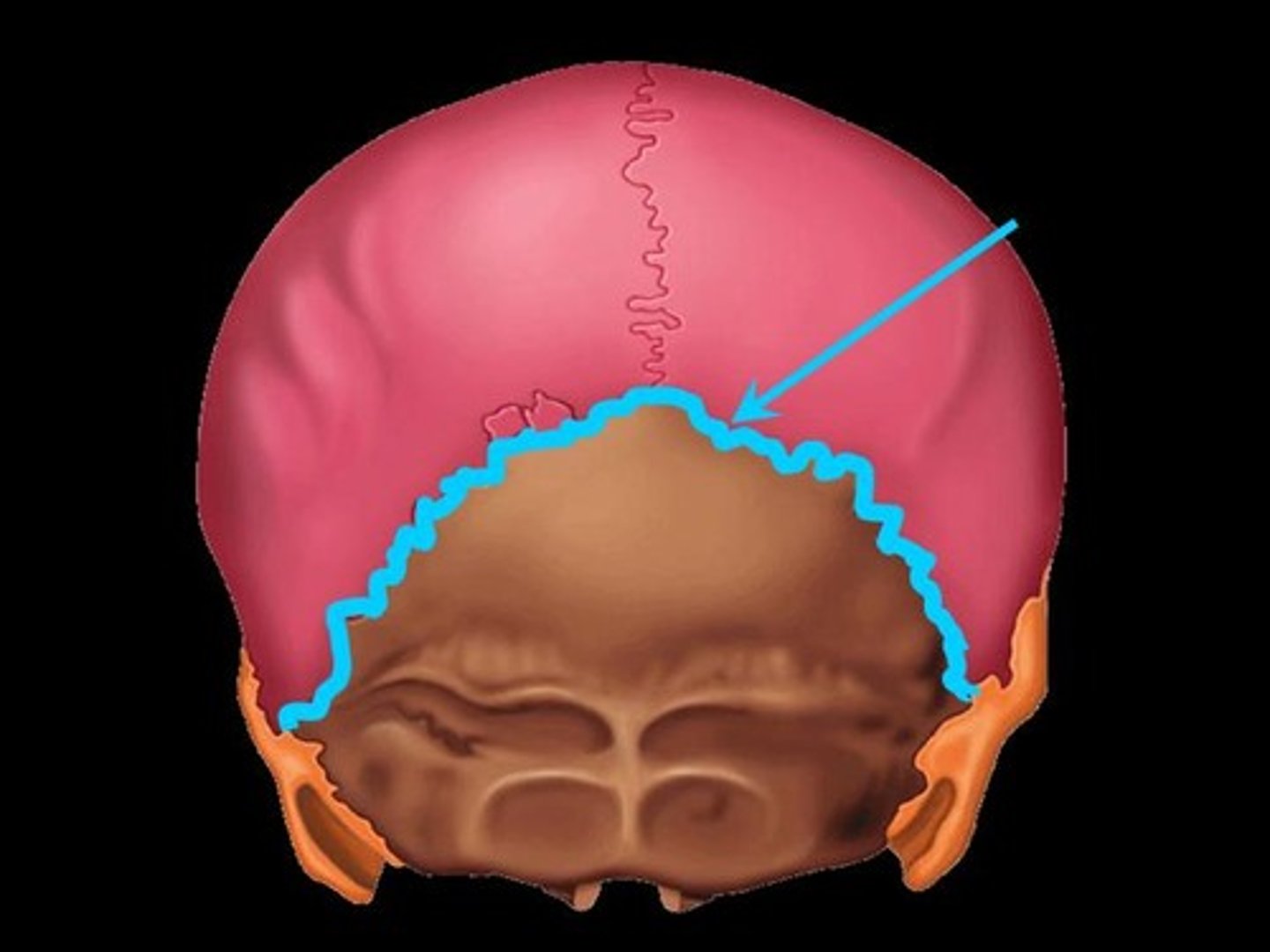
Squamous suture
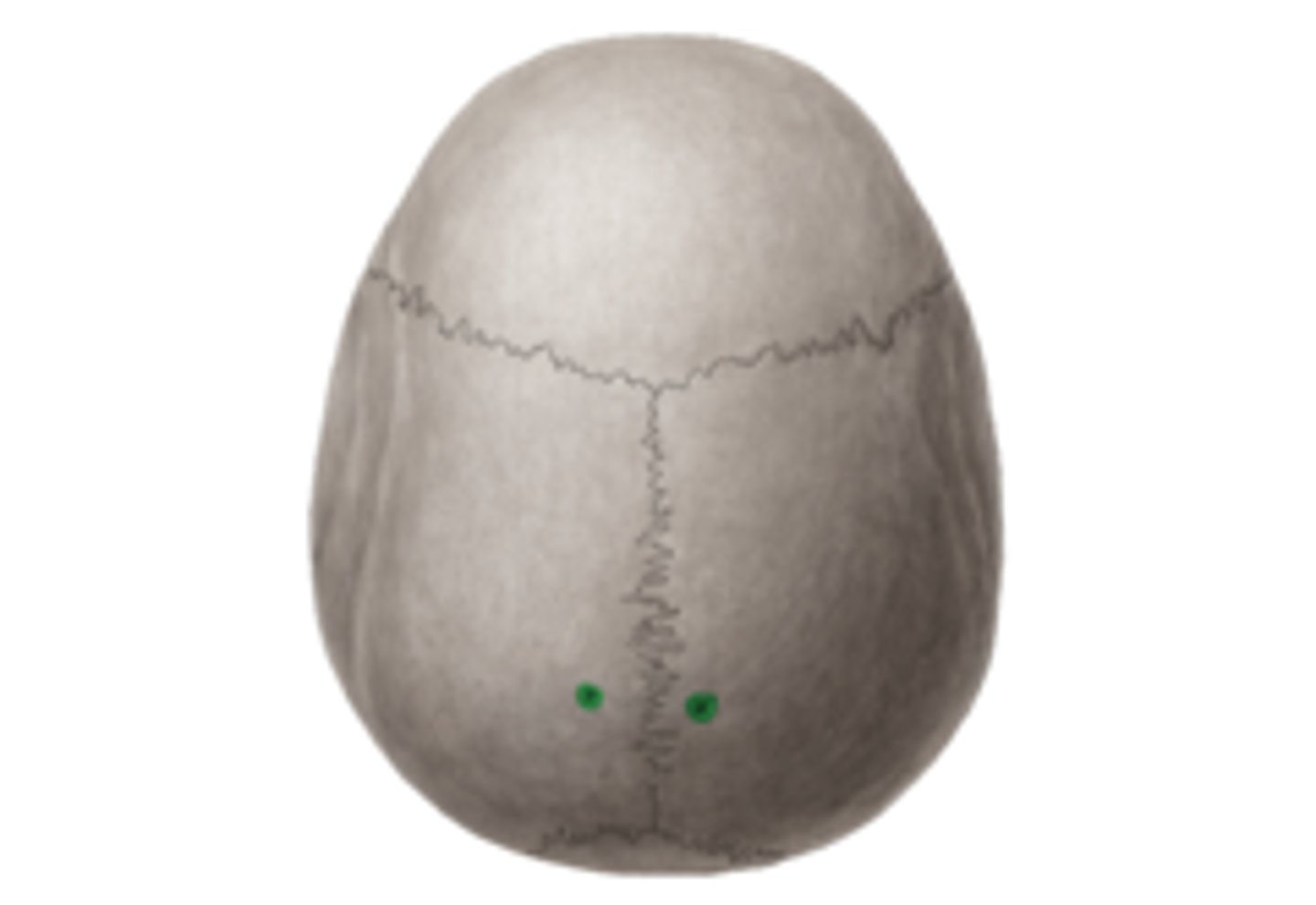
Parietal foramina
tiny hole-like depressions for nerves and blood vessels
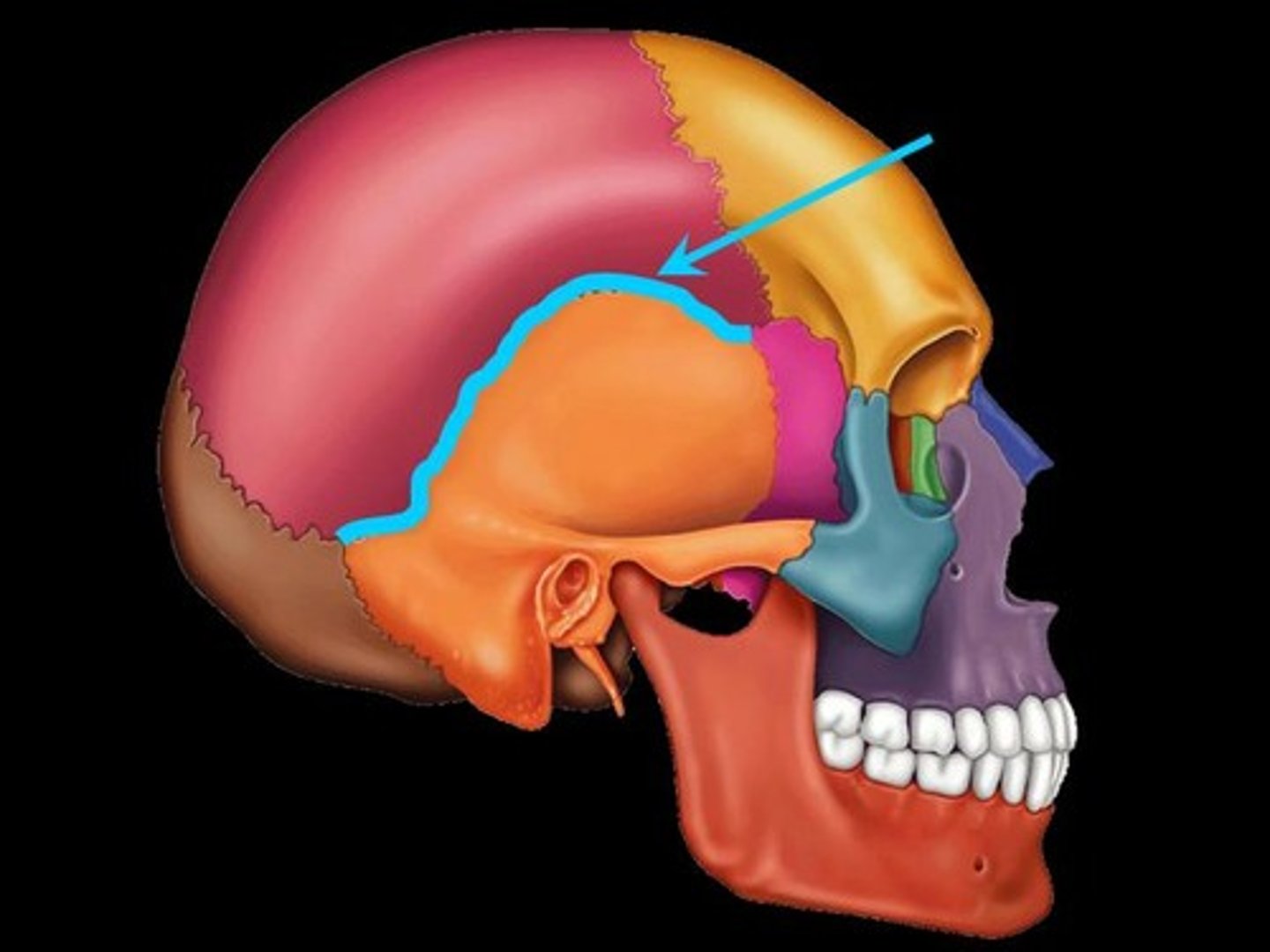
zygomatic arch
Zygomatic process articulates with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone
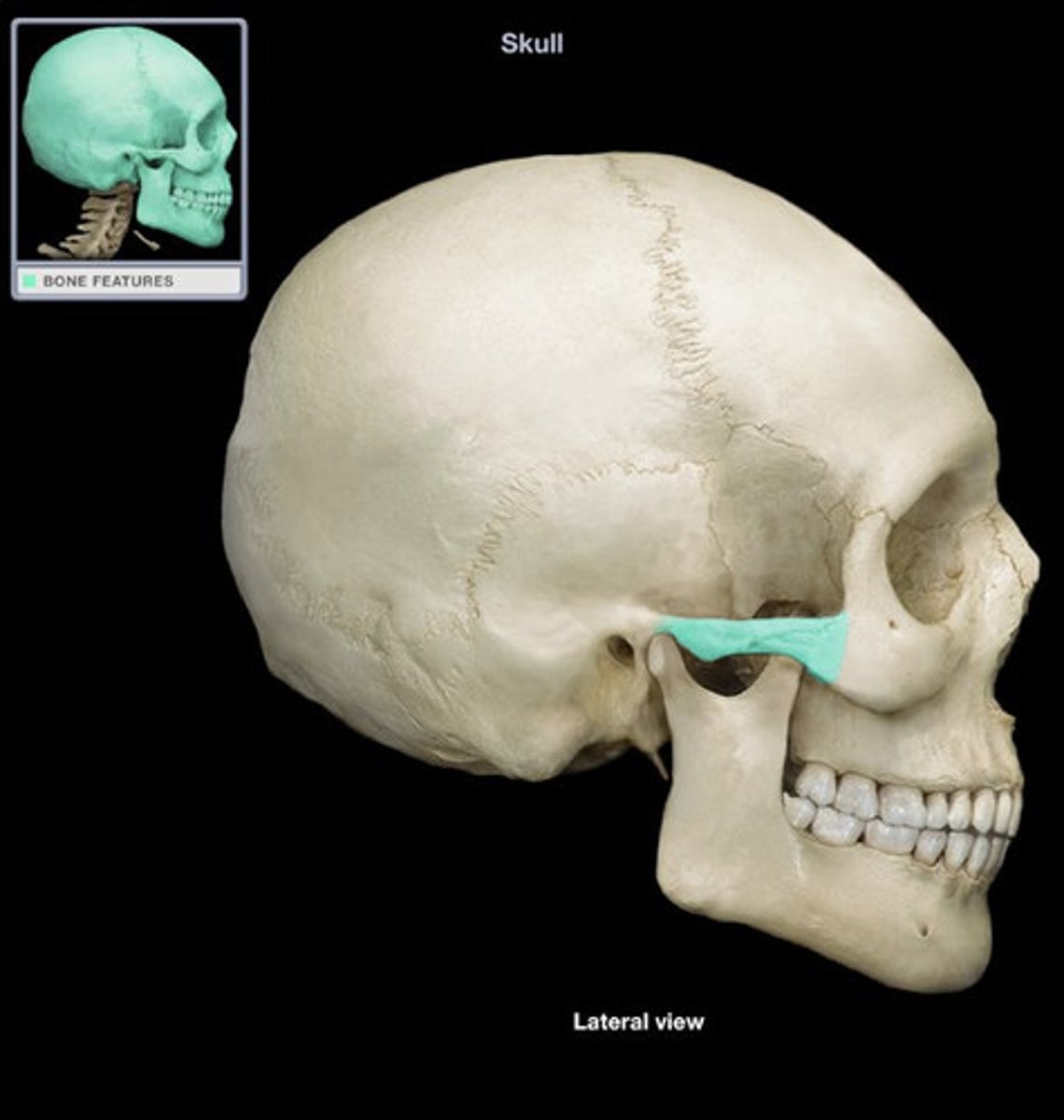
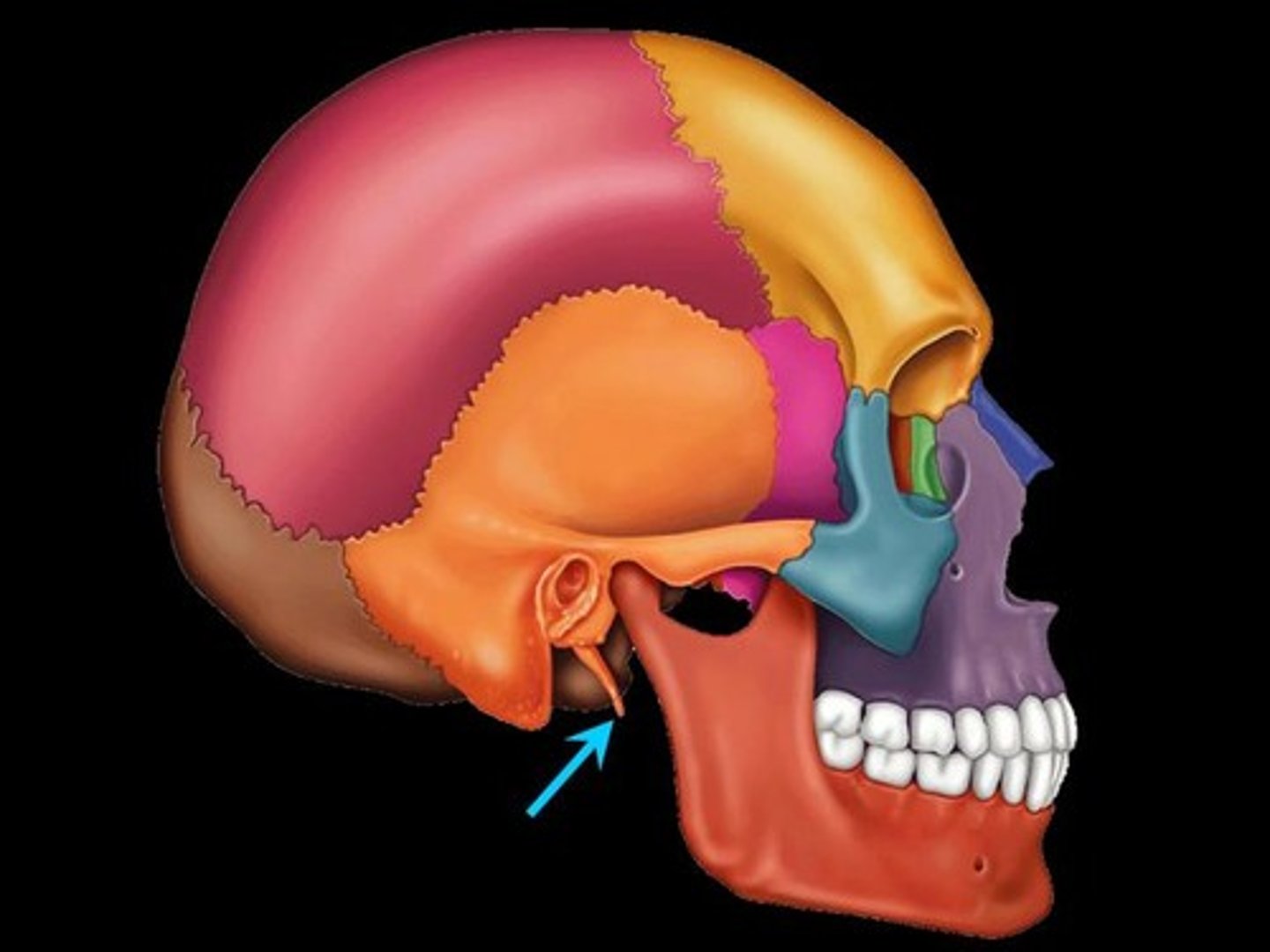
styloid process
pointed projection for attachment of ligaments and muscles of tongue and neck
Mastoiditis
Mastoid air spaces infection
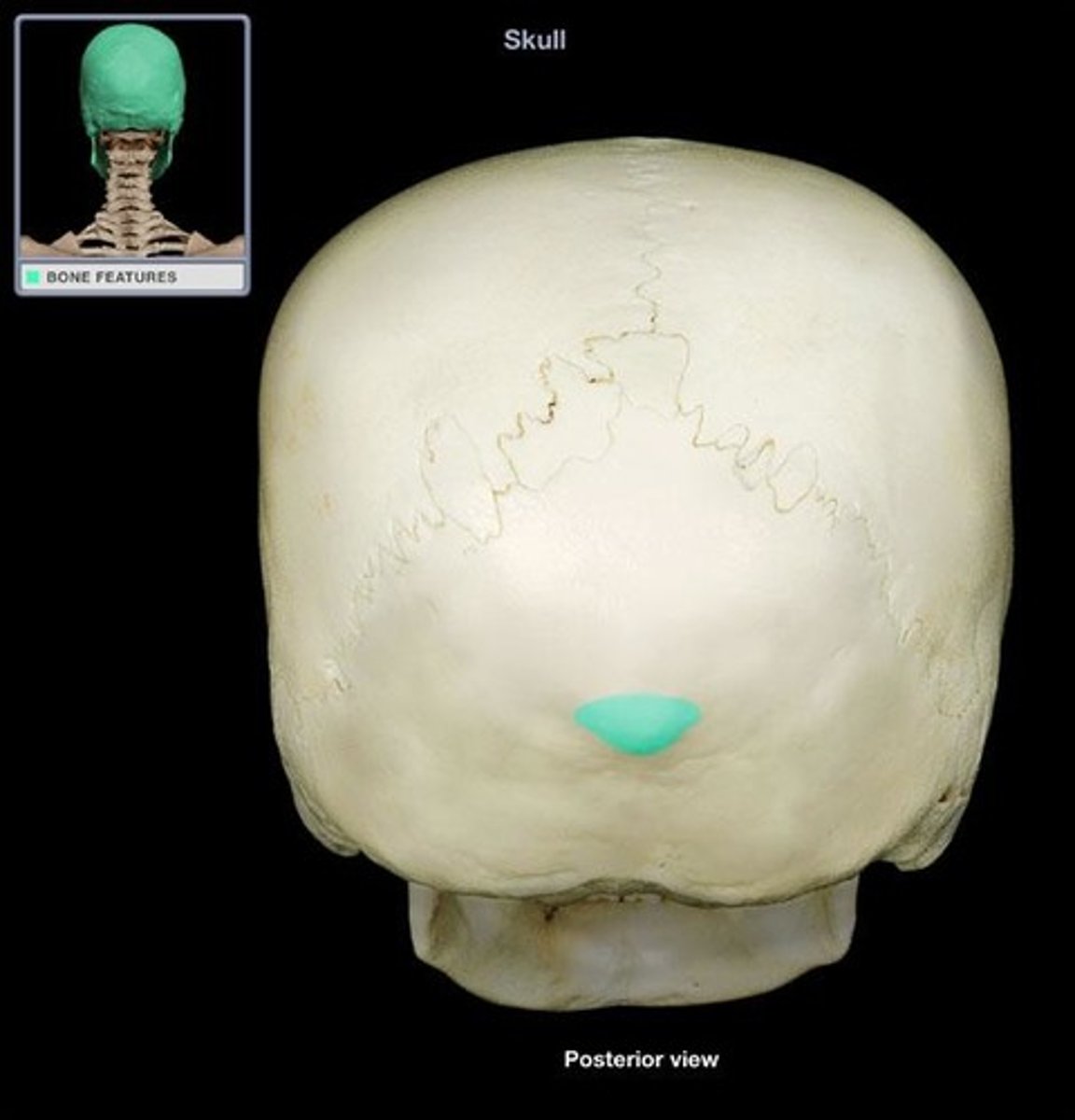
External occipital protuberance
Ligamentum nuchae attaches here and helps support the head
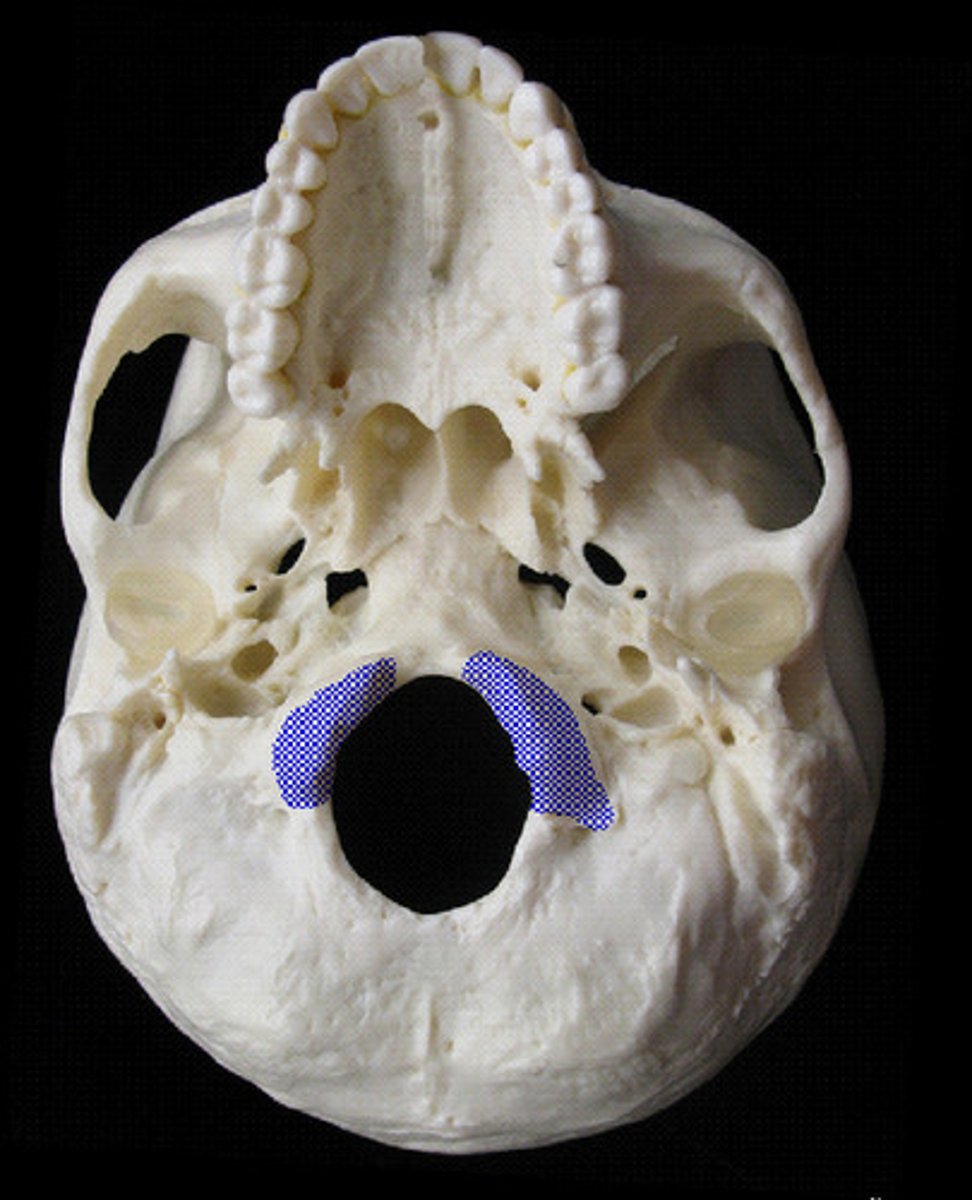
Occipital condyle
Oval processes next to foramen magnum, and articulate with atlas vertebra of neck
Foramen magnum
medulla oblongata of brain connects with spinal cord through this large hole
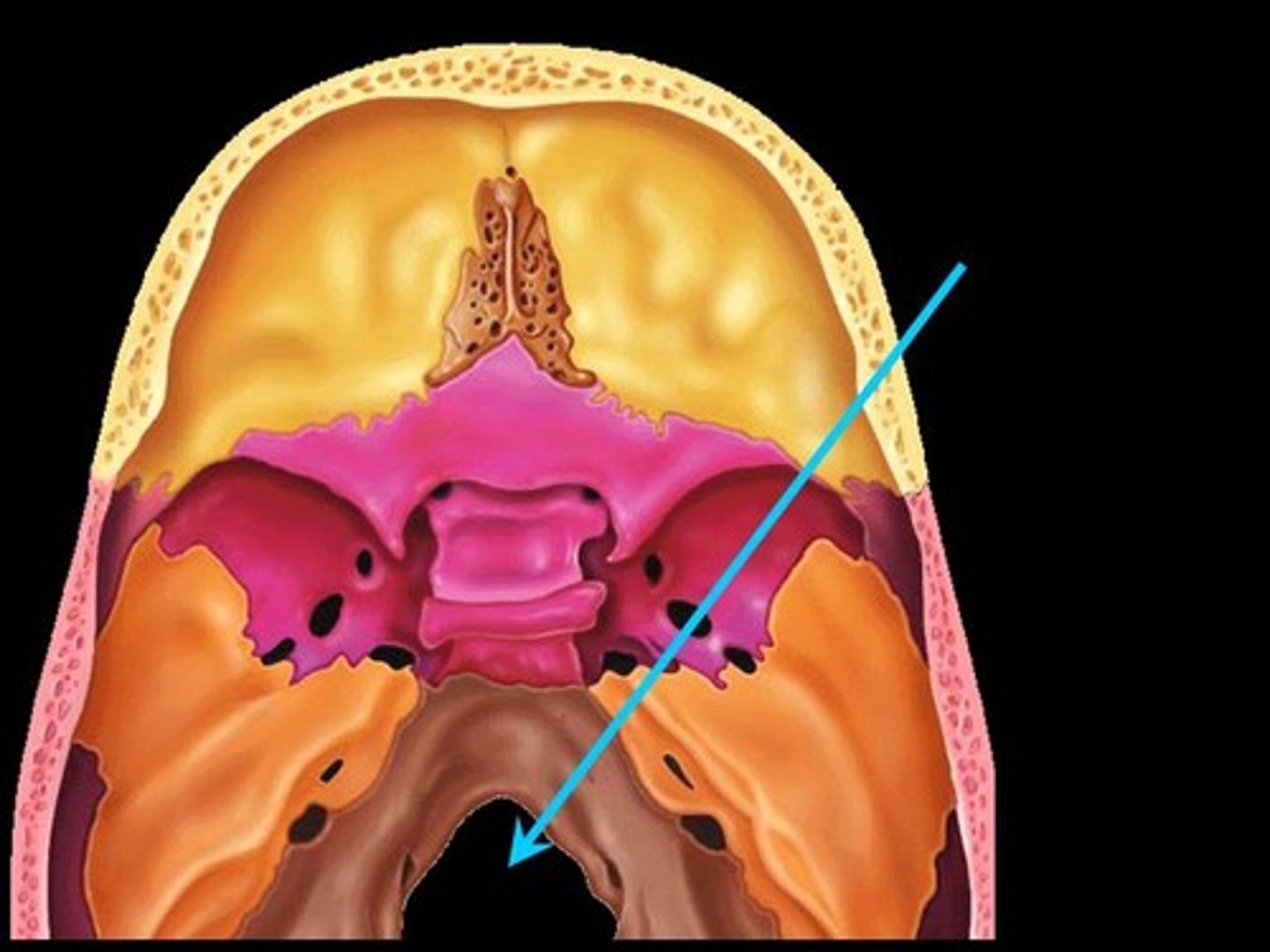
superior and inferior nuchal lines
sites for muscle attachment
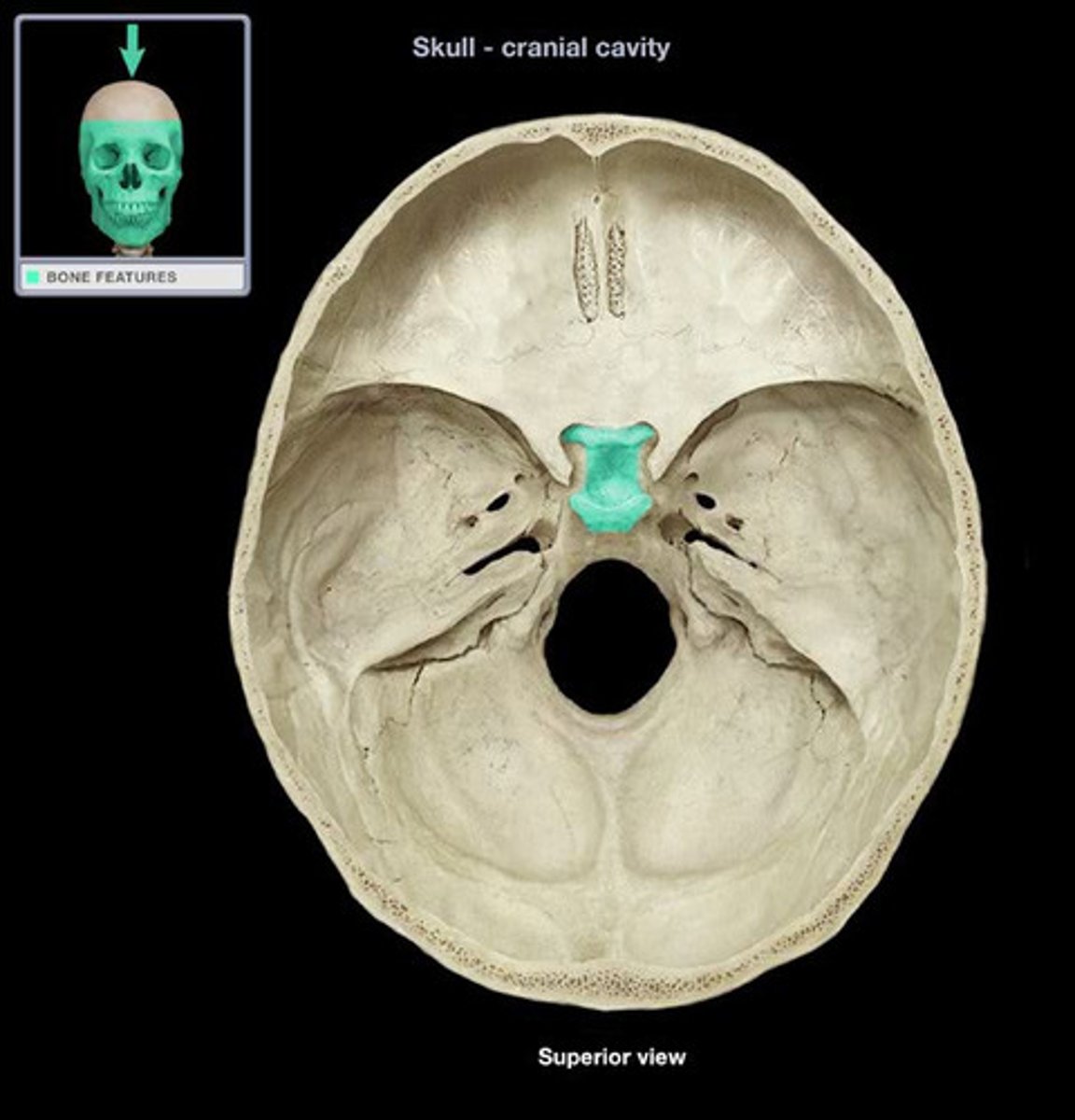
Sella Turcica
Protects the pituitary gland.
What makes up the ethmoid bone?
cribriform plate, crista galli
cribriform plate
forms the roof of the nasal cavity and contains olfactory foramina, where olfactory nerves pass for sense of smell
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid
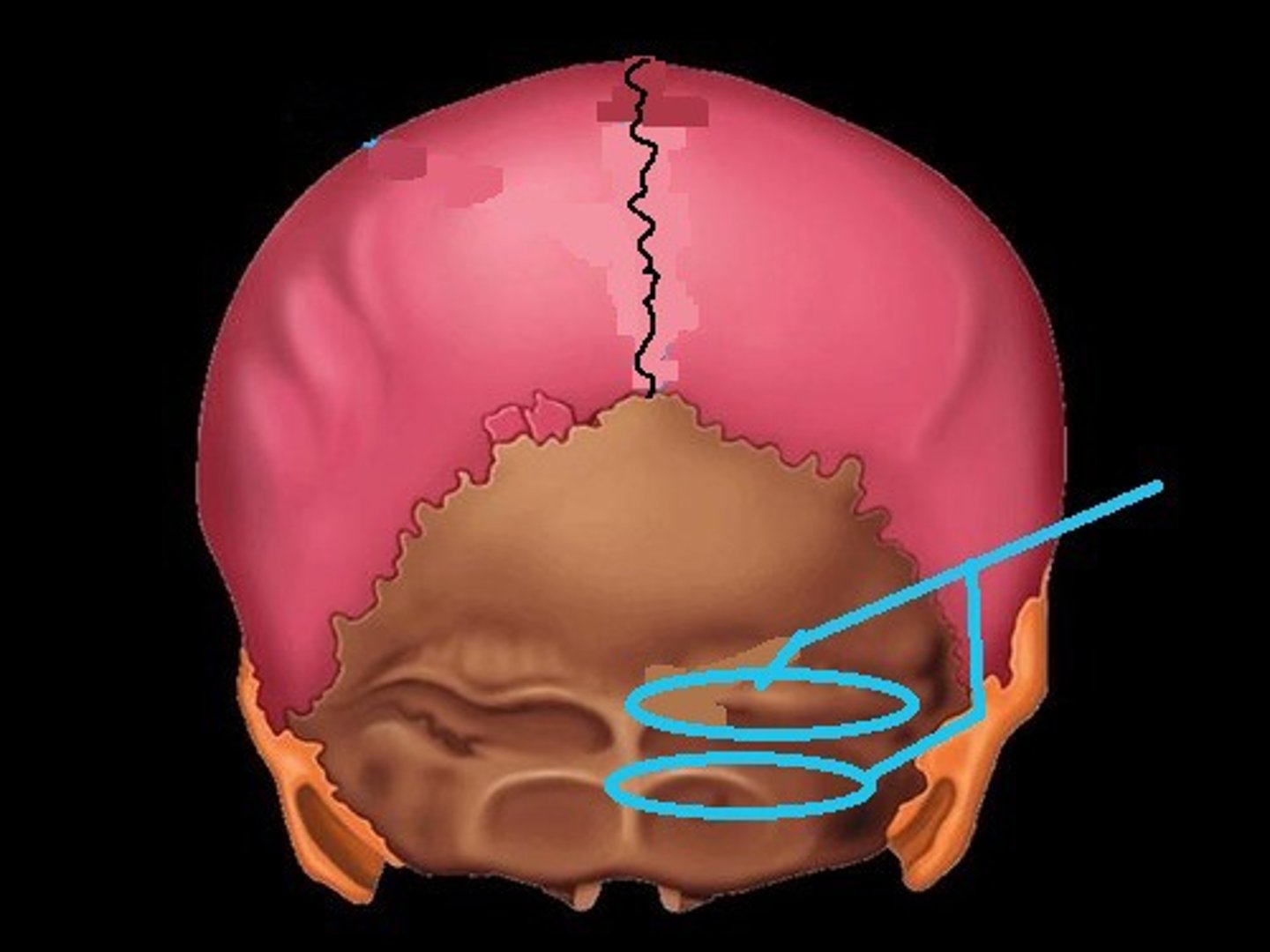
Foramen magnum
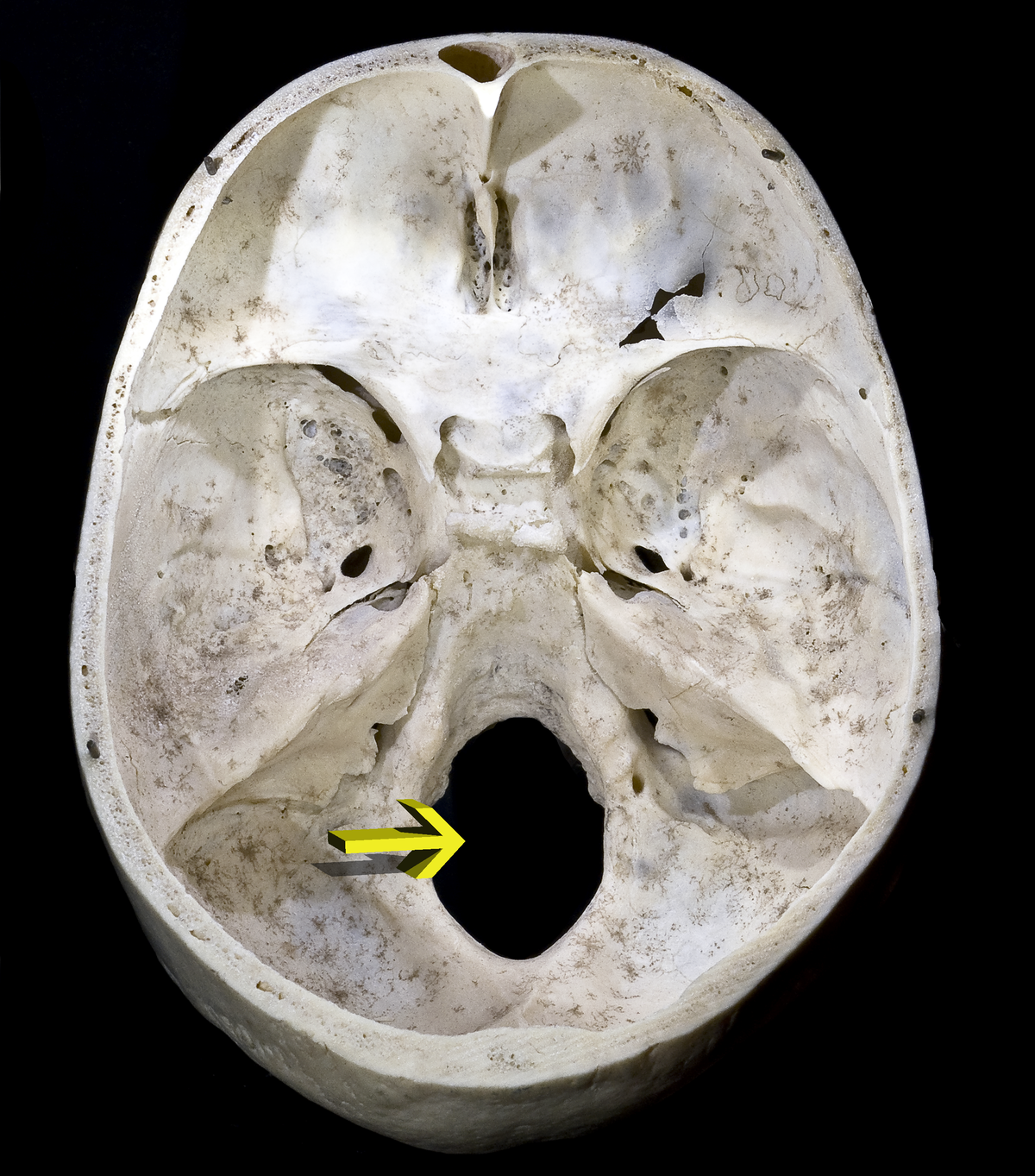
Jugular Foramen
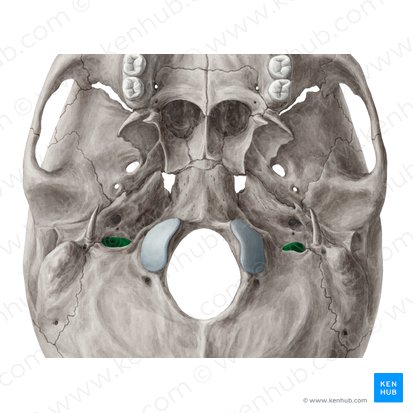
Foramen Spinosum
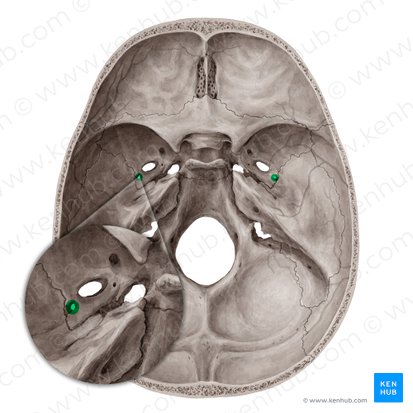
Foramen Ovale
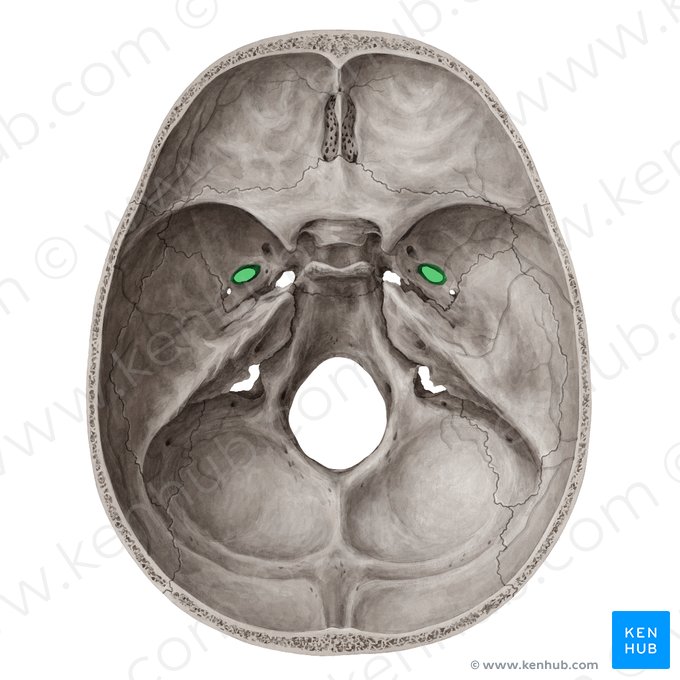
Foramen Lacerum
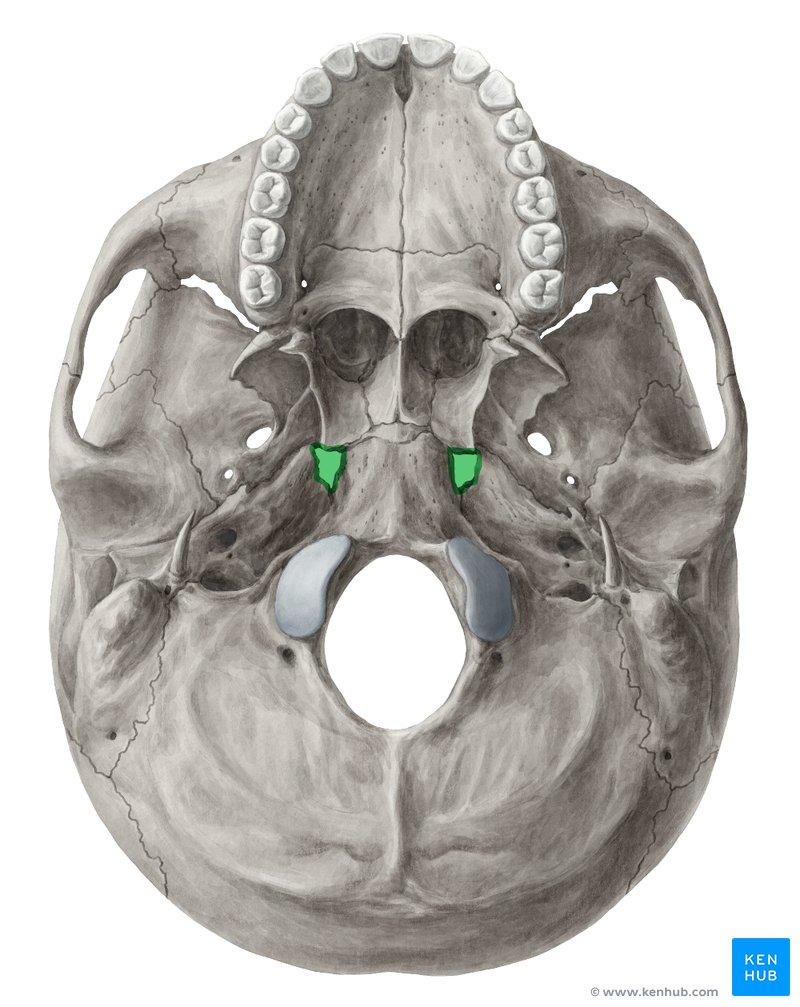
Foramen Rotundum
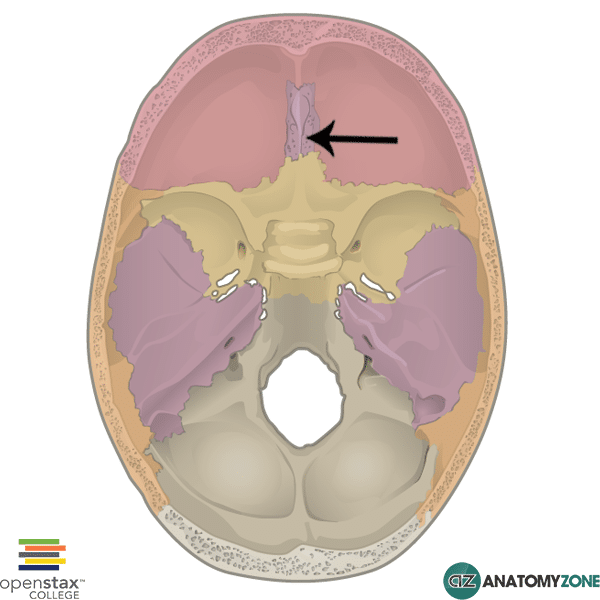
What separates the parietal bone from the occipital bone
Lambdoid suture
What suture separates the frontal bone from the parietal bone?
Coronal suture
What suture separates the two parietal ones?
Sagittal suture
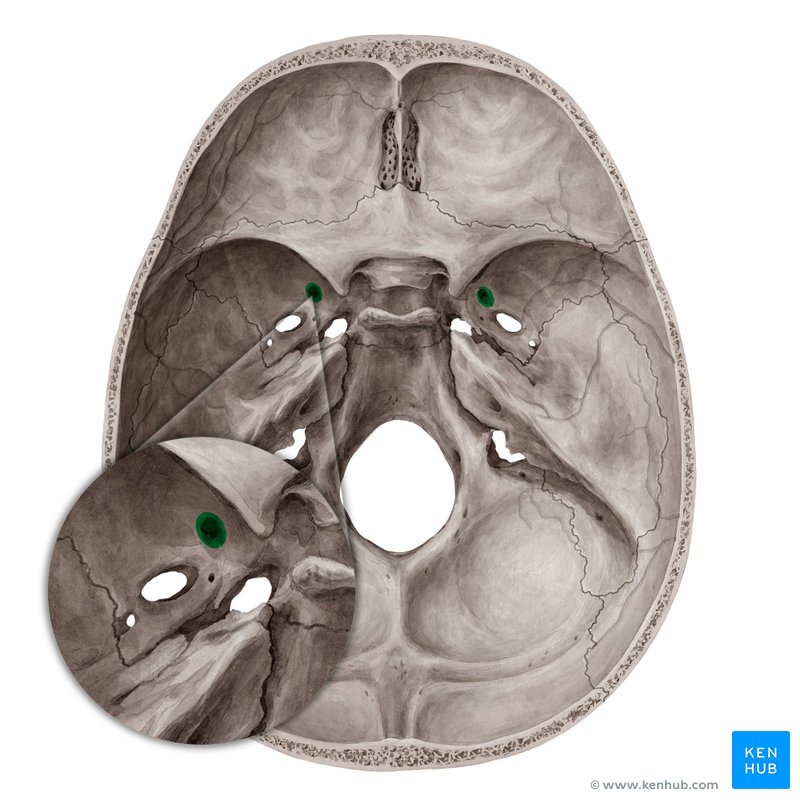
What nerve and artery pass through this foramen?
supraorbital nerve and artery
Frontal Squama
Forms the forehead
Frontal Sinuses
Hollow spaces where air is moistened by mucus membranes
What condyle articulates with the atlas vertebra of neck
occipital condyle
What is the keystone of the cranial floor?
Sphenoid
Why is the sphenoid a keystone of the cranial floor?
Greater and lesser wings articulate with the frontal, occipital parietal and ethmoid
What bone is butterfly-shaped
Sphenoid
What protects the pituitary gland?
Sella turcica
Cribriform plate forms the
roof of the nasal cavity
What does the cribriform plate contain?
olfactory foramina where olfactory nerves pass for sense of smell
Cribriform plate
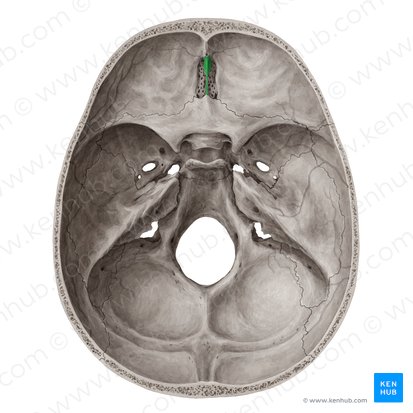
Crista galli
attachment ridge for brain membranes
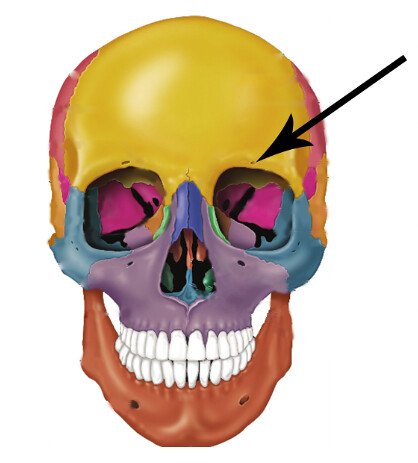
What bone forms the anterior part of the cranial floor, medial wall of orbits and superior part of nasal septum?
Ethmoid
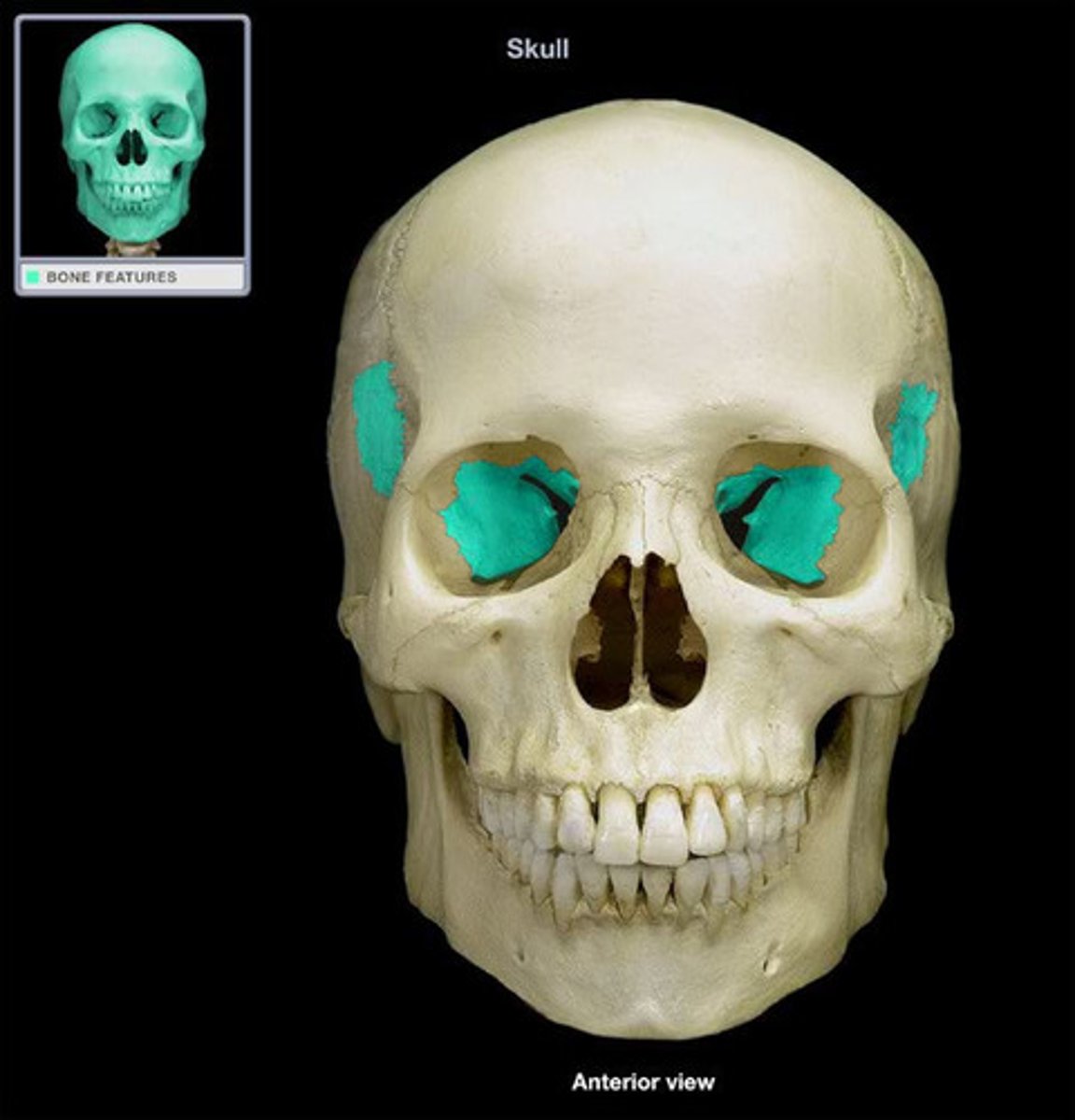
____ warm and moistens inhaled air before it flows into lungs and swirls inhaled air so that particles are trapped by moist mucus membranes
Nasal concha
What nasal concha helps with the sense of smell?
Superior nasal concha
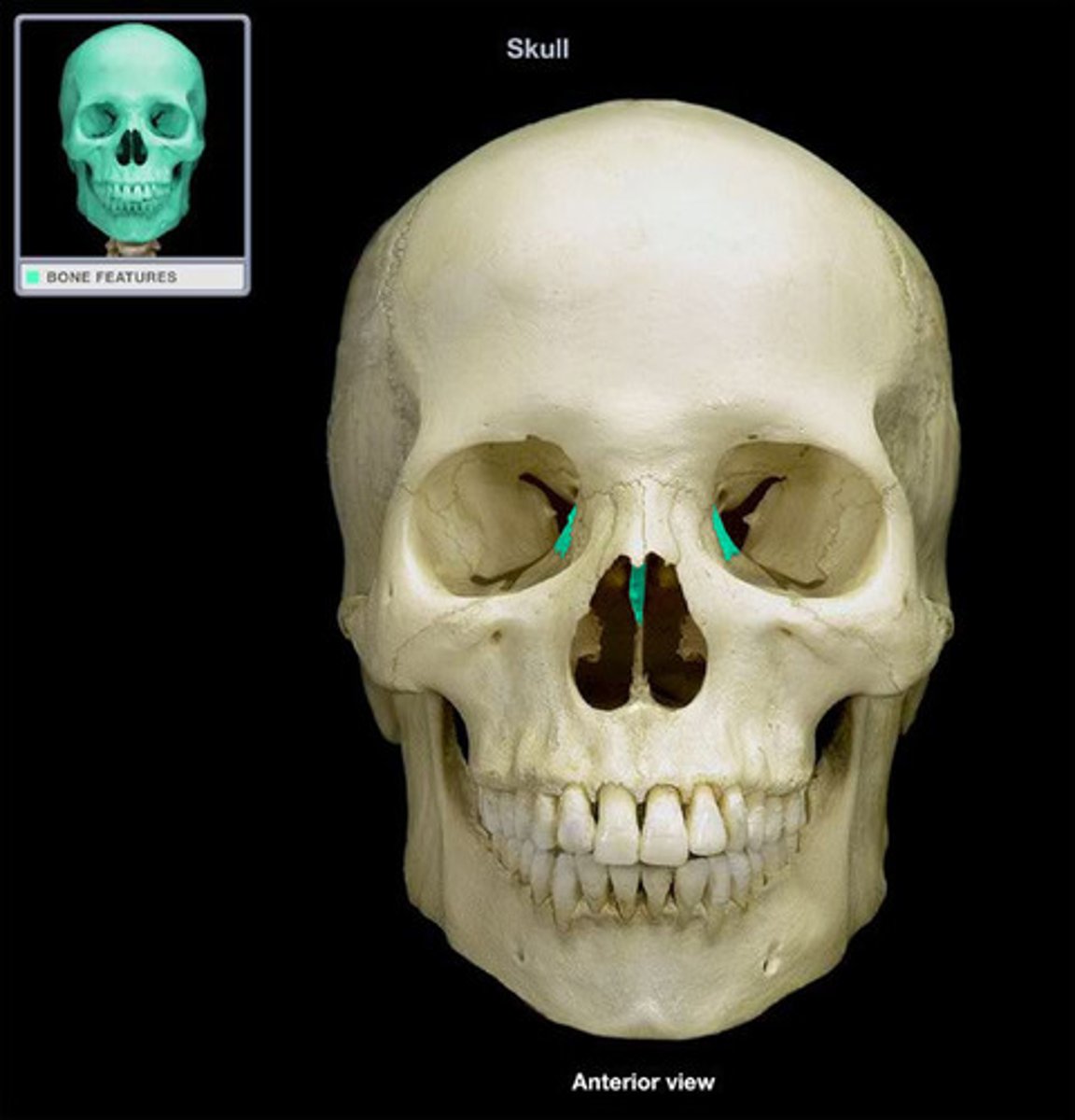
What divides the nasal cavity into right and left sides?
Perpendicular plate
superior nasal concha