Unit 6 APHUG Vocab
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/71
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1
New cards
site
the relationship between a city and the physical environment and landscape in which it is located (specific spot)
2
New cards
situation
the relationship between a city and the rest of the urban system in which it is located (where is it in relation to another place/building)
3
New cards
urbanization
the process by which the population of urban settlements grows
4
New cards
business services
the purpose of this is to facilitate the activities of other businesses (ex. transportation services, financial services, etc)
5
New cards
consumer services
the purpose of this is to provide services to individual consumers who desire them and can afford to pay for them (ex. retail, health, education)
6
New cards
public services
the purpose of this is to provide security and protection fir citizens and businesses (ex. police, construction)
7
New cards
service
any activity that fulfills a human need or want and returns money to those who provide it
8
New cards
settlement
a permanent collection of buildings where people reside, work, and obtain services
9
New cards
globalization
the process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale
10
New cards
megacity
a very large city, typically with a population of more than 10 MILLION PEOPLE (ex. tokyo, japan )
11
New cards
metacity
often centers of innovation and creativity, and they often have a significant influence on global trends and issues - major political, economic, and cultural centers on the globe (ex. london) - POPULATIONS OVER 20 MILLION
12
New cards
world city (global)
a dominant city in terms of its role in the global political economy: center of the flow of information and capital (ex. new york city, london, tokyo)
13
New cards
borchert model of urban growth
focuses on the development of cities in relation to the development of transportation and communication
14
New cards
central place theory
helps to explain how the most profitable location can be identified - the idea was proposed in 1930 but was further developed in the 1950s
15
New cards
food desert
an area that has a substantial amount of low-income residents and has poor access to a grocery store or healthy foods - defined as more than one mile away due to the fact that these residents most likely do not own cars
16
New cards
gravity model
a model that predicts the optimal location of a service and is directly related to the number of people in the area and inversely related to the distance people must travel to access it
17
New cards
law of the primate city
the largest settlement has more than twice as many people as the second ranking settlement - (example: mexico, its largest city is mexico city and it is 5 times larger than is second largest settlement, Guadalajara)
18
New cards
market area/hinterland
the surrounding area of a service from which customers are attracted
19
New cards
range
the maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service - typically the radius of a circle drawn to delineate a services market area
20
New cards
rank-size rule
population of a settlement that is inversely proportional to its rank in the urban hierarchy
21
New cards
threshold
the minimum number of people needed to support a service - every enterprise has a minimum number of sales required to generate profit
22
New cards
urban hierarchy
ranking of cities, with the largest and most powerful cities at the top of the hierarchy
23
New cards
central business district (CBD)
downtown is the most popular term of this area but it can aso be known as _____ ________ _____ to geographers
24
New cards
qualitative data
non-numeric information, such as in-depth interview transcripts, diaries, anthropological field notes, answers to open-ended survey questions, audio-visual recordings and images
25
New cards
quantitative data
data that can either be counted or compared on a numeric scale
26
New cards
african city model
a generalized diagram of an urban area in sub-Saharan Africa that contains pre-colonial, European colonial, and post-colonial elements and is or was segregated by race
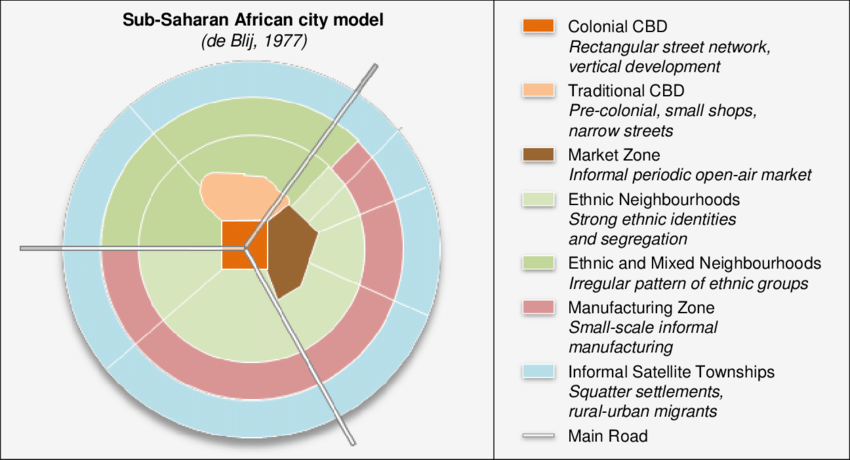
27
New cards
bid rent theory
a geographical economic theory that refers to how the price and demand for real estate change as the distance from the central business district increases
28
New cards
burgess concentric-zone model
a city grows outward form a central area in a series of concentric rings, like the growth rings of a tree
29
New cards
census tract
urban areas in the US are divided into these and each contain approximately 5,000 residents and correspond to neighborhood boundaries
30
New cards
disamenity zones
the very poorest parts of cities that in extreme cases are not even connected to city services (amenities) and are commonly controlled by gangs and drugs
31
New cards
edge cities
the nodes of consumer and business services around the beltway - originated as suburban residences for people who worked in the central city and then shopping areas were built to be near the residents
32
New cards
galactic city model (peripheral model)
an urban area consists of an inner city surrounded by large suburban residential and service nodes tied together by a beltway or ring road
33
New cards
harris-ullman multiple-nuclei model
the theory that a city is a complex structure that includes more that one center around which it revolves
34
New cards
high density housing
real estate developments that have a higher population than average
35
New cards
hoyt sector model
developed in 1939 - a city develops in a series of sectors - as the city grows, activities expand outward in a sector from the center
36
New cards
infrastructure
the basic physical and organizational structures and facilities (buildings, roads, power supplies) needed for the operation of a society or enterprise
37
New cards
latin american city model
a combination of elements of Latin American Culture and globalization by combining radial sectors and concentric zones
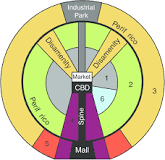
38
New cards
low density housing
residential areas occupied primarily by single-family homes or buildings with a small number of units
39
New cards
medium density housing
a category of residential development that falls between detached suburban housing and large multi-story buildings
40
New cards
southeast asian city model
features high-class residential zones that stem from the center, middle-class residential zones that occur in inner-city areas, and low-income squatter settlements that occur in the periphery
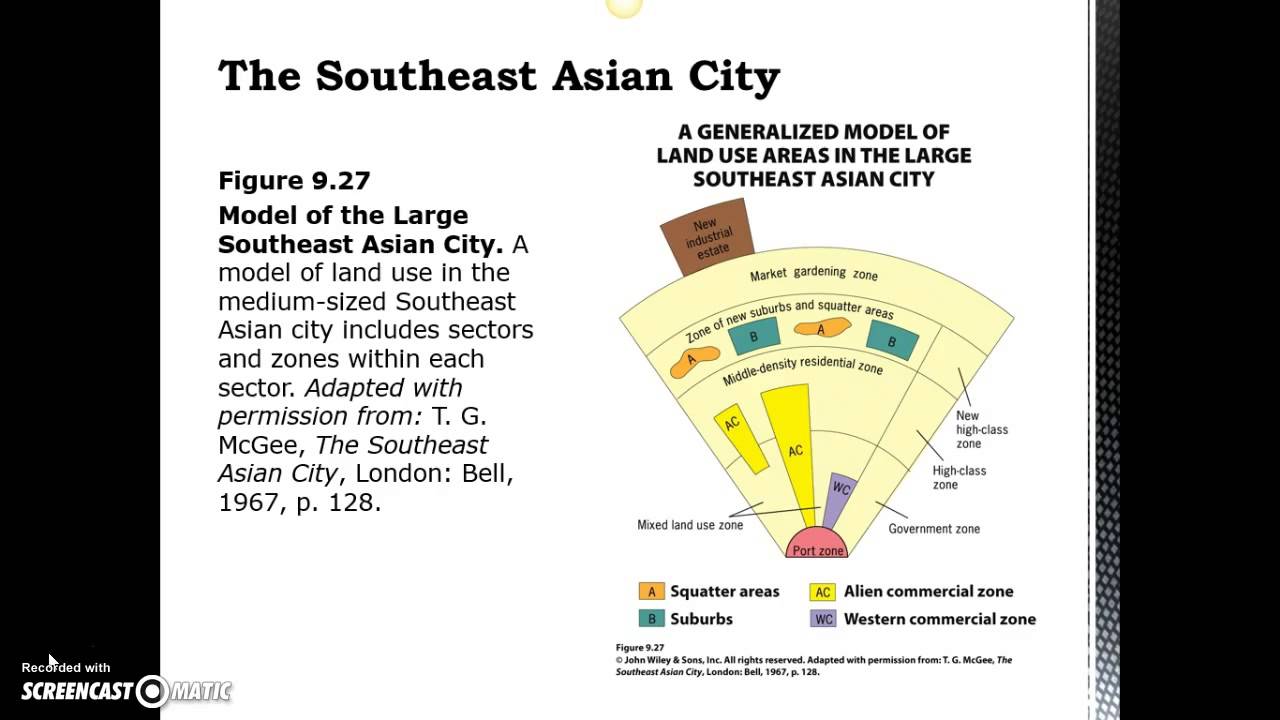
41
New cards
zones of abandonment
areas that have been deserted in a city for economic or environmental reasons - lack of desirable features in this area
42
New cards
boomburbs
an outlying residential community of a city that is expanding and growing rapidly
43
New cards
decentralization
the transfer of control over an activity or organization to several local groups instead of one single one
44
New cards
exurbs
a district outside of a city, beyond the suburbs
45
New cards
fragmentation (of governments)
the process of breaking or being broken into smaller, separate parts
46
New cards
greenbelts
an area of open land outside of a city that has laws saying building is restricted
47
New cards
infilling
development of vacant areas within existing urban areas
48
New cards
megacities
a large city, typically with a population over 10 million
49
New cards
megalopolis
a greek word meaning a “great city” - is very heavily populated
50
New cards
mixed land use
the integration of residential, commercial, and industrial land uses that allows them to all work together and function together
51
New cards
new urbanism
a planning and development approach based on the principals of how cities and towns had been built for the past several centuries - promotes being environmentally friendly
52
New cards
slow growth cities
urban communities where the planners have put into place smart growth initiatives to decrease the rate at which the city grows horizontally to avoid the adverse affects of sprawl
53
New cards
smart growth (policies)
legislation’s and regulations that have been made to limit suburban growth and preserve farmland
54
New cards
sprawl
the development of suburbs at relatively low density and at locations that are not contiguous to the existing built-up area
55
New cards
suburb
a residential or commercial area situated within an urban area but outside the central city
56
New cards
suburbanization
a population shift from central urban areas to the suburbs of a city
57
New cards
sustainable design initiatives
the plan to reduce negative impacts on the environment, and the health and comfort of building occupants, thereby improving building performance
58
New cards
transportation oriented development
a type of urban development that maximizes the amount of residential, business and leisure space within walking distance of public transport
59
New cards
urban growth boundaries
a regional boundary, set in an attempt to control urban sprawl by mandating the area inside the boundary be used for urban development and the area outside be preserved in its natural state or used for agriculture
60
New cards
walkability
a term for planning concepts best understood by the mixed-use of amenities in high-density neighborhoods where people can access said amenities by foot - USE LESS CARS!!
61
New cards
zoning ordinance (practices)
a law that limits the permitted uses of land and maximum density of development in a community
62
New cards
blockbusting
a business practice in the united states in which real estate agents and building developers convinced white residents in a particular area to sell their property at below-market prices “for fear of another ethnic group moving in”
63
New cards
brownfields
real property, the expansion, redevelopment, or reuse of which may be complicated by the presence or potential presence of a hazardous substance, pollutant, or contaminant
64
New cards
de facto segregation
\
65
New cards
farmland protection policies
law made by the governments that protects farmland and prevent it from being sold into other use
66
New cards
filtering
when houses pass from one social group to another as new housing is built and higher incomes move into it, leaving behind older housing stock for lower incomes
67
New cards
gentrification
the process of renewal and rebuilding accompanying the influx of middle-class into deteriorating areas that often displaces poorer residents
68
New cards
inclusionary zoning
municipal and county planning ordinances that require a given share of new construction to be affordable by people with low to moderate incomes - the planning of housing ordinances and new constructive
69
New cards
local food movements
movements that aim to connect food producers and consumers in the same geographic region, to develop more self-reliant and resilient food networks; improve local economies; or to affect the health, environment, community, or society of a particular place
70
New cards
redlining
a racially discriminatory and, now, illegal practice of devaluing homes in racially mixed or neighborhoods with few or no white residents
71
New cards
squatter settlements
a collection of buildings aimed to provide housing and shelter for poor people in a city - the people living in these do not have legal rights on the land and therefore live there illegally usually without sanitation and other basic household needs
72
New cards
urban renewal
the redevelopment of areas within a large city, typically involving the clearance of slums