PHYSICS: U4B Electromagnetic Waves & Light
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is white light?
The combo of primary additive colors (red, green, and blue)
What are the main types of waves on the electromagnetic spectrum?
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light spectrum, UV, X Ray, Gamma Rays
Electromagnetic waves in order from lowest frequency → greatest frequency
Radio waves (lowest)
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible Light Spectrum
UV
X Rays
Gamma Rays (greatest)
Electromagnetic waves in order from shortest wavelength → longest wavelength
Gamma Rays (shortest)
X Ray
UV
Visible Light Spectrum
Infrared
Microwaves
Radio Waves (longest)
What’s the equation for speed of a light wave?
n = c/v
n: refraction index of medium
c: speed of light in vacuum (3×10^8) — m/s
v: velocity of wave in medium (m/s)
What is specular light?
When light reflects off of a smooth surface to create a crisp, clear image (like when light reflects off the surface of a lake with no waves, creating a clear reflection)
What is diffuse light?
When light reflects off of a rough surface to create an unclear reflected image (like when light reflects off of the surface of choppy waters to create an unclear reflected image)
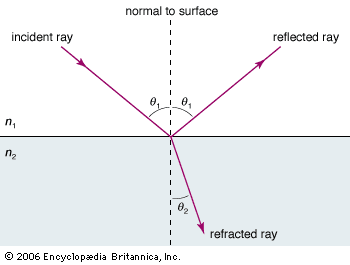
What’s the law of reflection?
When a ray of light reflects off of a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
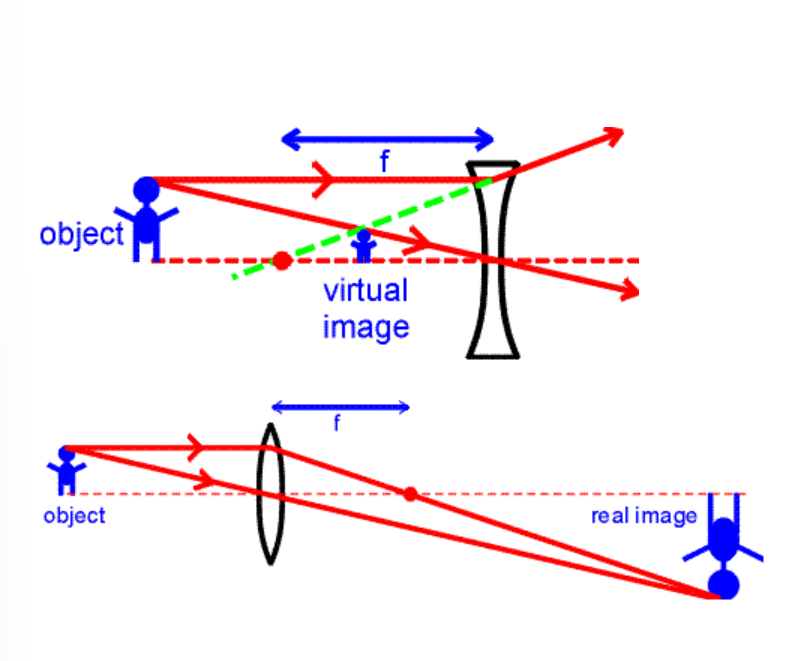
What’s a real image?
Formed by the actual convergence of light rays. can be projected onto a screen. Typically inverted
What’s a virtual image?
Formed by the apparent divergence of light rays. Cannot be projected onto a screen. Typically upright
Real and virtual sides of curved and flat mirrors
If object is on the left (real), virtual is on the right.
Flat mirrors ALWAYS produce virtual images, while curved mirrors can produce either.
Is a curved convex mirror diverging or converging light?
Diverging
Is a curved concave mirror diverging or converging light?
Converging
Is a convex lense diverging or converging light?
Converging
Is a concave lense diverging or converging light?
Diverging
Real and virtual sides of lenses?
How do additive colors of light work? What colors are created with various combinations of additive colors?
Primary additive colors of light include red, green, and blue which can be added together to produce white visual light
ie. red+blue+green = white
Different combinations of these primary additive colors produce secondary additive colors of light: magenta, yellow, and cyan - formed by adding together two primary colors.
Magenta, yellow, and cyan are called pigments, meaning they absorb certain colors of light and reflect others (the reflected colors is what determines its appearance). These colors are usually seen as paint, etc.
How do subtractive colors of pigment work? What colors are created with various combinations of these pigments?
Primary Subtractive Pigments: magenta, yellow, and cyan
When these secondary additive colors are all combined, black is formed.
ie. magenta+yellow+cyan = black
Secondary Subtractive Pigments: red, green, and blue
Red, green, and blue can also be created by mixing two primary subtractive pigments
ie. magenta + yellow = red
Magenta (green absorbed, red & blue reflected) + Yellow (blue absorbed, green & red reflected) = Red (blue & green absorbed, red reflected)
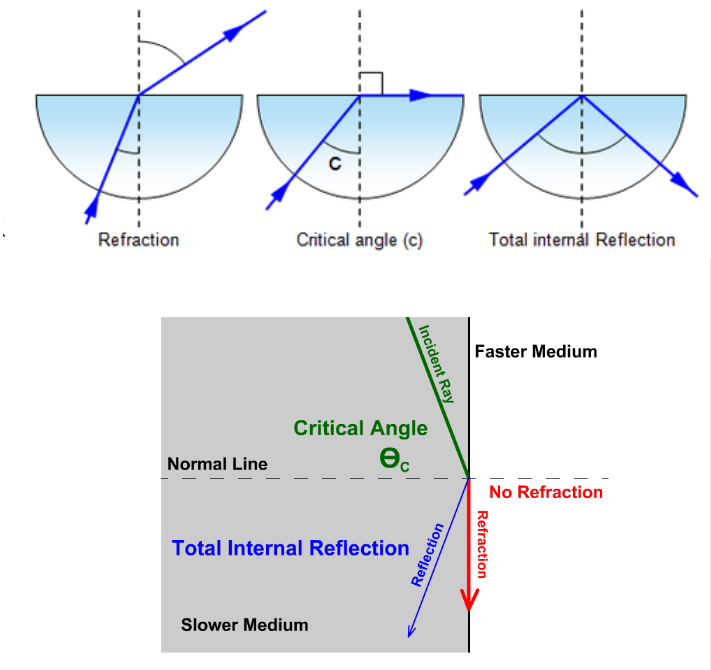
What’s the critical angle?
The angle of incidence at which light traveling in a medium with higher density (greater refraction index) cannot refract out into a less dense medium and is completely reflected back into the denser medium