Biology - Past Paper questions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
PAPER 2 (5/2/25)
PAPER 2 (5/2/25)
2b) Compare and contrast mitochondria and chloroplasts in terms of the substrates they use and the products they produce [2]
ATP produced by both
oxygen produced by chloroplasts and used by mitochondria
carbon dioxide produced by mitochondria and used by chloroplasts
carbon/organic compounds built up in chloroplasts (anabolism)
carbon/organic compounds broken down in mitochondria (catabolism)
2c) Outline how the compounds produced by chloroplasts are distributed throughout the plant [3]
compounds distributed using the phloem
loading into sieve tubes by active transport/by companion cells
entry of water to phloem by osmosis (due to high solute concentration)
causes high/hydrostatic pressure
flow from high pressure to lower pressure down the concentration gradient from source to sink
3a) Describe how the exchange of gases is brought about between the alveoli and the blood [3]
concentration of oxygen in the blood is lower than the concentration of oxygen in the air (blood arriving at the alveoli is deoxygenated)
oxygen moves into the blood by diffusion
oxygen moves down teh concentration gradient from the alveoli into the blood
During inhalation the concentration of oxygen in the alveoli increases establishing a concentration gradient
flow of blood in capillaries maintains concentration gradient
3b) Describe two features common to the exchange surfaces of alveoli and gills
rich capillary supply
large surface area
epithelium is one cell thick
moist surface
4b) Down syndrome is a genetic condition in which the cells of an individual contain three copies of chromosome 21. Explain how non-dijunction leads to trisonmy 21
sex cell contains one copy of chromosome 21
non-disjunction is when chromosomes do not separate during meiosis
for down-syndrome to occur the sex cells contain 2x copies of chromosome 21
chromosmes fail to separate in the first/second meiotic division
this sex cell with 2 copies, fertilizes normal sex cell with one copy of chromo 21
non-disjunction of chromosome 21 is more frequent in females and increases with age
5a) identify the recombinant phenotypes amongst the offspring
brown body, vestigial wings and black body, normal wings
unlinked genes
5b) Explain whether these results fit the predicted Mendelian ratios for this cross
No - Mendelian ratios are 1:1:1:1 wheras offspring phenotype ratios are 3:1:1:3
suggests linkage between genes
5c) Outline the statistical test that could be used to provide more evidence of the type of inheritance
chi-squared statistical test
compares expected ratios with real ratios
assume no sleective advantage to any of the genotypes
if tabulated value is exceeded then there is a significant difference
6a) Plasma cells (differentiated B cells) secrete antibodies against specific antigens. Outline how plasma cells become activated
macrophages/phagocytes engulf the pathogen and display the antigens
antigens bind to the T-helper cells
antigen binds to antibodies in membrane of the B cells
Activated T cells activate B cells
activated B cells divide to produce a clone of cells
active plasma cells develop from clone of cells
6b) A hybridoma is a cell produced by the fusion of a plasma cell with a tumour cell. Explain the advantages of using hybridoma cells in the production of monoclonal antibodies
endless cell divisions/unregulated mitosis
monoclonal antibodies are produced at a fast rate allowing the harvesting of antibodies
all cells in clone produce same type of antibody
large amount of chosen antibody can be produced
6c) State one use of monoclonal antibodies
pregancy testing - detection of hCG
producing antibodies for treating disease e.g. athritis or psoriasis - gives passive immunity
blood typing
testing urine for drugs
7a) Describe the genetic and hormonal control of male sexual characteristics in a human
male characteristics are determined genetically by XY chromosomes
gene on Y chromosome promotes development of the testes
testes secrete testosterone
testosterone stimulates sperm production
testosterone stimulates the development of male genitals/sexual characteristics in fetus
secondary sexual characteristics are determined by hormones e.g. testosterone
7b) Outline how the hormone auxin controls phototropism in plant shoots
auxin causes shoot to grow/bend towards the light
auxin moves from the light side to the shadier side
auxin is moved by auxin efflux pumps
auxin promotes cell elongation
more growth on shady side of stem due to auxin concentration gradient
auxin binds to auxin receptors in target cells
auxin promotes growth gene expression
7c) Toxins often act as inhibitors. Compare and contrast competitive and non-competitive enzyme inhibition
similarities:
slow down enzyme activity
interact with R chains of amino acids at the surface of the enzyme molecule
differences:
C inhibitor binds to active site, NC inhibitor binds to allosteric site
C - substrate cannot bind due to blocakge of active site/NC - substrate cannot bind due to change in shape of active site
C - inhibition is reversible/ NC - inhibition is permanent
C - inhibitor has similar shape to substrate
C - can be reversed by increasing substrate concentration / NC - adding substrate does not reuce inhibition
8b) Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal communication
Similarities
communication between cells/parts of the body
both cause response in target cells
both use chemicals that bind to receptors
both can stimulate/inhibit processes
both can work over long distances
both under overall control of brain/CNS
both use feedback mechanisms
Differences
chemical vs electrical
transported in blood vs neurons
slower vs faster
carried throughout body vs carried to specific cell
wide range of tissues affected vs only muscles/glands receive signals
long term vs short duration
8c) Describe barriers that exist to hybridisation between species
courtship behavior is complex and unique to species
rejection if characteristic behaviour not exhibited
species spefic egg feritilisation
sterility of hybrids
differences in chromosme number
PAPER 1 - MAY 2024 HL
PAPER 1 - MAY 2024 HL
What explains the movement of glucose molecules down a concentration gradient across the cell surface membrane?
They move through hydrophilic channels because they are polar
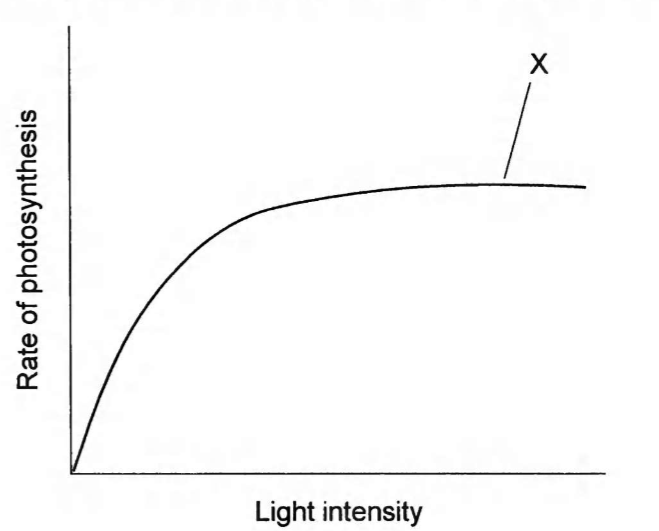
The graph shows the effect of increasing light intensity on teh rate of photosynthesis during an experiment carried out at optimum temperature and normal atmospheric CO2 concentration. Which factor could be limiting photosynthesis at point X?
carbon dioxide concentration
The Human Genome Project complete the sequencing of the human genome by the year 2003. Which could have been a source of the entire genome in humans?
The nucleus and mitochondria of a skin cell
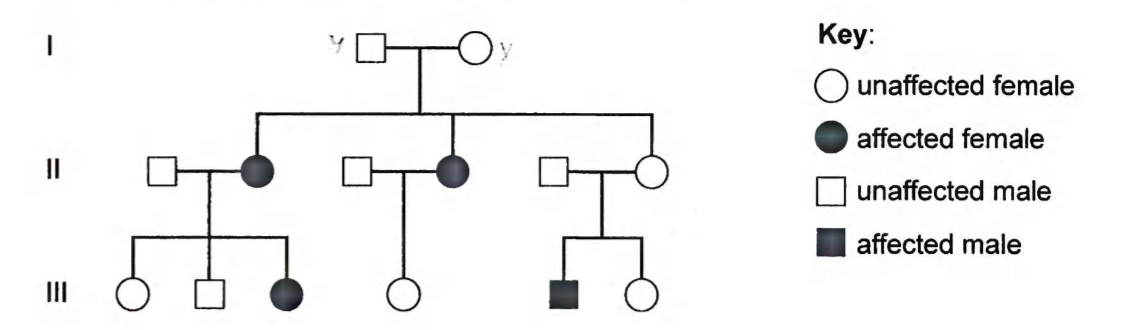
Nonsyndromic Hearling Loss and Deafness is an inherited cause of deafness in humans. The pedigree chart shows this inheritance in a family. Where is the allele found in family members with this condition?
on a pair of autosomes
What can be found in each band of a DNA profile?
Dna fragments with the same number of base pairs
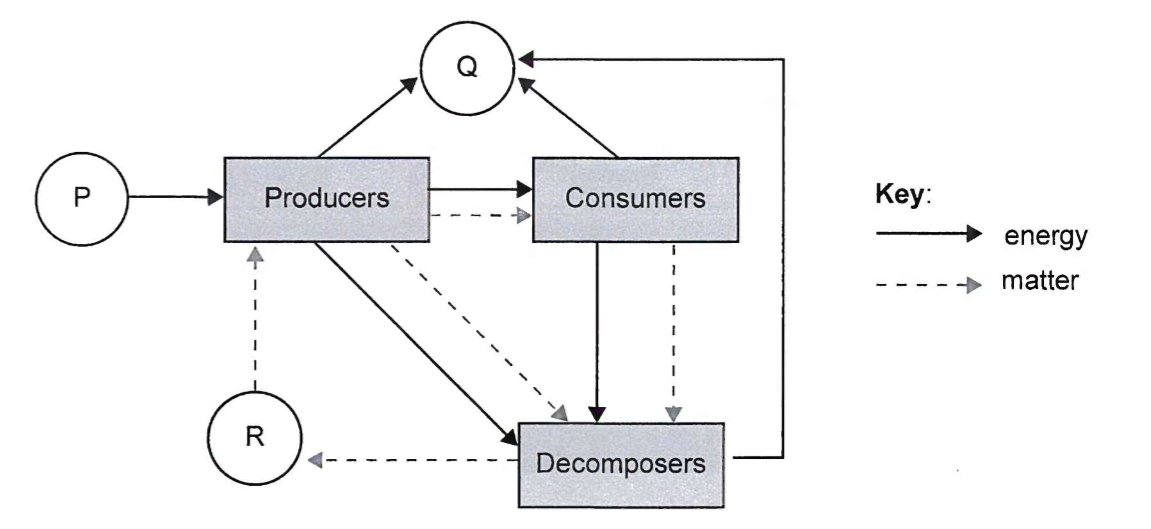
What do teh letters P, Q and R represent in an ecosystem?
P = Light
Q = heat
R = inorganic nutrients
how does lignin contribute to the transport of water up the stem? (xylem)
They allow xylem vessels to withstand low pressure
Which structures are sources and sinks? (potato)
source = tuber
sink = developing stems
NOV 2022 P2
NOV 2022 P2
2a) Identify the stage of meiosis where exchange of genetic material occurs
prophase 1
2b) Explain the reasons why the results do not agree with expected Mendelian rations in a dihybrid cross
a) gene linkage/genes located on the same chromosome
b) independent assortment does not occur
c) no recombination unless there is crossing over
3b) Explain how increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide contribute to global warming
carbon dioxide absorbs long wave/infra-red radiation
more heat trapped in/less heat escapes atmosphere with more carbon dioxide
short wave/UV radiation from the sun passes through the atmosphere and reaches earth’s surface
radiation from the sun/sunlight warms the surface of the Earth
long wavelength/infrared radiated from the warmed Earth’s surface
4b) Outline how nucleosomes affect the transcription of DNA
can promote and inhibit the transcription of genes
nucleosomes can prevent transcription by condensation/supercoiling of DNA
nucleosomes can allow or prevent the binding of RNA polymerase or transcription factors
acetylation/methylation of nucleosomes/histones can respectively promote/inhibit transcription
movement of histones/nucleosomes along DNA can affect which genes are transcribed
4c)i) Which enzyme copies the DNA sequence
RNA polymerase
4d) Explain the role of lactose in the expression of the gene for lactase production
a) lactose binds to repressor protein
b) repressor protein with lactose bound cannot bind to the promoter
c) RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and transcribes gene
d) lactase producedif lactose is present/lactase production inhibited if lactose is absent