Sensation and Perception - Chapters 1 & 2
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Perceptual Process
Begins with stimuli, ends with perception, recognition, and action
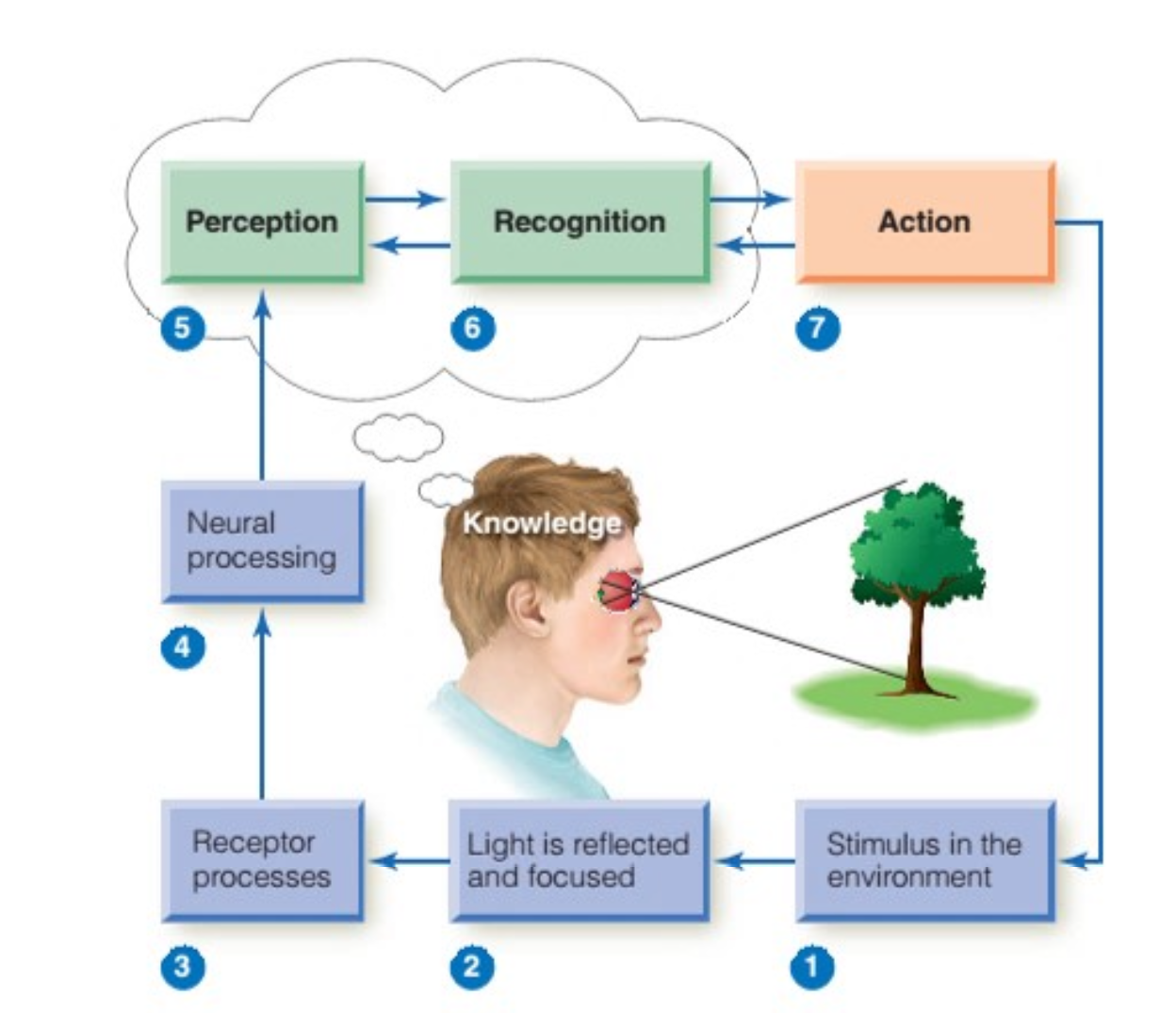
Perception vs Sensation
Perception: higher level brain processes involved in interpreting events and objects
Sensation: detecting elementary properties of a stimulus
Distal Stimulus
The real physical thing in the environment
called distal because it is ‘distant’
principle of transformation
stimuli and responses created by stimuli are transformed, or changed, between the distal stimulus and perception
proximal stimulus
image created on the retina
principle of representation
everything a person perceives is based not on direct contact with stimuli, but on representations of stimuli that are formed on the receptors and the resulting activity in the person’s nervous systems
sensory receptors
cells specialized to respond to environmental energy
visual pigment
light-sensitive chemical found in visual receptors
transduction
the transformation of one form of energy to another (light to electrical for sight)
neural processing
transformation of signals in the brain
primary receiving area
where electrical signals from each sense arrive in the cerebral cortex
cerebral cortex
layer of the brain that creates perceptions and other functions such as language, memory and thinking
occipital lobe
used mostly for vision
temporal lobe
used mostly for hearing
parietal lobe
used for the skin sense; touch, temperature, and pain
frontal lobe
receives signals from all senses, plays an important role in perceptions that involve two or more senses
visual form agnosia
an inability to recognize objects
knowledge
any information that the perceiver brings to a situation
bottom-up processing
perception based off of stimuli reaching the receptors
top-down stimuli
perception based off of knowledge
stimulus-perception relationship
relates stimuli to behavioral responses
stimulus-physiology relationship
stimuli and physiological responses (i.e. brain activity)
method of limits
threshold measurement where the experimenter adjusts the intensity until the subject can no longer detect the stimuli
absolute vs difference threshold
absolute: smallest simulus level that can be detected
difference: smallest change in stimuli where the change can be detected
method of adjustment
the subject adjusts the level of the stimuli
method of contant stimuli
stimuli in a range are presented to the subject in a random order
*most time consuming and accurate test
magnitude estimation
a numeric value is assigned to an intensity level, and the subject is asked to assign a new numeric value to different levels of intensity based off of the first one they were shown
phenomenological report
describing something that you see
What visible light can humans see?
400-700 nanometers (nm)
fovea
center spot on the back of the eye where focused light is directed, contains a much higher concentration of cones than the periphery of the eye
macular degeneration
destruction of the fovea, more common in older people, makes a blind spot in the center of your vision
retinitis pigmentosa
degeneration of the periphery rods, causes ‘tunnel vision’
accomodation
the change in the lens’s shape that occurs when the ciliary muscles at the front of the eye increase the curvature of the lens, to help focus light on the retina
Myopia
When light is focused in front of the retina (near-sightedness)
presbyopia
loss of the ability of the eye to accommodate (old eye)
hyperopia
light focuses behind the retina (farsightedness)
isomerization
when the retinal part of the visual pigment bends and changes its shape
dark adaption
increasing sensitivity to light in the dark
dark adaptation curve
increases rapidly in first 3-4 minutes, than steadily until 20 or 30 minutes. dark-adapted sensitivity is about 100,000x better than light-adapted sensitivity when the darkness began
dark adaptation rods vs cones
cones start out much more sensitive, but by ~5 minutes hit their max and stop increasing sensitivity
rods steadily increase sensitivity throughout and end up more sensitive than cones after ~7 minutes
two important connections between perception and physiology
our sensitivity to light depends on the concentration of visual pigment
The speed at which our sensitivity increases in the dark depends on the regeneration of the visual pigment
Purkinje shift
We are more sensitive to low wavelength light (blues and greens) during dark adaptation
Changing the stimulus intensity
does not affect the size of the action potentials, but does affect the rate of firing