3.3.5 Communication of design ideas - AQA GCSE DT
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Designing and making principles textbook: Section 6 designing principles, chapter 45 - 2D and 3D drawing techniques, modelling, recording, scale and dimensions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
annotated drawing
a drawing (using any technique) labelled with details and explanations
freehand sketching
drawing without guides and equipment to quickly note initial ideas
systems diagrams
show different stages eg. input, process and output
schematic diagram
represent systems eg. circuit diagrams, flats
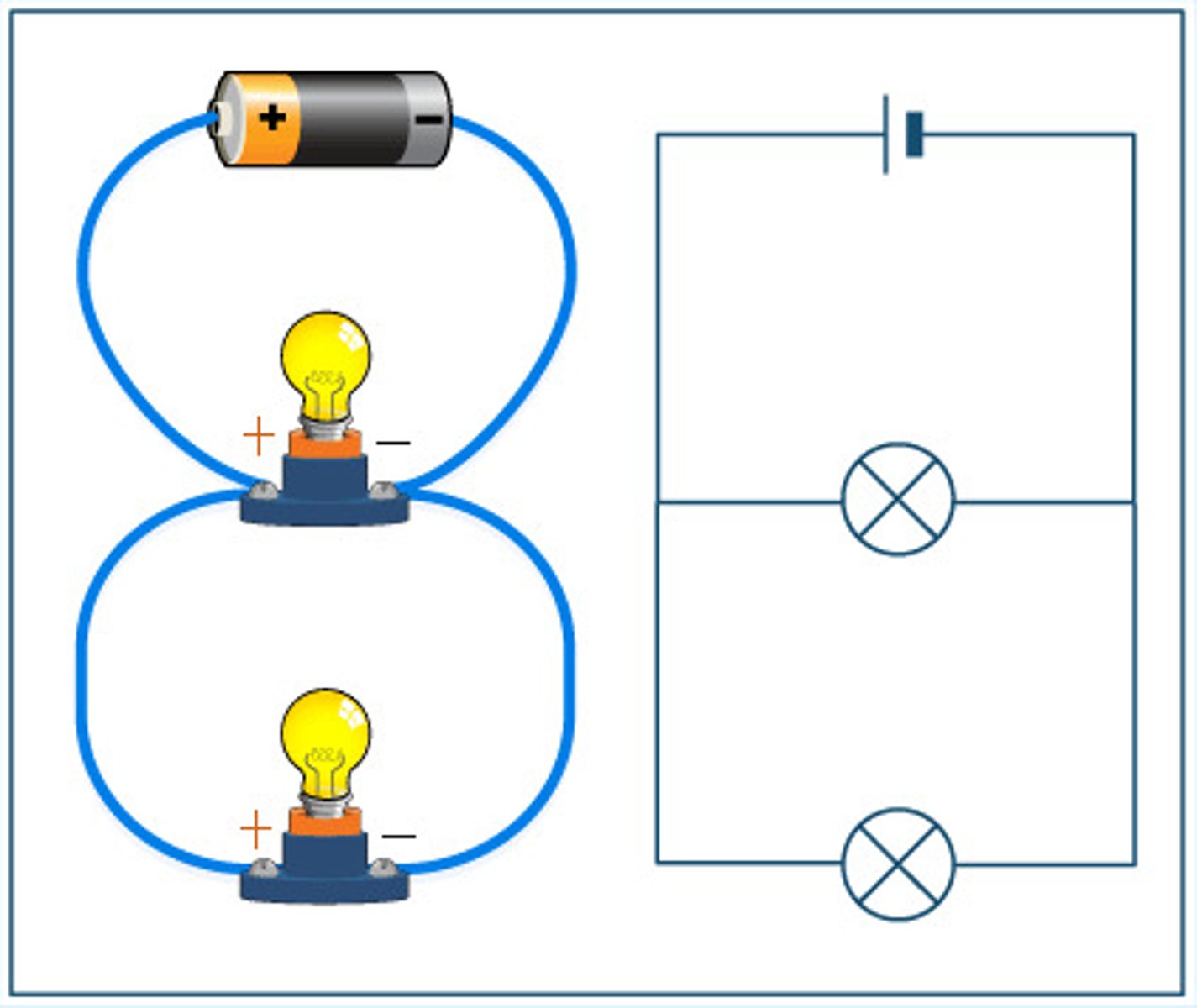
flat
technical schemtic diagram of clothing without a body
digital, symmetrical, and with accurate proportions
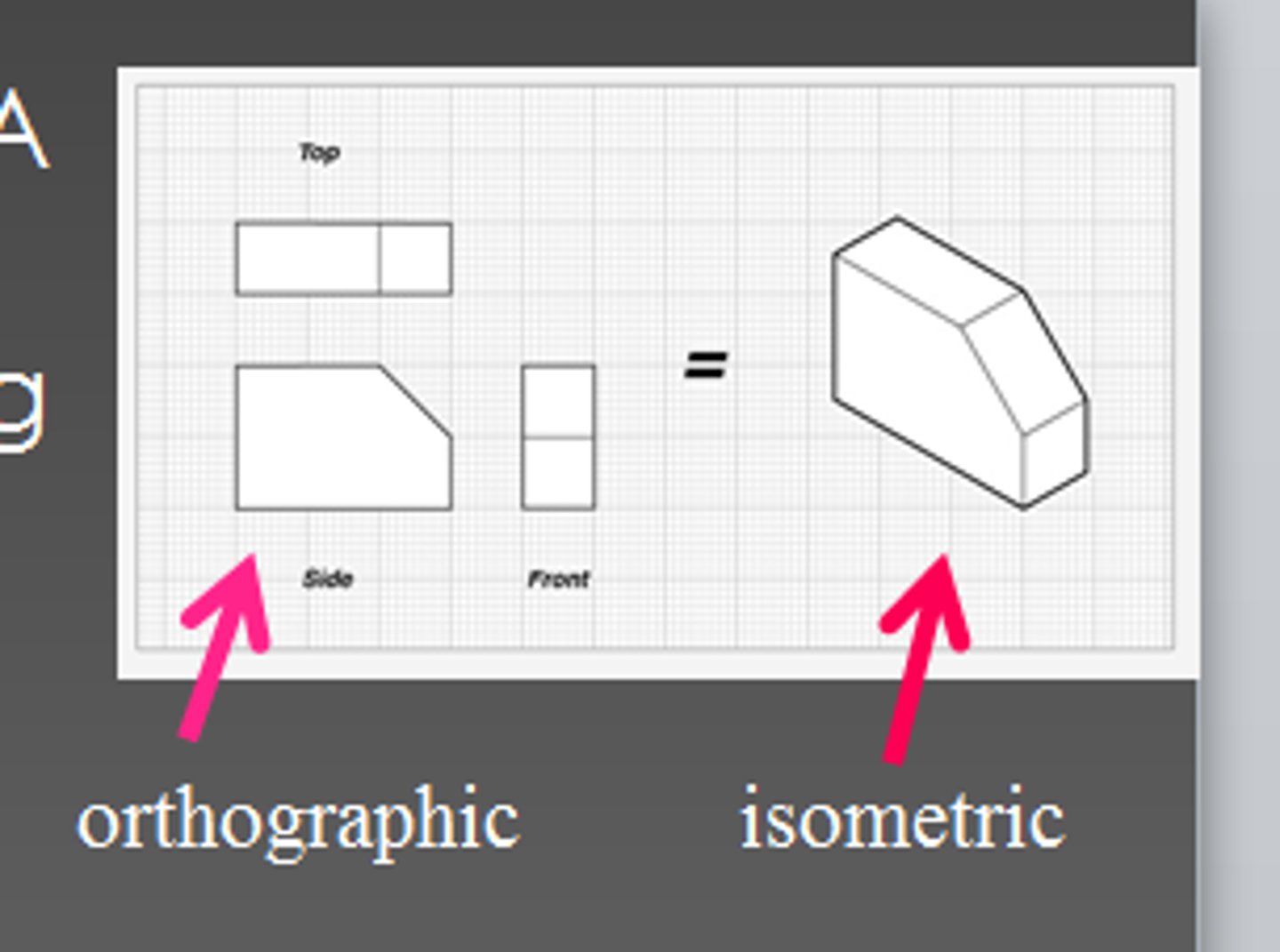
working drawings (3rd angle orthographic projection)
shows object in 2D plan (top), front and side views accurately and to scale
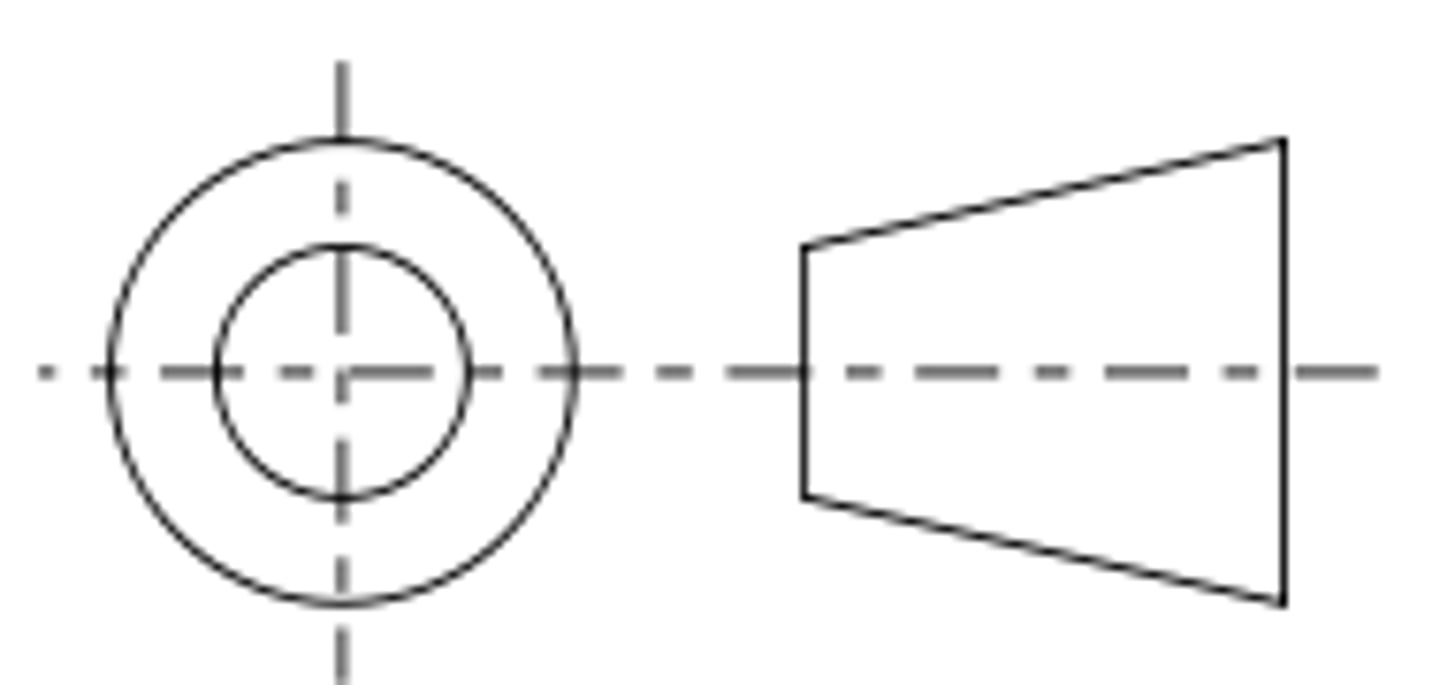
uses a symbol to indicate its a 3rd angle orthographic projection
3rd angle orthographic symbol
scale
drawn length : actual length as a ratio
dimensions
show the real measurements of an object in mm
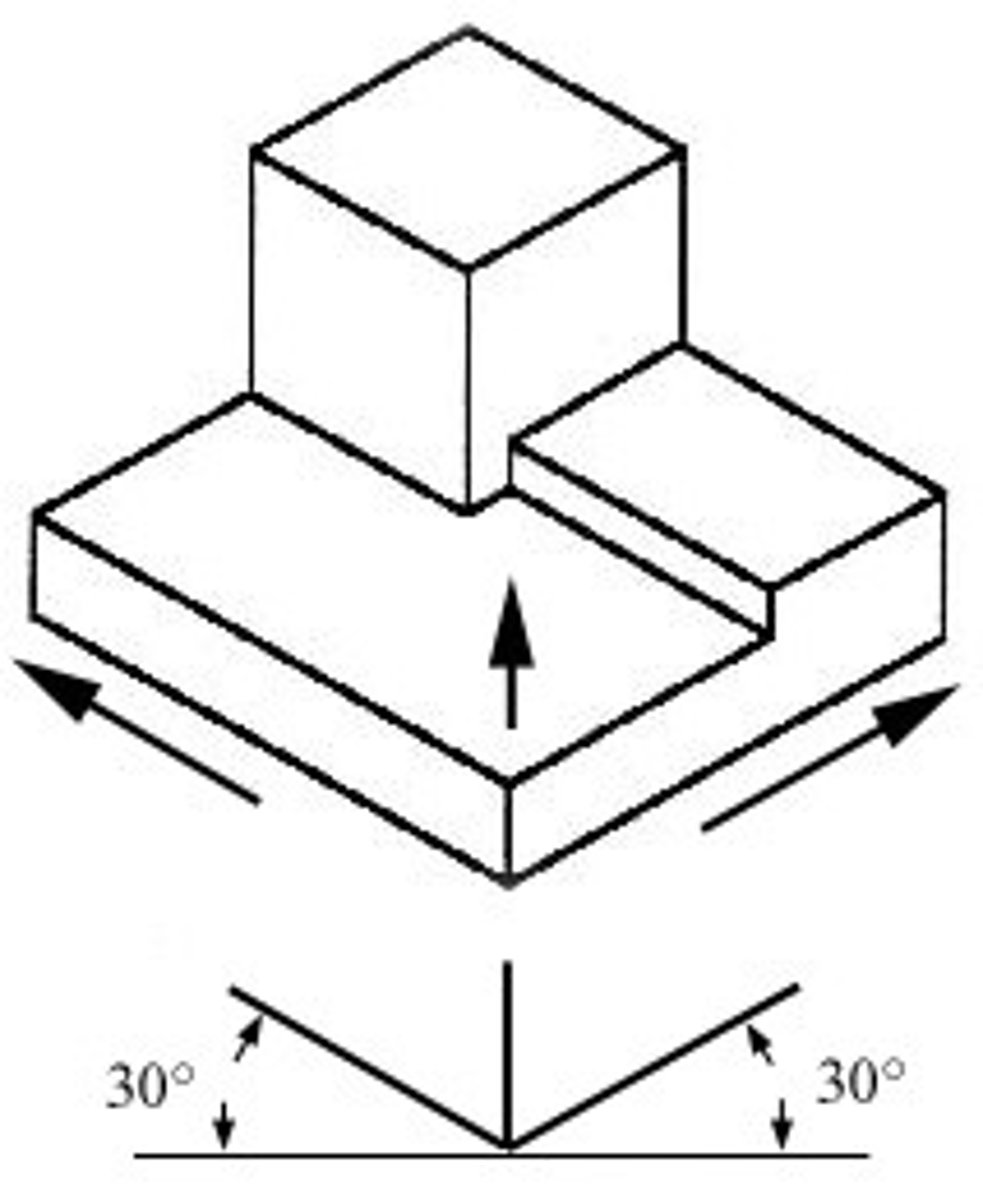
isometric projection
3D drawing with horizontal lines at 30 degrees, doesn't distort view
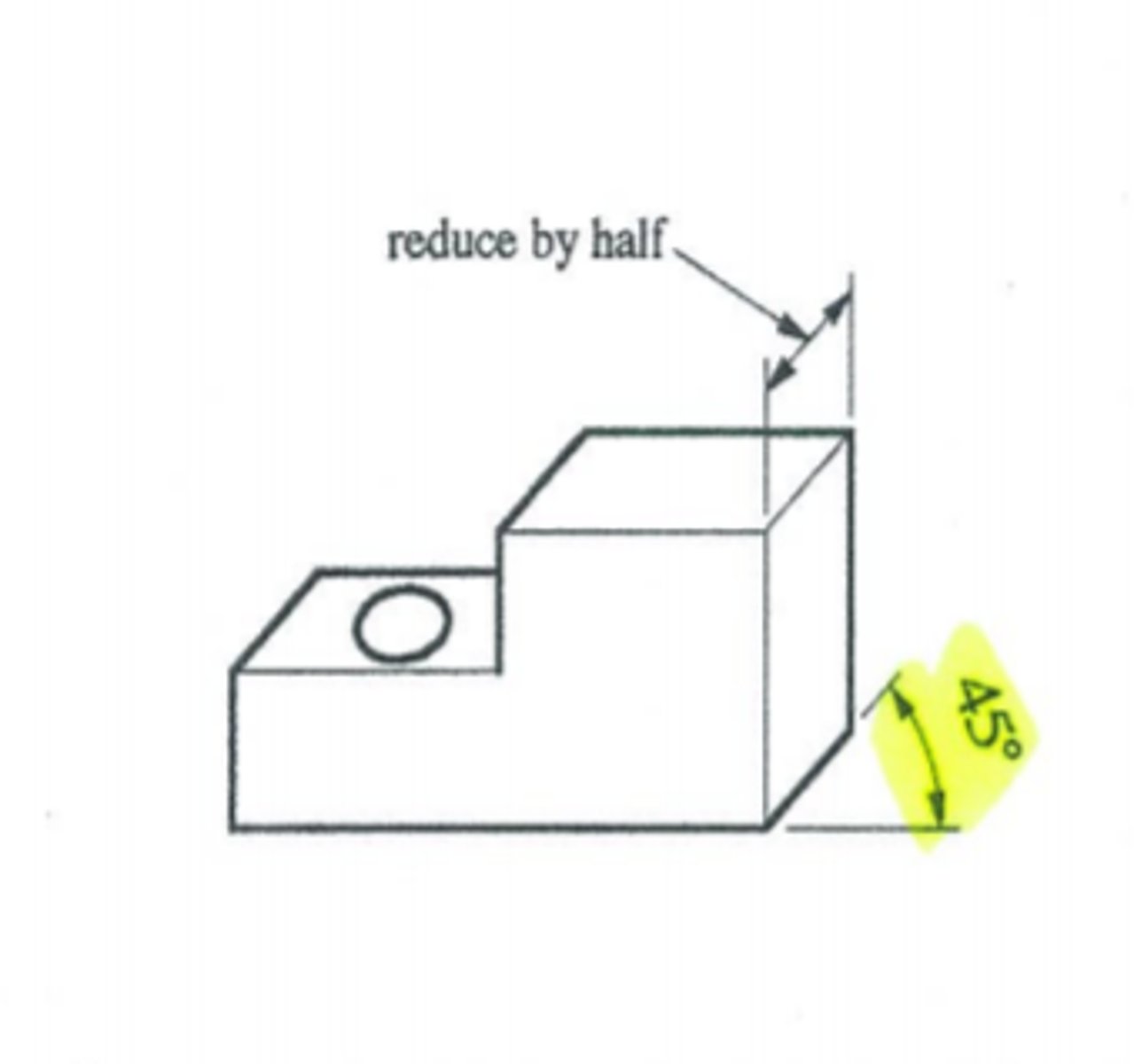
oblique projection
3D drawing using 45 degree angles to show front, distorts view
1 point perspective
1 vanishing point for front view, distorts view
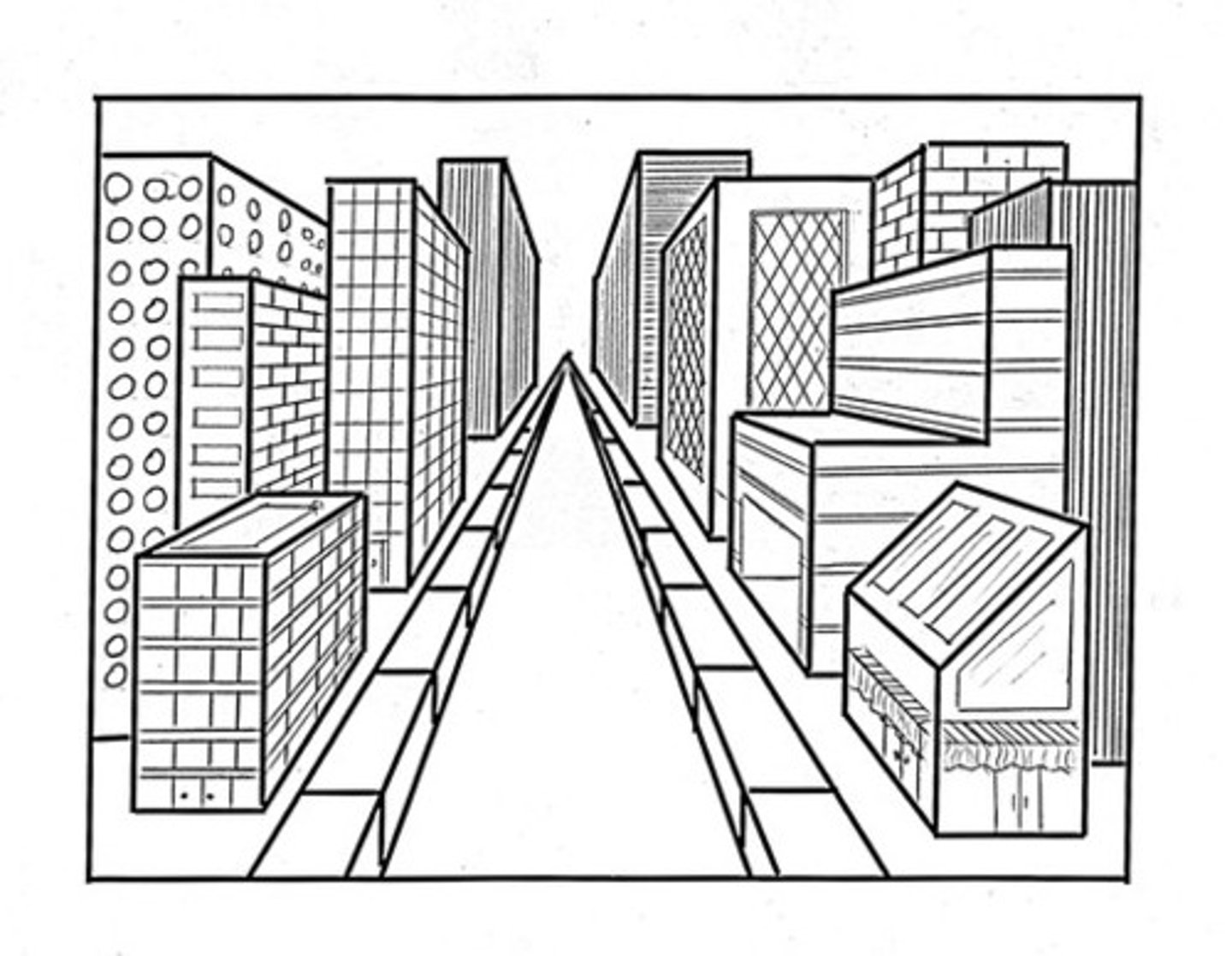
2 point perspective
2 vanishing points to show 2 sides, distorts view
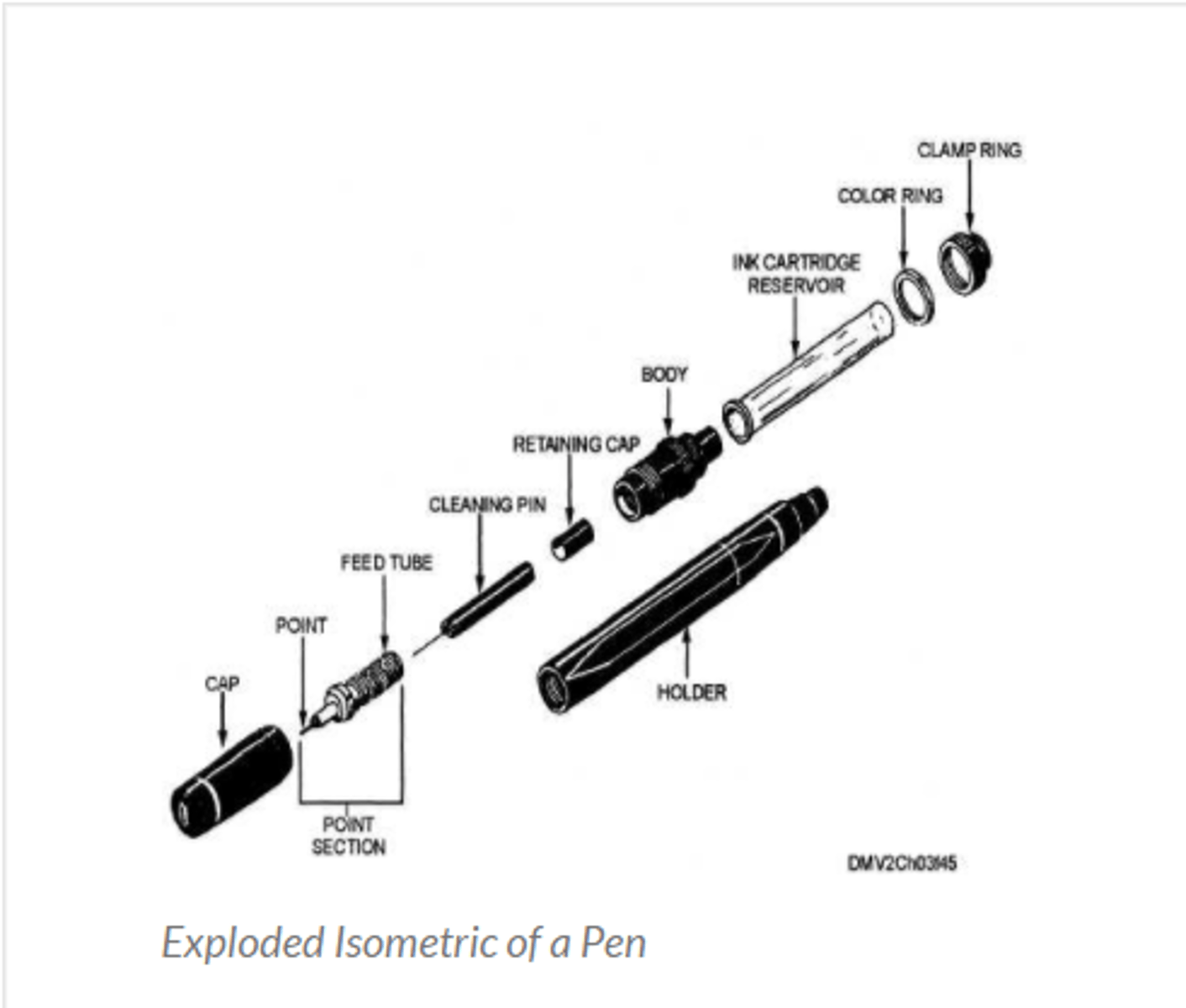
exploded drawing
shows how components fit together using alignment and lines, used for construction and assembly
mathematical modelling
using simulations and visual depictions to present mathematical info
modelling
used to see product in 3D using physical materials or digital CAD/CAM software
CAD modelling
computer aided design, used for precise, digital and technical drawings in 2D or 3D
audio and visual recording
used to record how a product works, testing, interviews etc. for reference