Nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Nasal cartilage
major alar cartilage
nasal septal cartilage
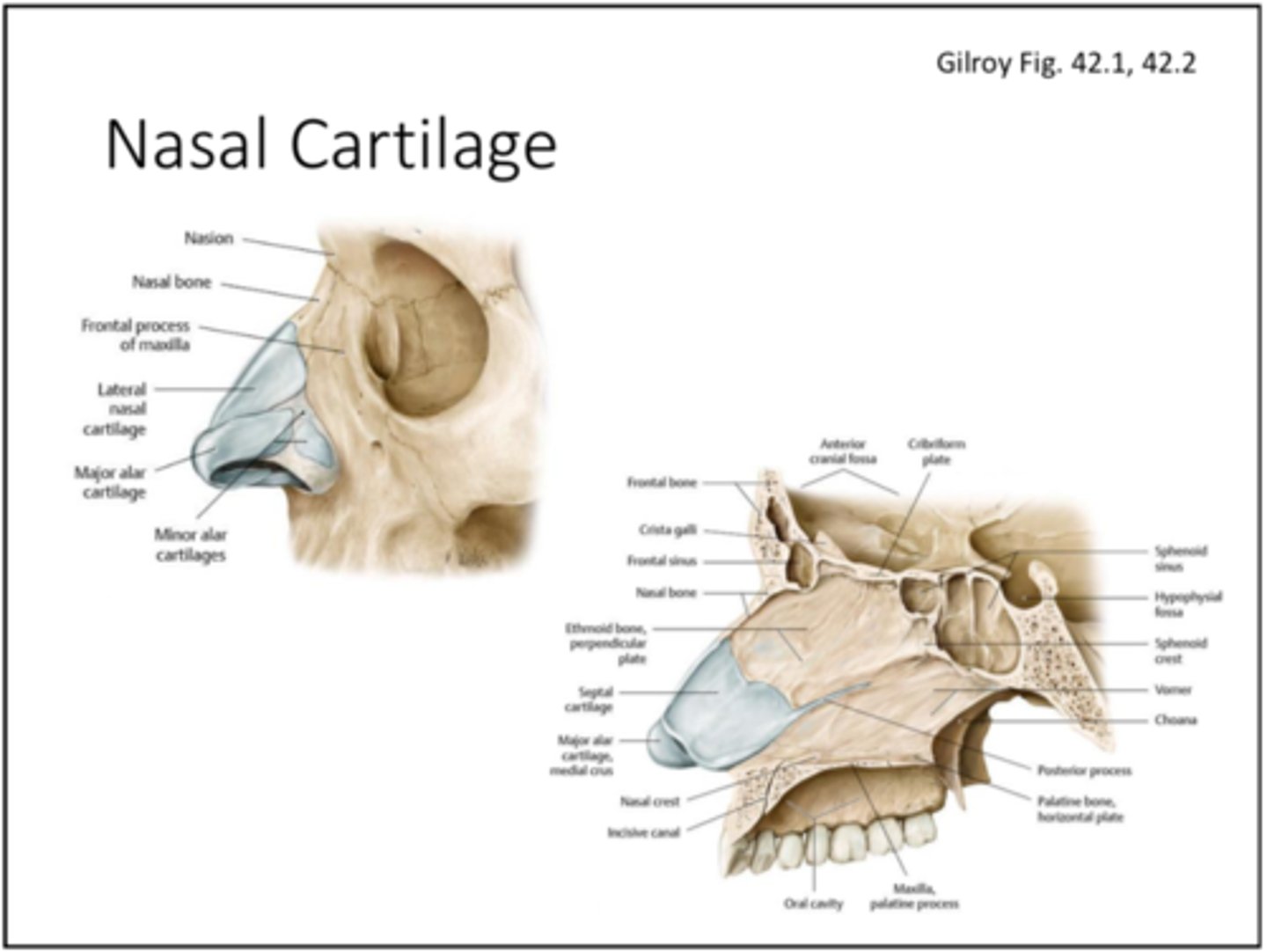
Nasal bones
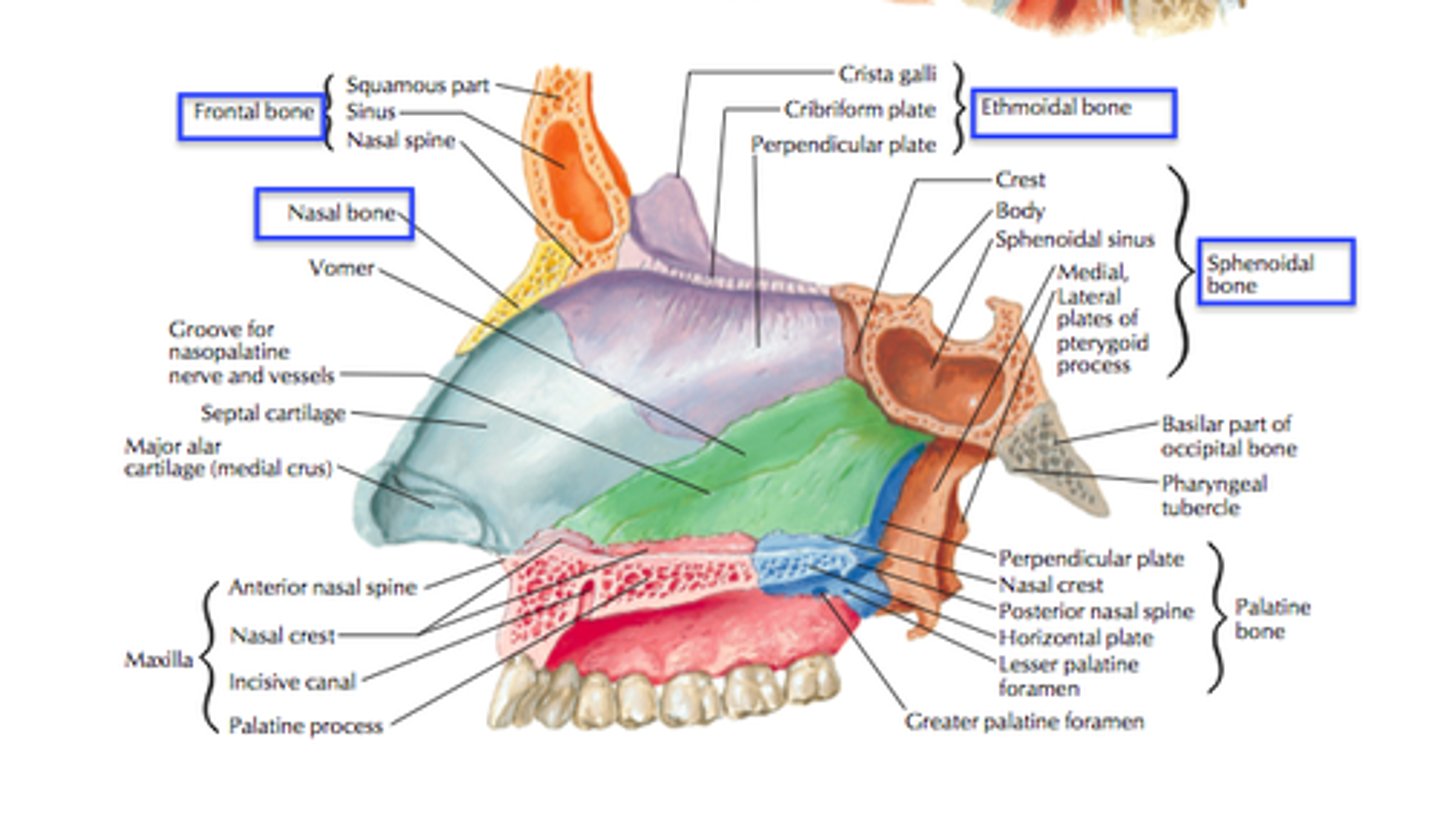
ethmoid
vomer
maxilla
palatine
sphenoid
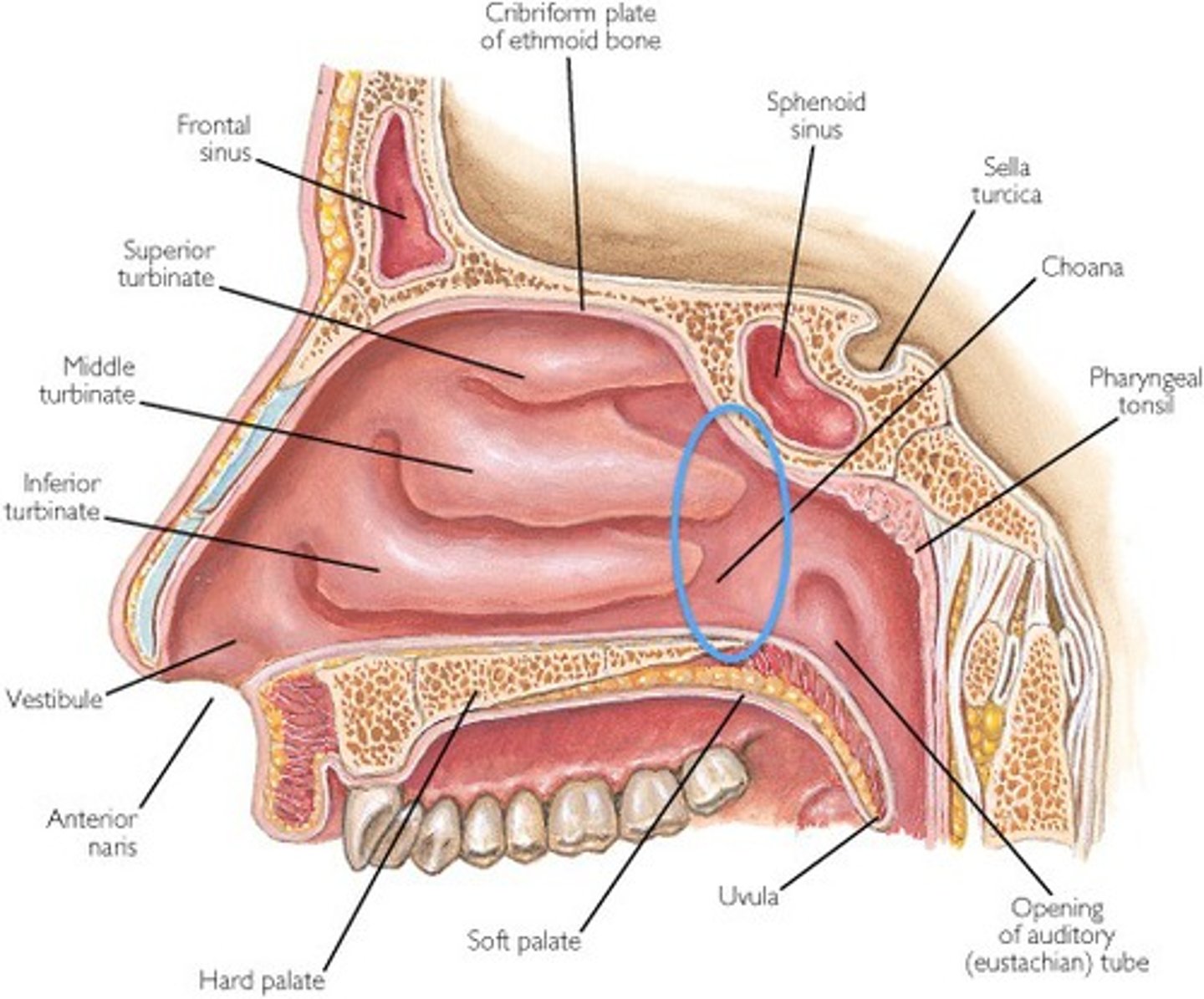
Nasal Cavity
Superior 1/3 is the olfactory area
inferior 2/3 is the respiratory area
Nasal concha
aka turbinates; create turbulent airflow during inspiration
1. modifies air: warms, humidifies and filters particles
2. senses smell: olfactory area, organ of smell; sniffing draws air to the area
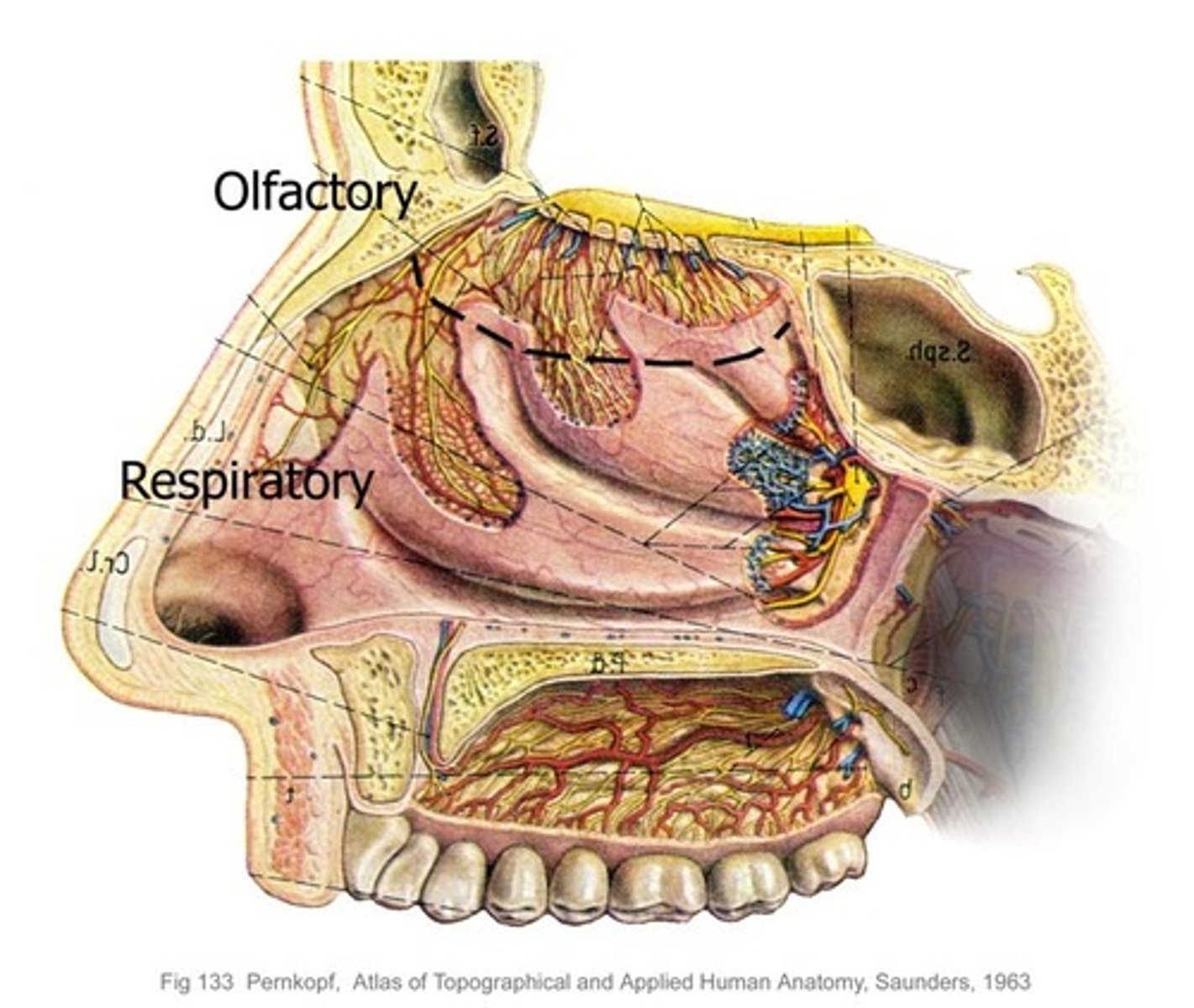
Conchae fill majority of nasal cavity
foreign objects or inflammation of mucosa can inhibit airflow
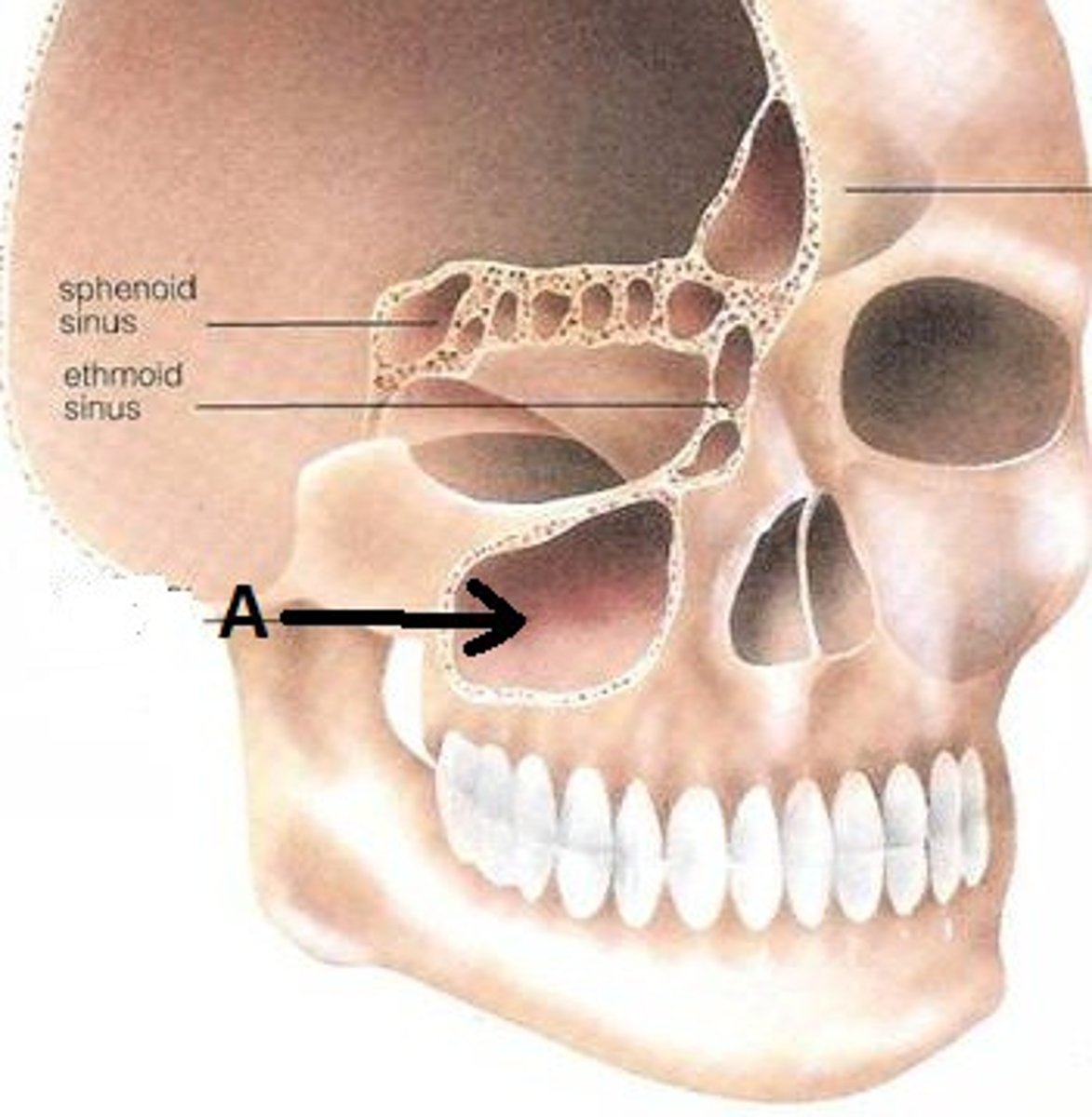
paranasal sinuses
sir filled, lined by resp epithelium. FXNs: warm and humidify air, reduce weight of the skull, contributing to voice resonance
Maxillary sinus must
drain against gravity
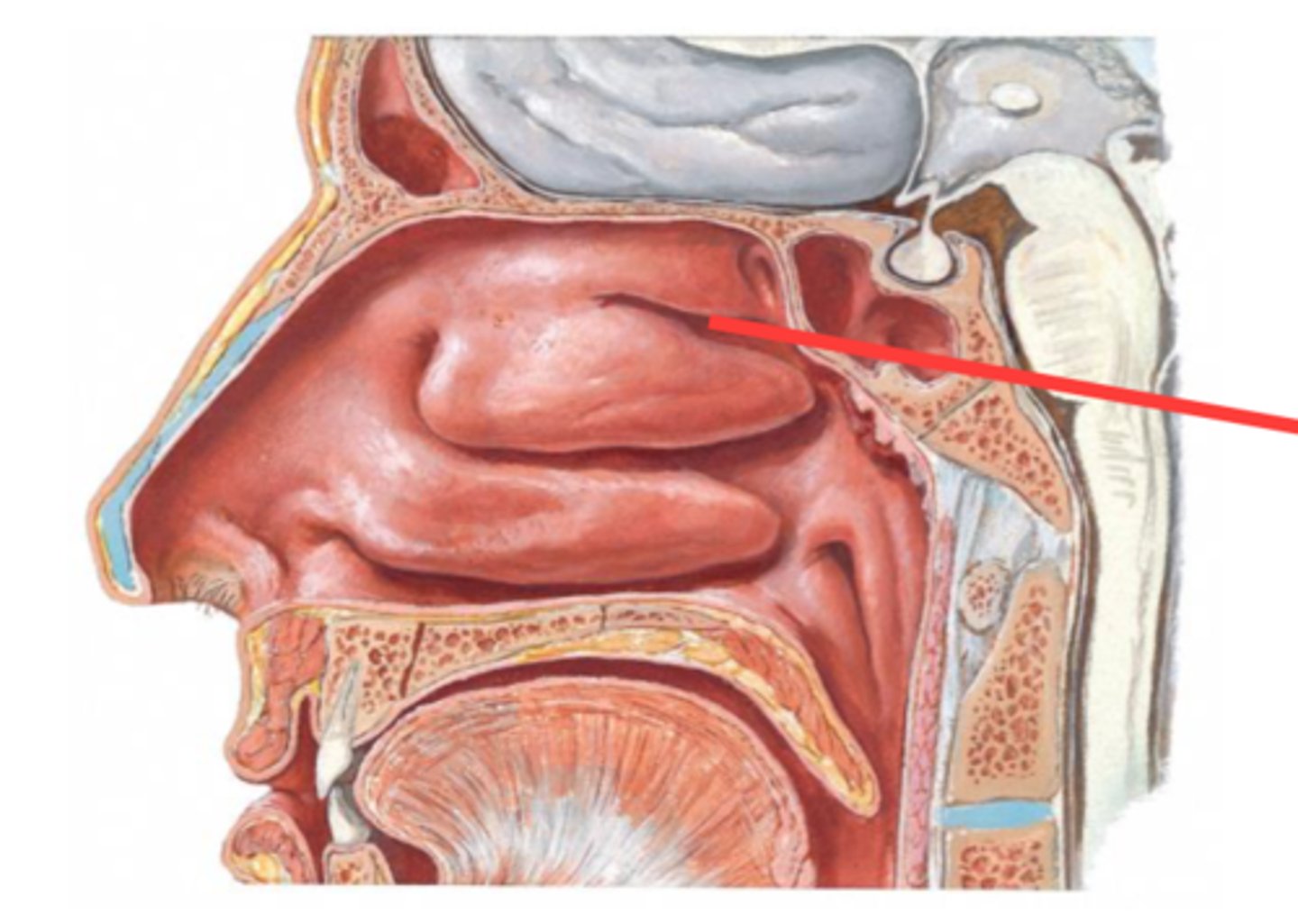
Superior meatus
openings of posterior ethmoidal air cells
Middle meatus
ethmoidal bulla
Semilunar hiatus: frontonasal duct, openings of anterior ethmoidal air cells, opening of maxillary sinus, openings of middle ethmoidal air cells
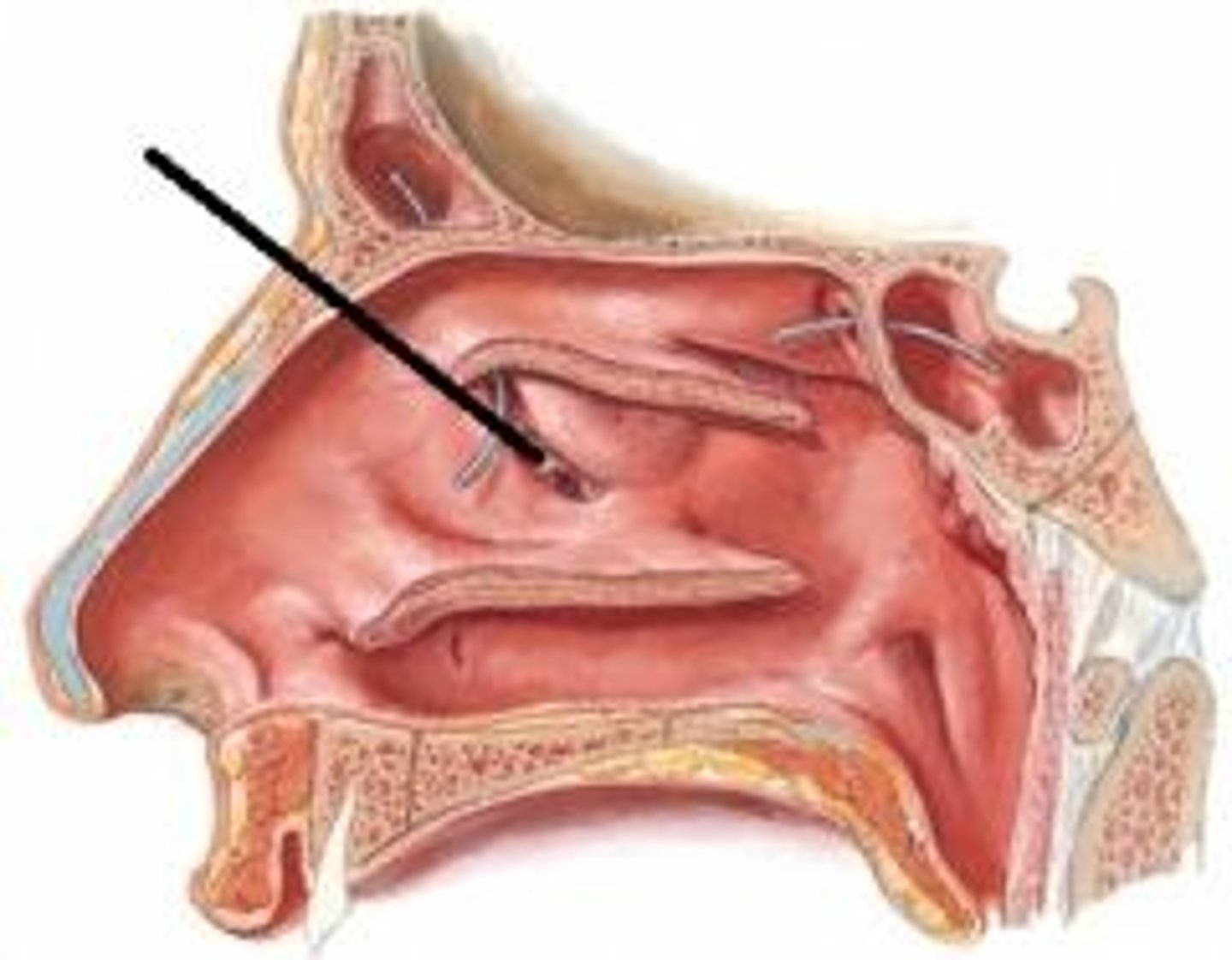
Inferior meatus
opening of nasolacrimal duct
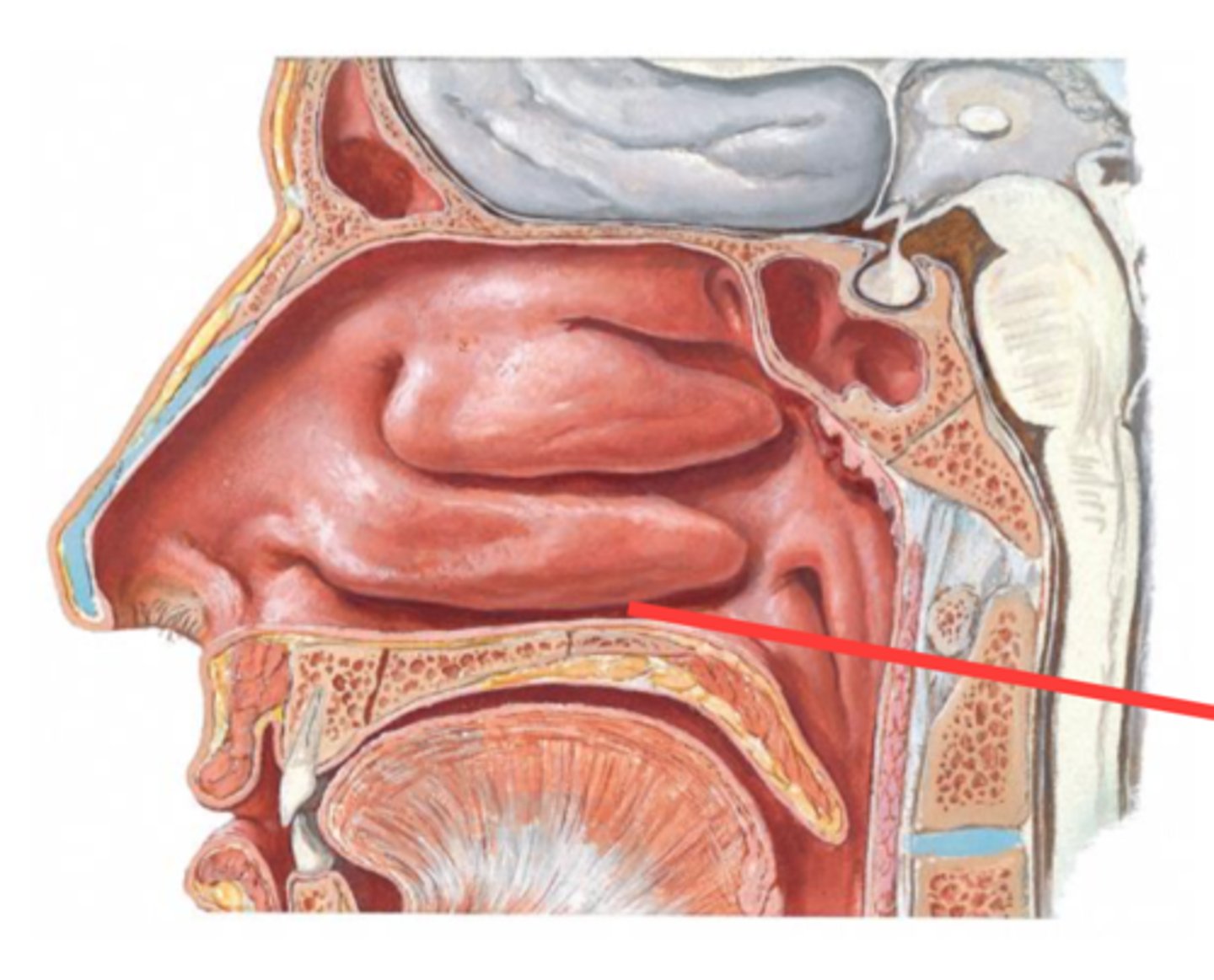
sphenoethmoidal recess
opening of sphenoid sinus
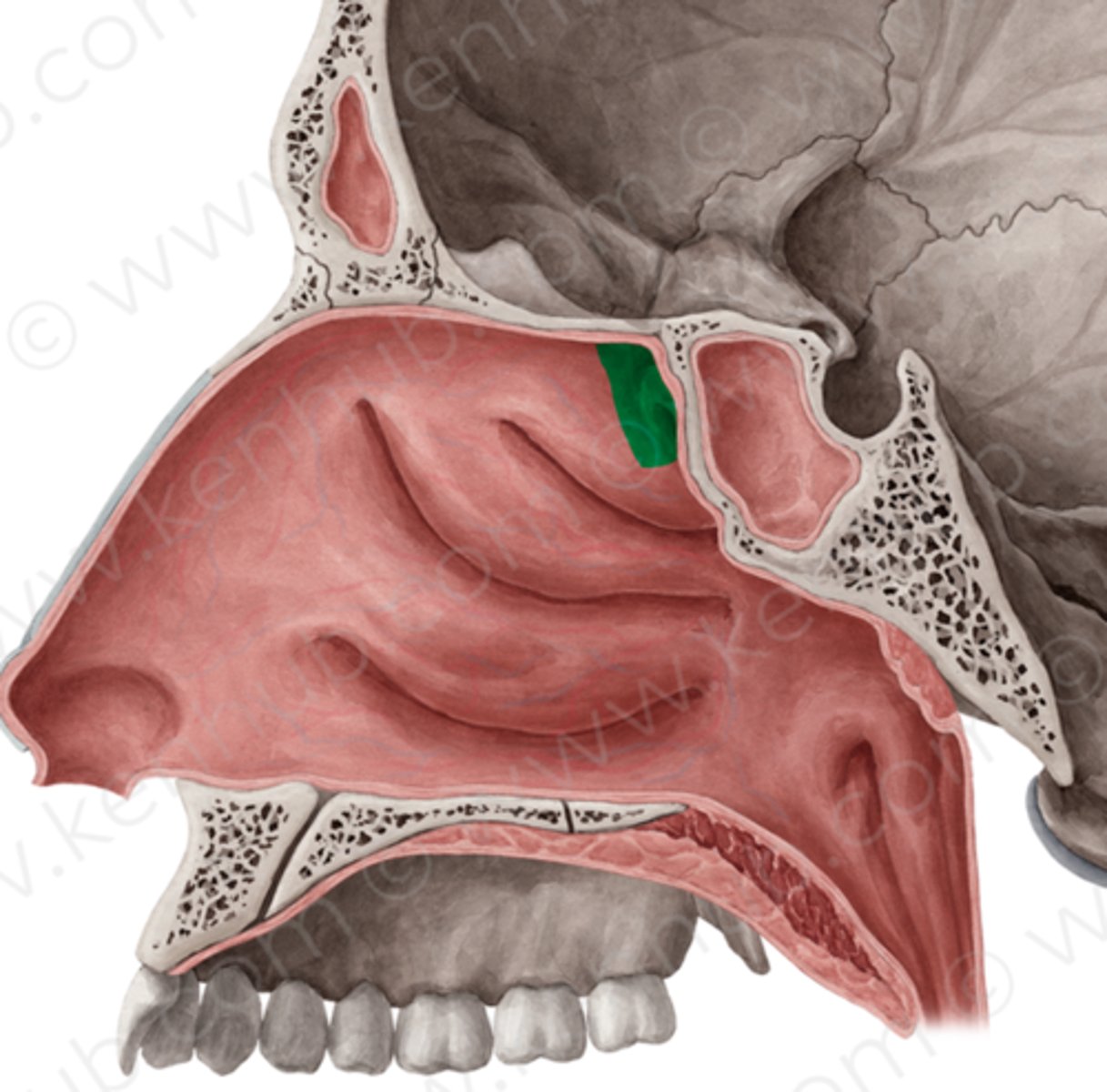
Sphenoid sinus drains into
sphenoethmoidal recess
posterior air cells
drains into the superior meatus
nasolacrimal duct drains
into the inferior meatus
Frontal, middle ethmoidal air cells, anterior ethmoidal air cells, and maxillary sinus
drains into the middle meatus
Nasolacrimal apparatus
tears produced in lacrimal gland--through punctum into lacrimal canaliculi--collect in lacrimal sac--travel down nasolacrimal duct to inferior nasal meatus
lacrimal fluid stimulation
via CN VII
Arteries of the nasal cavity
ophthalmic artery, maxillary artery, facial artery
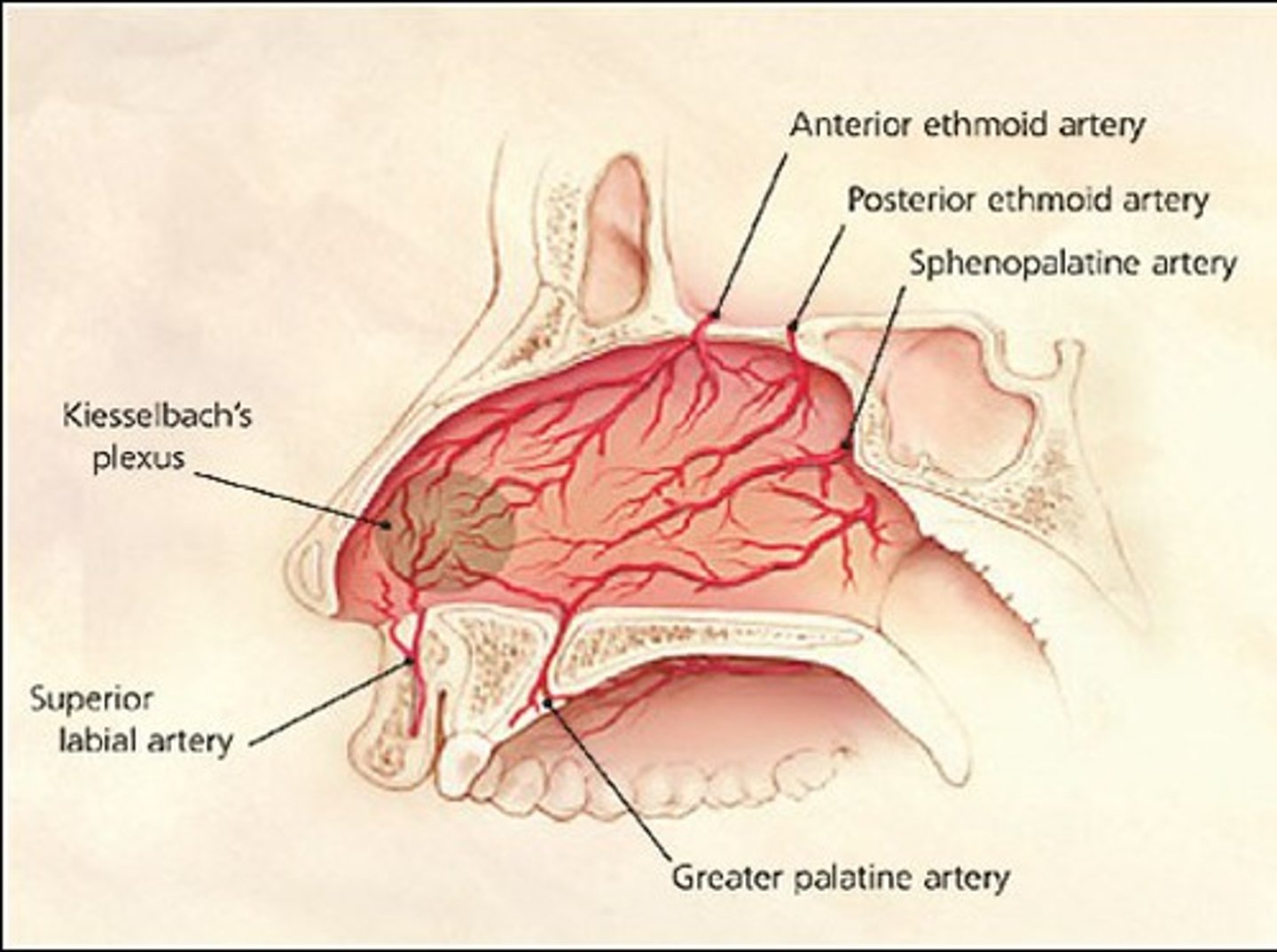
Nasal cavity has rich blood supply
anastomosing arteries meet at kiesselbach's plexus
epistaxis (nose bleeds)
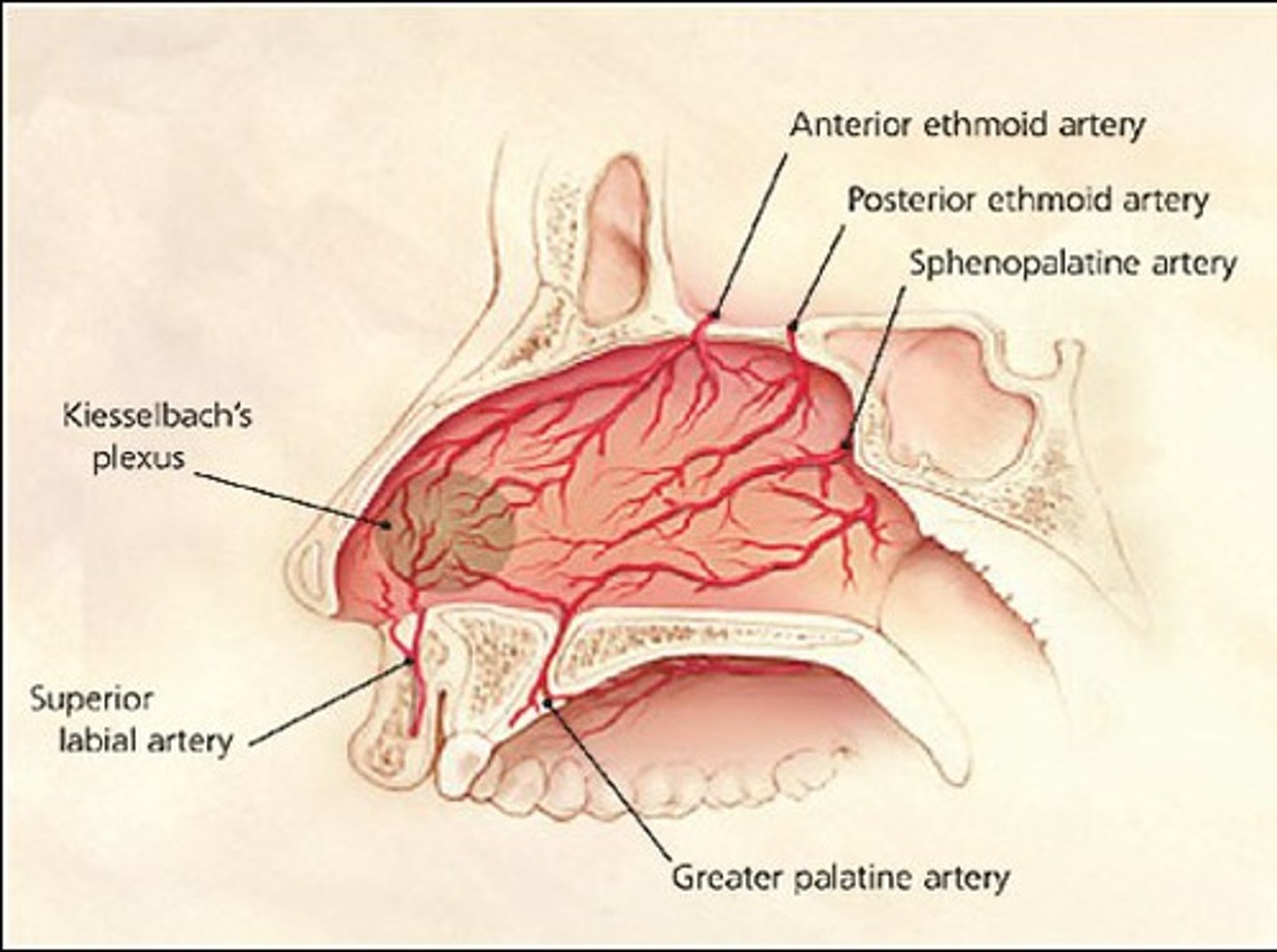
From Ophthalmic a
anterior and posterior ethmoidal a
supply the superior nasal cavity
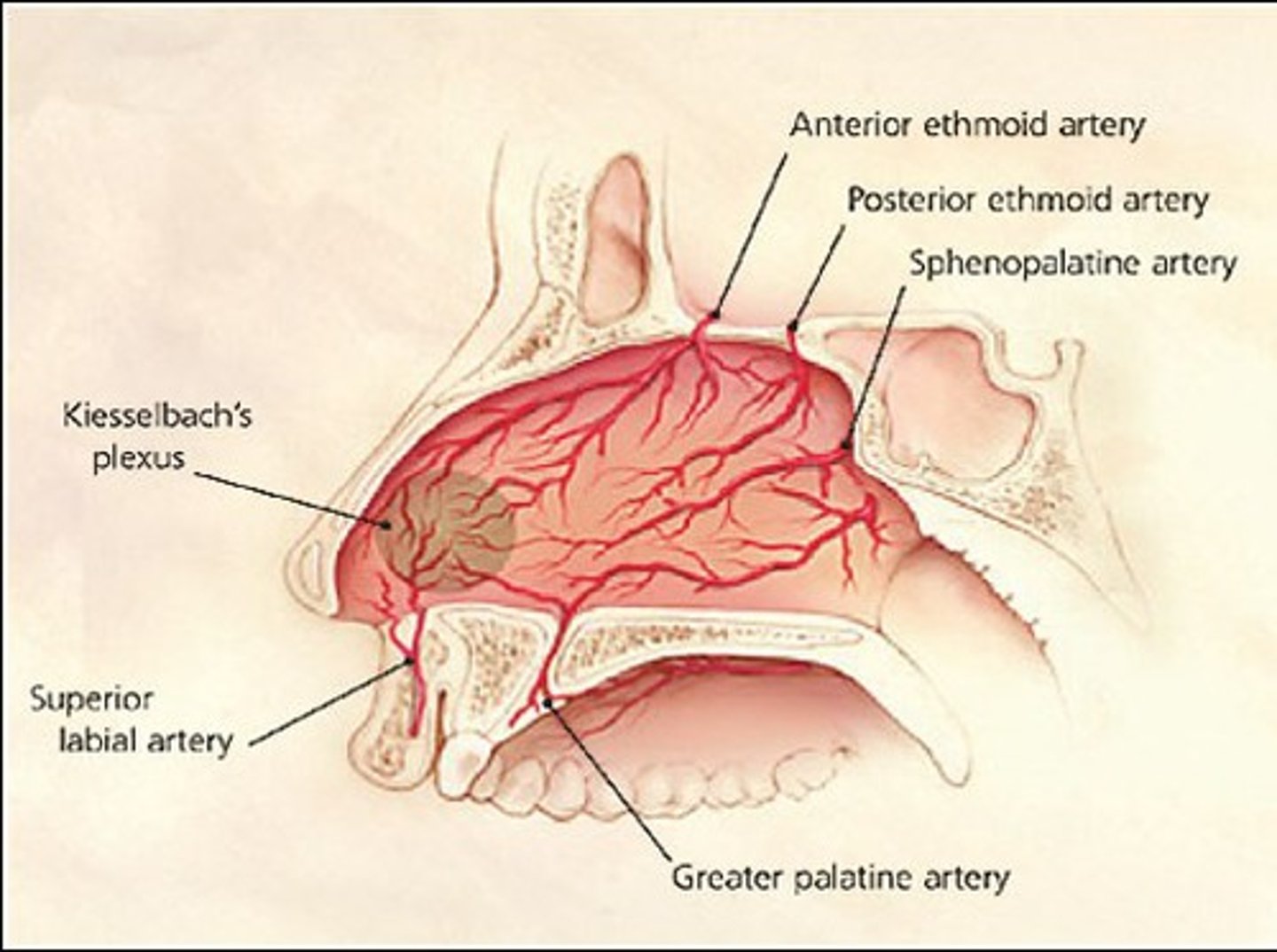
From maxillary a
sphenopalatine and greater palatine a
perfuses majority of nasal cavity, perfuses floor and septum
sphenopalatine enters through sphenopalatine foramen
Descending palatine a enters
oral cavity via the greater palatine foramen as the greater palatine a. Then enters nasal cavity via incisive foramen
From facial a
superior labial a which supplies the inferior nasal cavity
Venous drainage of the nasal cavity
pterygoid venous plexus--facial vein--ophthalmic veins to the cavernous sinus--nasal emissary v to superior sagittal sinus
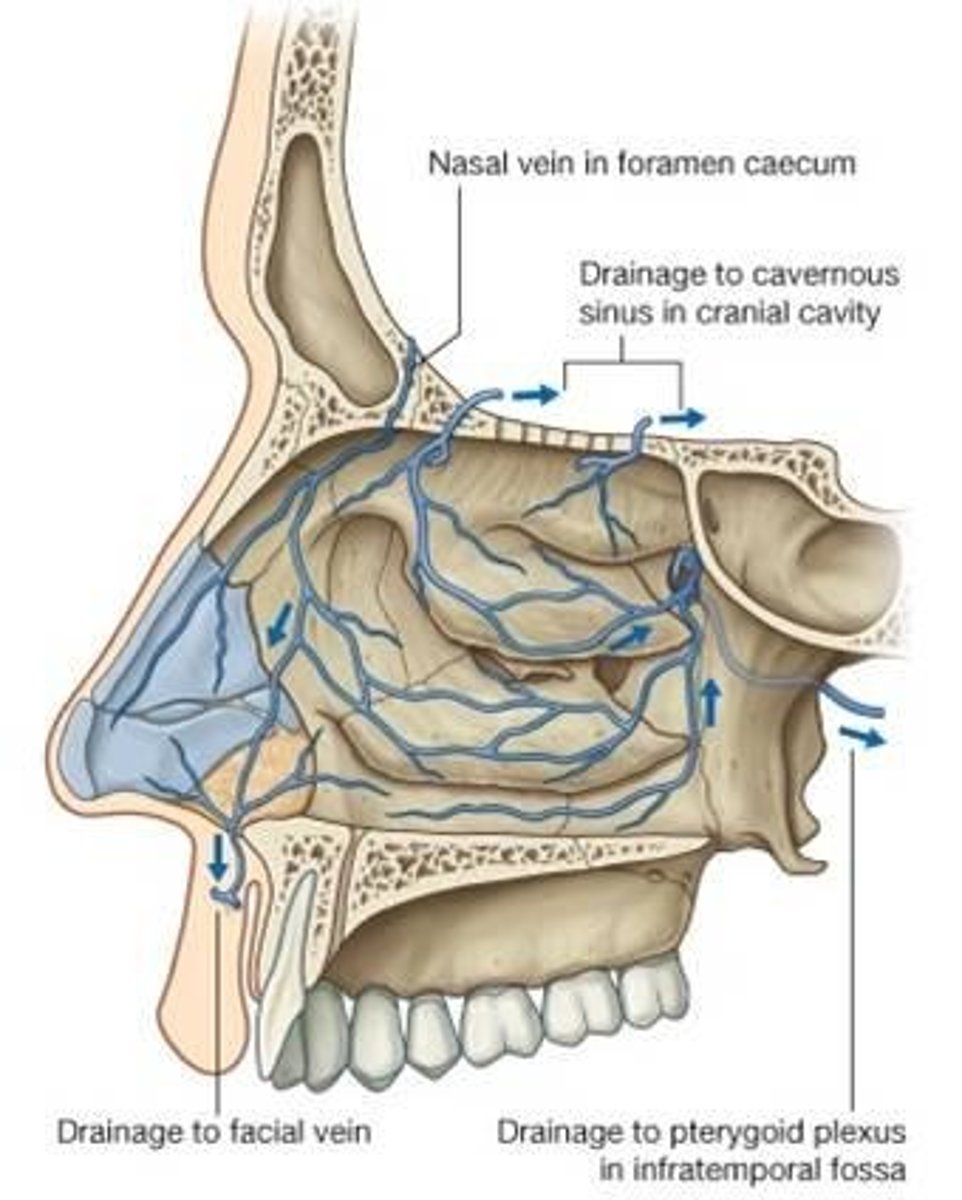
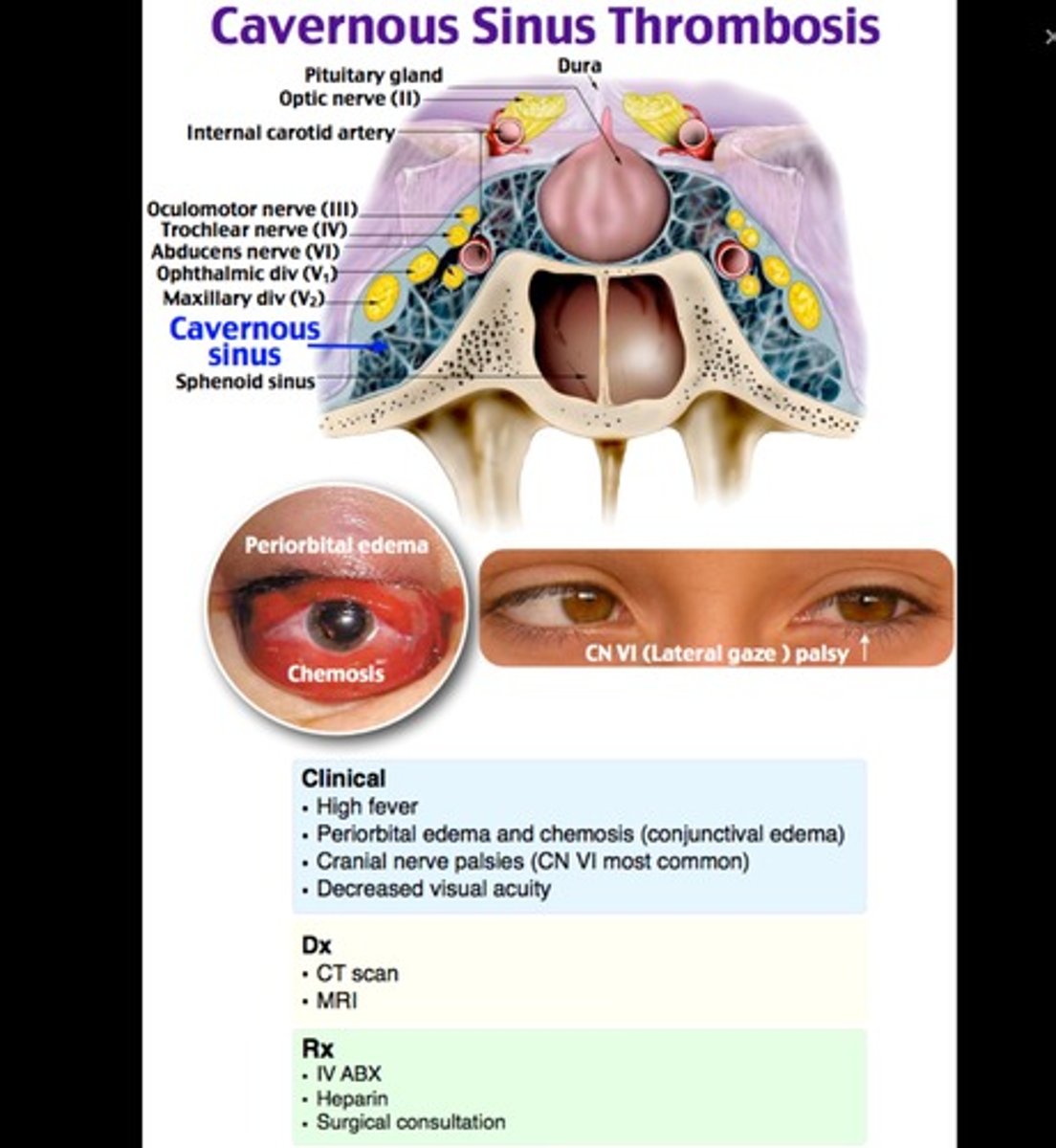
Sinus infection leads
to cavernous sinus thrombosis
Lymphatic drainage of nasal cavity
anterior regions drains into submandibular nodes--deep cervical nodes (palpable)
posterior regions drain into the deep cervical nodes or via the retropharyngeal nodes (not palpable)
SVA of nasal cavity
Olfactory n CN I
GSA of nasal cavity
Branches of trigeminal n: ophthalmic (v1) and maxillary (v2)
anterior ethmoidal innervates nasal cavity
posterior ethmoidal innervates air cells and sphenoid sinus.
GVE-P CN VII of nasal cavity; stimulate mucosal glands
1. superior salivatory nucleus in brainstem
2. Preganglionic fibers: greater petrosal nerve
3. joins with postganglionic neurons towards the pterygoid canal
4. postganglionic cell bodies in pterygopalatine ganglion
5. distribute w/ V2 branches throughout the nasal cavity
GVE (sympathetics) regulate blood flow to venous plexus
1. Pre starts at T1-T3 and synapse at postgang in superior cervical ganglion
2. postgang fibers distribute via a plexus around the internal carotid and becomes deep petrosal n
3. joins greater petrosal n to become nerve of the pterygoid canal
4. post gang fibers pass thru pterygopalatine ganglion to distribute w/ V2 thruout nasal cavity