Anaemia + haemoglobinopathies
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What causes microcytic anaemia?
Reduced rate of haemoglobin synthesis
Iron deficiency (affects haem synthesis)
Thalassemia (affects globin synthesis)
Chronic inflammation/ malignancy
What are chronic inflammatory conditions characterised by?
low serum iron
Normal/ raised serum ferritin
Bone marrow iron storage is normal
Reduced TIBC
High levels of IL-6 → unregulates hepcidin→ decreased iron absorption + increased iron retention → less iron available
IL-1 + TNa→ decrease EPO → reduced half life of RBC
What is iron deficiency anaemia characterised by?
Reduced serum iron
Reduces serum ferritin
No bone iron stored in bone marrow
Raises TIBC (total iron binding capacity)
What is the iron transporter called?
Transferrin
What is sideroblastic anaemia?
Rare inherited microcytic anaemia → due to defect in haem synthesis (mutation in ALAS-gene , X chromosome )
Rings of iron form in RBC
** high serum iron and serum ferritin
name some causes of normocytic anaemia
anaemia of chronic disease
Renal failure
Acute blood loss
Endocrine failure (hypothyroidism, hypopituitarism)
What are the 2 different normocytic anaemia?
Hypoproliferative (normal/ decreased reticulocyte count): due to chronic disorders, liver disease, leukaemia
Hyperproliferative (high reticulocytes count): due to blood loss , haemolytic anaemia)
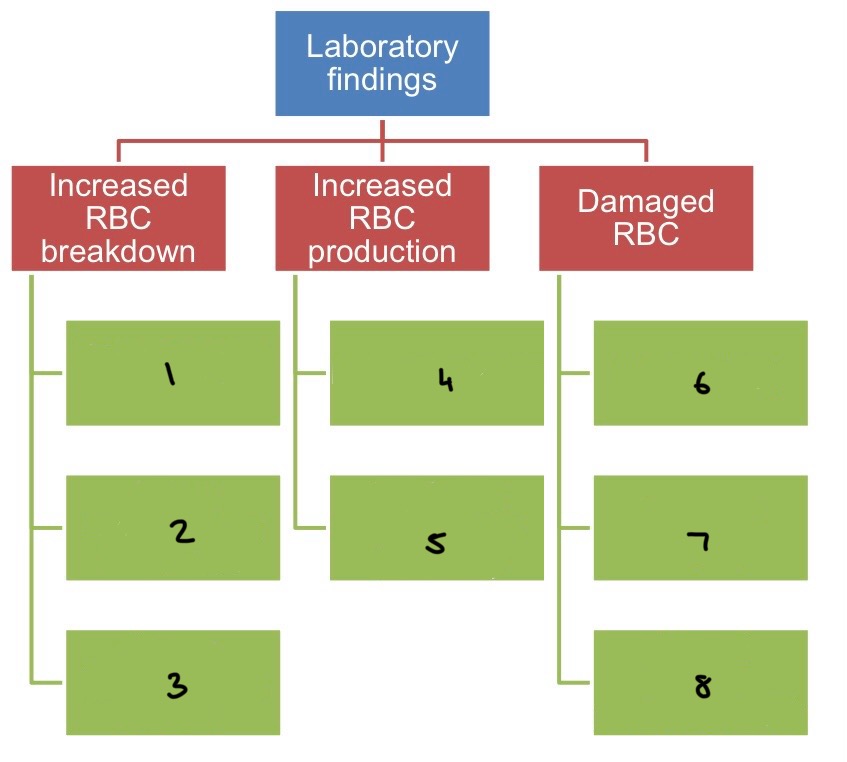
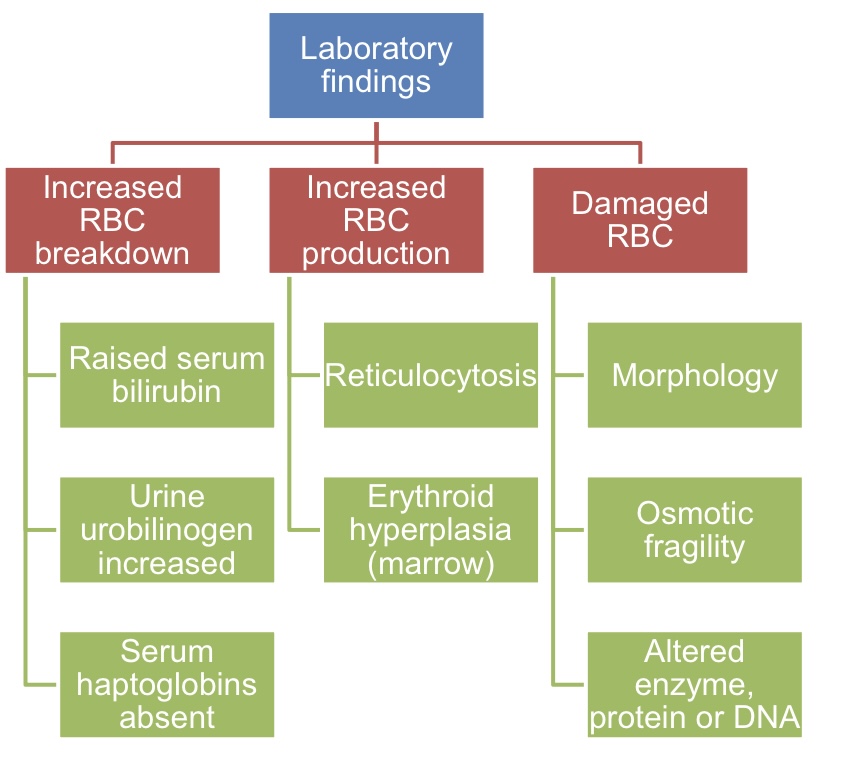
What does haemolytic anaemia cause?
Increased RBC destruction
→ can be due to: autoimmune, infections (eg. malaria), hereditary (eg. G6PD deficiency, Pyruvate kinase deficiency, spherocyrosis, elliptocytosis)
How do people with haemolytic anaemia present?
Pallor of mucous membranes
Fluctuating jaundice and splenomegaly
High reticulocytes count
How do you test for acquired (autoimmune) haemolytic anaemia?
Direct antiglobulin test (DAG) = Coombs test
Warm/ cold autoimmune disease (antibody reacts better at warm/ cold)
How does an alloimmune haemolytic anaemia occur?
Alloimmune- antibodies produced by 1 individual react with the RBC of another
Can occur in blood transfusion/ pregnancy
Pregnancy:
Has a Rh+ baby when she is RH-
Blood cross over during birth → has anti-Rh antibodies in her blood
Antibodies attack her next baby if Rh+
What are come causes of macrocytic anaemia?
Megaloblastic: low B12 + folate
Non-megaloblastic: alcohol, liver disease, pregnancy, smoking
Mutation in sickle cell
GAG → GTG on chromosome 11
Glutamic acid → valine
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia
jaundice + gallstones
Splenic atrophy due to splenic infarction due to infection with strep pneumonia / meningitis
Sickle cell crisis:
→ Hand foot syndrome (painful dactylic caused by infarcts of small bones in hands)
→ If they block the blood vessels → infection: pooling of blood
What do patients with sickle chest syndrome present with and how do you treat it?
dyspnoea
Falling arterial PO2
Chest pain
Pulmonary infiltrates on chest x-ray
treatment: analgesia, oxygen
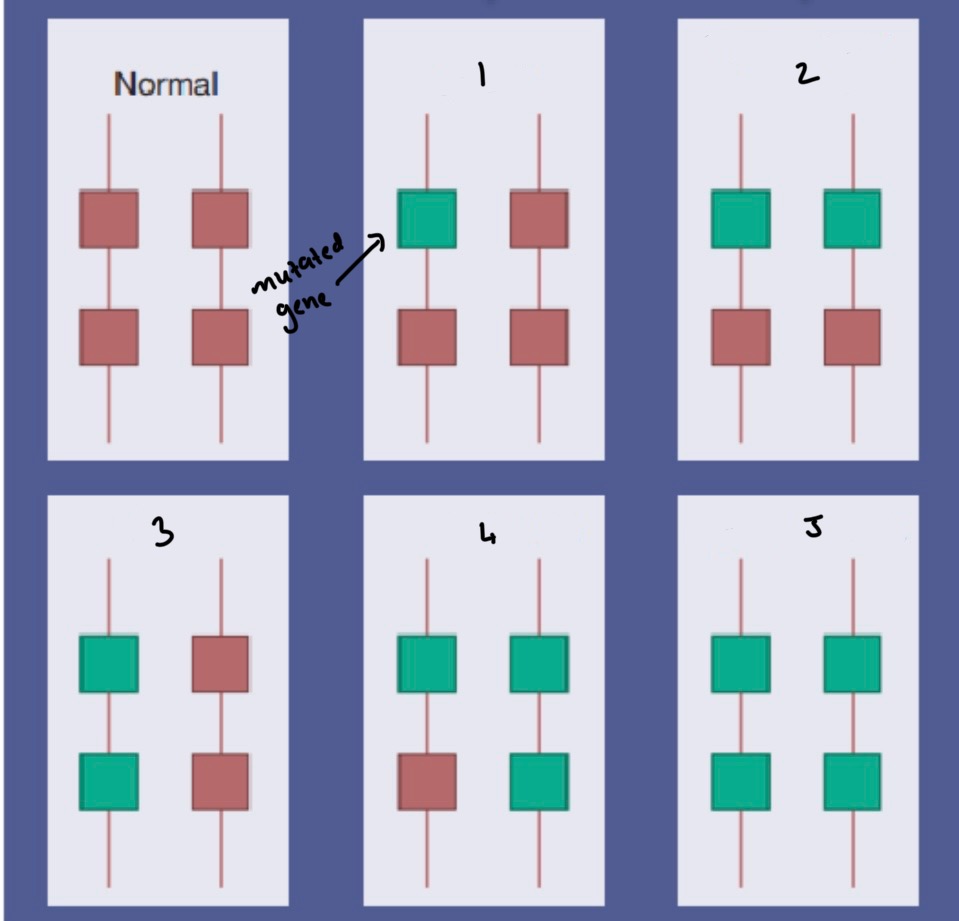
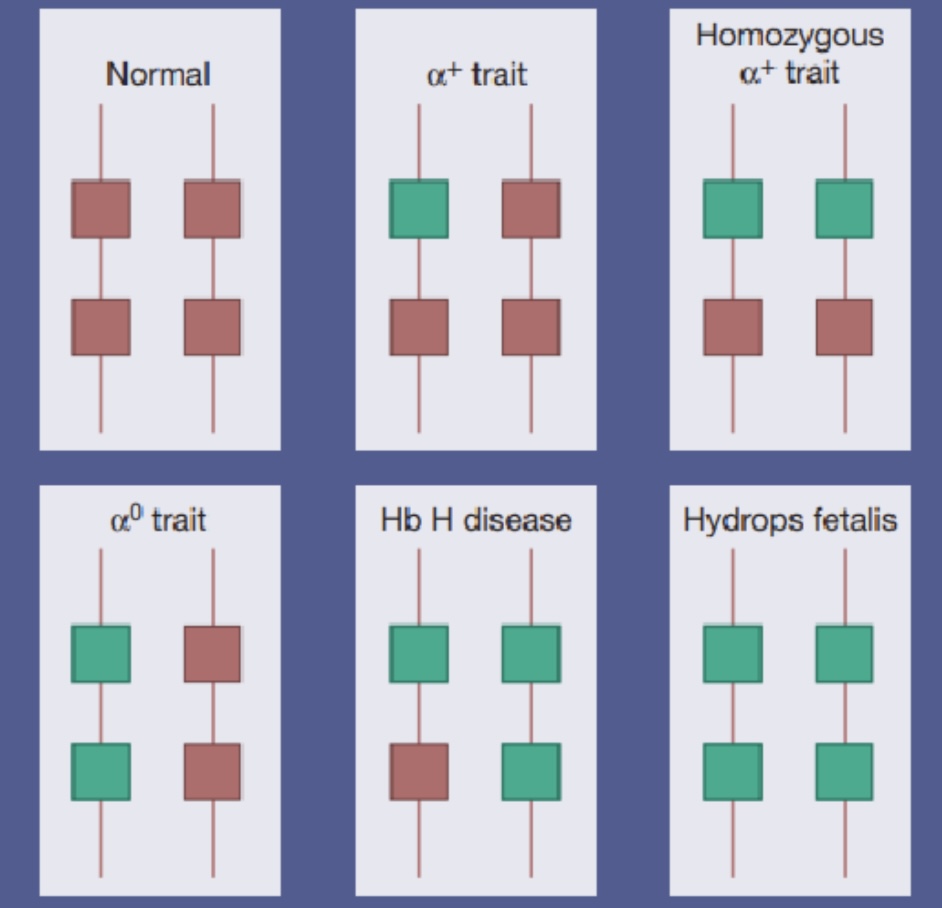
How is Alpha Thalassemia caused?
Deletion/ kids of function of 1 or more of the 4 alpha glob in chains
What is Bart’s disease?
No alpha chain in haemoglobin
What are Alpha Thalassemia traits caused by and how is
Loss of 1 or 2 genes that are not associated with anaemia
MCV + MCH are now
Haemoglobin electrophoresis is normal + need a DNA analysis using PCR
What is the difference between between beta Thalassemia major, intermedia and minor?
Major: transfusion dependent (no beta chains)
Intermedia: non-transfusion dependent but moderate anaemia
Minor: carrier with not many symptoms
Symptoms of beta Thalassemia major
severe anaemia at 3-6 months, failure to thrive, swollen abdomen
Hepatosplenomegaly
Expansion of bones due to intense marrow hyperplasia
Thalassaemic face
Infections
Liver disease
Symptoms of beta Thalassemia intermedia
bone deformity
Enlarged liver and spleen
Leg ulcers
Gall stones
Osteoporosis
Venous thrombosis
Why does sickle cell lead to jaundice?
Sickled RBC survive 30 days
Normal RBC survive 120 days
More haemolysis of sickle cells → increased bilirubin released