Interpretation of Venous Duplex Imaging
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is this image showing?
acute blood clot
What is this image showing?
chronic blood clot
-the vein is almost completely occluded
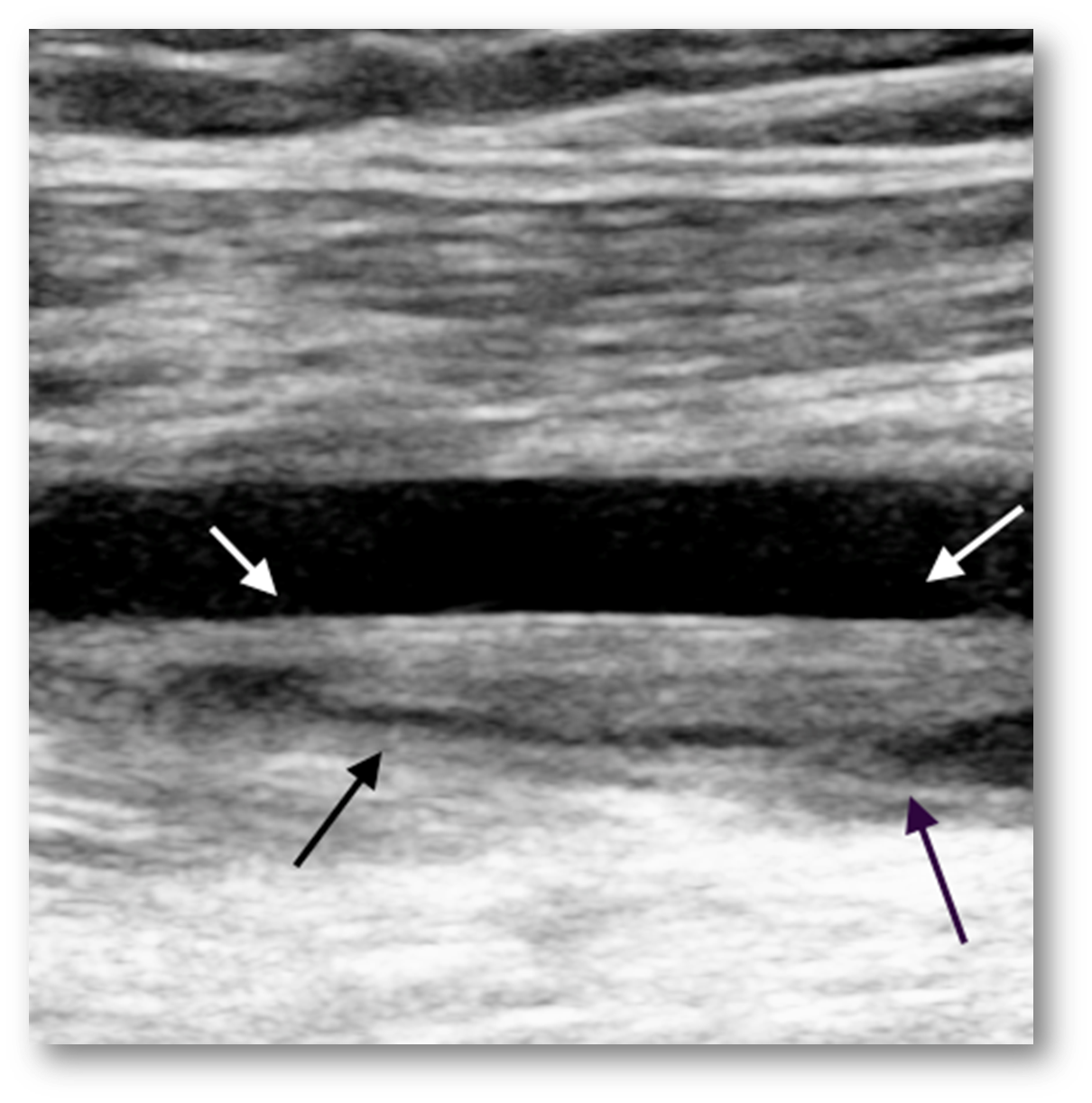
What is this image showing?
chronic blood clot
Blood clots are commonly formed by the?
valves
What is this image showing?
blood clot by a venous catheter
What is the purpose of venous reflux testing?
is to identify the presence and location of incompetent venous valves
Patients that suffer from chronic venous insufficiency may benefit from
study
Symptoms of venous reflux include:
-chronic leg swelling
-induration (leathery skin, hard)
-sometimes ulcers
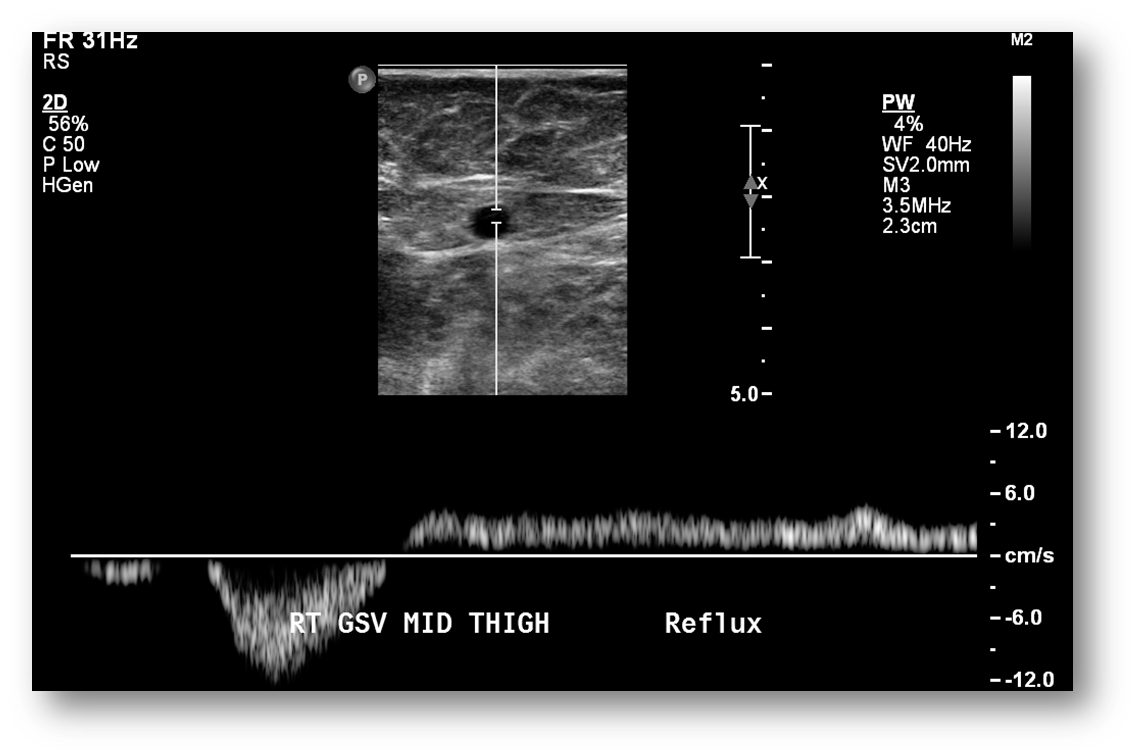
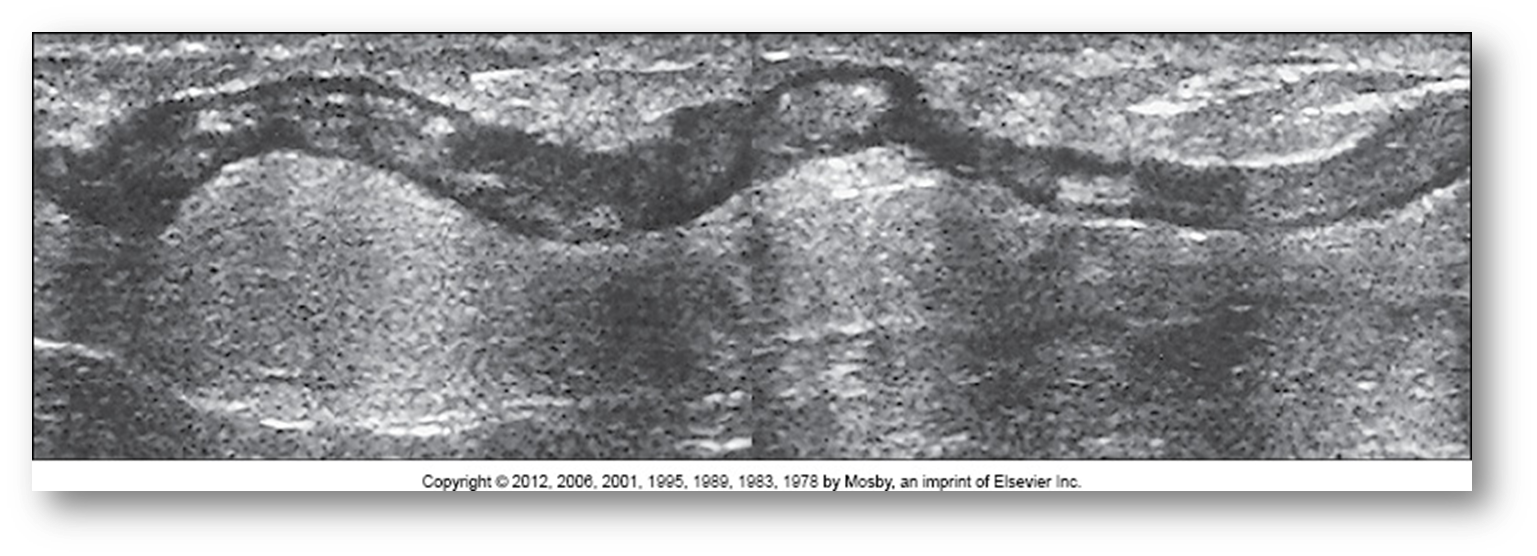
What is this image showing?
venous reflux
we do not want it to flow backwards or reflux
What is the purpose of superficial vein mapping?
is to determine vein’s suitability for use as bypass conduit and to identify its anatomic route
superficial vein mapping is usually performed before
lower extremity arterial bypass or coronary bypass operations, a-v fistula for dialysis
Information gathered about the superficial vein include:
vein patency
position
depth
size
Vein mapping allows for
selection of optimal vein used for surgery
adequate vein diameter may vary based on
surgeon preference and intended use of the vein
Generally, most surgeons will not
use a vein with a diameter of less than 2 mm
Most surgeons prefer vein diameter of
2.5 to 3 mm
smaller veins may be prone to spasm and are difficult to suture
What is the bakers cyst also called?
popliteal cyst
What is a baker cyst?
fluid collection that can be found in the popliteal fossa
The bakers cyst is a ____________ bursa
communicating bursa
Excess fluid can be related to
any type of arthritis
trauma or tears can affect the baker cyst
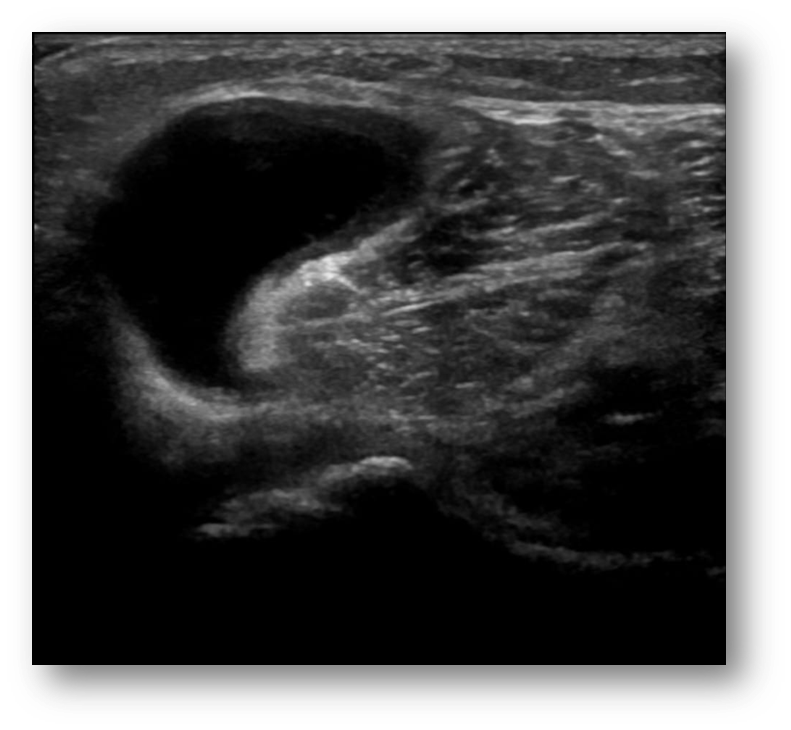
What is this image showing?
bakers cyst
Bakers cyst can be
unilateral or bilateral
Symptoms of bakers cyst can mimic
DVT symptoms include swelling and tightness behind the knee, or severe pain in the upper calf in cases of cyst rupture and dissection into the upper calf muscles
What are other pathologies:
-abscesses
-cellulitis
-hematomas
can cause focal areas of redness and swelling that may mimic symptoms of DVT
Cellulitis is caused by
a bacterial infection
Proving no ________ in deep venous system is first goal; evaluating _______ _______ is secondary goal
DVT
focal area
Small fluid collections may be seen within
tissue or muscle planes
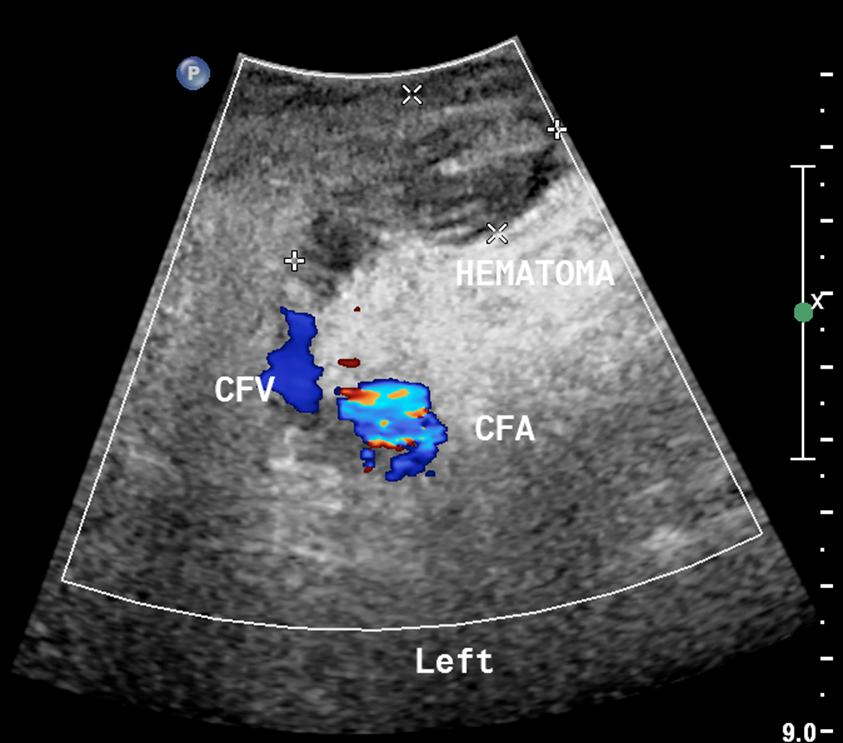
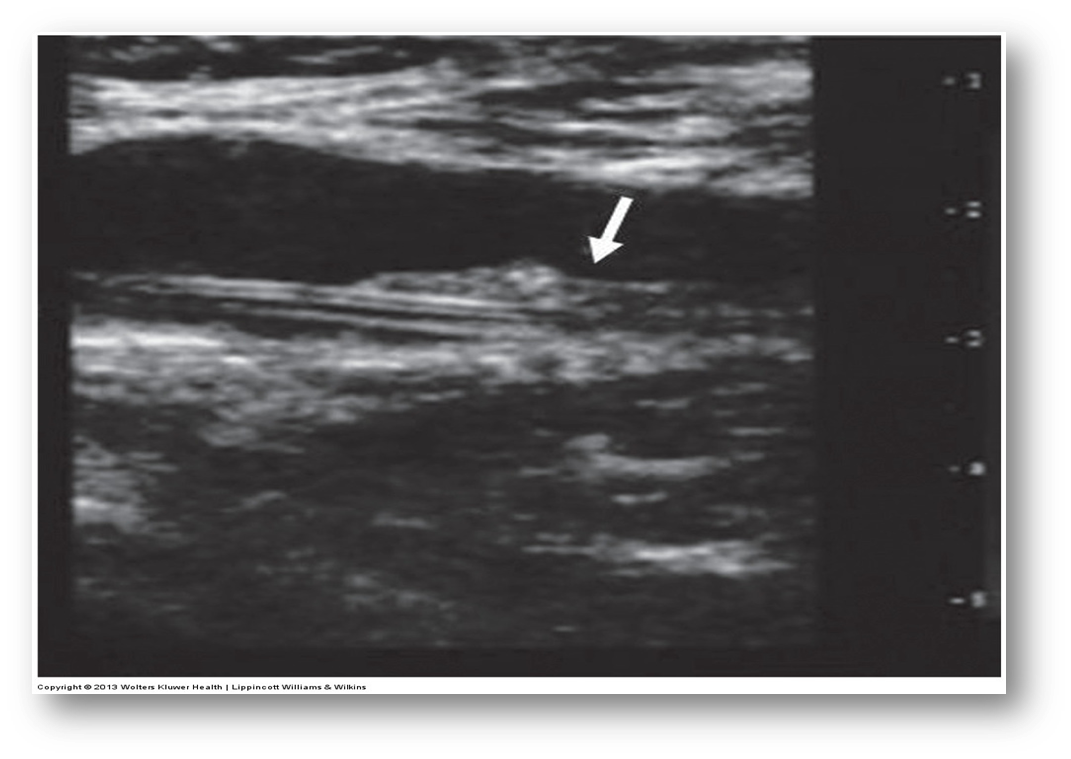
What is this image showing?
a hematoma
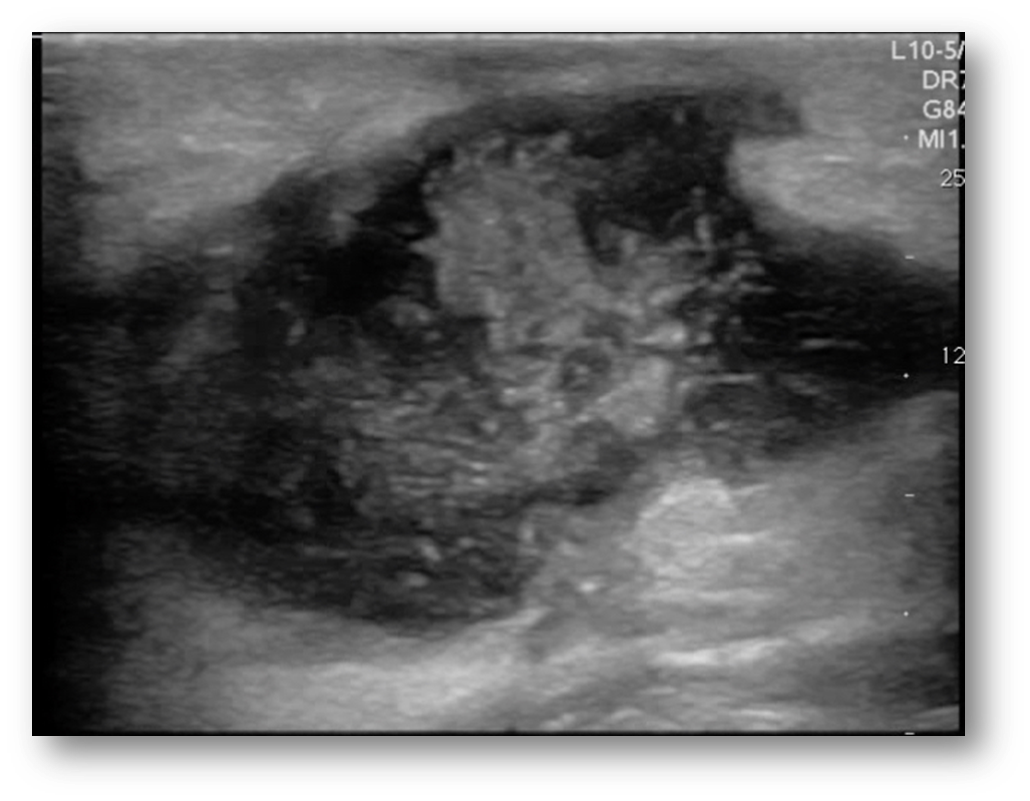
What is this image showing?
a abscess
What are the characteristics of an abscess?
elevated WBC, fever, red, and hot to the touch
What can sometimes be mistaken for DVT in common femoral or external iliac veins?
lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are very common in
in the groin
Visualizing lymph nodes in transverse and sagittal excludes them from
venous pathology
Enlarged lymph nodes should be
documented when seen
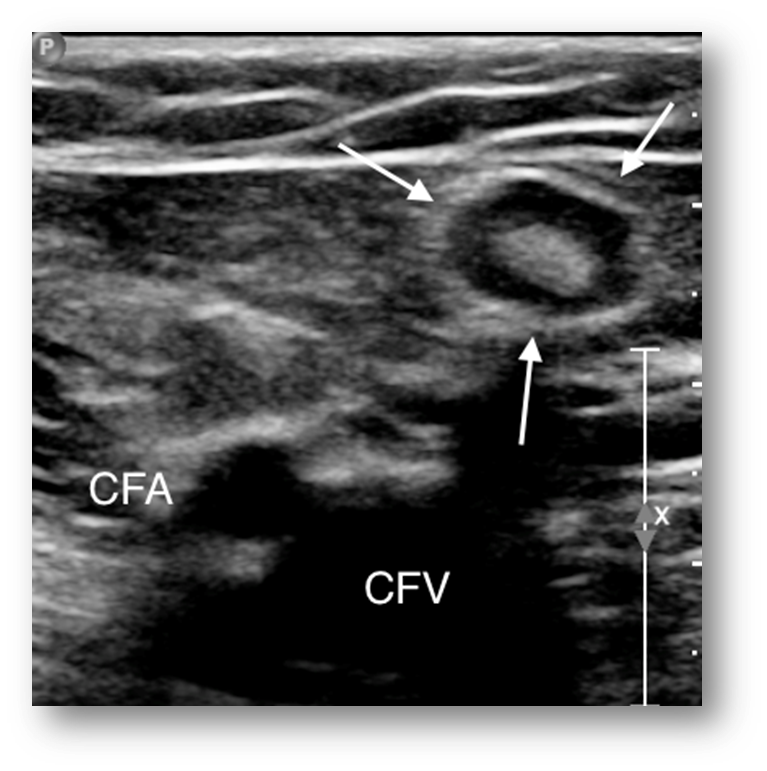
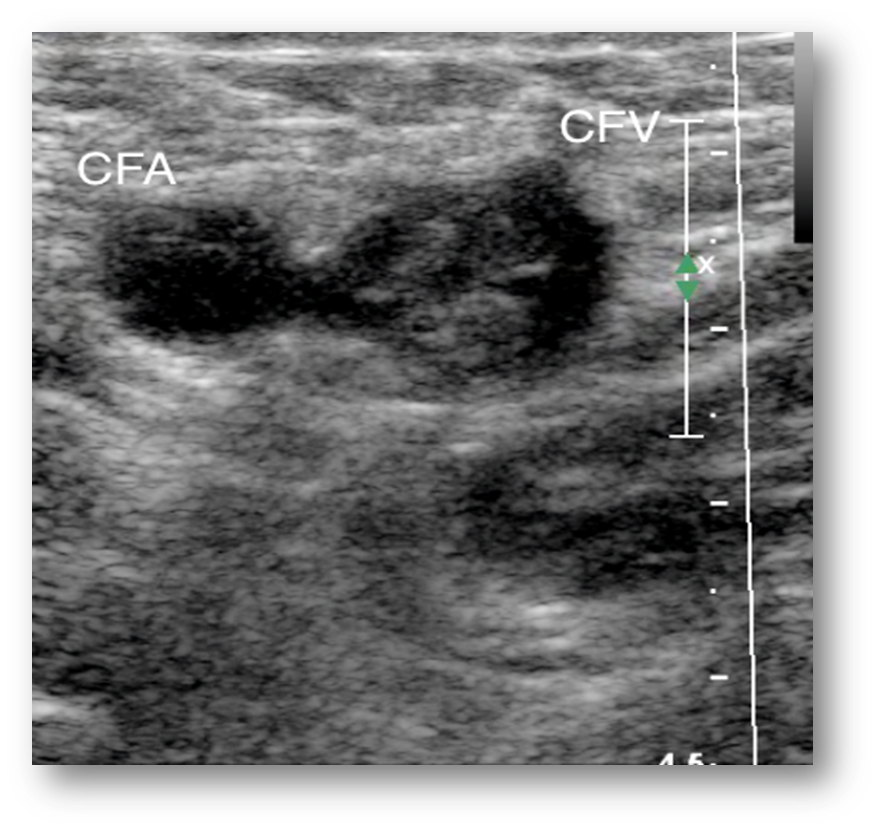
What is this image showing?
lymph node
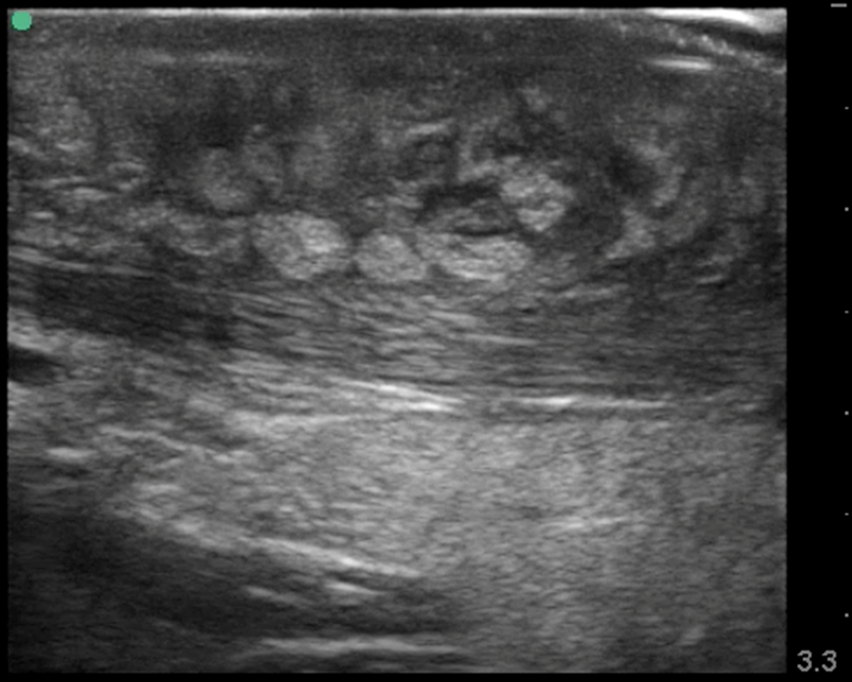
What is this image showing?
cellulitis/edema