Final Exam BIOL 3000
1/591
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
592 Terms
What is spontaneous generation?
The outdated belief that living organisms can arise from non-living matter without descent from similar organisms.
Who disproved spontaneous generation and how?
Louis Pasteur with the Swan Neck Flask experiment.
What is preformationism?
The belief that organisms develop from miniature versions of themselves.
What did Darwin's theory of pangenesis propose?
That all parts of the body shed "gemmules" which collect in reproductive organs and determine inheritance.
What was Lamarck's theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics?
Traits acquired during an organism's life could be passed to offspring.
How was Lamarckism disproven?
August Weismann cut off rats' tails over many generations; offspring still had normal tails.
What are Mendel's major contributions to genetics?
The laws of inheritance, including dominant and recessive traits.
What is "blended inheritance" and how does it conflict with Mendel's findings?
The outdated idea that traits are a mix of parental traits; Mendel showed traits follow specific patterns.
What is epigenesis?
The theory that an embryo develops from the successive formation of new parts, not from preformed parts.
What is epigenetics?
The study of how gene expression is regulated without altering the DNA sequence.
What is genetic linkage?
The tendency of genes located close together on a chromosome to be inherited together.
What is gene expression?
The process by which genetic information is used to make proteins.
What processes are involved in gene expression?
Transcription and translation.
What are four key characteristics of life?
Complexity, growth and change, adaptation, and response to stimuli.
What are the 4 macromolecules of life?
Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Which atoms are common to all macromolecules?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur.
What is the basic unit and function of carbohydrates?
Sugar; provides energy and support.
What is the basic unit and function of lipids?
Fatty acids; provide energy, cushioning, and insulation.
What is the basic unit and function of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides; store and transmit genetic information.
What is the basic unit and function of proteins?
Amino acids; perform various functions like metabolism and transport.
What did Frederick Griffith discover?
The "transforming principle" in bacteria.
-smooth and rough bacteria
What did Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty conclude in 1944?
DNA is the hereditary material.
-lystate
What did the Hershey-Chase experiment prove?
DNA, not protein, is the genetic material.
-bacteriophages
What is recombinant DNA technology?
Manipulating DNA to produce proteins (e.g., insulin, HGH).
What is PCR used for?
Amplifying DNA for disease detection (e.g., HIV, cancer).
What is rBGH and its purpose?
Recombinant bovine growth hormone; used to increase milk production in cows.
-not an active receptor in humans, doesn't affect humans
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
A phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
What was the major conclusion from Griffith, Avery-MacLeod-McCarty, and Hershey-Chase experiments (1928-1952)?
DNA is the molecule of heredity.
What did William Astbury's X-ray diffraction studies reveal about DNA?
DNA has a regular, repeating structure; bases are stacked 0.34 nm apart.
What are Chargaff's Rules?
In natural DNA, %A = %T and %G = %C; base composition varies by species.
What was Rosalind Franklin's key contribution to DNA structure?
She captured B-51, which revealed the helical structure and dimensions of DNA.
What did Watson and Crick propose in 1953?
The double helix model of DNA, with base pairing via hydrogen bonds.
What are the three molecular components of a nucleotide?
Nitrogenous base, deoxyribose sugar, and phosphoric acid.
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases?
Purines (two-ring) and pyrimidines (one-ring).
Which bases are purines and which are pyrimidines?
Purines: Adenine and Guanine; Pyrimidines: Cytosine and Thymine.
What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide?
Nucleoside = base + sugar; Nucleotide = base + sugar + phosphate.
What kind of bond links the nitrogenous base to the sugar?
N-glycosidic bond.
What is the name of the bond connecting nucleotides in a strand?
Phosphodiester bond (between 5' and 3' carbon atoms).
What is the directionality of the two DNA strands?
Anti-parallel; one runs 5'→3' and the other 3'→5'.
Where are the phosphate groups located in the DNA molecule?
On the outside of the helix.
What direction do the nitrogenous bases point?
Inward, perpendicular to the helix axis.
Which base pairs form hydrogen bonds, and how many?
A-T forms 2 hydrogen bonds; G-C forms 3 hydrogen bonds.
What does Watson and Crick's model suggest about replication?
Specific base pairing suggests a possible copying mechanism for DNA.
What causes the twist in the DNA double helix?
Base stacking and hydrophobic interactions cause partial overlaps, leading to helical twisting.
What are the major and minor grooves of DNA?
Unequal spaces between backbone strands due to base pair geometry.
What are the three major forms of DNA?
A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA.
Describe B-DNA.
Most common, right-handed helix; hydrated form; anti-parallel strands; bases stacked inside.
Describe A-DNA.
Right-handed; dehydrated form; wider and shorter than B-DNA; tilted bases.
Describe Z-DNA.
Left-handed helix with zig-zag shape; compact; alternating syn and anti base conformations.
What is DNA replication?
The process by which genetic information is duplicated so that each new cell receives an exact copy of the DNA.
During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur?
S phase (Synthesis phase).
What is the purpose of cell division in relation to DNA?
To ensure each daughter cell receives a full copy of the genome.
What did Watson and Crick's model of DNA imply about replication?
That replication occurs via complementary base pairing in a semi-conservative manner.
What are the three models of DNA replication?
Conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive.
Which model of replication was supported by the Meselson-Stahl experiment (1958)?
Semi-conservative model.
What are the four major stages of DNA replication?
Initiation, Unwinding, Primer Synthesis, and Elongation.
What enzyme begins replication by binding to the origin of replication?
DnaA (initiator protein).
What enzyme unwinds the DNA double helix?
Helicase
What enzyme reduces torsional strain during unwinding?
Topoisomerase (also known as gyrase).
What proteins stabilize single-stranded DNA during replication?
Single-strand binding proteins (SSBs).
What enzyme lays down the RNA primer?
Primase
What is the function of DNA polymerase III in prokaryotes?
Main enzyme for elongation of the new DNA strand.
What is the role of DNA polymerase I?
Removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA.
What does DNA ligase do?
Seals the gaps between DNA fragments by forming phosphodiester bonds.
What direction does DNA polymerase synthesize DNA?
5' to 3' direction.
What is the leading strand?
The DNA strand synthesized continuously toward the replication fork.
What is the lagging strand?
The DNA strand synthesized discontinuously in fragments (Okazaki fragments) away from the fork.
How is high fidelity in DNA replication maintained?
Through proofreading by DNA polymerase III and mismatch repair mechanisms.
How do replication origins differ between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes have multiple origins; prokaryotes have one origin (OriC).
What is the role of telomerase in eukaryotic replication?
Extends the ends of linear chromosomes to prevent loss of genetic material.
What are telomeres?
Repetitive DNA-protein complexes at chromosome ends that protect genetic information.
What is a replicon?
A region of DNA where replication occurs.
Which of the following statements best represents the theory of PANGENESIS?
Particles called gemmules, which originate in each part of the body, collect in the sperm or egg of an organism and are passed on to the next generation.
Which of the following groups of atoms, as part of the macromolecules of life, are part of RNA and a PROTEIN? (i.e. the atoms must be present in BOTH molecules).
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen & Nitrogen.
What kind of bond is formed between the 5' phosphate group (PO4) of one nucleotide and the 3' hydroxyl (OH) group of the adjacent nucleotide?
Phosphodiester Bond
What kind of bond is formed between complementary base pairs to join the two DNA strands into a double helix?
Hydrogen Bond
Which enzyme is the MOST active during the replication of DNA?
DNA Polymerase
After replication, chromosomes consist of how many molecules of DNA (assume one chromatid is equal to one molecule of DNA)?
two
During DNA replication, nascent DNA strands are synthesized in only one direction. Nucleotides are added ONLY to which end of the growing nascent strand?
3'
DNA replication is defined as ____________ because the newly replicated DNA consists of a parental strand (from the original DNA) and a newly synthesize daughter strand.
semi-conservative
There are sixty one different codons that code for amino acids, but only twenty different amino acids. This means that the genetic code is __________.
redundant
Watson and Crick used evidence from several studies to determine the structure of DNA. What SPECIFIC conclusion were they able to draw from Rosalind Franklin's X-ray diffraction data provided by Photograph B51?
DNA is a duplex with two strands forming a double helix.
What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleoside?
A nucleoside does not have a phosphate group attached while a nucleotide does.
In their famous experiment, which of the following would Meselson and Stahl have observed after one cycle of replication in 14N medium if DNA replication was conservative?
An equal number of DNA molecules containing two 15N-DNA strands and DNA molecules containing two 14N-DNA strands.
Based on the following replication bubble, which of the following statements is TRUE?
W and Y are leading strands, X and Z are lagging strands.
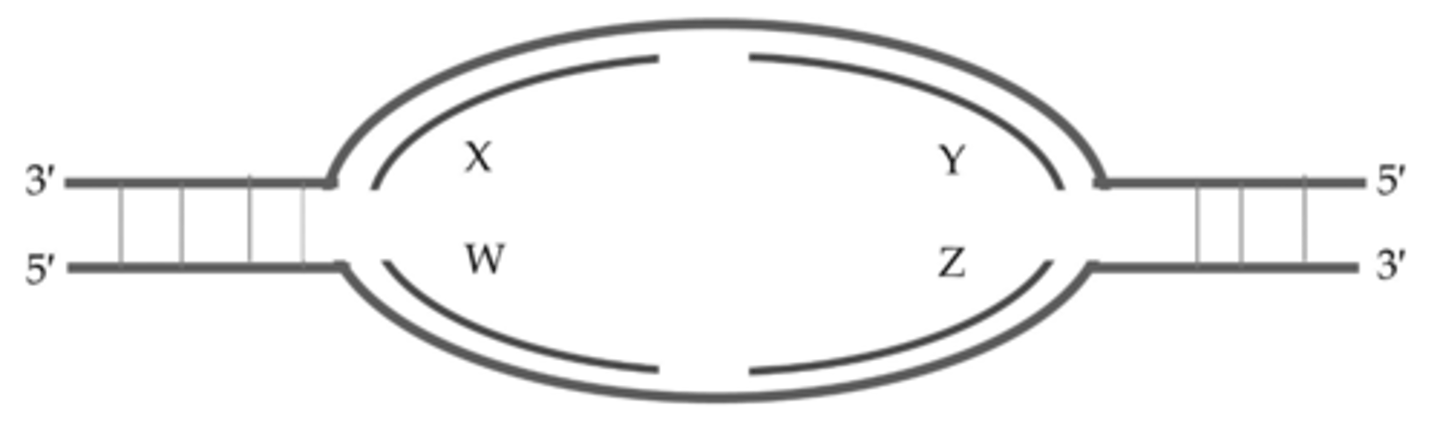
Which arrow(s) point(s) to the location of helicase in the following image?
B and D
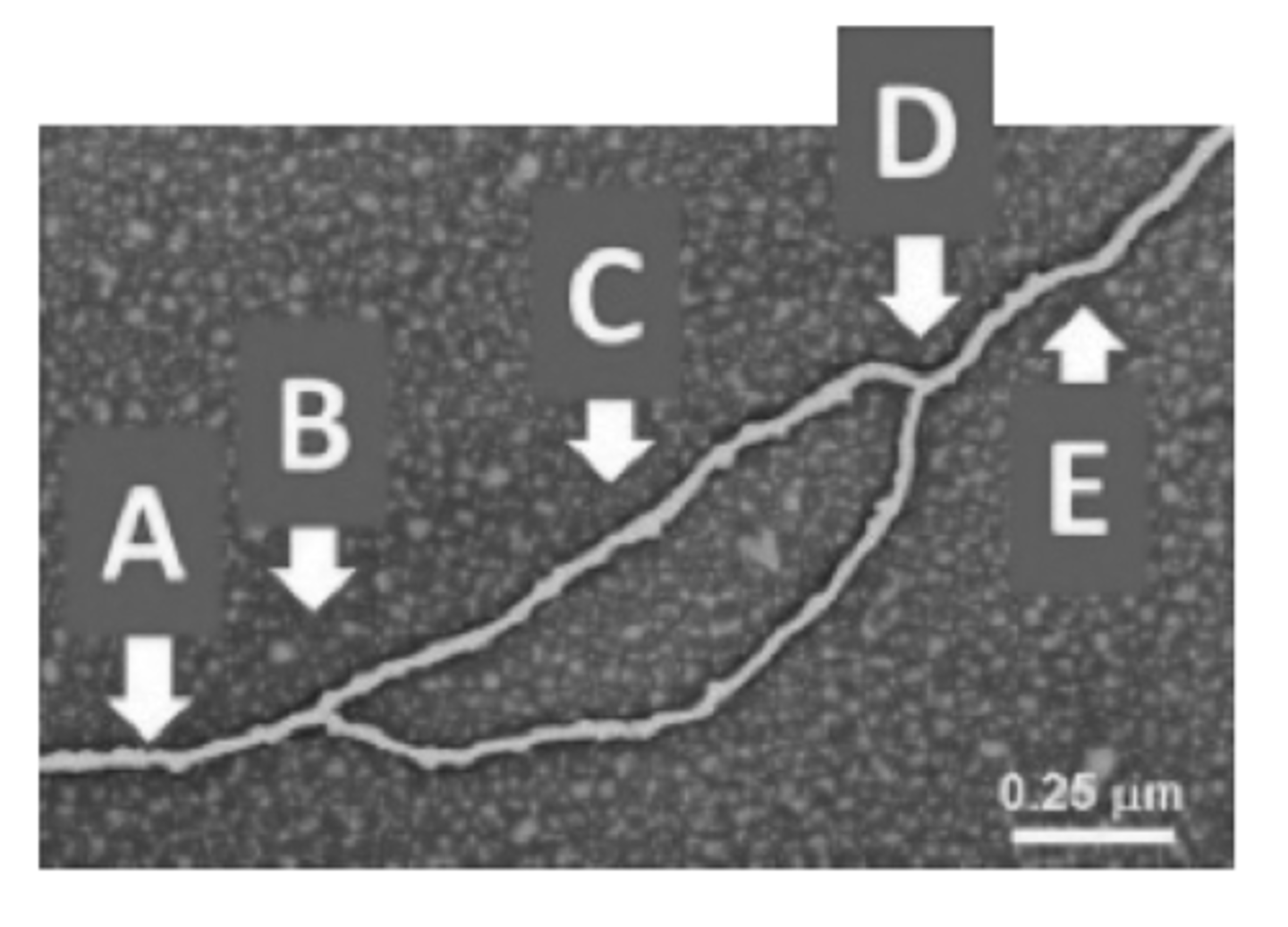
DNA helicase inhibitors are well studied as potential drug targets. What would you expect to see if DNA helicase activity is inhibited?
Helicase catalyzes ATP hydrolysis and DNA strands separation, so the helix cannot be unwound and strands will not separate.
What is the term for the daughter strand synthesized continuously during DNA replication?
leading strand
If THYMINE makes up 21% of the DNA nucleotides in a particular genome, what are the percentages of the other nucleotides in the genome?
ADENINE = 21%; CYTOSINE = 29%; GUANINE = 29%
In terms of polarity, what is the direction of DNA synthesis?
5' to 3' with addition of new nucleotides to the 3' end
What are the DNA regulatory sequences recognized by RNA polymerase called?
promotors
What is a true-breeding plant?
A plant that consistently produces offspring with the same traits as the parent.
-homozygous parents
What is a reciprocal cross?
A cross where the sexes of the parents are reversed to test for sex-linked inheritance.
What did Mendel observe in the F1 generation of round × wrinkled peas?
All offspring were round - the round trait is dominant.
What was the ratio in the F2 generation for seed shape?
3:1 round to wrinkled.
What key conclusion did Mendel draw from the 3:1 ratio?
Traits are inherited as discrete units (genes), and one can be dominant over the other.
What is the multiplication rule in probability?
The probability of two independent events occurring together is the product of their probabilities.
What is the addition rule in probability?
The probability of one of multiple mutually exclusive events occurring is the sum of their probabilities.
What is a gene?
A unit of inheritance; a DNA sequence encoding a trait.
What is an allele?
Alternative versions of a gene.