Chemical Weathering - labeled diagram
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Karst Landscape
A type of terrain characterised by distinctive landforms that result from chemical weathering and erosion of soluble rocks.
Particularly limestone, dolomite and gypsum.
Limestone and Carbonation
A rock mainly composed of calcium carbonate, that is susceptible to weathering processes, especially carbonation.
In Ireland it is seen in the Burren in Co. Clare.
The Burren is a limestone-rich landscape, formed approximately 350MYA during the Carboniferous period.
The Process of Carbonation
A chemical weathering process in limestone regions.
Occurs when rainwater absorbs carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air and soil.
This creates a weak carbonic acid.
Formation of Calcium Carbonate
This acidic rainwater reacts with the calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) in the limestone, to form calcium bicarbonate.
(Calcium carbonate dissolves in water & is carried away)
As this reaction occurs, it gradually dissolves limestone, enlarging joints and bedding planes.
Finally leading to distinct surface features typical in karst landscapes.
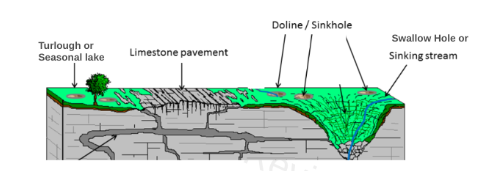
Surface Karst Features: Limestone Pavements and Swallow Holes
One defining feature of a karst landscape is the limestone pavement.
Which is an exposed, often flat area of limestone bedrock.
Limestone Pavements
Overtime, carbonation widens joints in limestone.
Creating distinctive patterns of clints and grikes.
Clints - the flat slabs of rock.
Grikes - deep, narrow fissures between clints.
The landscape looks rugged and checkerboard like.
Karrens - small shallow hollows, marking clints.
Water pools and dissolves the rock further here.
Fluting - Grooves that add texture to the landscape, created by acidic water that runs off the edges of clints.
Swallow Holes
Another important feature.
Formed where rivers encounter areas of permeable limestone.
Rivers flow over impermeable rock.
They divert and sink underground, when they reach limestone.
The water dissolves rock along cracks and bedding planes.
The river eventually disappearing below the surface.
Rivers of resurgence - rivers resurface, often leaving a dry valley downstream of the swallow hole.
Other features of karst landscapes
Dolines/sinkholes - develops as rock collapses into underlying voids formed by carbonation.
Turloughs - Seasonal lakes that appear when underground passages fill with water during wet seasons, causing water to pool on the surface temporarily.