lipids
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
why are lipids non polar
because elections are evenly distributed
what is the biological roles of lipids
controlling fluidity of the cell membrane
electrical insulation
hormone production
waterproofing
what are triglycerides made off
one glycerol and 3 fatty acids
what is the general formula of triglycerides
CnH(2n+1)COOH
what’s the function of triglycerides
energy storage
thermal insulation (buoyancy, and around vital organs cushioning)
the long fatty acids chains release lots of energy when broken down.
what is glycerols
a small 3 carbon molecule with three alcohol groups (C3H8O3)
why are triglycerides good for energy store
they yield more energy per unit mass than other compounds so are good for energy storage
properties of fatty acids
fatty acids have a carboxyl group and a hydrocarbon chain
the chain can be from 14-22 carbon long
fatty acids have the same basic structure but the hydrocarbon tail varies
the tails are hydrophobic (they repel water molecules) therefore lipids are insoluble
what are saturated fats
they have no C=C bonds in the chain
this makes them saturated and straight chains
what are mono saturated fats
they have one C=C bond in the chain
this causes a kink and bends in the chain
bending in the chains means they cannot pack closely together
this makes them liquid at room temp
what are poly saturated fats
they have several C=C bonds
this makes them unsaturated
this causes kinks and bends in the chain
the bends lower the melting point
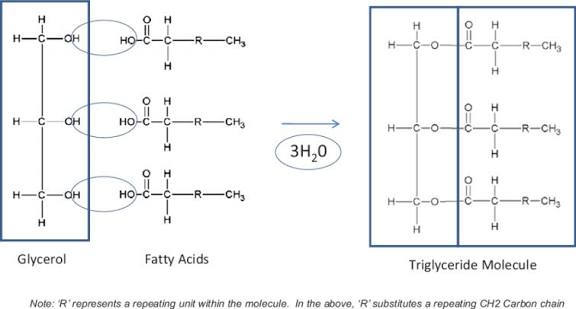
how are triglycerides formed
triglycerides are made of one glycerol and 3 fatty acids joined together
each hydroxyl group interacts to form an ester bond between the glycerol and each fatty acid
during the ester bond formation three water molecules are released
this reaction is called esterification
when triglycerides are broken down, 3 water molecules are needed to be supplied to reverse the reaction
structure of triglycerides
what are phospholipids
lipids with a phosphate group rather than a fatty acid chain.
what’s the property of the phosphate group in phospholipids?
it’s hydrophilic
what’s micelle
when mixed with water, phospholipids form droplet spheres
the hydrophilic head gave the water
the hydrophobic tails gave each other
this is called micelle
what’s a phospholipid bilayer
Made of phospholipids (hydrophilic heads + hydrophobic tails)
In water, tails hide from water, heads face water
Two layers form: tails inside, heads outside → bilayer
Basis of cell membranes; creates a semi-permeable barrier
what are sterols also known as
steroid alcohols
what are sterols
complex alcohol molecules based on a 4 carbon ring structure with a hydroxyl group at the end of
the hydroxyl group is polar and therefore hydrophilic
the rest of the molecules is hydrophobic
where is cholesterol made
it’s manufactured in the liver and intensifies.
what’s the function of cholesterol
it positions itself between the phospholipids in the membrane,
it adds stability to the membrane (fluid at low temp and not too fluid at high temp)
vitamins D, steroid, hormones and bile at
produced using cholesterol
what’s the steps for the emulsion test for lipids?
lipids do not dissolve in water but they do in ethanol to find out if there is fats in a sample, you do an emulsion test.
add ethanol to a test substance and shake throughly for about a minute so it dissolves
add water to the solution
if lipid is present, it will show as a milky emulsion. The more lipids, the more noticeable the milky colours will be.
(the rest can be improved by adding dye Sudan III, which will stain the lipids red)