Intro to American Government I - Chapter 3, 4, and 8
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The textbooks used are Governing Texas (7th Edition) and We The People (15th Edition). This goes over the Texas in the Federal System, Public Opinion and the Media, Federalism, Civil Liberties, and Political Participation and Voting chapters of those textbooks. Specific course is Intro to American Government I (POLS-2301)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
federalism
sharing of power between central and regional/state, while some have expressed/specific powers
solves problems in articles of confederation
sovereign
possessing supreme political authority within a geographic area
federal system
diverse backgrounds, own laws and policies, has competition
national → states and people of states
states → people of states
confederal system
loose union of sovereign nations with a weak federal government
states → federal and people of states
unitary system
dominated by central government, lower levels have little power and only implement central’s decisions
national → people
intergovernmental relations
federal, state, and local negotiate and compromise over policy and responsibility
policy varies due to ideological differences
national powers
expressed: 17 powers given in the constitution
implied: interpreted, not written
where are the expressed national powers in the constitution?
congress: article 1, section 8
president: article 2
where are the implied national powers in the constitution?
ending paragraph of article I, section 8
mcculloch vs maryland (1819)
congress has the power to charter a bank, helped create the necessary and proper/elastic clause
elastic/necessary and proper clause
central government gets unexpressed powers to do its job
interpreted from the ending paragraph of article I, section 8
supremacy clause
national government law > state and local government law
article VI
judicial review
power of the courts to review actions of the other branches to see if they’re constitutional or not
not in the constitution, happened thanks to marbury vs madison (1803)
state/reserved powers
powers of coercion/police power
10th amendment
powers of coercion/police power
power of the state government to regulate health, safety and morals
health and safety rules
regulate families
define property
develop and enforce criminal codes
concurrent powers
shared by federal and state
charter banks, licensing, taxing, policing, maintaining the courts, building roads, etc
full faith and credit clause
states must honor other state decisions as legal and valid, excluding strong public policy
article IV, section 1
loving v virginia: recognizing an interracial marriage in different states
obergefell v hodges: recognizing same-sex marriage in different states
public policy exception
full faith and credit clause doesn’t have to be obeyed when they violate strong public policy
privileges and immunity/comity clause
states cannot grant special privileges to their residents or discriminate against citizens of other states
fugitive return to og states
article IV, section 2
article I, section 10
compacts between states are legally binding ways to solve problems
local government in the constitution
aren’t outlined, left up to the states to establish
home rule
powers delegated by the state government for the local government to manage their own affairs
non interference
dual federalism took place from
1789-1937
dual federalism
2 layers of government, very distinct divide
federal: small, only for foreign affairs and assisting commerce via encouragement
state: day to day life, most power
economic regulations
property law
civil and criminal law

gibbons vs ogden (1824)
national commerce law trumps state commerce law
commerce clause
commerce clause
congress can regulate commerce between states, foreign nations, and native american tribes
article I, section 8
us v lopez
struck down gun-free school zones act as it was outside of the commerce clause
herbert hoover (1928)
the great depression of the 1930s
25% unemployment
state and local should handle it
FDR (1932)
new deal
expanded powers and made the federal government more active
used states to meet federal goals
expanded social programs, school lunches, and highways
NLRB vs jones and laughlin steel corp (1937)
dual federalism favored business post-civil war, but this brought about the end of it
expanded national government power over commerce
cooperative federalism took place from
1937-1960
cooperative federalism
more cooperation between federal and state, division between federal and state becomes less clear
caused by NLRB vs jones and laughlin steel corp (1937) ruling

grants-in-aid programs/what is a grant
money spent on federally predetermined purposes
matching grant
matches how much money is put in
state gives $, federal essentially pays it off, back to neutral
categorical grant
money spent on a specific purpose
90% federal, 10% state money
formula grant
federal formula is used to give money
project grant
state/local gov submit proposals and compete for funding
block grant
states have discretion in how to spend federal money
brought by new federalism
regulated federalism took place from
1960-1970s
regulated/coercive federalism and national standards
one size fits all states through grants and regulations
unfunded mandates
preemption

unfunded mandates
federal says states must do something but they do not give any funds, the states have to fund it themselves
no child left behind
technically an unfunded mandate, increased accountability and testing of students
preemption
national government can override state/local law in certain areas
fractious federalism has taken place since
2000
fractious federalism
partisan identity influences whether state officials cooperate with national policy
independent state grounds
states can expand rights beyond those provided by the us constitution
state’s rights
states distrust growing federal authority
big prior to the civil war
tarnished by racism
reason why the civil happened
southern manifesto against integration
nullification
10th amendment
nullification
states don’t carry out federal law
deferred action for parents of americans and lawful permanent resident (DAPA)
obama admin decision to help undocumented immigrants who have lived in the US since 2010 and have children that are either American citizens or lawful permanent residents avoid immediate removal
challenged
deferred action for childhood arrivals (DACA)
obama admin decision that undocumented immigrants brought to the US as children would not be deported
challenged
individual mandate
requirement of the affordable care act/obamacare that health insurance be purchased
challenged
new federalism took place from
1970s-now
new federalism
returning state power due to lack of coordination
reagan + nixon used block grants for this
can be used to cut overall spending
revenue sharing
devolution
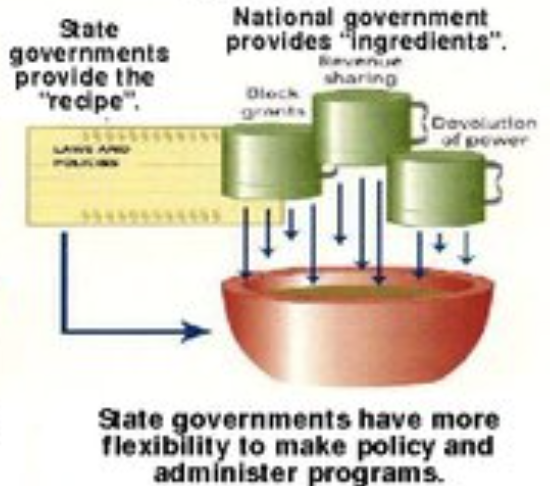
revenue sharing
1 unit of government yields a % of tax revenue to another unit of government with no strings attached
devolution
policy responsibility shifts down from federal to state or local
1970s
flexible
can help with policy diffusion
policy diffusion
policy decisions in a political jurisdiction are influenced by choices made in another
federalism in the modern day
still a struggle between federal and state
currently prioritizes innovation and diffusion
unfunded mandates are still an issue
many policies are still an issue
welfare reform
immigration
marijauna
abortion
preemption
redistributive programs
transfers income through taxing and spending
helped people in poverty
civil rights
government responsibility to protect citizens, prevents discrimination
civil liberties
protection of citizens’ personal freedoms from government power/interference
bill of rights
limits national government
habeas corpus
judge must review one’s cause for detention/imprisonment to see if it is legal
(no imprisonment without cause)
article I, section 9
only suspended during rebellion or invasion
bill of rights
ratified in 1791, pushed by the antifederalists
first 10 amendments
citizens have additional civil liberties not in the document
selective incorporation
process by which different parts of the bill of rights were incorporated into the 14th amendment, protecting citizens from the state as well, not just the national government
only 3rd and 7th aren’t officially incorporated
1st amendment
freedoms of RAPPS
religion
establishment clause
free exercise clause
assembly (1939)
press (1931)
petition
speech (1925)
establishment clause
wall of separation between church and state
lemon v kurtzman (lemon test)
it must have a secular purpose, doesn’t advance or inhibit religion, and doesn’t entangle the government with religion
kennedy v bremerton (2022): changed this, free exercise > establishment usually
lemon v kurtzman (lemon test)
government action towards religion is fine as long as it is secular and doesn’t promote/inhibit religion
free exercise clause
right to practice or not practice any religion
freedom of the press
can’t prevent publishing/do prior restraint
can be compelled to reveal sources
can be sued for libel/slander
prior restraint
government blocks the publication of material that it thinks is libel or harmful
mostly forbidden
near vs minnesota
libel
written statement made in disregard of the truth that is damaging to a victim
slander
spoken statement made in disregard of the truth that is damaging to a victim
freedom of speech
absolute: political speech, truth, symbolic, political ads
conditional: hate speech (usually fine though), student speech, commercial speech, libel, slander, obscenity, speech plus (action), fighting words
student speech: tinker v des moines, morse v frederick, it really depends on how much it disrupts learning or causes harm
private regulation makes this also a little unclear
clear and present danger test
speech can be limited if it causes an immediate and clear and present danger
fighting words
speech that incites damaging conduct
conditionally protected
speech plus
speech accompanied by conduct like sit-ins, picketing, demonstrations
conditional, depends on state and local restrictions and interpretations of public order
2nd amendment
you have 2 arms
right to bear arms to establish a militia
district of columbia v heller: dc law that banned handguns was overturned
mcdonald v chicago: chicago ordinance to own a gun in city limits was overturned
new york state rifle and pistol association inc v bruen: public carry is a right
us v rahini: some people can be barred from having guns
3rd amendment
3 is company
no quartering of soldiers during peacetime
due process
procedural civil liberties, rights of the accused
4, 5, 6, 7, 8
4th amendment
what are you looking 4
your rights before and during arrest
warrants are needed, no unreasonable searches or seizures
exclusionary rule
exclusionary rule
evidence obtained illegally is inadmissible in court
us v grubbs: fine if its anticipatory warrants
us v jones: gps attached to vehicle is bad
maryland v king: dna testing of arrestees is fine
riley v california: no taking a cellphone to look through it
whren v us: minor traffic stops for vehicle searches are fine
5th amendment
your rights to a fair trial
right to a grand jury
no double jeopardy
no self incrimination
due process rights
property rights
takings clause
grand jury
jury determines on whether sufficient evidence is there to justify a trial
double jeopardy
a person cannot be tried twice for the same crime
miranda rule
miranda v arizona
prior to police interrogation of rights to remain silent and have legal counsel
very loosened now
takings clause
can’t take public property without just compensation
eminent domain
eminent domain
government can take private property for public use
6th amendment
your rights during a criminal trial
speedy trial
jury trial
right to an attorney
7th amendment
your rights during a civil trial
trial by jury in civil cases
8th amendment
your rights after trial
NO
excessive bail or fines
supported by timbs v indiana
cruel or unusual punishment
controversy over jones v mississippi letting juvenile offenders get life in prison
death penalty controversy
death penalty
due process must be followed, state decides methods
not very often
very controversial
9th amendment
people still have more!
people have rights that aren’t in the Constitution
unenumerated rights
rights that aren’t in the constitution
right to privacy
interpreted from the 1st, 4th and 9th amendments
right to be left alone from griswold v connecticut
controversies
birth control: yes
abortion: states now decide
roe v wade: yes
dobbs v jackson: no
homosexuality: yes
obergefell v hodges
right to die: depends
10th amendment
some of the more is at the state level
powers not delegated to the federal government go to the states or people
states’ rights, reserved powers
public opinon
attitudes citizens have about public policies, politicians, political institutions, and events
political socialization
the process by which individuals acquire political information and develop their political
family
school
religion
socioeconomic group
events
the media
elected officials
political efficacy
belief that you can make a difference in politics
political ideologies
frameworks/belief systems that frame how people think about the world and politics
informational shortcuts/heuristics
people using informational cues from family, friends, or political leaders about politics
scientific polling
practice of securing a representative sample in a poll that accurately represents and predicts public opinion and election outcomes