Penn Foster Orientation to HVACR
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Comfort Control
Management of temperature, humidity, air filtering, airflow.
Heating Systems
Devices for warming indoor spaces, central or separate.
Central Heating System
Forced air system, can be electric or gas.
Wall Mounted System
Baseboards or radiators using hot water or steam.
Hydronic System
Uses heated water from a boiler for warmth.
Warm-Air Distribution System
Transfers heat via air movement throughout spaces.
Ducted Warm-Air System
Forced warm air distribution through ducts.
Heat Exchanger
Transfers heat from burner to air in furnace.
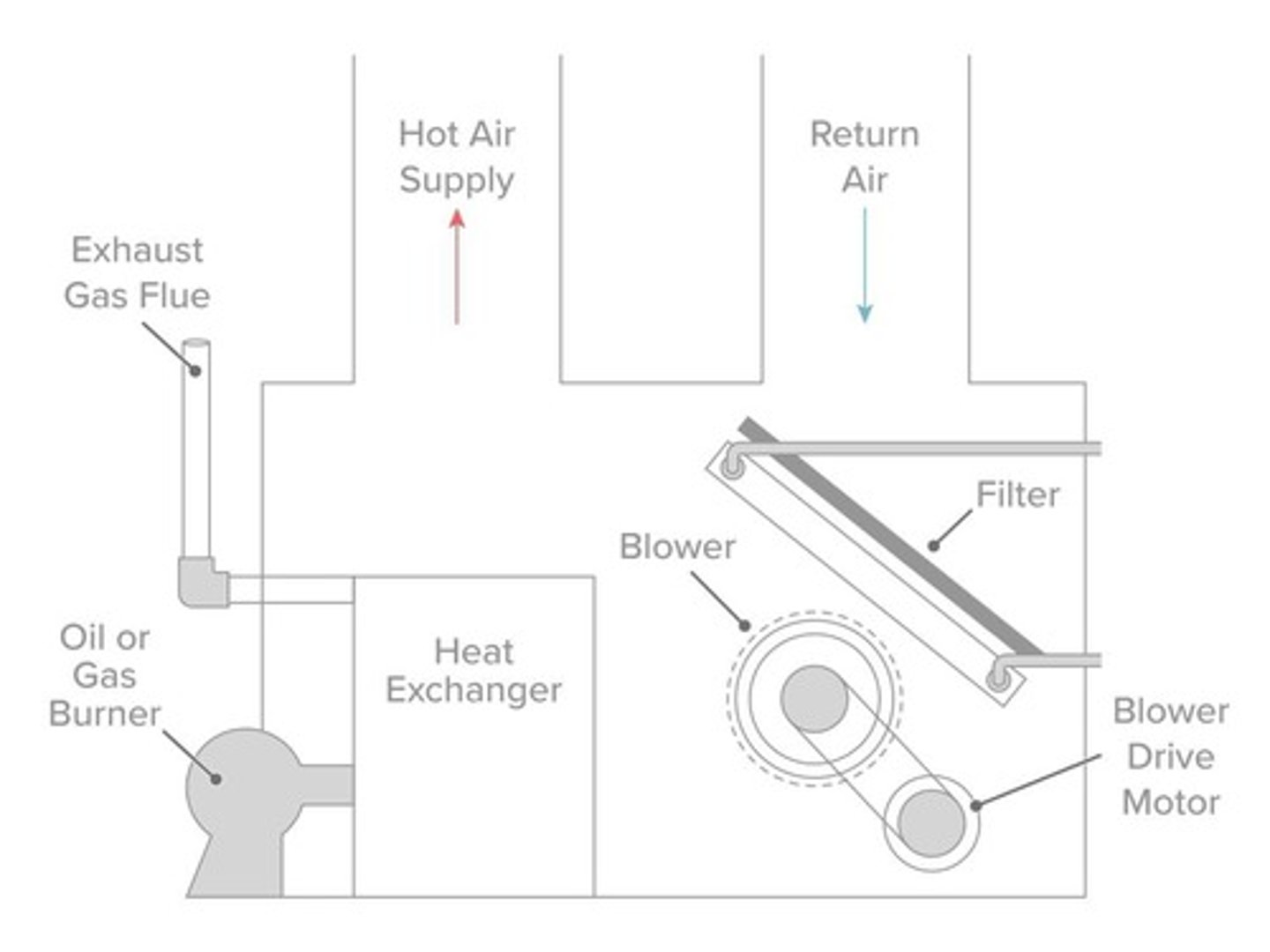
Blower
Fan that circulates heated air through ducts.
Supply Plenum
Pathway for distributing heated air to rooms.
Return Plenum
Pathway for returning air to be reheated.
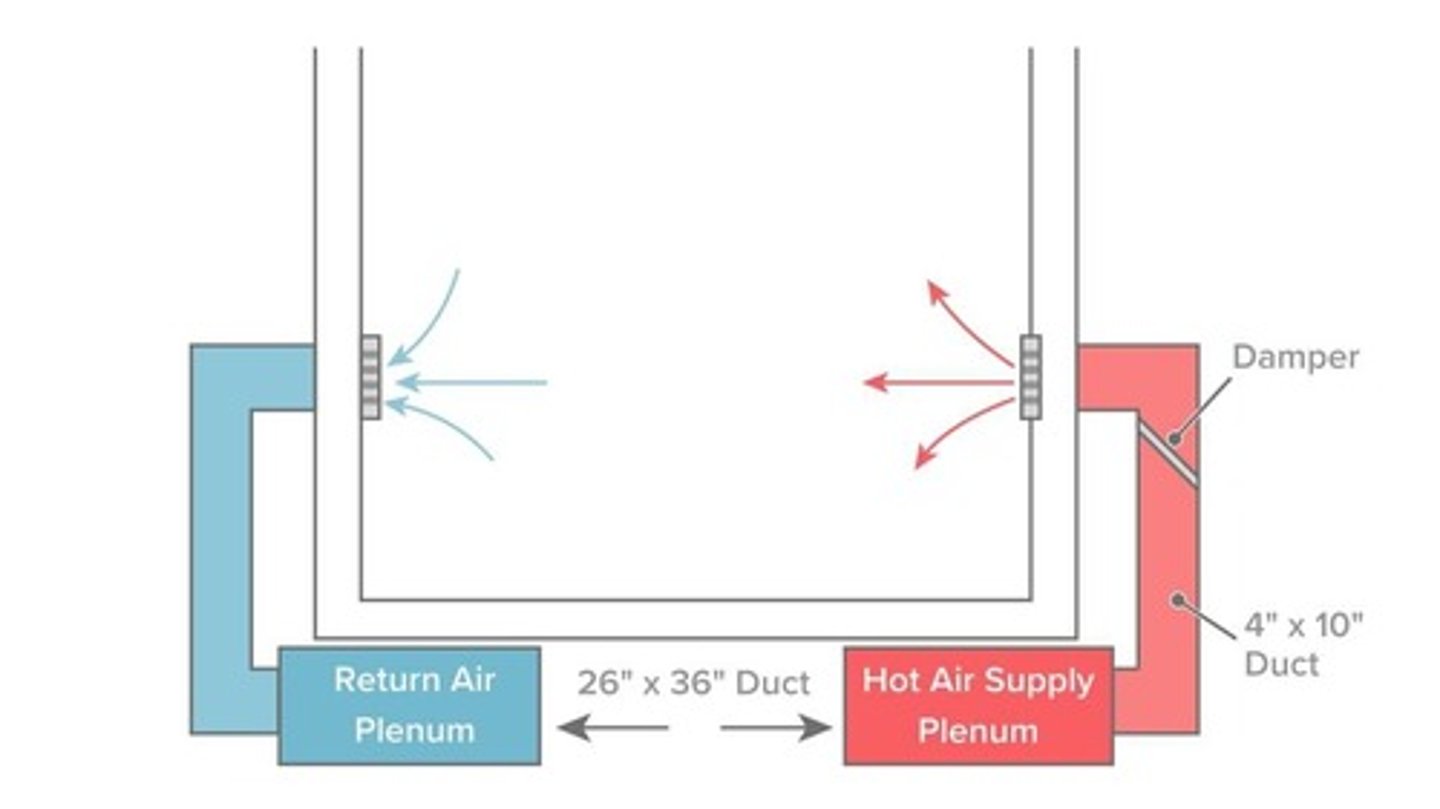
Damper
Controls airflow in supply duct for rooms.
Central Air Conditioning
System for cooling using evaporator and refrigerant.
Evaporator Coil
Cools air by absorbing heat into refrigerant.
Heat Pump
Device that can heat or cool a space.
Humidity Control
Regulates moisture levels in indoor air.
Bypass System
Adds humidity by circulating water into airflow.
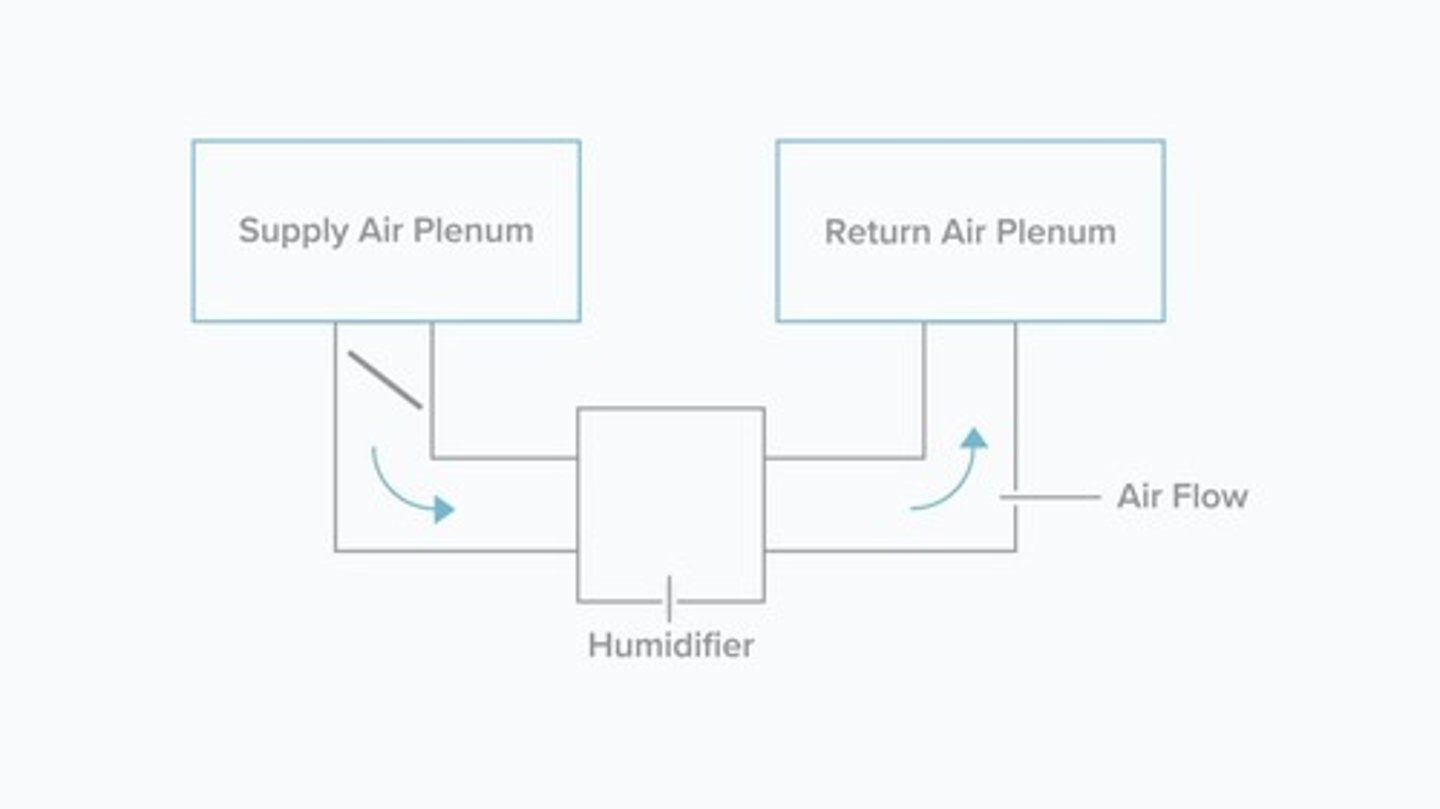
Humidistat
Device controlling damper in humidity systems.
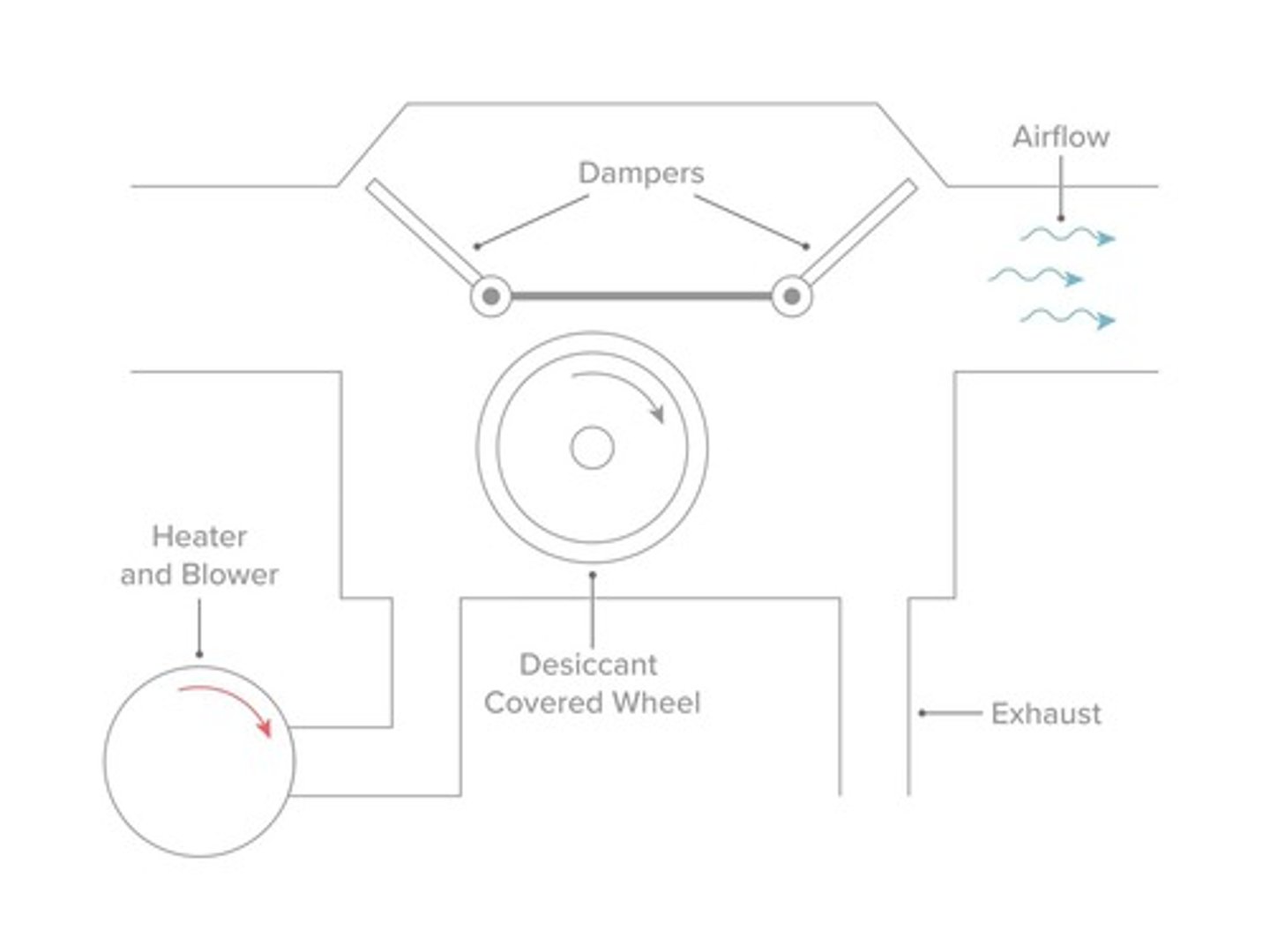
Desiccant
Material that absorbs moisture from the air.
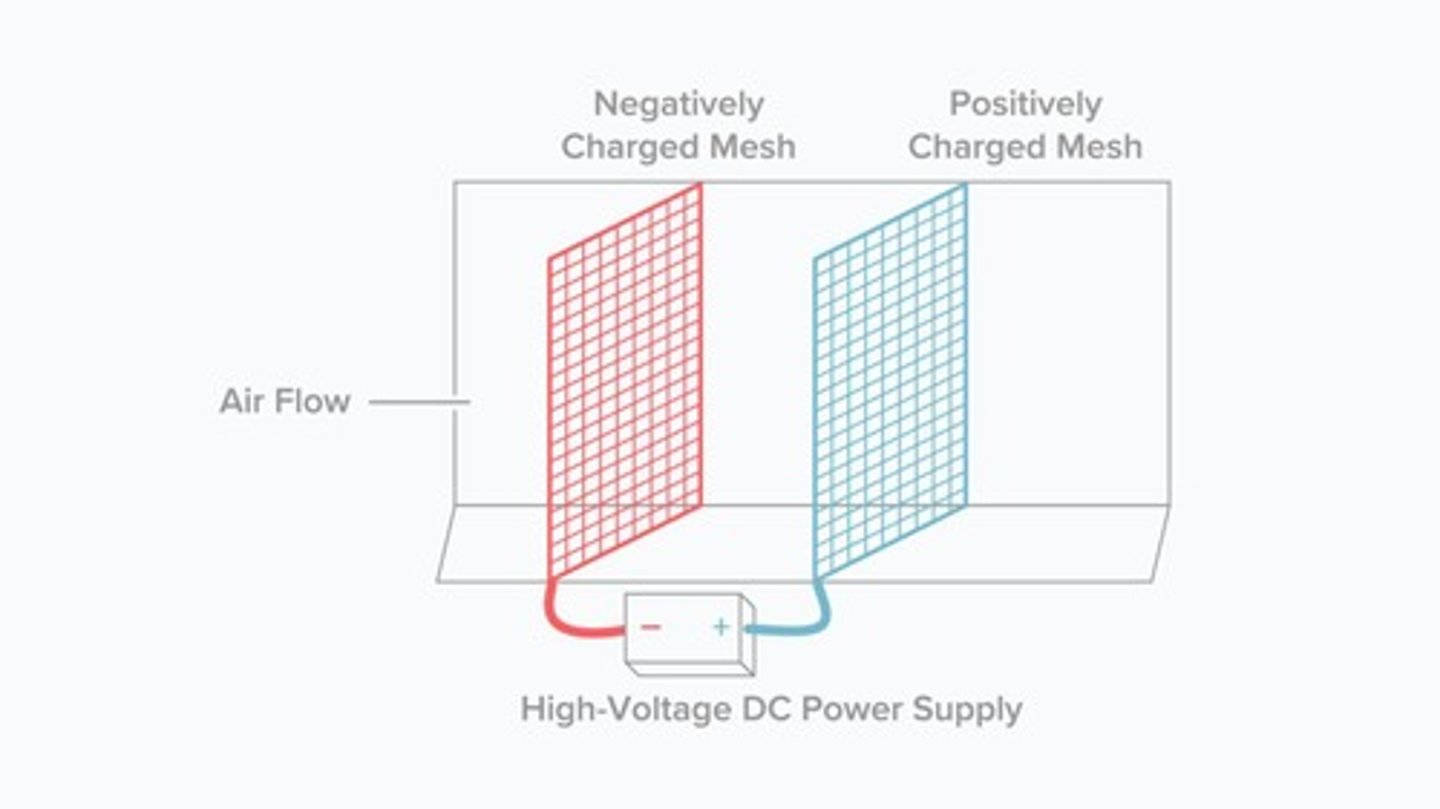
Electrostatic Filter
Uses charged screens to trap air impurities.
Pleated-Paper Filter
Common filter type with increased surface area.
Reusable Filter
Foam or metal-mesh filters for multiple uses.
Electrostatic Precipitator
Air-cleaning unit using charged mesh screens.
Moisture Removal Process
The process of extracting moisture from the air to maintain humidity levels.
Heating System Types
Includes baseboard, radiant, and air-movement systems.
Fossil Fuel Heating
Uses coal, gas, or oil for heating.
Air Filtering Systems
Removes impurities from indoor air.
Centrifugal Chiller
Device used to cool water for air-conditioning.
Refrigeration Cycle
Process involving compressor, condenser, and cooler.
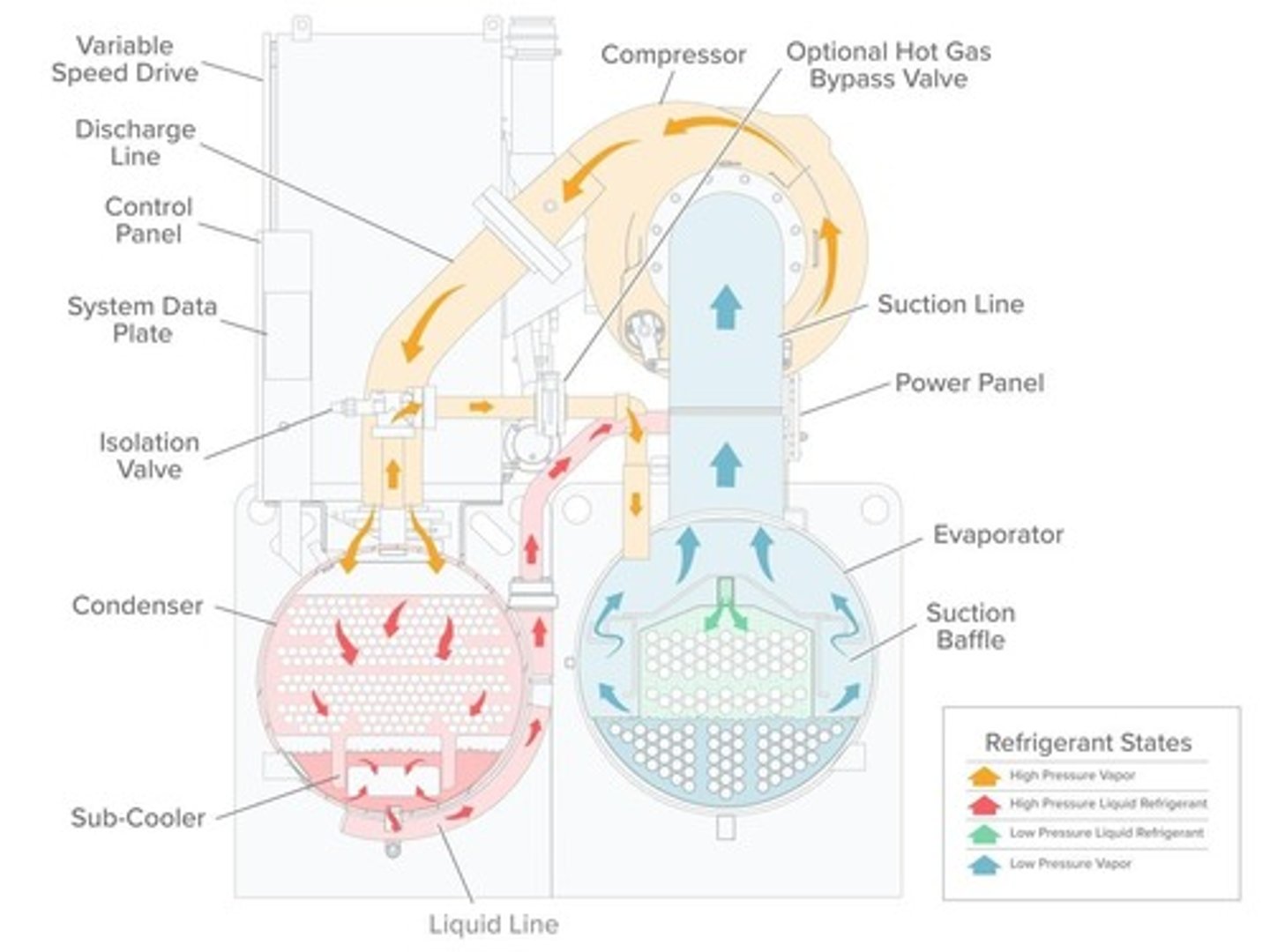
Compressor
Motor-driven component compressing refrigerant in chiller.
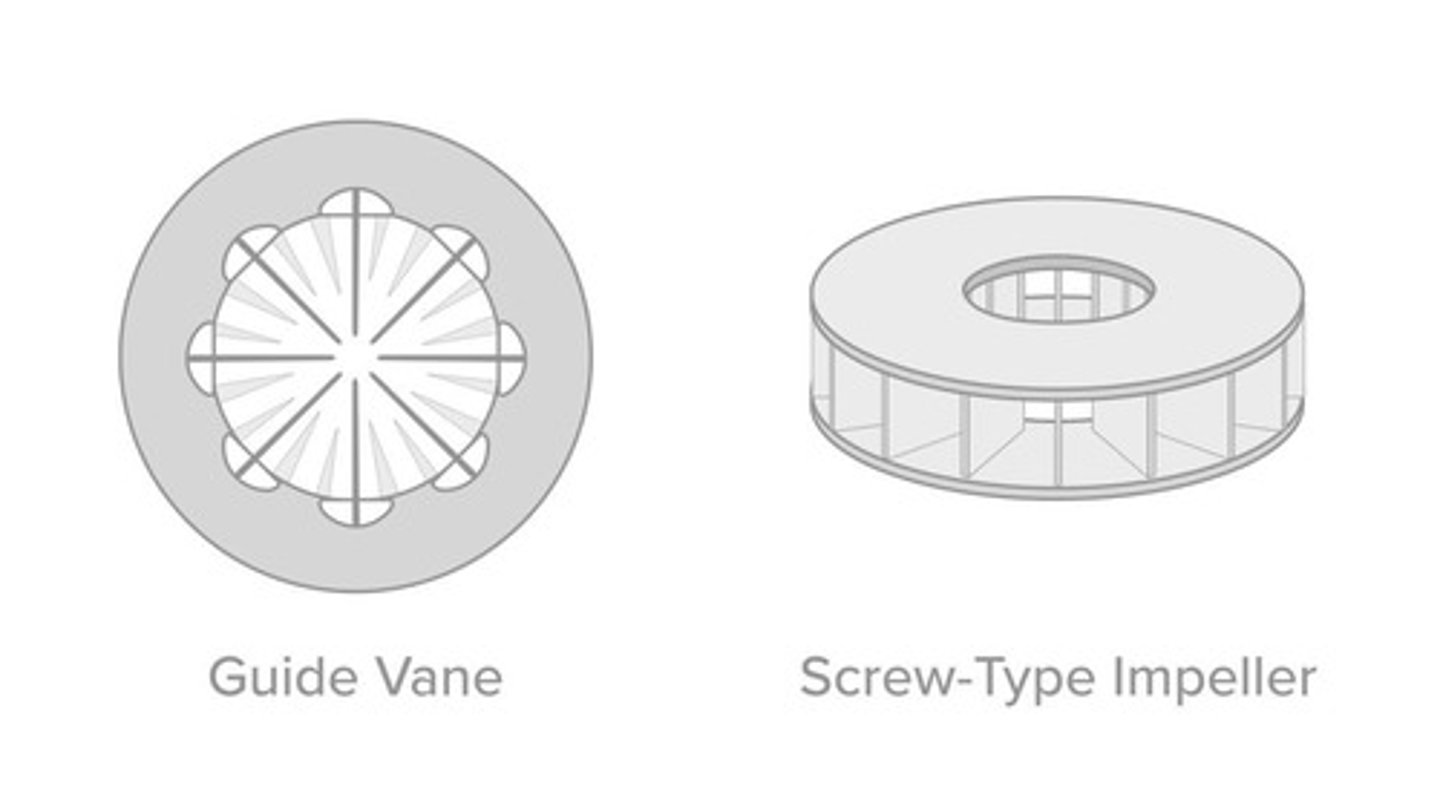
Impeller
Rotating component increasing refrigerant pressure.
Guide Vanes
Direct refrigerant flow into the impeller.
Condenser
Component where refrigerant loses heat.
Cooling Tower
External source cooling the condenser's water.
Refrigerant
Fluid used to transfer heat in chillers.
High-Capacity Chiller
Chiller type commonly found on commercial rooftops.
Condenser Fans
Fans used to dissipate heat from refrigerant.
Variable Air Volume (VAV)
System controlling airflow in air distribution.

Air Terminal
Device delivering conditioned air to spaces.
Diffusers
Devices distributing air evenly in a room.
Return Air Ducts
Ducts returning used air to chiller.
Thermostat
Device regulating temperature by controlling dampers.
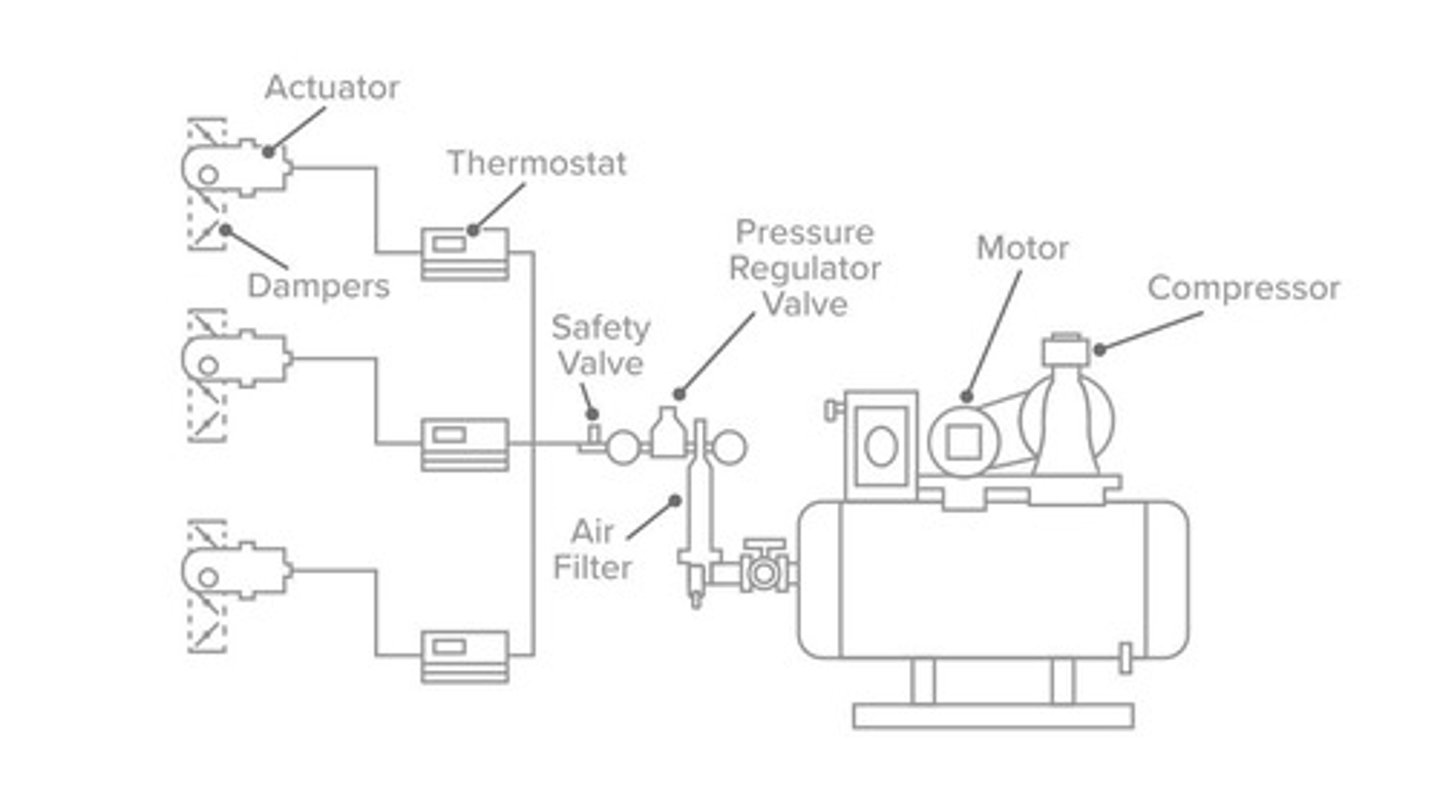
Pneumatic System
System using compressed air for control functions.
Pneumatic Control System
System regulating air flow with pneumatic thermostats.
Direct Digital Control (DDC)
Electronic system managing HVAC operations intelligently.
Communication Bus
Wiring system connecting DDC components.
Thermistor
Temperature sensor changing resistance with temperature.
Humidistat
Device measuring humidity in the air stream.

Pressure Sensor
Device monitoring airflow within the system.

Air Handling Unit
Unit conditioning air before distribution.
Electric Heating Elements
Components heating air in air terminals.
Dampers
Valves controlling airflow in ducts.
Mechanical Refrigeration System
Transfers heat from low to high temperature.
Latent Heat
Heat generated during phase changes of substances.
Compressor
Pressurizes gaseous refrigerant for circulation.
Condenser
Releases heat from refrigerant to surrounding air.
Metering Device
Lowers pressure of liquid refrigerant.
Evaporator
Absorbs heat, converting refrigerant to gas.
Heat Pump
Regulates indoor temperature by transferring heat.
Cooling Function
Removes heat and discharges it outside.
Heating Function
Draws heat from outside to warm indoors.
Reversing Valve
Changes refrigerant flow direction for heating or cooling.
Efficiency Enhancements
Utilizes solar, lake water, or geothermal sources.
Dual-Fuel Heat Pump
Combines electric and natural gas heating.
Evaporative Cooling
Uses evaporation to provide cool, dehumidified air.
Desiccant Dryer
Removes excess moisture after evaporative cooling.
Air Conditioning System
Consists of compressor, condenser, expansion device, evaporator.
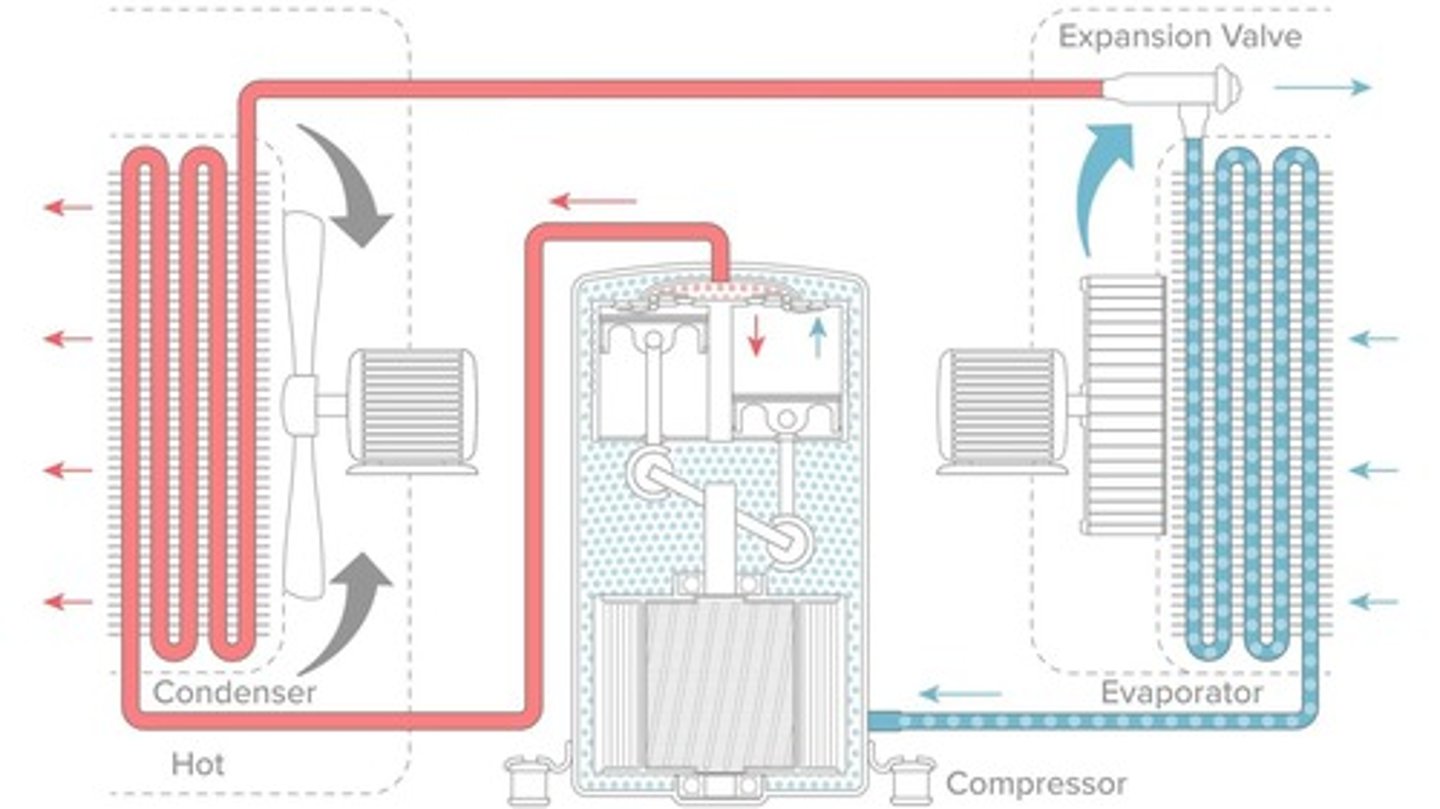
Summer Operation
Evaporator cools while condenser absorbs heat.
Winter Operation
Evaporator absorbs heat; condenser discharges indoors.
Transfer Valve
Automatically reverses heat pump functions.
Environmentally-Friendly Cooling
Uses evaporating water for natural cooling.
Building Integration
Evaporative cooling systems fit into architecture.
Components of Comfort Control
Temperature. Humidity. Air Filtration. Air-volume management.
Heating Systems Include . . .
Wood. Gas. Oil. Electric. Solar. Heat pumps. Geothermal.
BTU
The amount of energy needed to heat one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit [British Thermal Unit]
BTUH
British thermal units per hour
COP
Coefficient of Performance. The ratio of Total heat output divided by heat input
HSPF
Heating Seasonal Performance Factor. Rates a heat pump on its efficiency in its heating mode
What does SEER stand for?
Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. The cooling delivered by equipment per dollar spent on electricity
Ton
A ton of air conditioning or refrigeration is equal to 12,000 BTU.
Entry-Level Helper
A first-year helper may be an apprentice who provides help to the senior technician in the field while servicing and installing HVACR equipment or systems.
Rough-in Installer
"Rough-in" is the initial HVACR system installation process, and the workers typically consist of first- through third-year technicians.
Start-Up Technician
Once a new system has been installed, a fourth- or fifth-year technician will go through the manufacturer's procedures for start-up.
Service Technician
A service technician has at least four years of field experience and provides individual system owners with repairs and maintenance.
Equipment Operator
Equipment operators are responsible for the safe operation of large commercial and industrial HVACR plants. They typically must hold a state or city license
Facility Maintenance Personal (FMP)
FMP are Responsible for planned and routine minor service on commercial equipment. They may perform duties on other facility equipment and be part of a crew.
Service Manager
This is a highly skilled technician with several years of experience who is responsible for overseeing the operation of an HVACR company.
System Designer
These contractors size and design HVACR systems for small to large buildings based on industry standard and design guidelines.
Sales
These workers specialize in either inside or outside sales. Inside sales technicians focus on parts and equipment for individual contractors. Outside sales technicians focus on parts and equipment for facility owners and contractors.
The Watkins have an air conditioner with oil furnace system in their home. When it's time to cool the house, they turn off the furnace's oil burner, which then turns on the air-conditioning system. This will supply _______ to the evaporator coil.
Liquid Refrigerant
Ryan is an HVACR technician repairing the compressor on a refrigeration system. In what form is the system’s refrigerant as it enters the compressor at its inlet?
Vapor
Kelsey is seeking a career as an HVACR technician. What certification must she have before she can start working?
EPA 608
Michael and his team of HVACR technicians are installing a high-capacity chiller on the roof of a warehouse. They've installed a large duct that will deliver the cooled air to a main distribution plenum that runs down the center of the building. How will the air be further distributed from there?
VAV Air Terminal
Ron is installing registers for a hot-air heating system. Where are these being placed?
The Walls
Sebastian is doing work at an older industrial plant that still uses a pneumatically controlled system. What component of the system supplies the clean air and opens or closes the valves depending on the room temperature?
Thermostats
The Galvins want to modernize their home's heating system. Their current system is hydroponic and fueled by fossil fuels. What are the four most widely used fossil fuels?
Coal, Natural Gas, Propane, Fuel Oil
Paula is a technician working on the HVAC system at a mall that's controlled by a digital direct control system. She's checking area conditions with a type of electronic sensor that changes its resistance based on temperature. What's the sensor?
Thermistor
An HVACR service technician is applying a desiccant to a device in the heating system. What component of the system is the technician working on?
Humidity Control
What component of a hot air system controls the air flow through a duct?
Damper