Unit 7 DNA, Protein Synthesis, Gene Expression, and Point Mutations
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
DNA function
responsible for carrying and retaining the hereditary information in a cell
DNA
universal genetic code for all living things, creates proteins to regulate itself
coding regions (1%) and noncoding regions (99%)
DNA is divided into...
coding regions (1% of genome)
identical to all humans
coding regions (1% of genome)
code for RNA→tRNA, rRNA→involved in protein synthesis
coding regions (1% of genome)
code for regulatory proteins→involved in cell specialization
coding regions (1% of genome)
code for proteins that directly/indirectly influence traits
ex. hormones, enzyme, pigments
coding regions (1% of genome)
large percent of our coding regions code for identical proteins
noncoding regions (99% of genome)
completely different from other people, useless, no affect on appearance
noncoding regions (99% of genome)
found between genes and regions within genes (introns)
noncoding regions (99% of genome)
determines most of the diversity between individuals; leads to our unique "genetic fingerprint"
central dogma
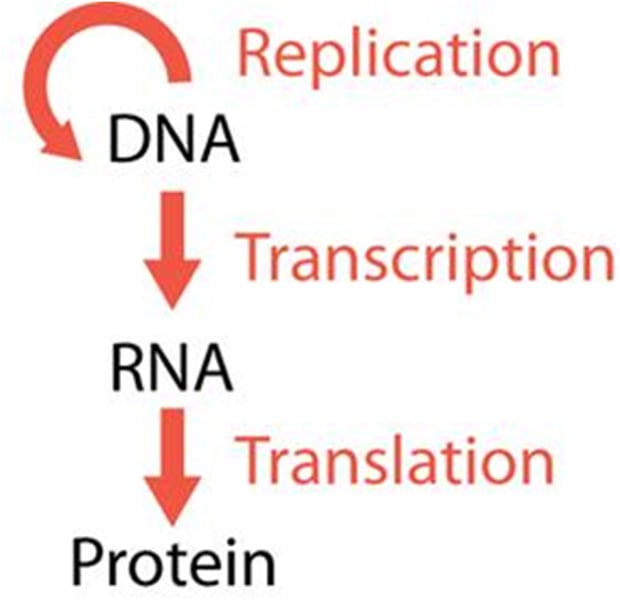
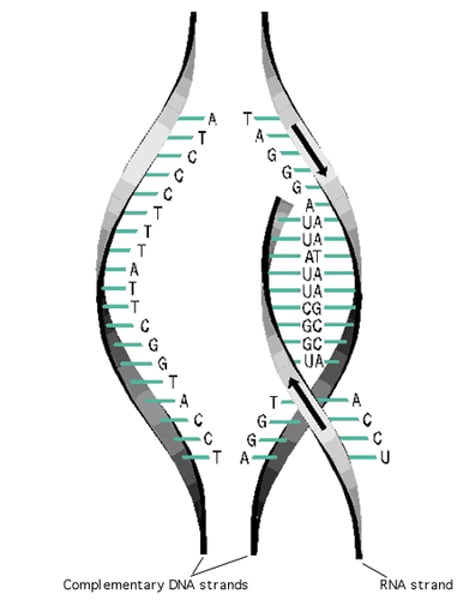
transcription
the process of transforming a region of DNA code (gene) onto messenger (mRNA) form
RNA polymerase (enzyme) binds to a specific region of DNA called the promoter. In a eukaryotic cell, each gene has its own promoter region.
1st step of transcription
as RNA polymerase moves along the DNA molecule, it causes a region of DNA, called a gene, to "Unzip" into 2 separate exposed strands. (contains hydrogen bonds that can be easily unzipped)
2nd step of transcription
promoter
marks the beginning of a DNA region (gene) that will be transcribed
bases of RNA nucleotides found in the nucleus bond to complementary bases found on one separated strand of DNA (template strand)
3rd step of transcription
Separate RNA nucleotides are linked together by an enzyme along the sugar-phosphate backbone to form mRNA molecules
4th step of transcription
when a termination of bases is reached on the DNA template strand, RNA polymerase detaches and the newly formed mRNA is released
5th step of transcription
pre-mRNA transcript containing both introns and exons is modified
6th step of transcription
introns
intervening segments; removed from pre-mRNA; embedded within DNA but does not need to be there
extrons
expressed segments; remain in completed RNA transcript; needed
the intron loops out as snRNPs bind together to form the spliceosome. then the intron is cut out, the exons are spliced together and the mRNA exits the nucleus which can then be translated in the cytoplasm
How are introns "cut out"?
a 5' cap is added to one end of the mature mRNA transcript and a poly-a tail is added to the 3' end of the mature mRNA transcript
7th step of transcription
the mRNA travels through the nuclear membrane to the ribosome; several more mRNA molecules will be synthesized before DNA recoils
8th step of transcription
the exact same
RNA and coding strands are...
complementary
RNA and template strands are...
5'→3'
RNA is always built from...
mRNA
transfers DNA code from the nucleus to the ribosome; translated into a protein
rRNA
makes up the structure of the ribosome
tRNA
transfers a specific amino acid to the correct matching position along the mRNA; contains an anticodon (assists in translation)
snRNA
small nuclear RNA: with proteins, forms spliceosomes that aid in modification of RNA before it leaves the nucleus
translation
the process of assembling protein molecules that form an mRNA code
mRNA arrives at the ribosome (rRNA) and binds to the 5' end. It begins to be read in groups of 3 bases (codon) starting with the start codon that codes for the amino acid methionine. The mRNA is shifted from codon to codon; many ribosomes may work simultaneously to create multiple copies of the protein
1st step of translation
codon
a group of 3 sequential bases found on the mRNA which codes for a specific amino acid
tRNA molecules found in the cytoplasm transport specific amino acids to the correct position along the mRNA strand. Each tRNA molecule contains an anticodon that is complementary to the mRNA codon
2nd step of translation
anti-codon
a specific region of tRNA that is complementary to a specific mRNA codon
amino acids are linked together with peptide bonds to form a polypeptide (protein)
3rd step of translation
when a termination or a stop codon is reached on the mRNA the polypeptide chain is released. After being read a finite number of times the mRNA is degraded within the cell
4th step of translation
gene expression
- the activation of a gene, results in the formation of a protein
- a gene is expressed or "turned on" when transcription occurs
- mechanisms have evolved to ensure proteins are only produced when they are needed
- regulating gene expression enables cell to control which portion of the genome is expressed and when
genome
the complete genetic code found in an individual
structural genes
code for the actual enzymes needed to break down lactose
promoter region
recognizes the enzyme RNA polymerase and promotes transcription
operator
DNA segment that serves as a binding site for an inhibitory repressor protein that blocks transcription and prevents protein synthesis
structural genes, promoter, and operator
What forms the operon?
operon
series of genes that code for specific proteins and the regulatory elements that control the expression of those genes
regulatory gene
codes for the production of the repressor protein that inhibits a specific gene from being transcribed
lac operon
specific operon required to produce the enzymes involved in lactose metabolism
inducer
a molecule that initiates gene expression
repressor protein
- protein that inhibits a specific gene from being expressed
- attachment of the repressor protein to the operator prohibits RNA polymerase from binding to structural genes, STOPS TRANSCRIPTION
Repression of gene expression
in the absence of lactose, a protein called a repressor attaches to the operator
activation of gene expression
when lactose is present, it temporarily binds to the repressor protein on the operator and removes it
gene activation
initiation of transcription by removal of repressor proteins
alternative splicing
a process by which exons or portions of exons or noncoding region within a pre-mRNA transcript are differentially joined or skipped, resulting in multiple possible protein forms being encoded by a single gene
- it increases the informational diversity and functional capacity of a gene
point mutation
a change in the DNA or mRNA that affects the specific amino acid sequence resulting in an incorrectly assembled protein
diabetes
mutation in insulin
sickle cell anemia
mutation in protein hemoglobin, less of an ability to carry oxygen in blood
addition
adding a base to the DNA or mRNA sequence and causes a frameshift
deletion
removing a base from the DNA or mRNA sequence and causes a frameshift
substitution
replacing one base with another in a DNA or mRNA sequence; does not cause a frameshift; potentially does the least damage
missense mutation
amino acid changed to a different amino acid
nonsense mutation
amino acid changes to a "stop"
silent mutation
codes for the same amino acid
Mutagen
agent that can induce or increase the frequency of mutation in organisms
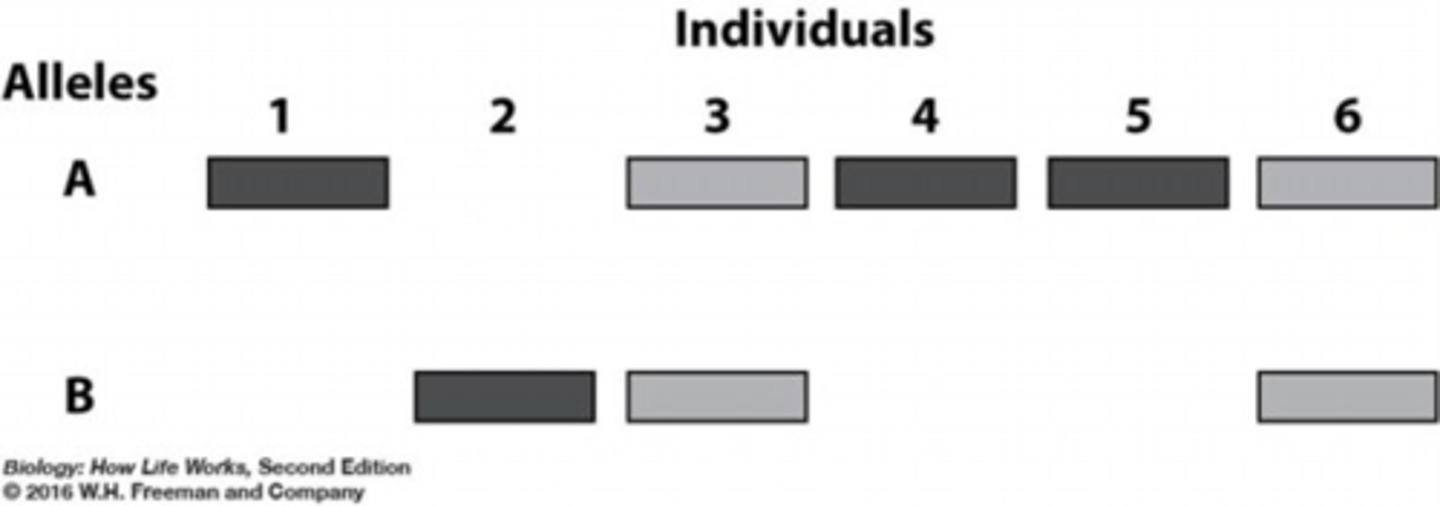
Electrophoresis
a technique using an agarose gel and electric current to distinguish differences between individual's DNA or differences between normal and abnormal proteins based on their size and charge
comparing DNA
- fragmented by restriction enzymes (tiny chemical scissors), cut DNA at specific base sequences
- different individuals will have different number/sizes of fragments
- fragments of different sizes/mass move at different rates from the (-) pole of an electric field toward (+) pole
- fragments that have migrated are stained to indicate their position after a period of time
restriction enzymes
Enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotide fragments; used during electrophoresis
RFLP (genetic fingerprint)
unique banding pattern of an individual's DNA after being treated by several restriction enzymes
Comparing Isolated Proteins
- proteins have overall (-) charge as a result of the amino acids they contain; the overall charge is different for different proteins
- when comparing a "normal" protein to a "mutated" protein, they will have slightly different overall charges due to differences in amino acid sequences
- comparing the amount of migration of a "normal" protein to that of a "mutated" protein on an electrophoresis gel enables differentiation between the 2 forms of the protein
gel diagram