Section 7: Shoulder complex
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Shoulder joint is attached to the...
axial skeleton
Scapula movement occurs with the movement of the
humerus
The wide ROM of the shoulder joint in multiple planes requires....
laxity
Common instability problems of the shoulder
Rotator cuff impingement, subluxations, dislocations
Joints that are more mobile are less ______
stable (and opposite- more stable, less mobile)
What bones serve as an attachment for shoulder joint muscles?
scapula, clavicle, and humerus
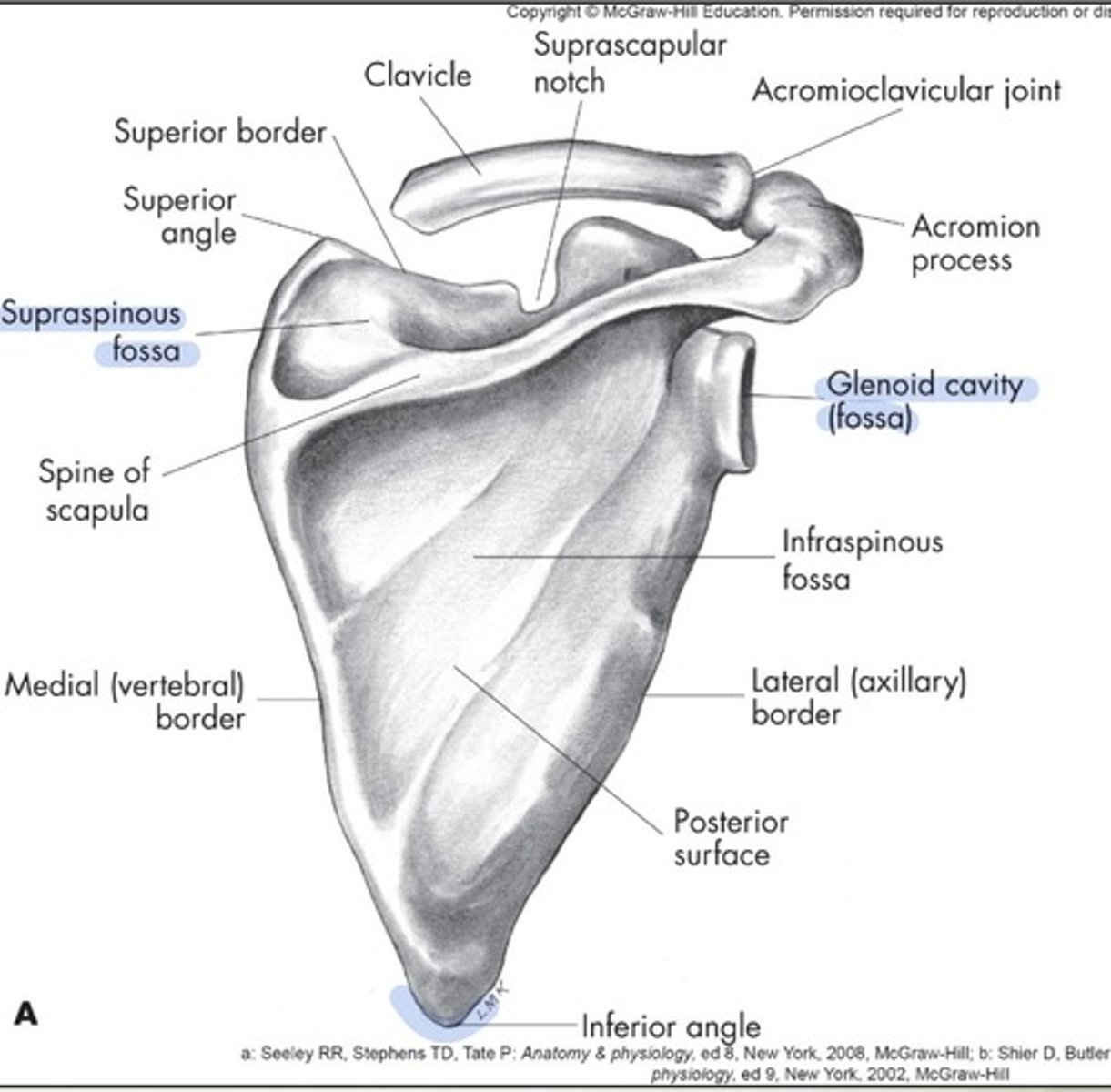
Scapular landmarks
supraspinous fossa, infraspinous fossa, subscapular fossa, spine of scapula, glenoid cavity, coracoid process, acromion process, superior and inferior angle, and medial border
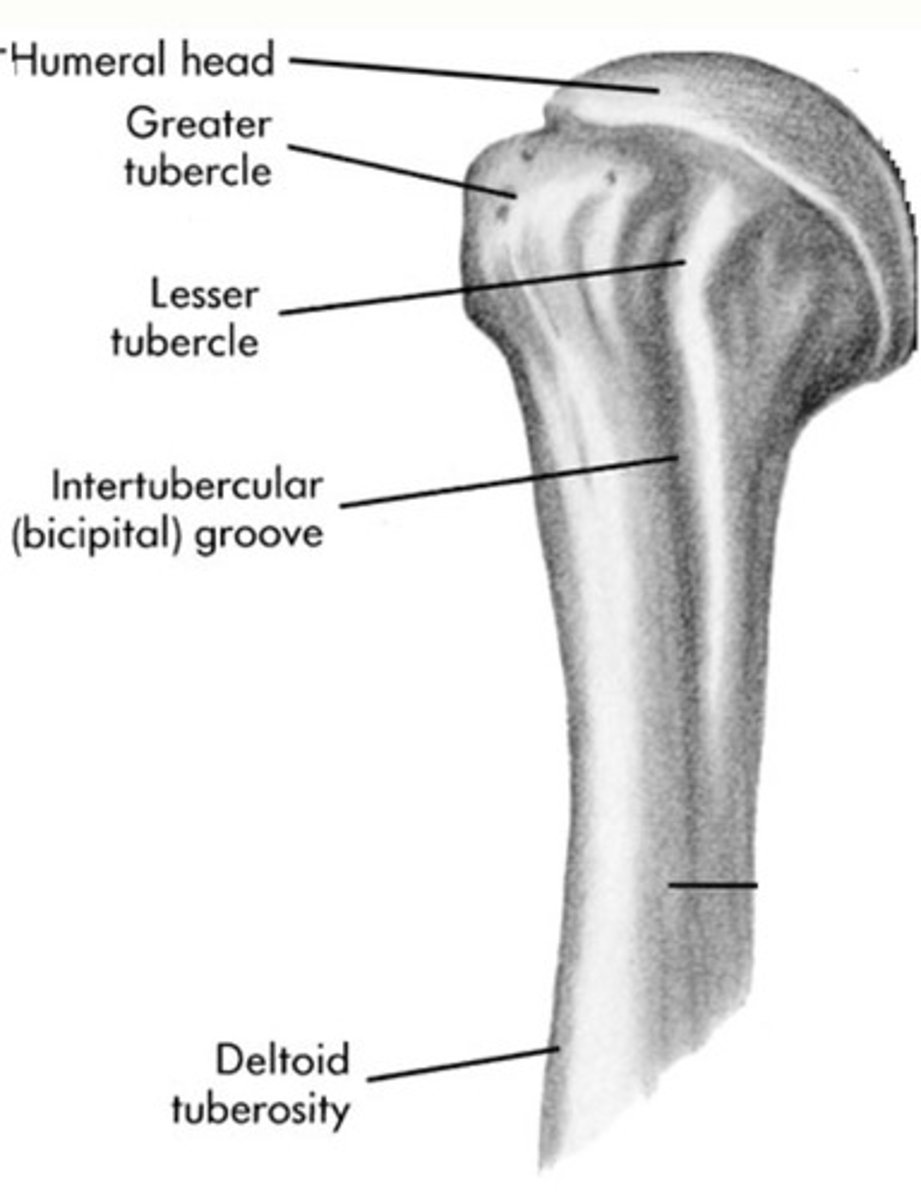
Humeral landmarks
Humeral head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, bicipital groove, deltoid tuberosity
The GH joint (shoulder joint) is a
multi axial ball and socket and enarthrodial
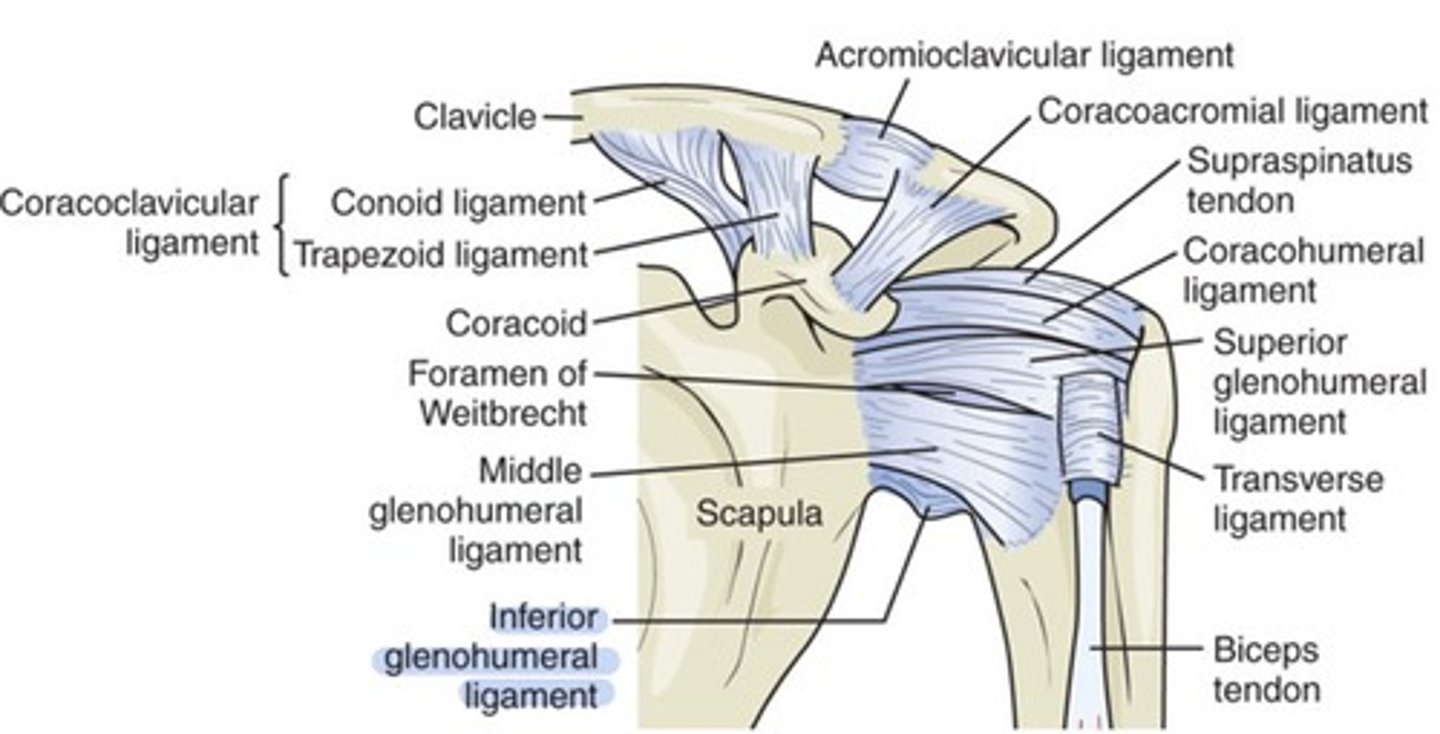
What ligament enhances stability in the shoulder
Glenoid Labrum
Glenohumeral ligaments provide stability... (position)
anteriorly and inferiorly
Inferior GH ligament
Glenohumeral joint is paired with shoulder girdle to accomplish...
total shoulder ROM
170-180 degrees of total shoulder abduction includes
60 degrees scapula upward rotation, 0-25 degrees scapula elevation, 95-120 degrees of gh abduction
Scapulohumeral rhythm ratio
2:1. for every 2 degrees of glenohumeral motion, 1 degree of scapula motion
Scapula position
20-30 degrees anteriorly angled. scapula can achieve adequate ROM when it sits appropriately.
GH flexion
40-60 degrees
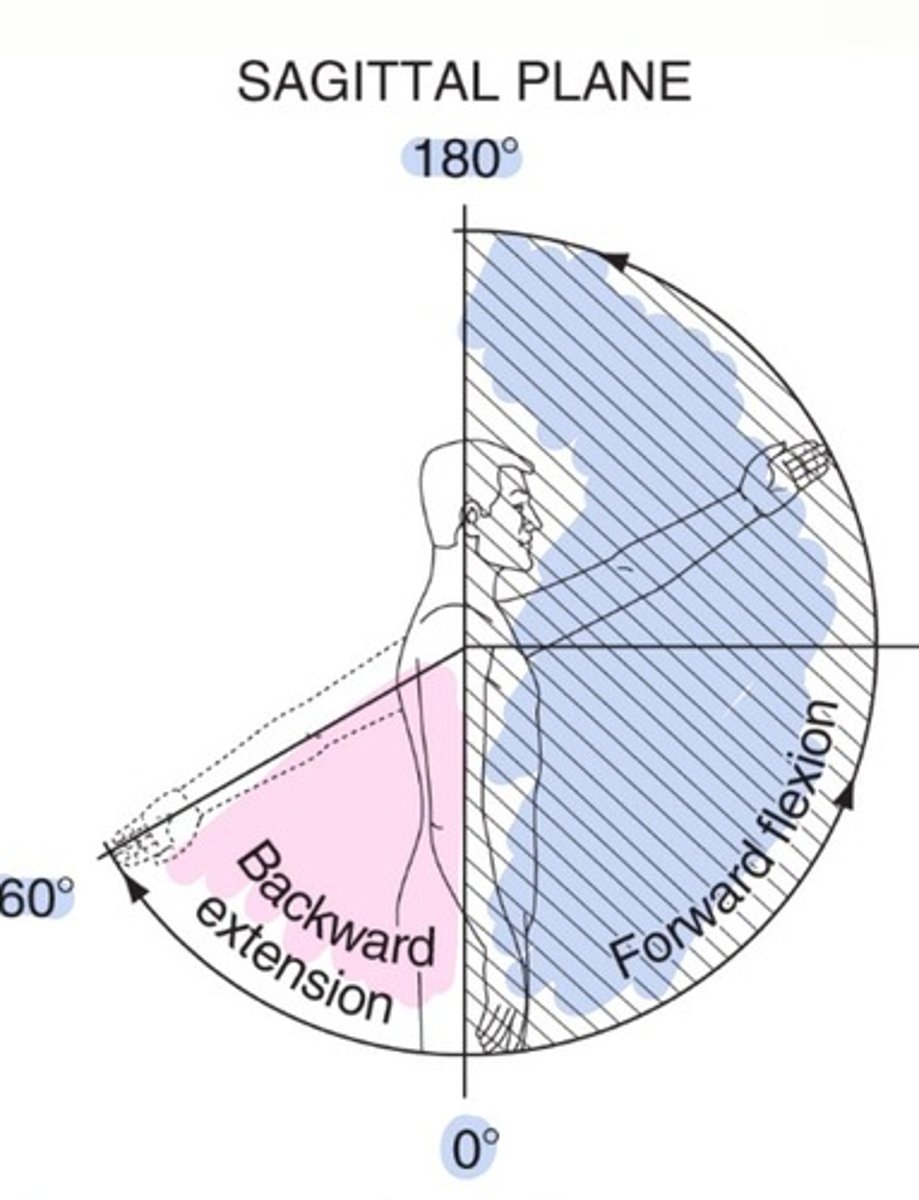
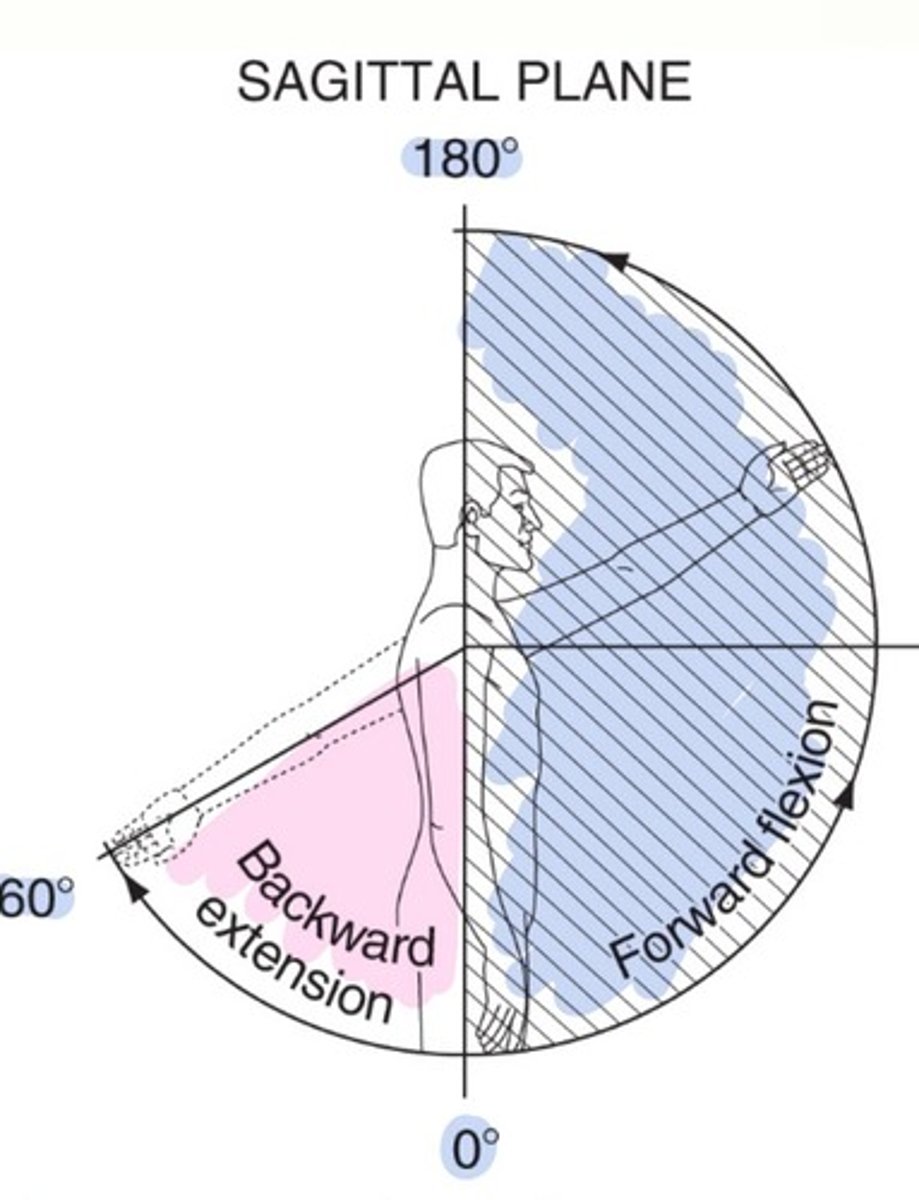
GH extension
90-100 degrees
GH abduction
120 degrees
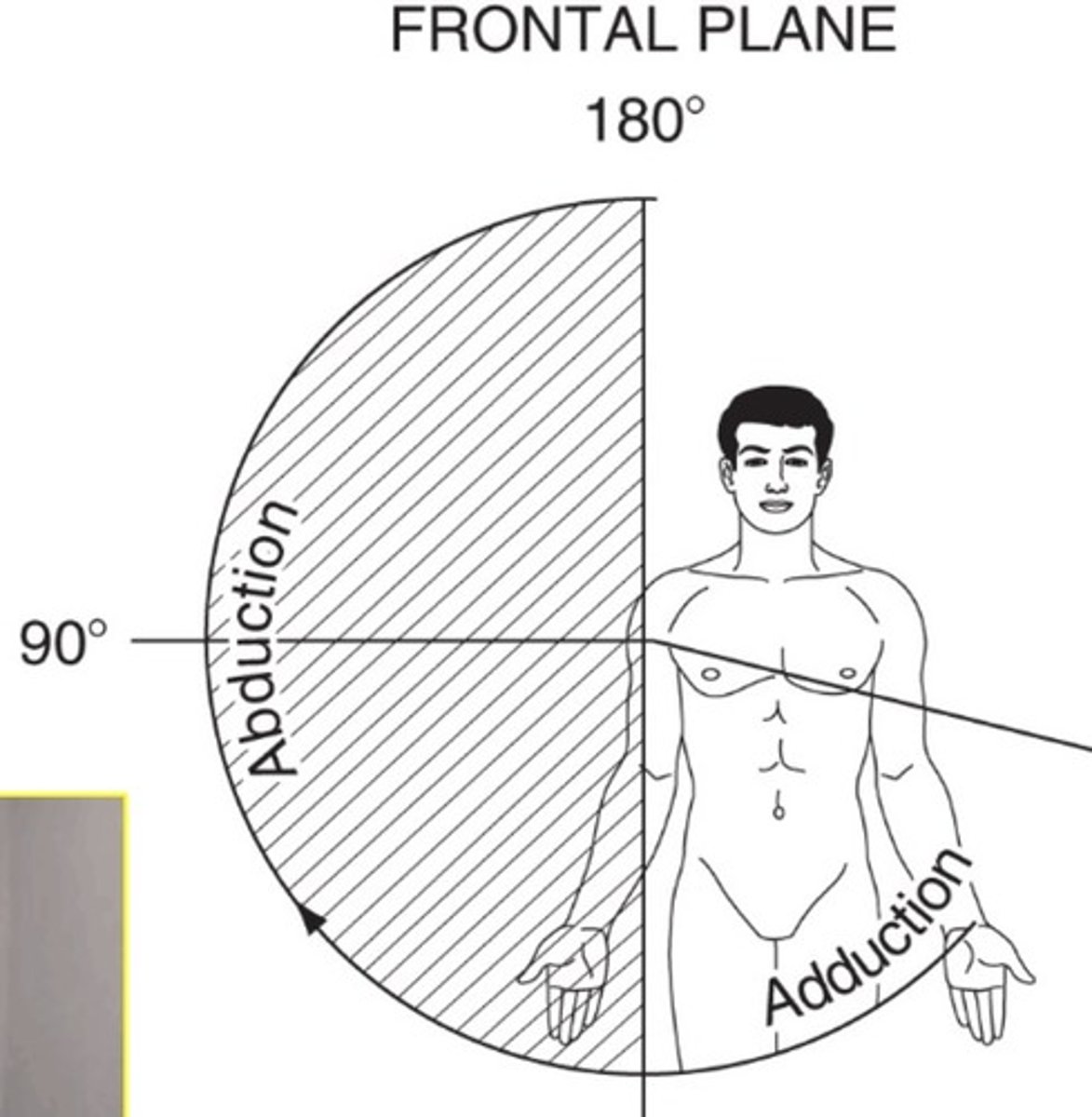
GH adduction
75 degrees across body
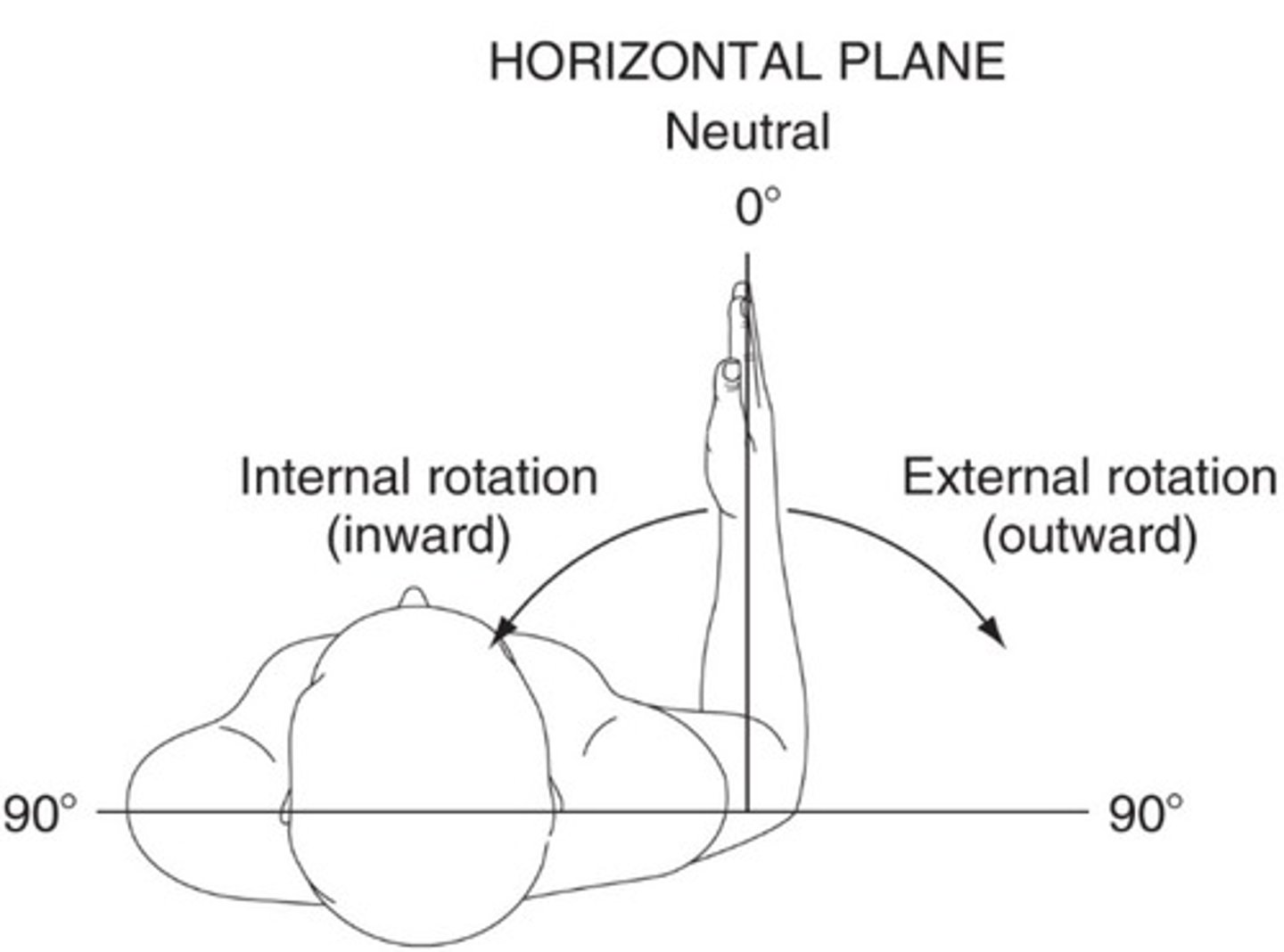
GH external/internal rotation
70-90 degrees
GH horizontal abduction
45 degrees
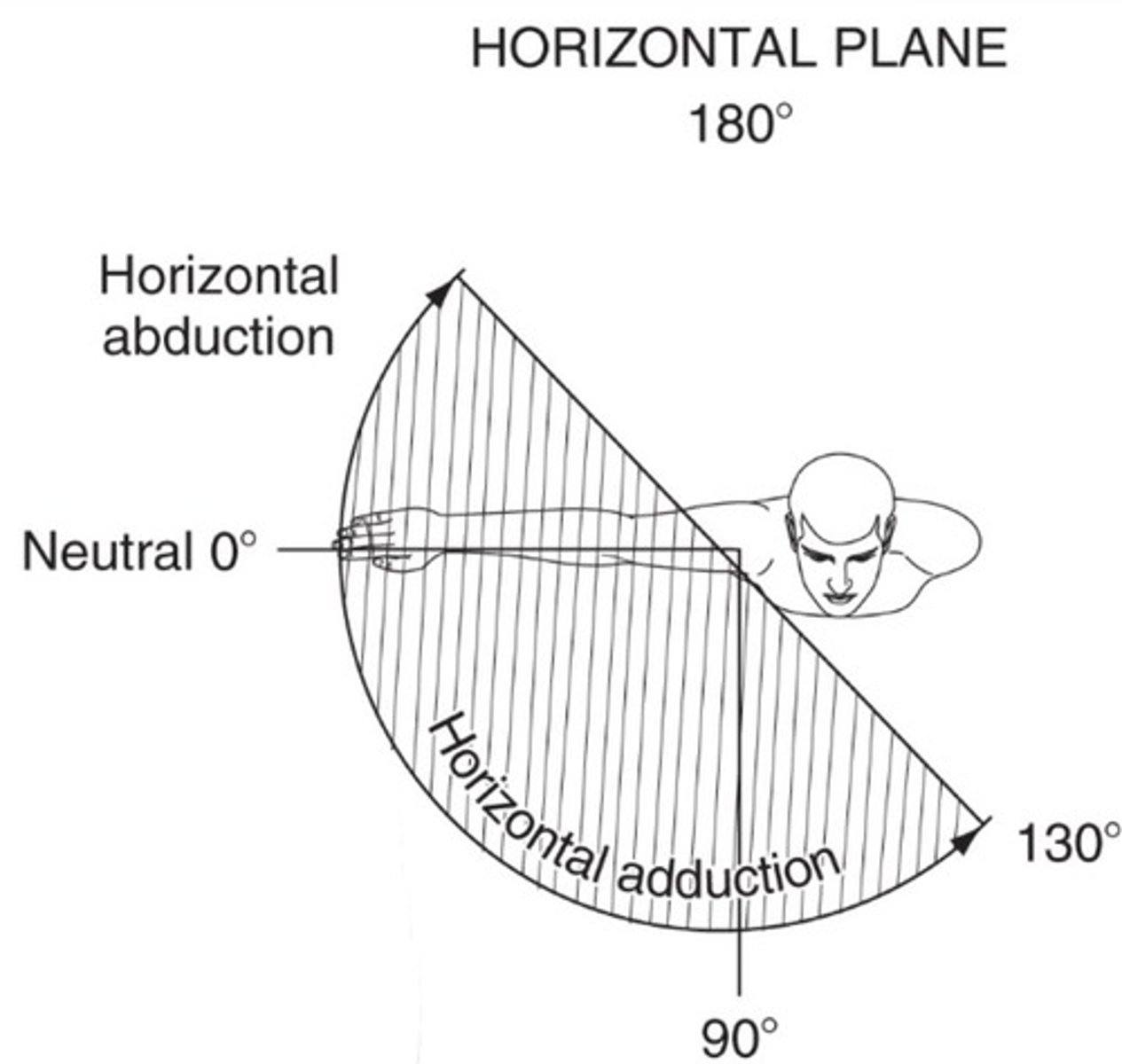
GH horizontal adduction
130 degrees
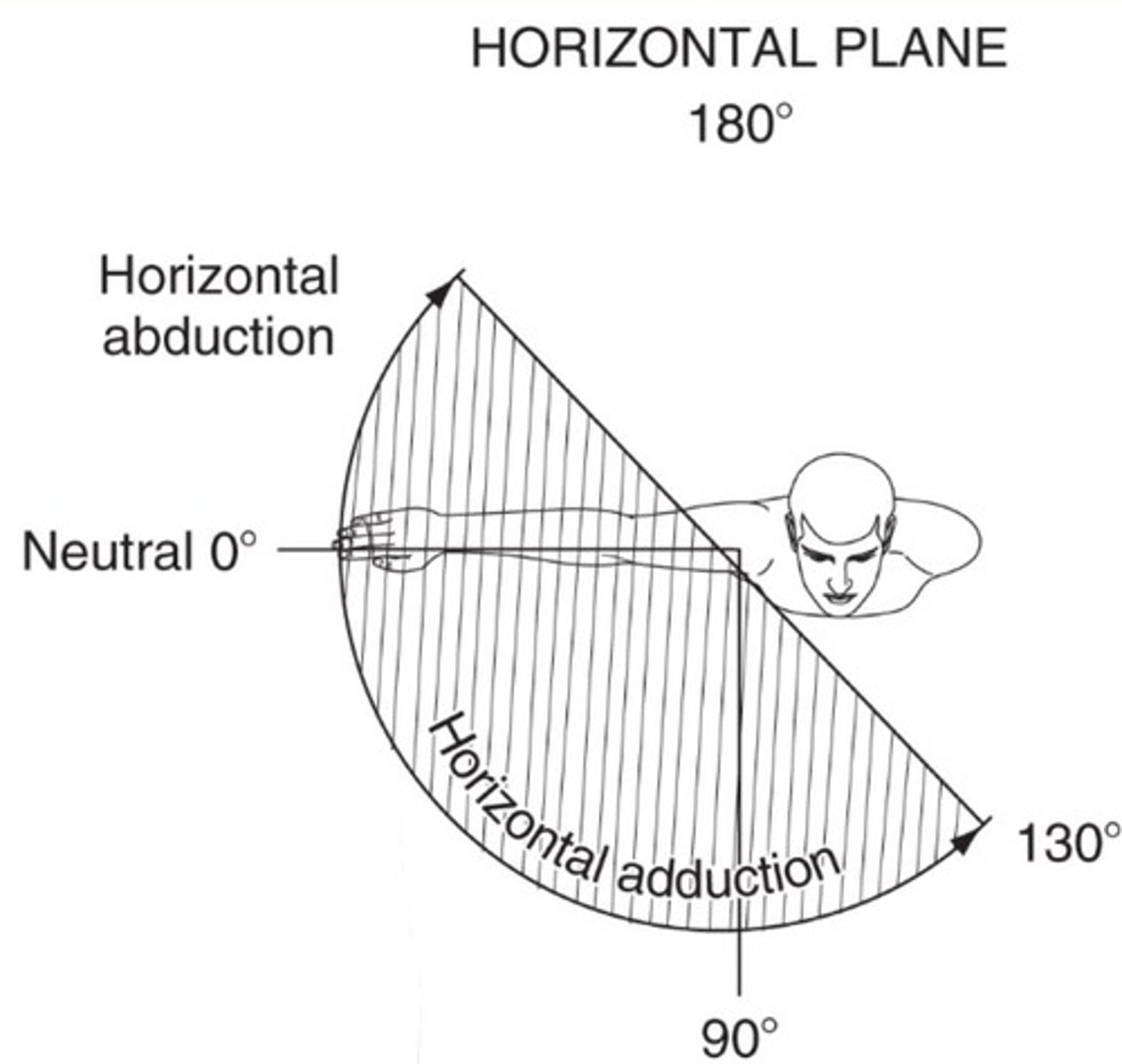
Diagonal abduction and adduction

GH joint is frequently injured due to its...
anatomical design
GH joint injury reasons
shallowness of glenoid fossa, laxity of ligament structures, weak muscles
Common subluxations and dislocations
anterior and anteroinferior
Rare dislocation
posterior
Ligaments are quite lax until...
extreme ROM is reached
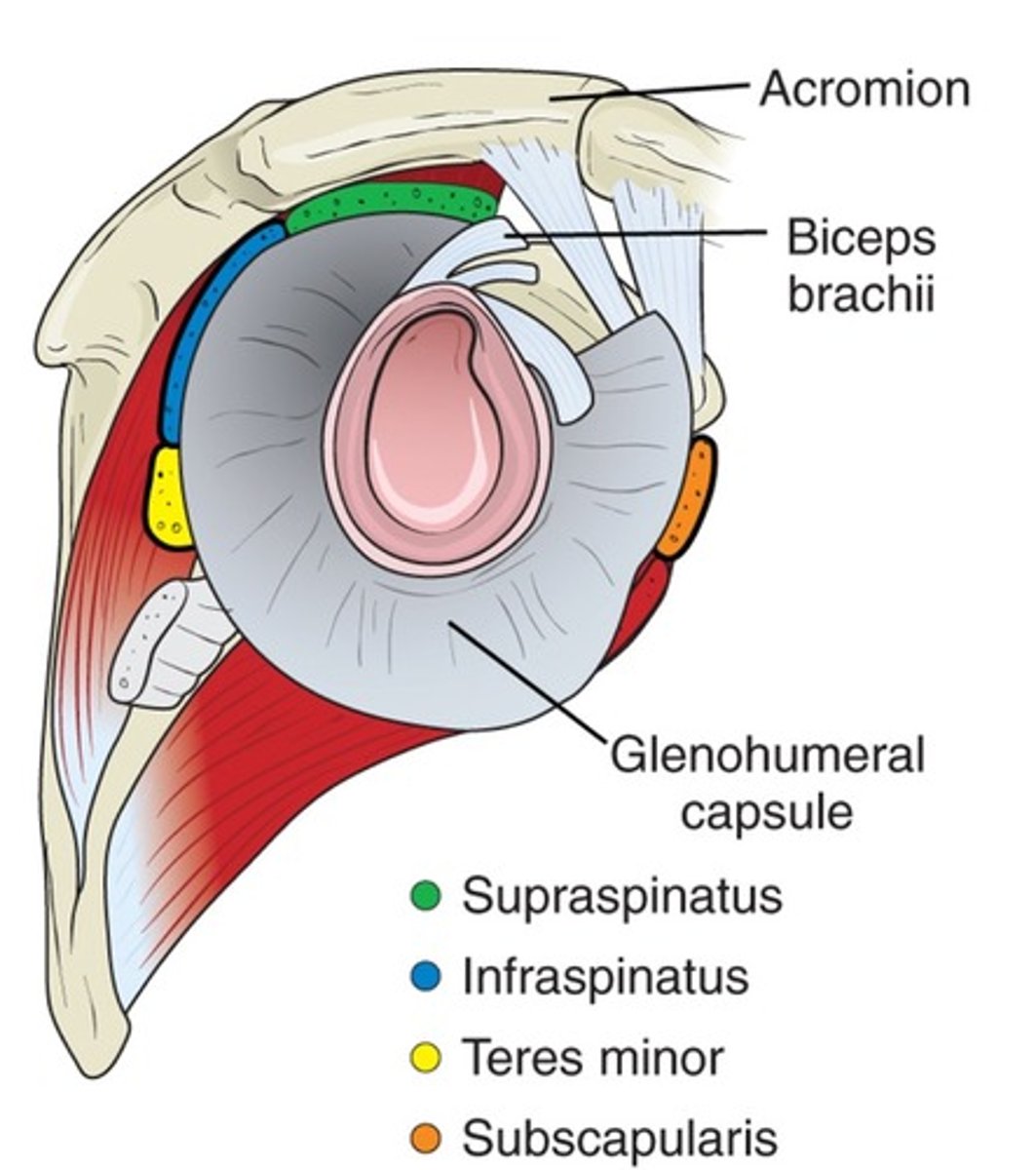
Rotator cuff muscle group
subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor
Rotator cuff muscles are
- not very large
- must possess strength & muscular endurance
- stabilize humeral head in glenoid cavity
Point of insertion for rotator cuff muscles enable
humeral rotation
Rotator cuff muscles attach to
front, top, and rear humeral head
Glenohumeral Internal Rotation Deficit (GIRD)
difference in internal rotation range of motion between an individual's throwing & non-throwing shoulders
GIRD increases the risk of injury by more than
20%, Stretching regains internal rotation and reduces likelihood of injury
Intrinsic GH muscles (stabilization)
deltoid, coracobrachialis, teres major, rotator cuff group
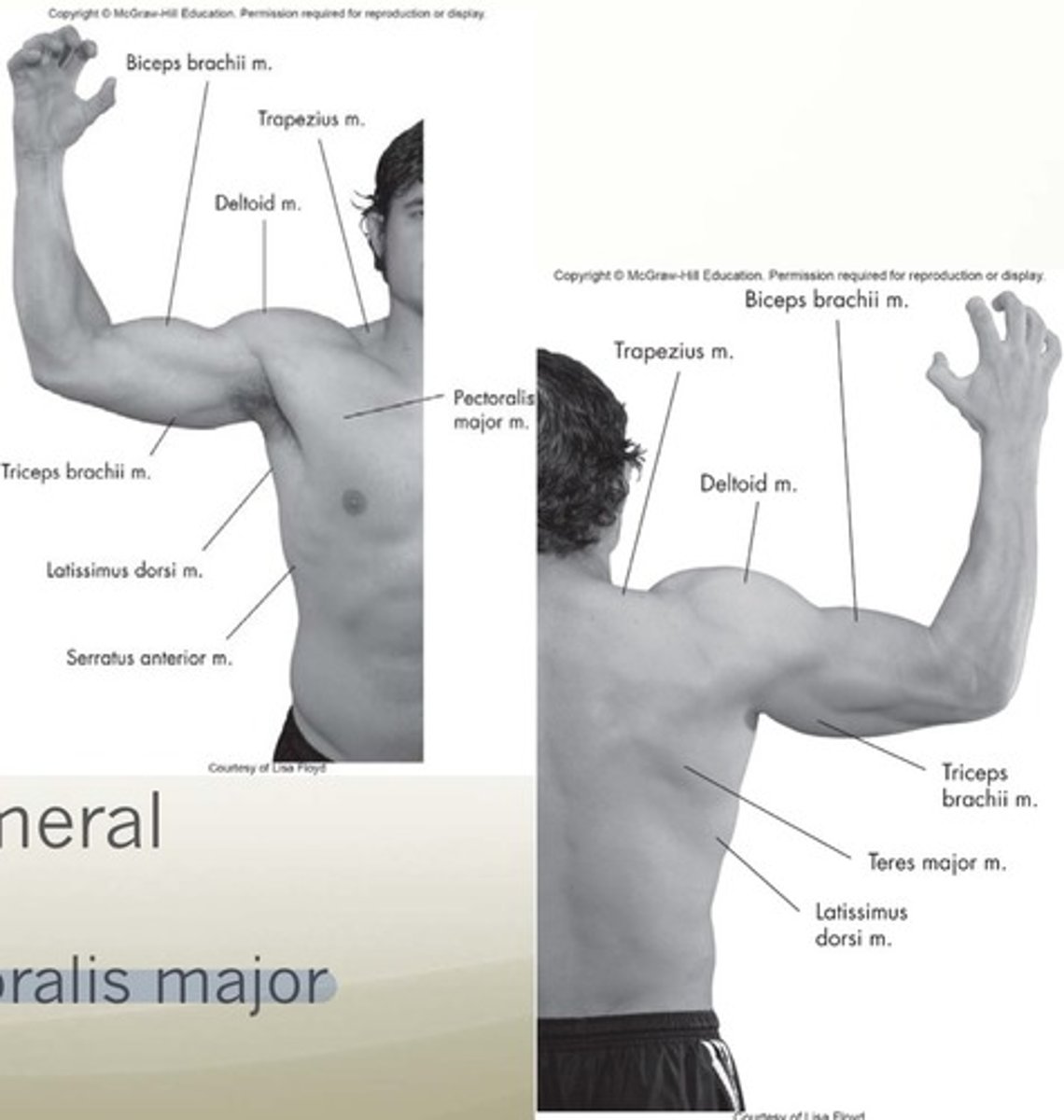
Extrinsic GH muscles (motion)
Latissimus dorsi and pec major
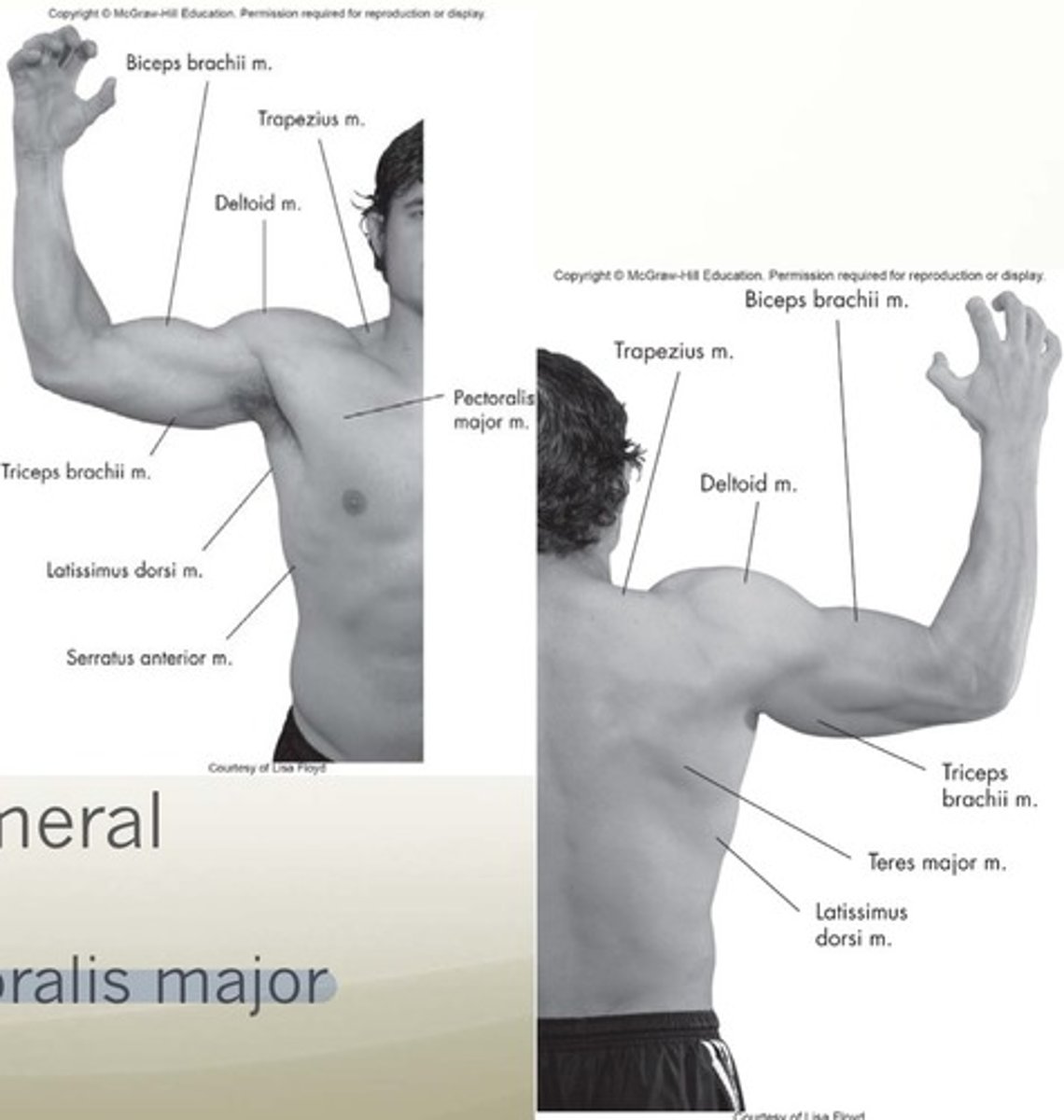
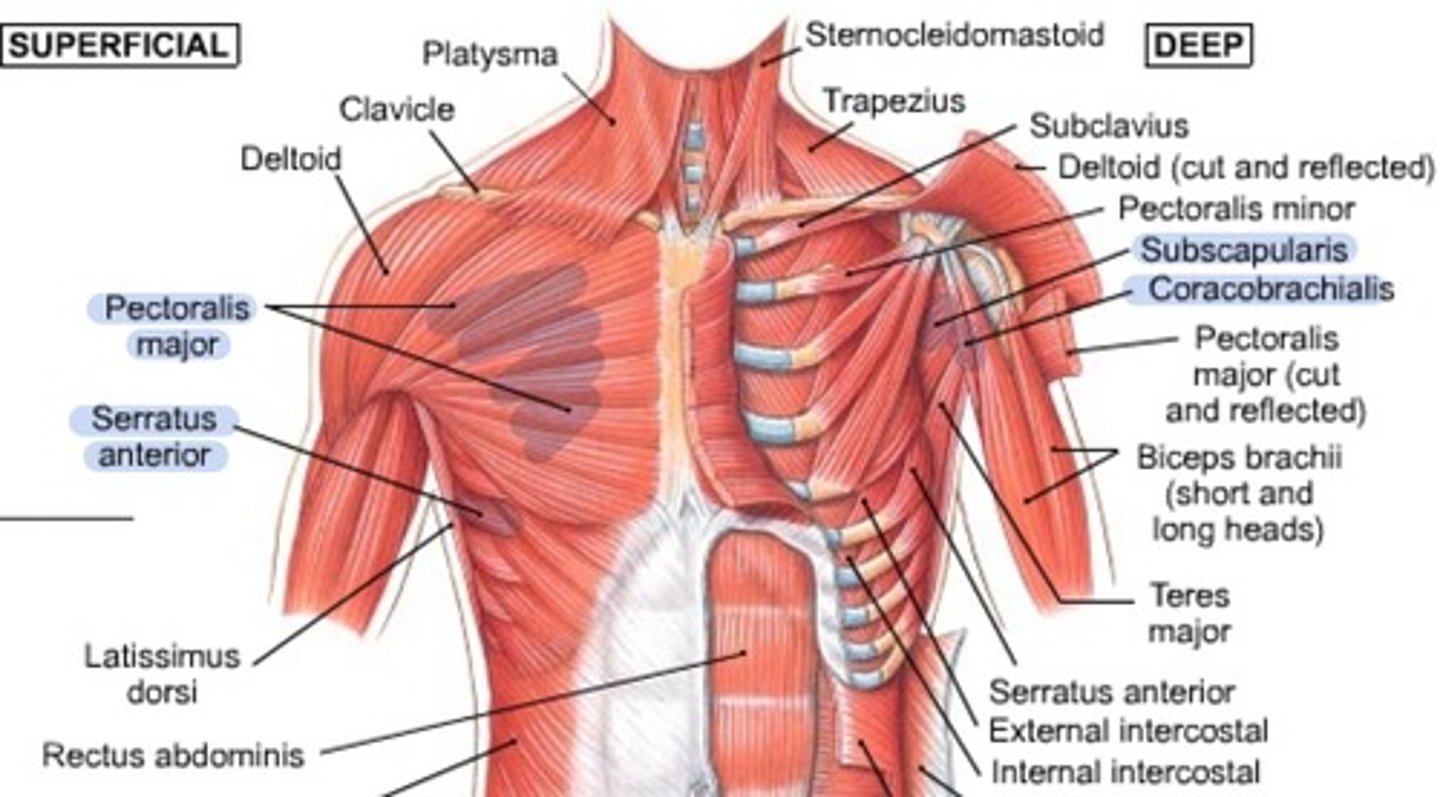
Anterior muscles
pectoralis major, coracobrachialis, subscapularis, serratus anterior
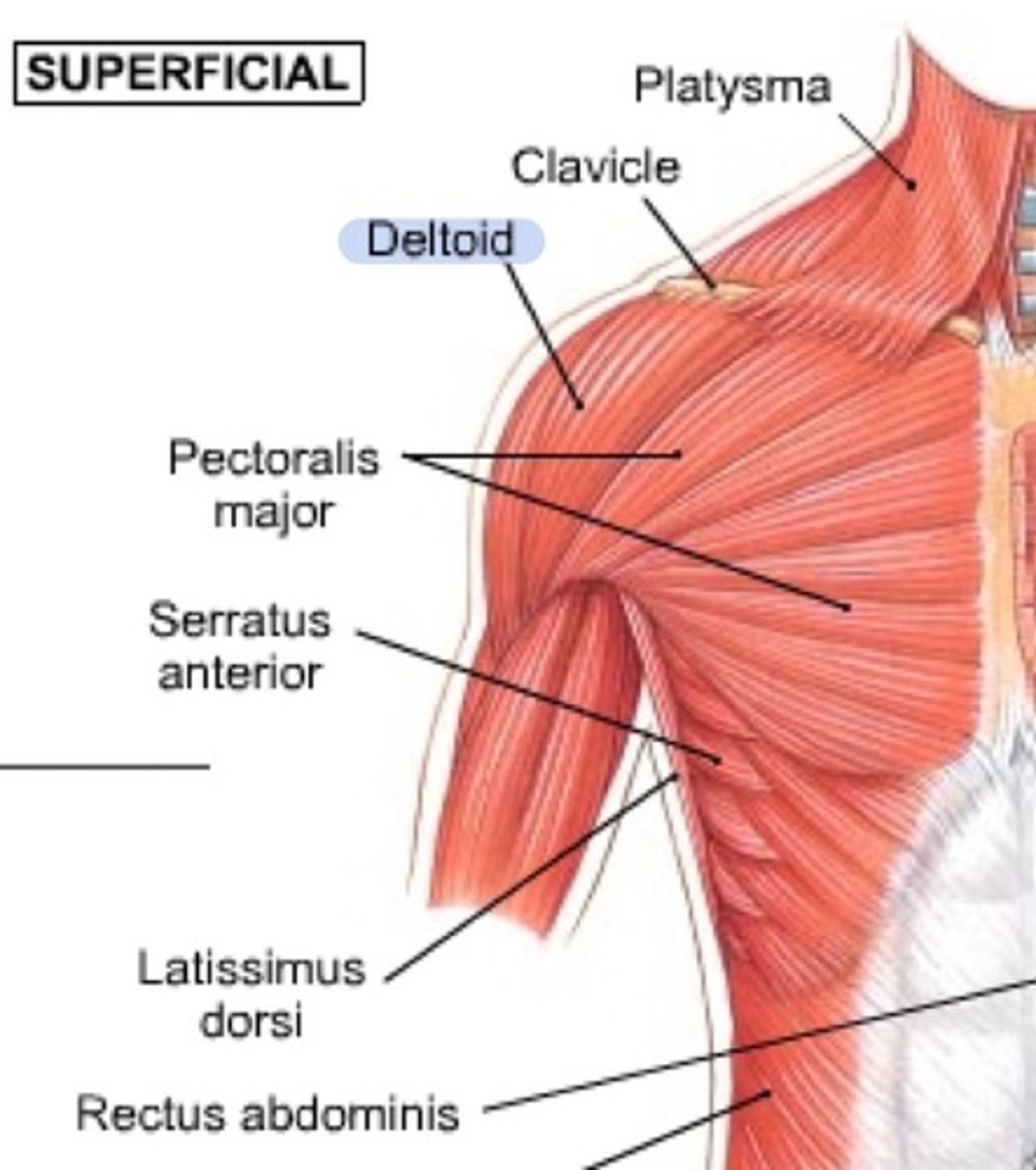
Superior muscles
Deltoid, supraspinatus
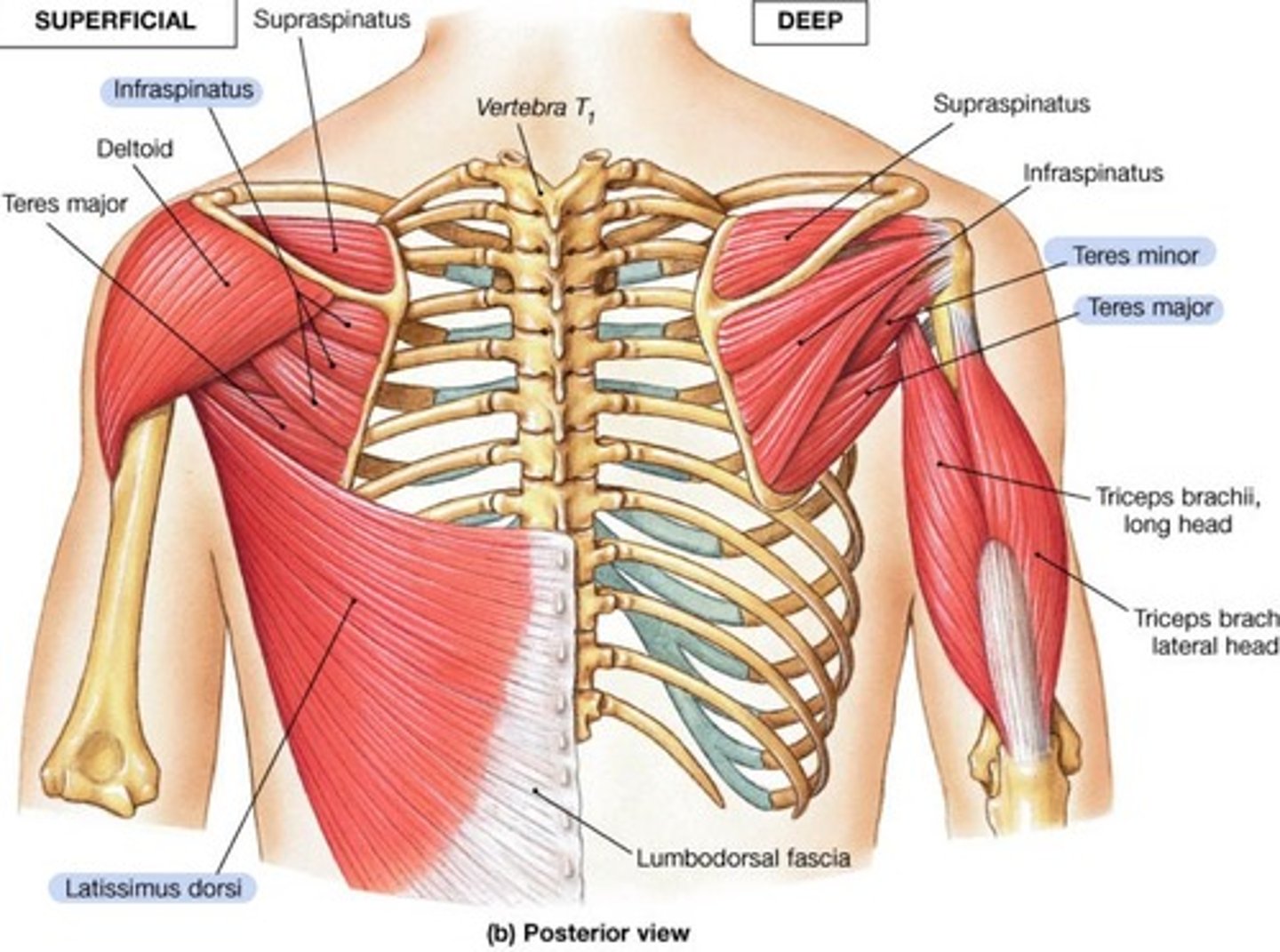
Posterior muscles
Latissmus dorsi, teres major/minor, infraspinatus
Brachial Plexus
C5-T1
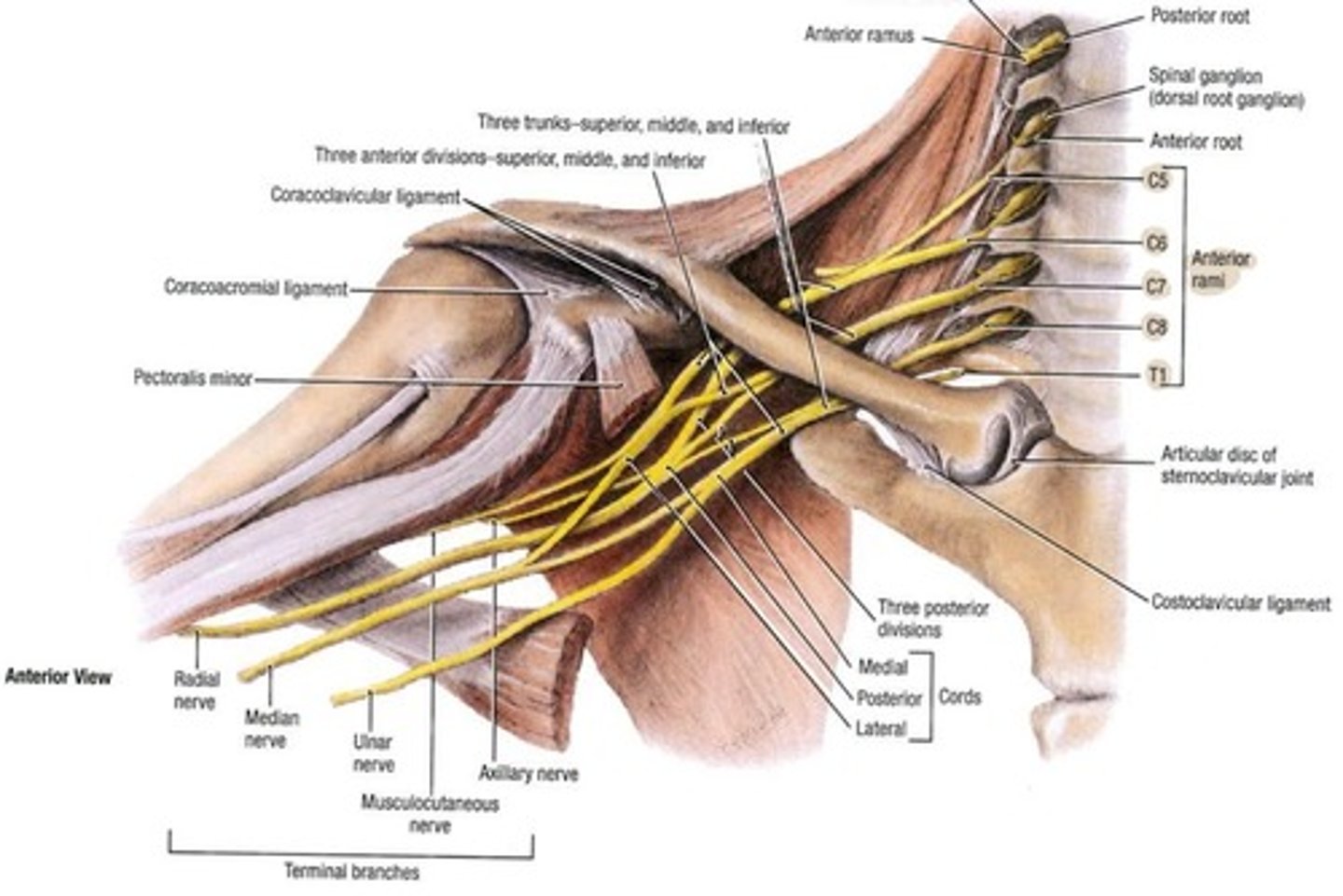
Lateral pectoral nerve
C5, C6, C7, pectoralis major (clavicular head)
Medial pectoral nerve
C8-T1, pectoralis major (sternal head)
Thoracordosal nerve
C6, C7, and C8, Latissimus dorsi
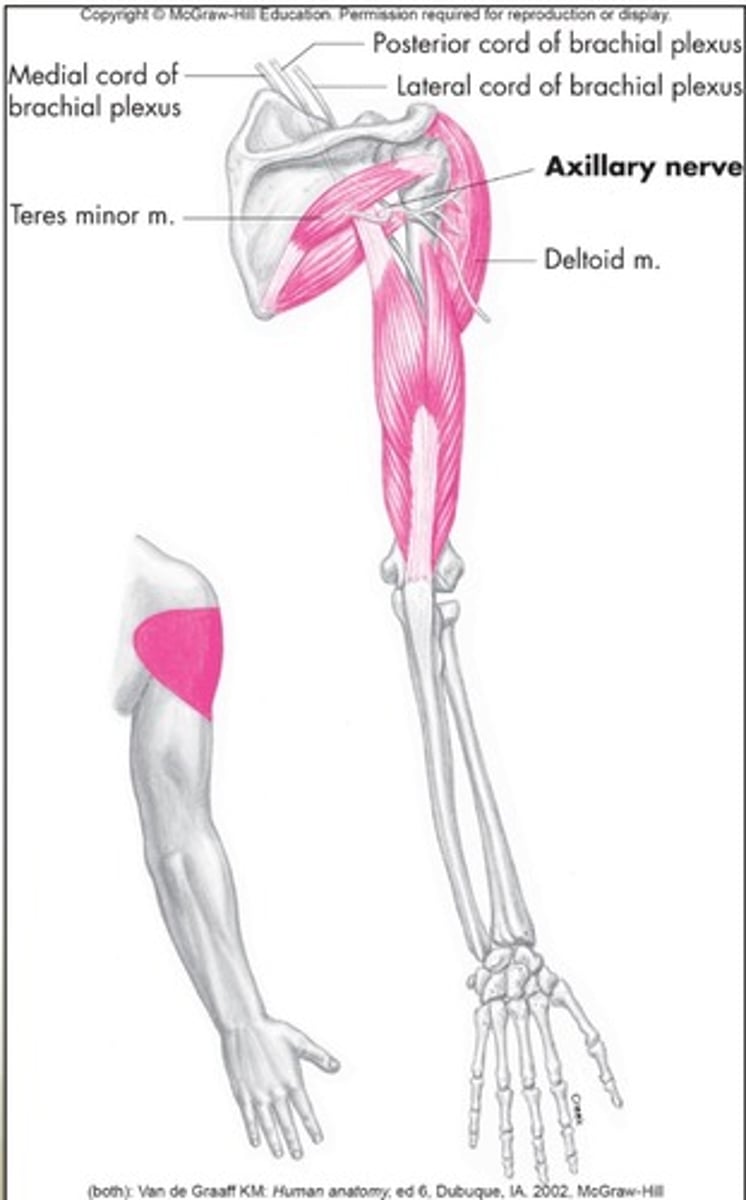
Axillary nerve
C5 and C6, innervates deltoid and teres minor
Upper subscapular nerves
C5-C6, Subscapularis
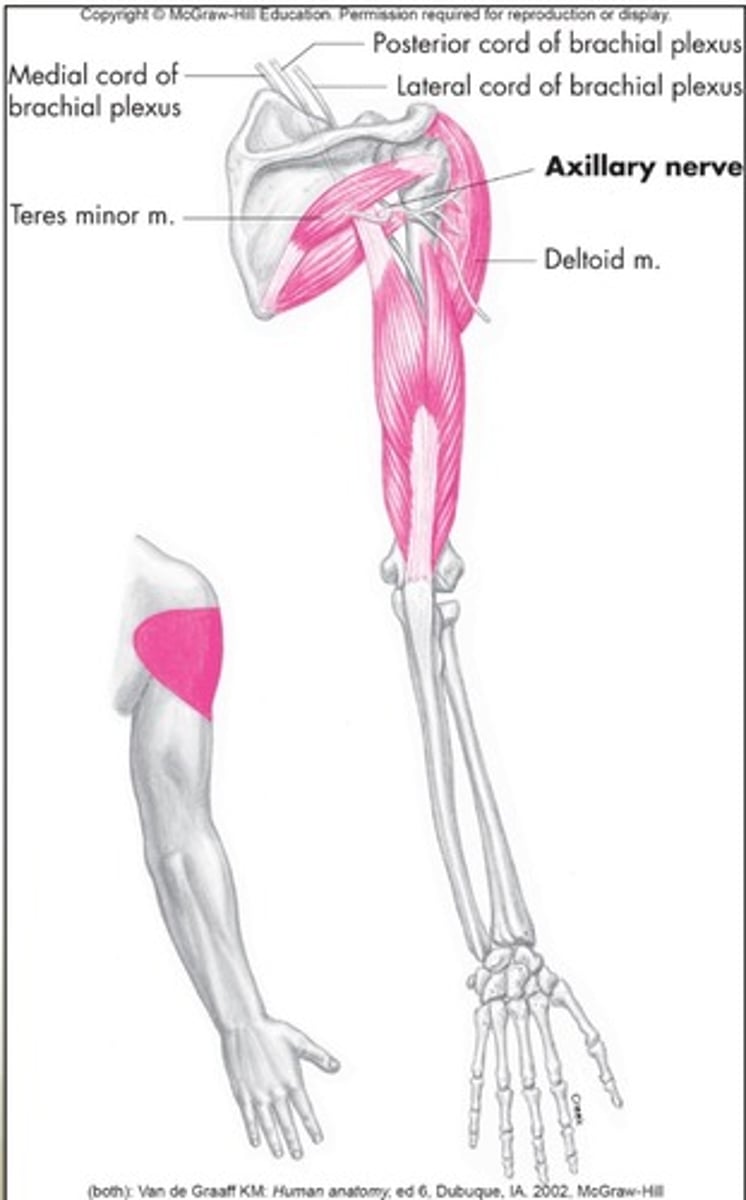
Lower subscapular nerves
C5 & C6, subscapularis and teres major
Suprascapula nerve
C5-C6 Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus
Musculotaneous nerve
C5, C6, ,C7, coracobrachialis
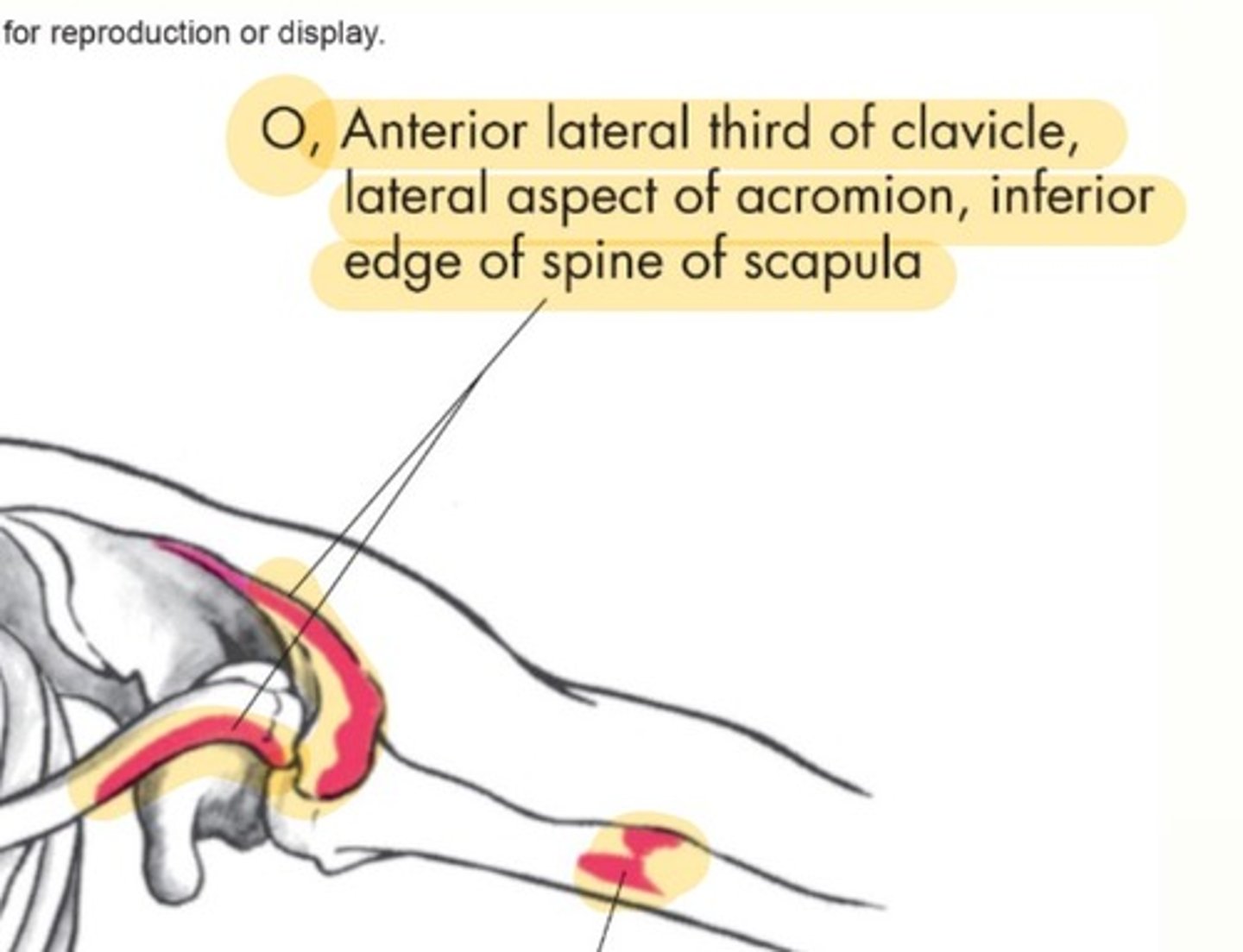
Deltoid origin
anterior lateral third of clavicle, lateral aspect of acromion, and inferior edge of spine of scapula
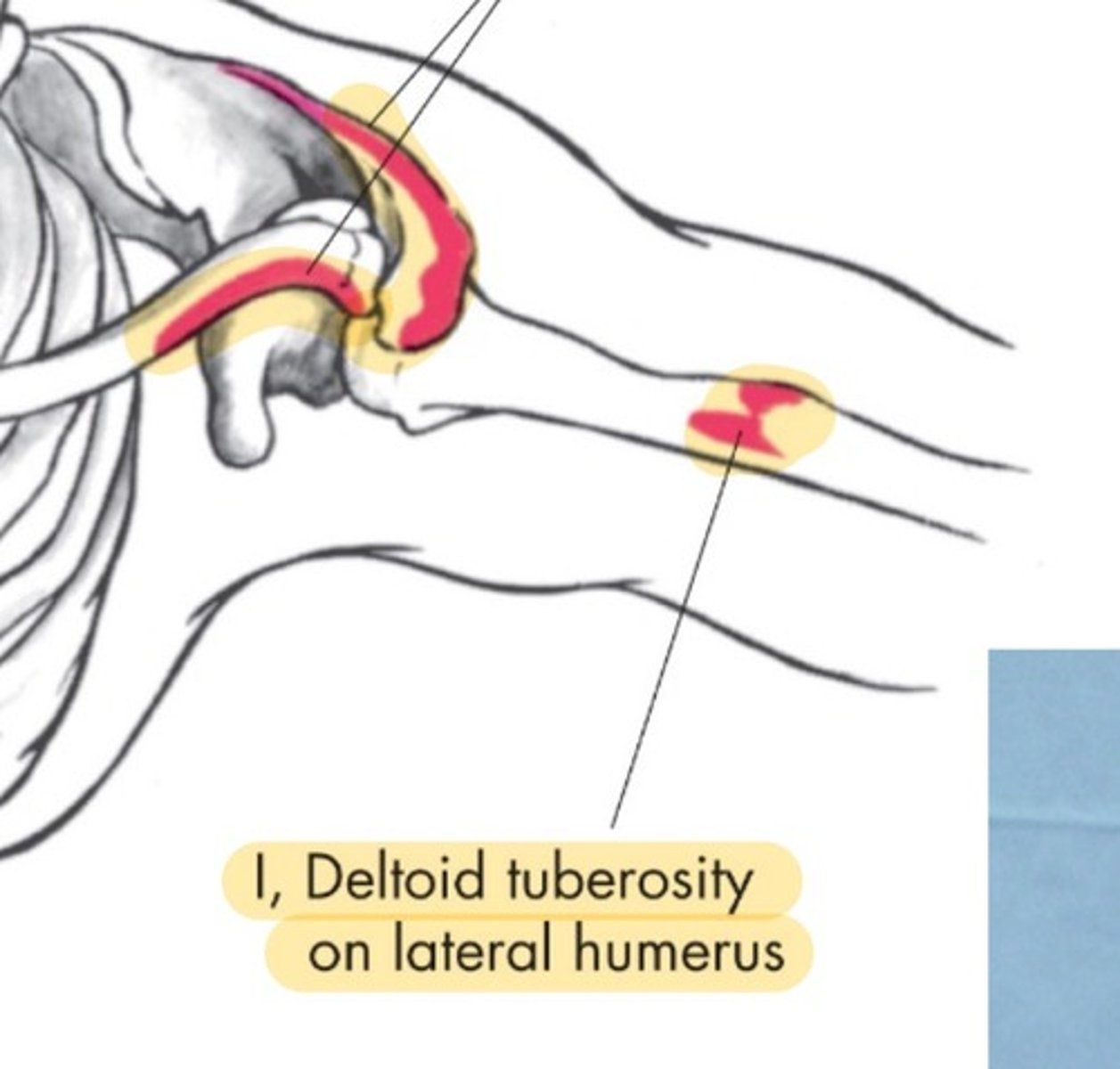
Deltoid insertion
deltoid tuberosity
Pec Major origin
Medial half of anterior surface of clavicle and costal cartilages, adjoining portion of sternum
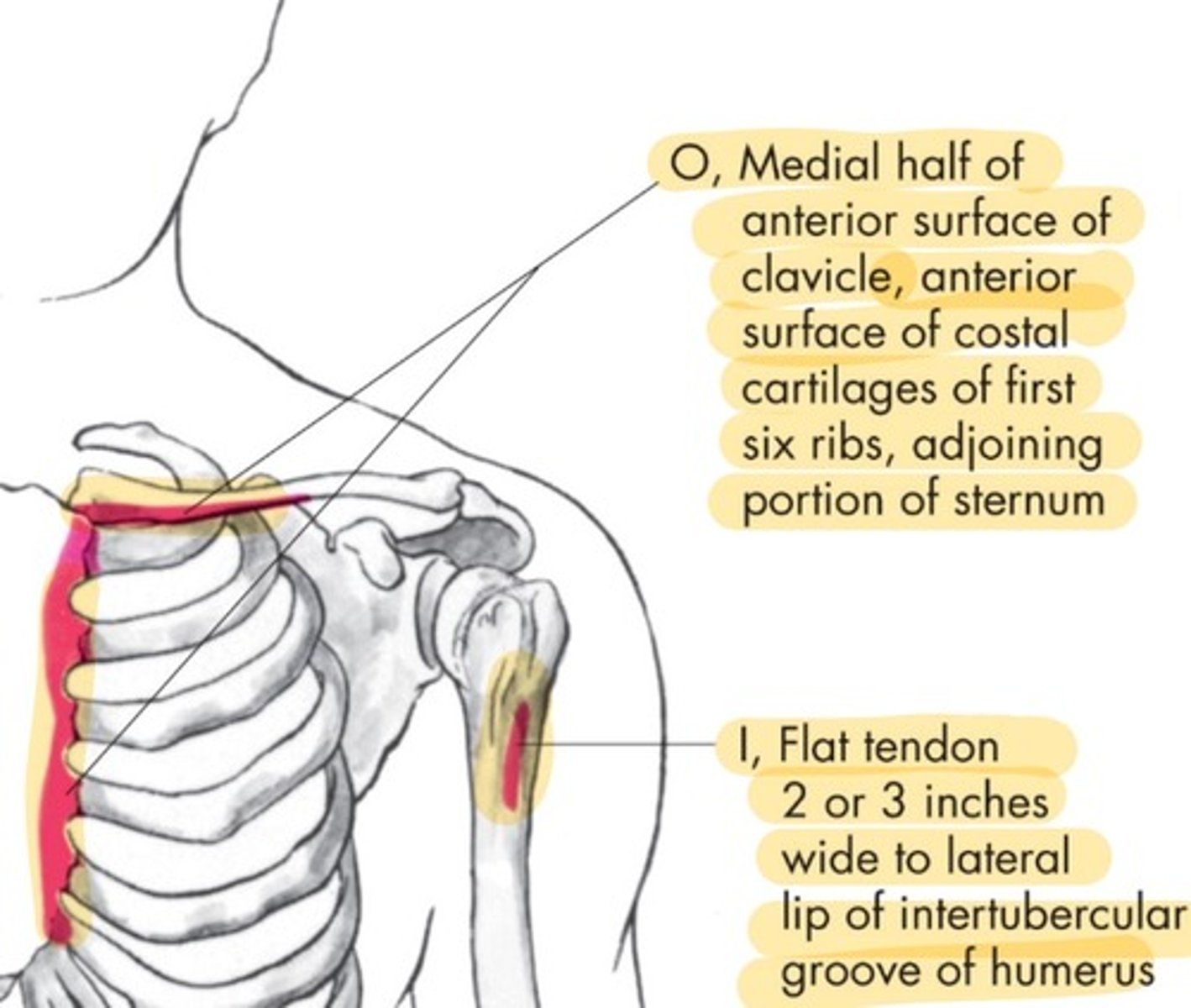
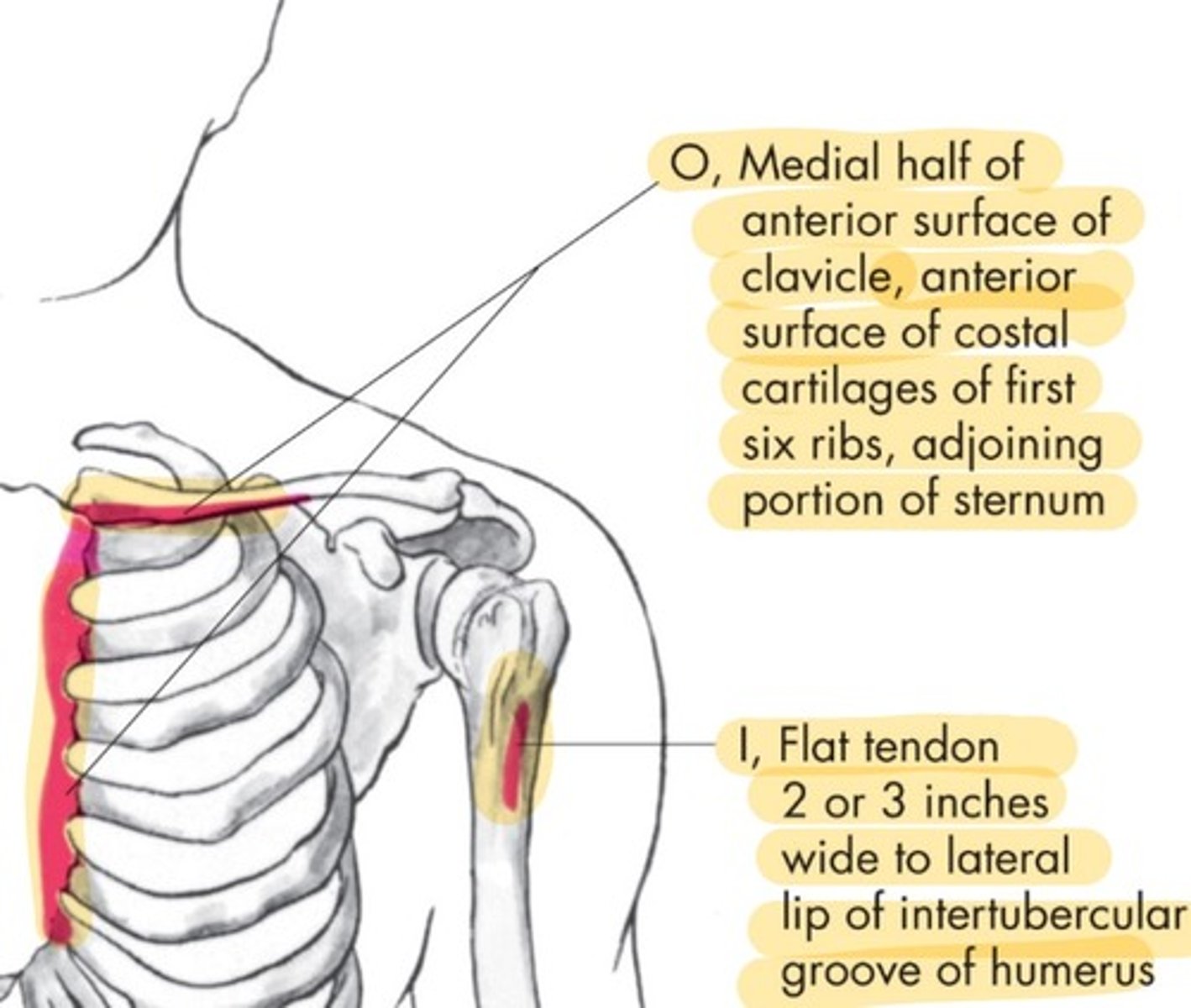
Pec Major insertion
Flat tendon 2 or 3 inches wide to lateral lip of intertubercular groove of humerus
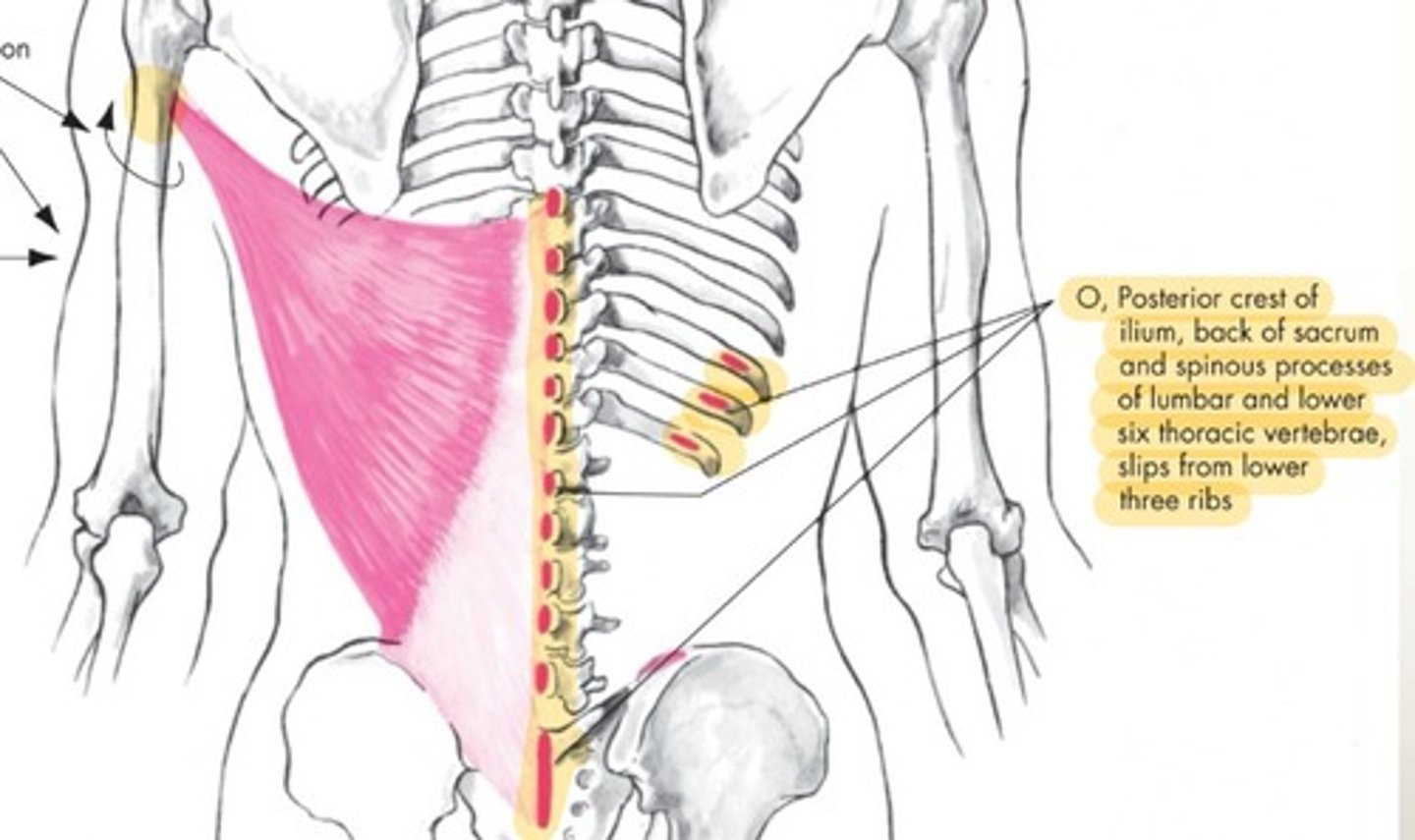
Latissimus Dorsi origin
Posterior crest of ilium, back of sacrum and spinous processes of lumbar and lower 6 thoracic vertebrae, posterior distal surfaces from lower three ribs
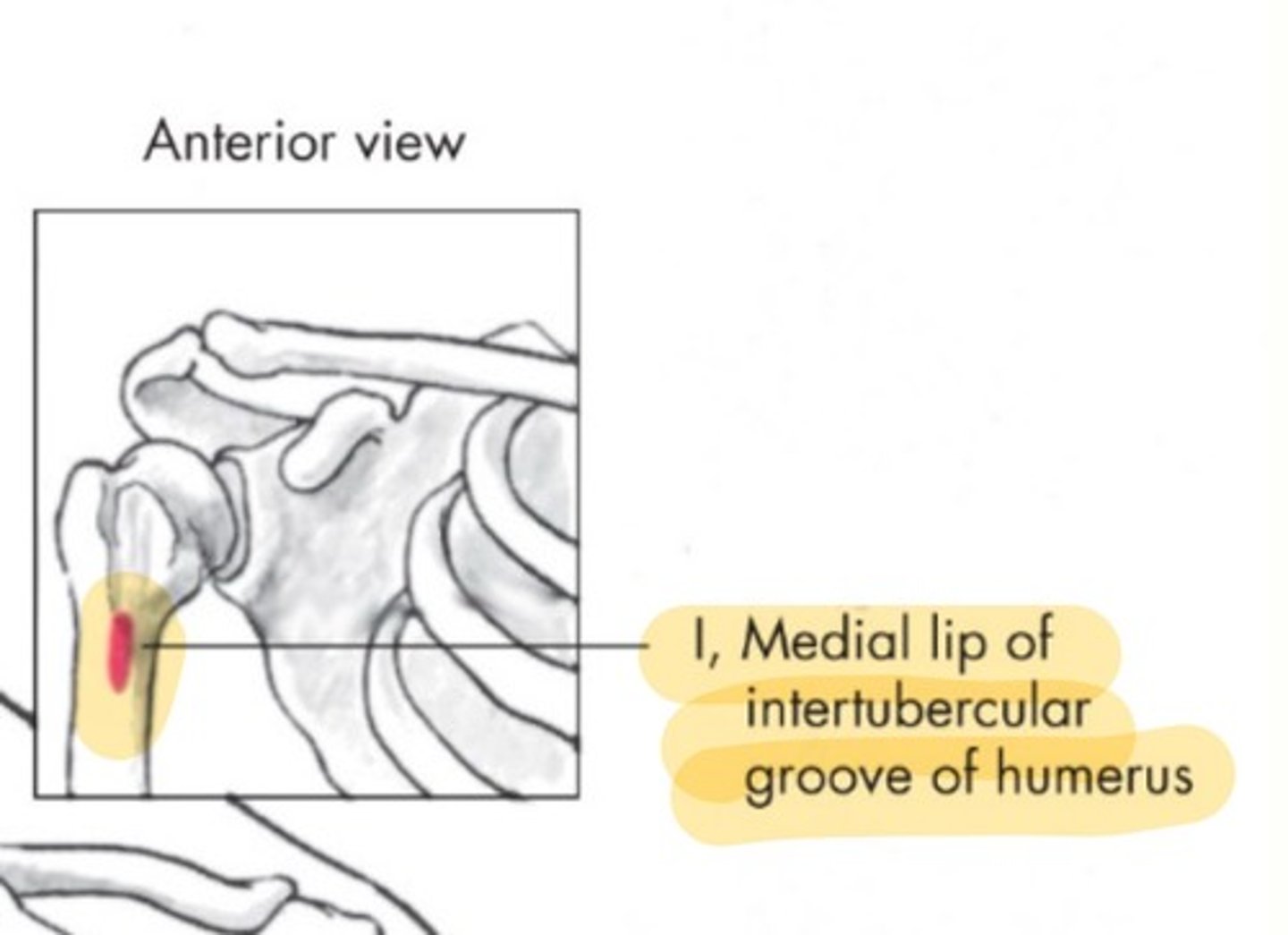
Latissimus Dorsi insertion
Medial lip of intertubercular groove of humerus
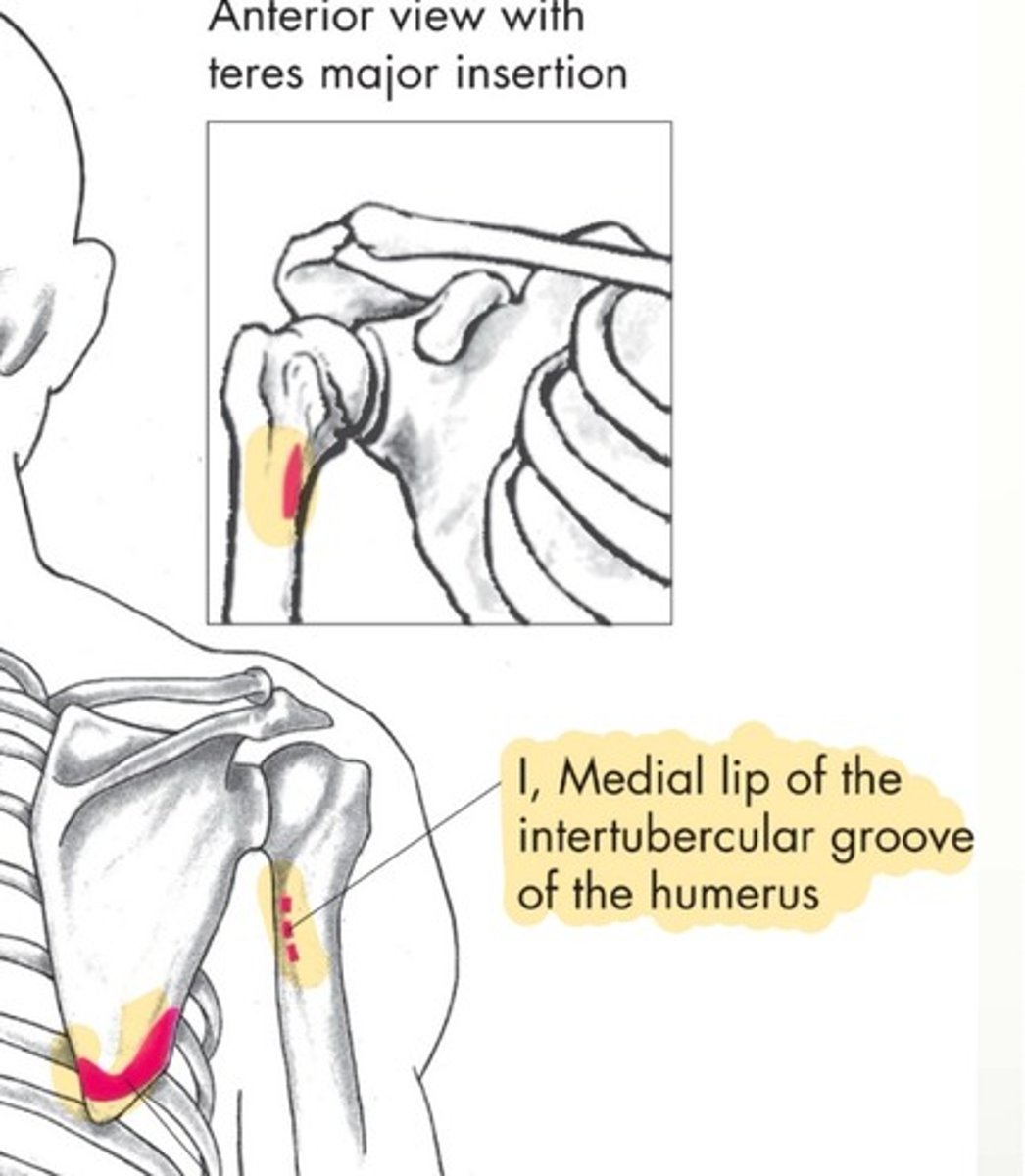
Teres Major origin
inferior third of lateral border of scapula
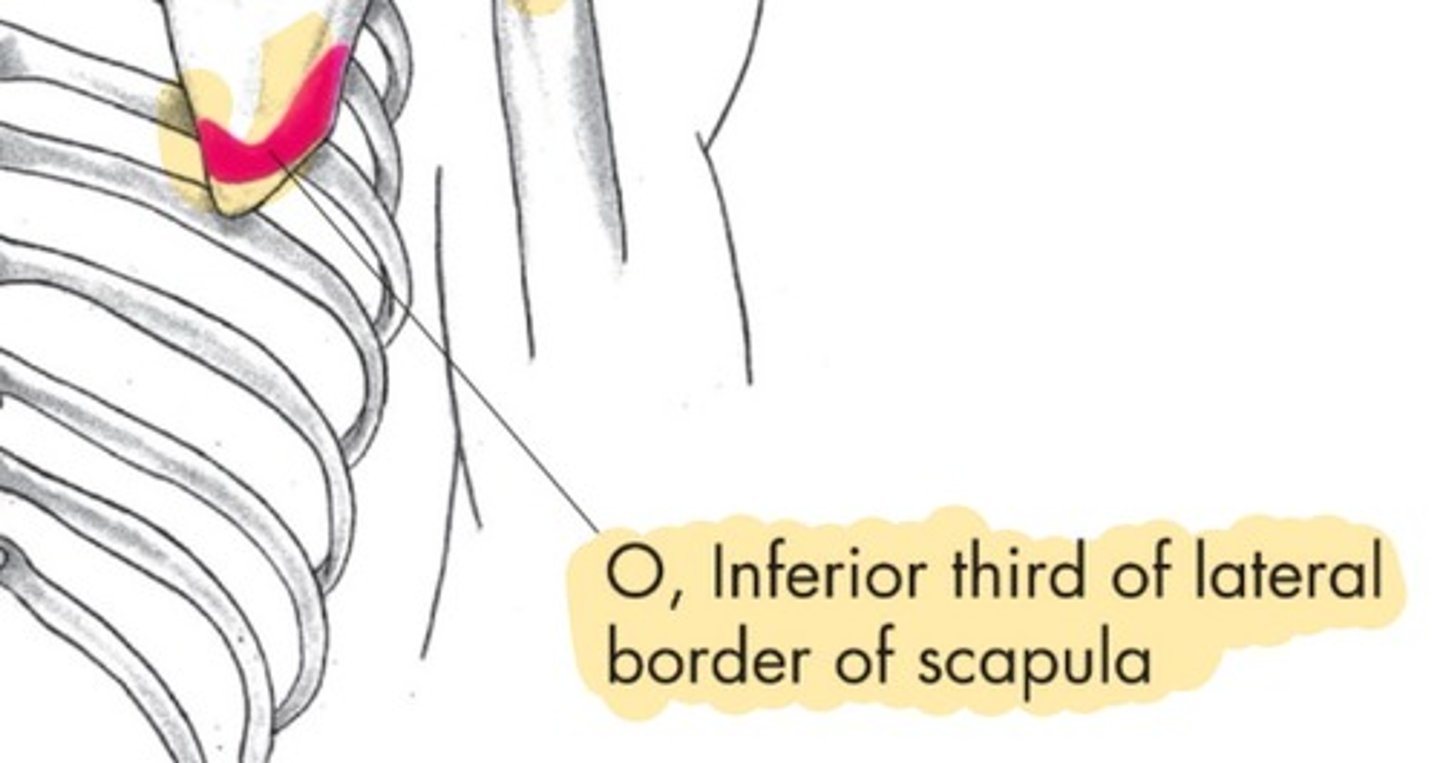
Teres Major insertion
Medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus
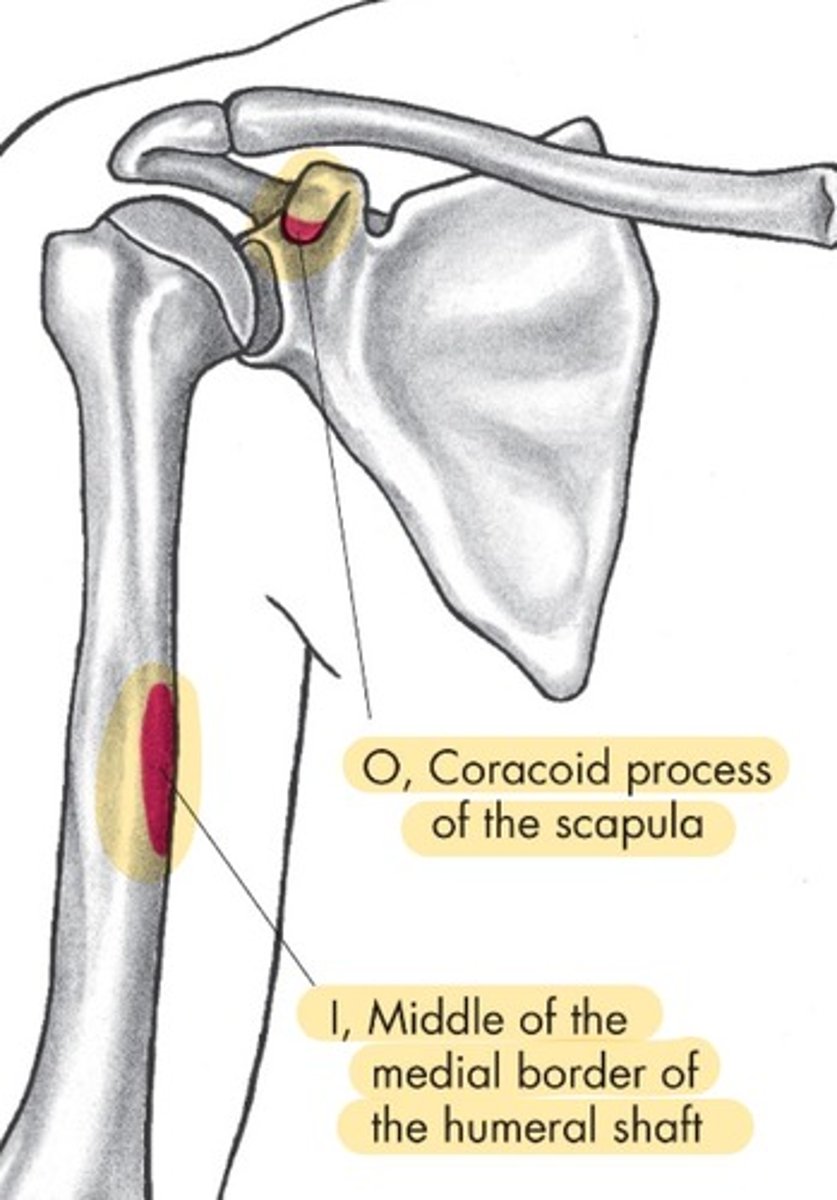
Coracobrachialis origin
coracoid process of scapula
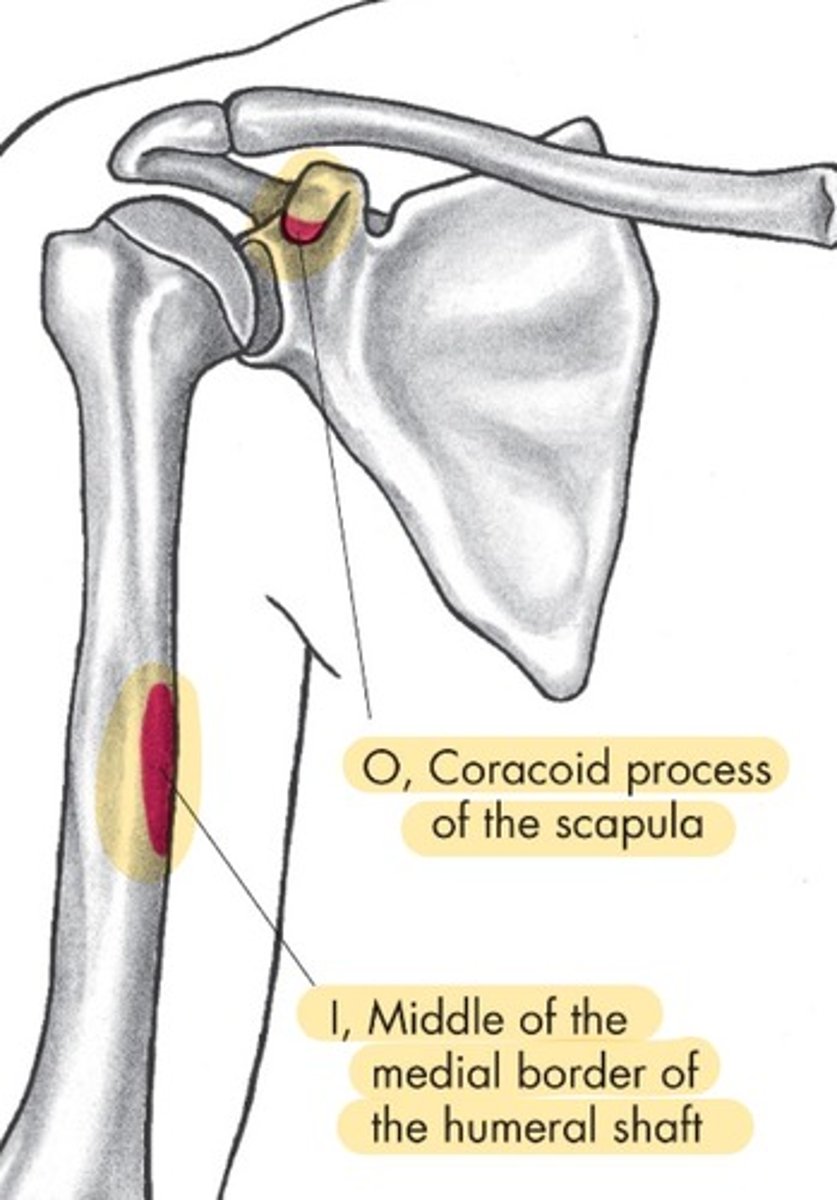
Coracobrachialis insertion
middle of medial border of humeral shaft
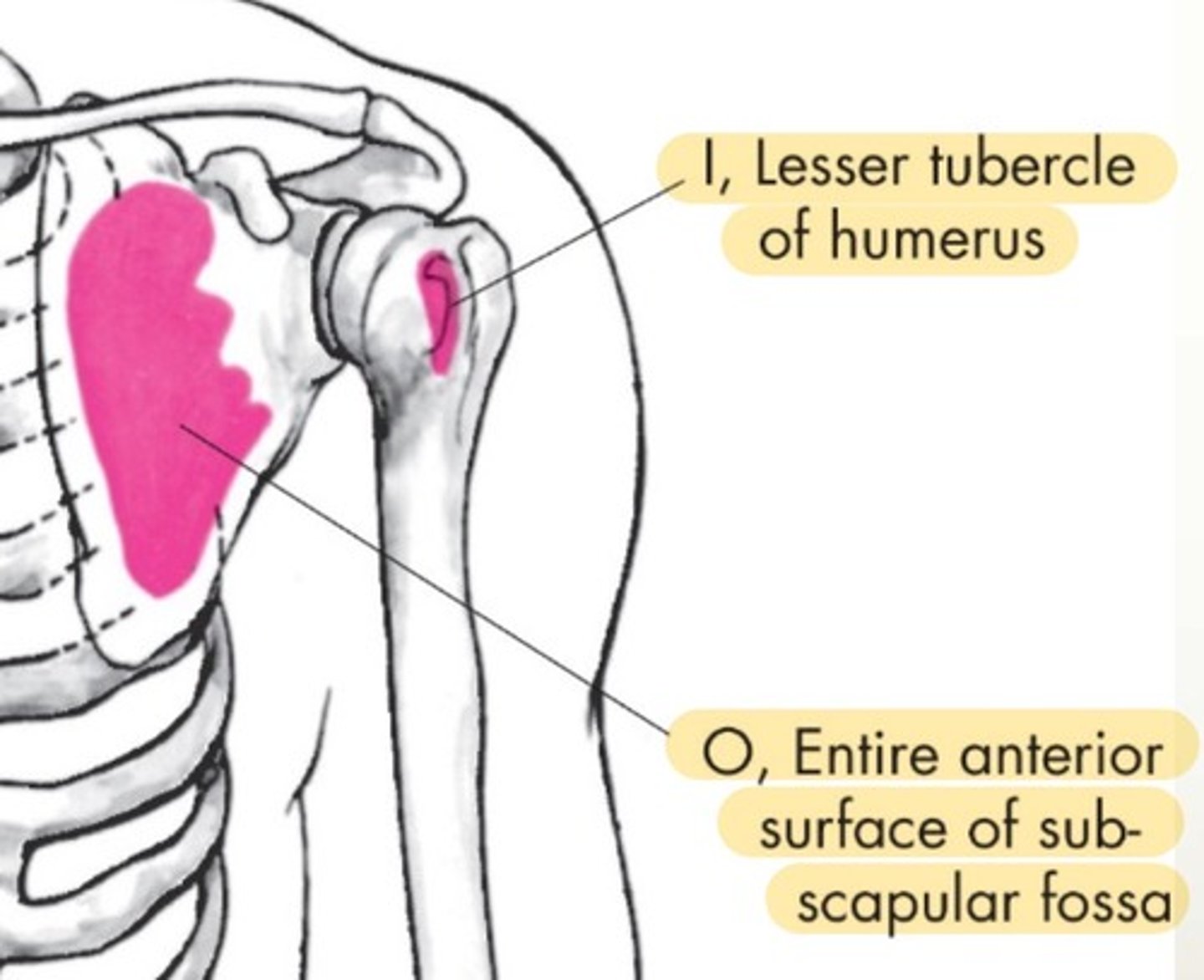
Subscapularis origin
enter anterior surface of subscapular fossa
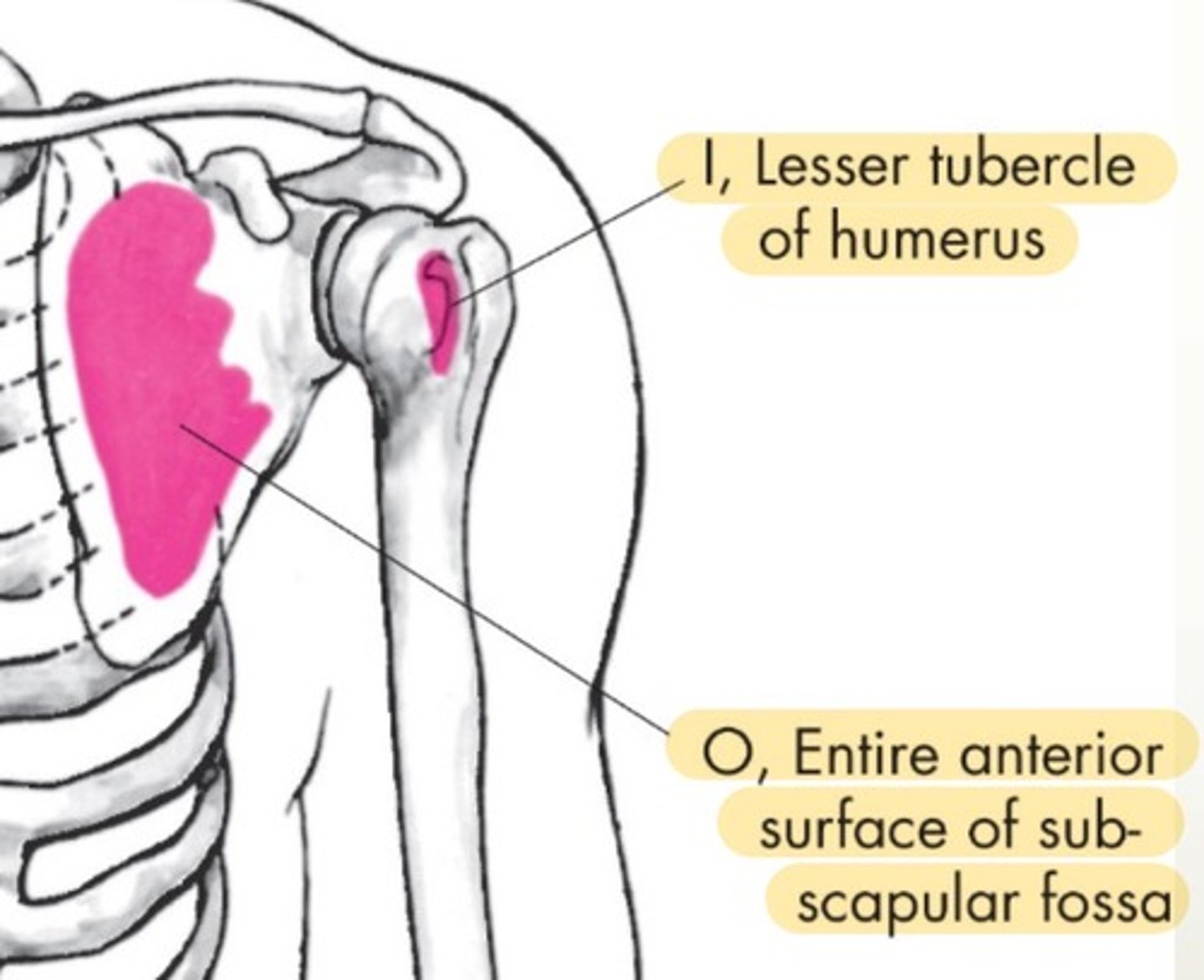
Subscapularis insertion
lesser tubercle of humerus
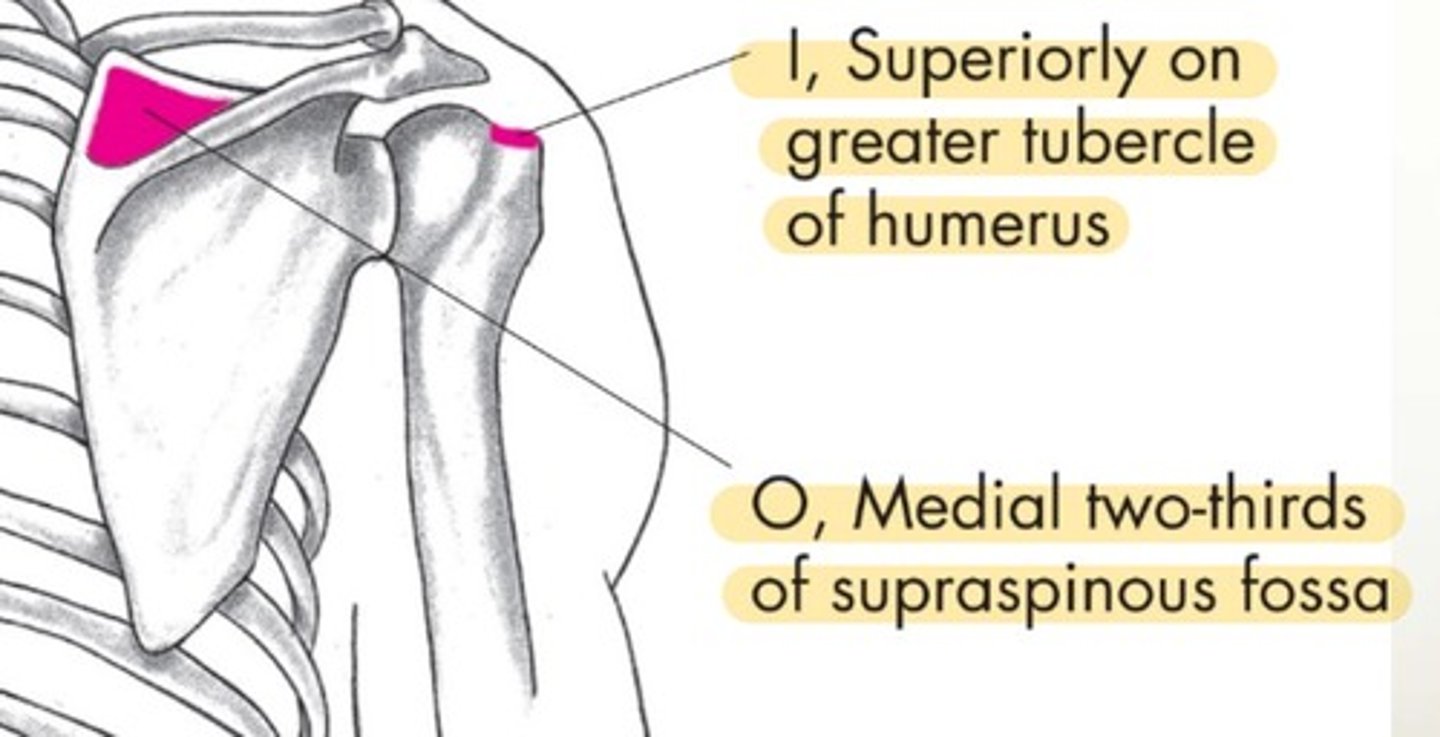
Supraspinatus origin
medial 2/3 of supraspinous fossa
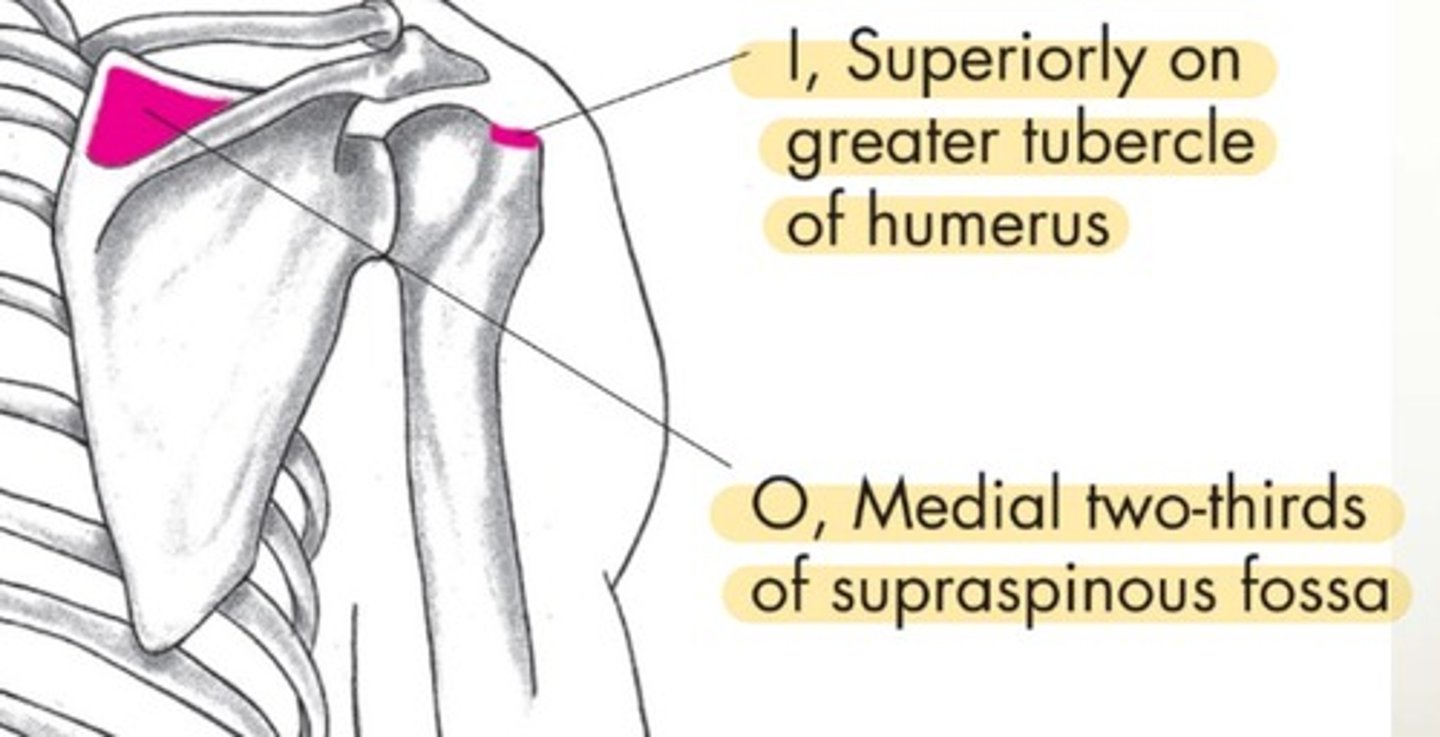
Supraspinatus insertion
superiority on greater tubercle of humerus
Infraspinatus origin
posterior surface of scapula below spine
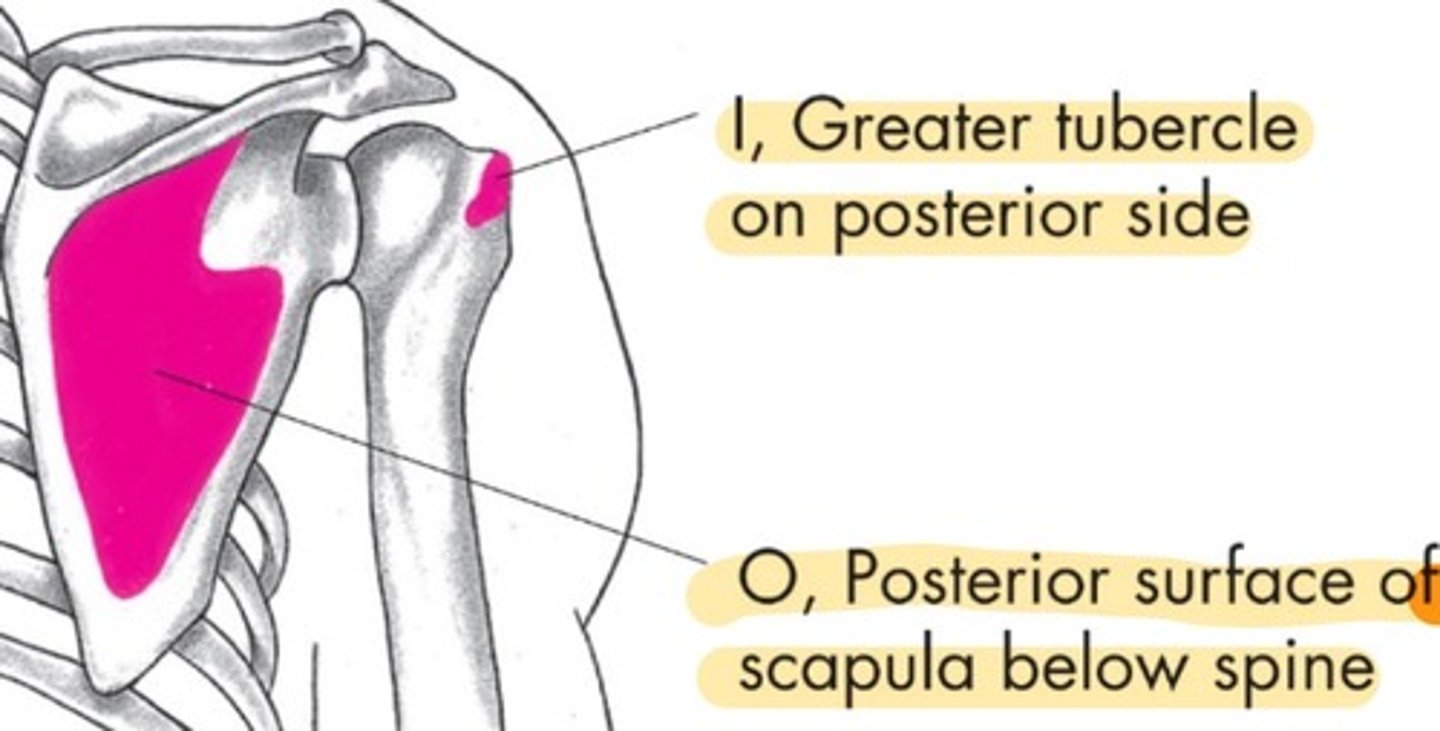
Infraspinatus insertion
greater tubercle on posterior side
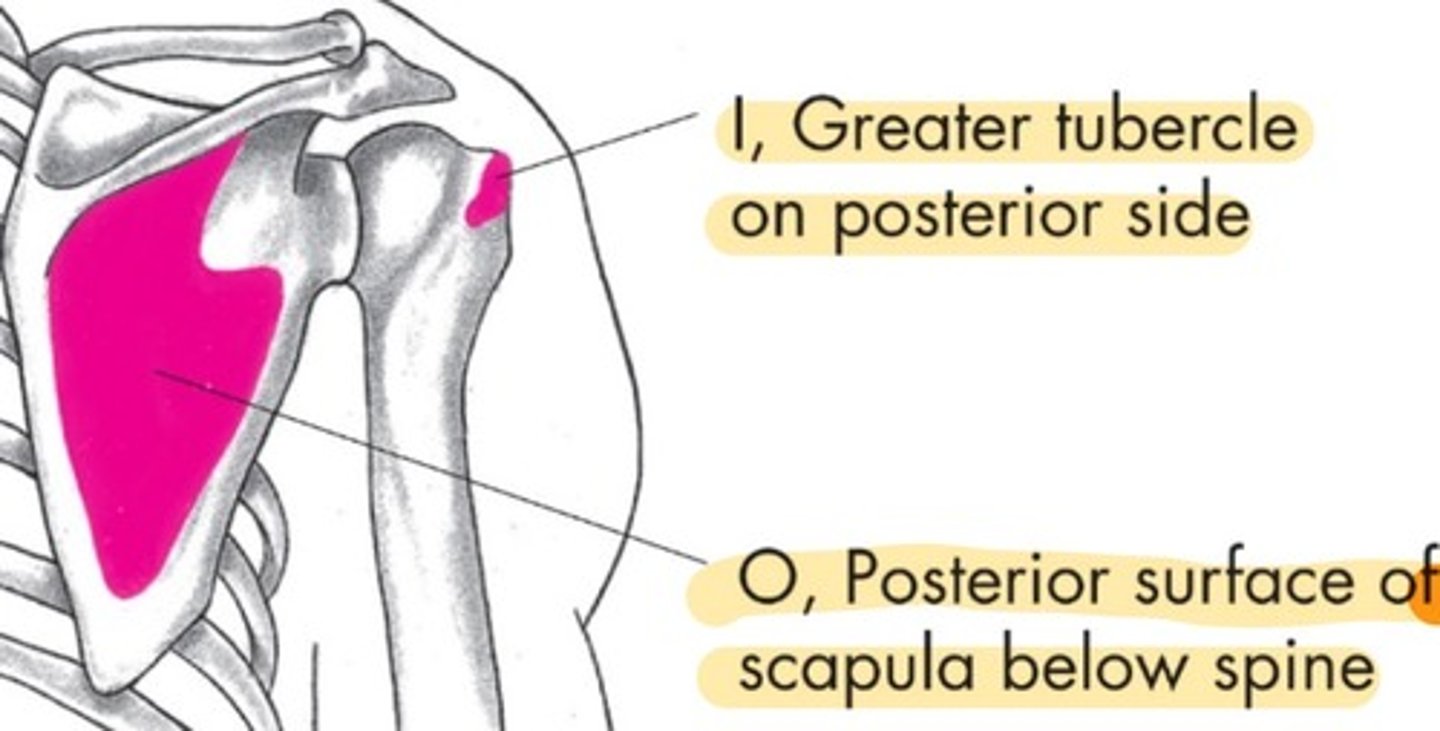
Teres minor origin
posterior scapula lateral border
Teres minor insertion
greater tubercle of humerus on posterior side
Rotator Cuff muscles location
Shoulder girdle
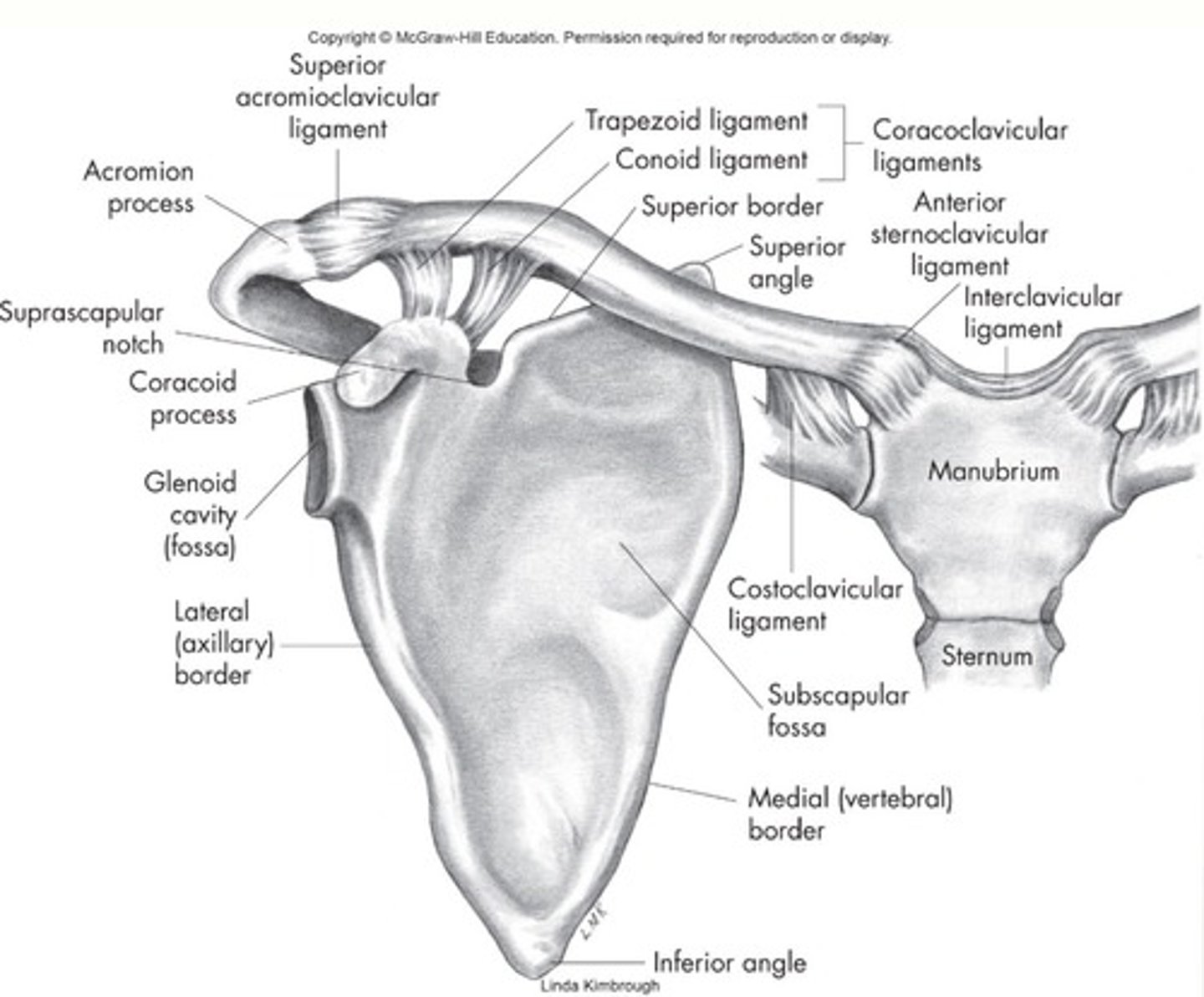
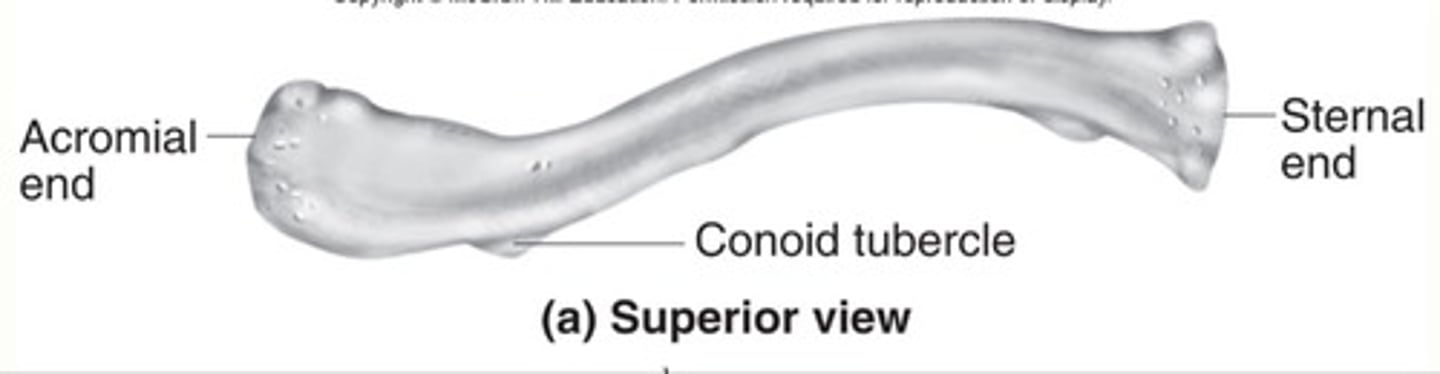
Clavicle Landmarks
acromial end and sternal end
Sternoclavicular ligamentous support
costoclavicular and interclavicular ligaments
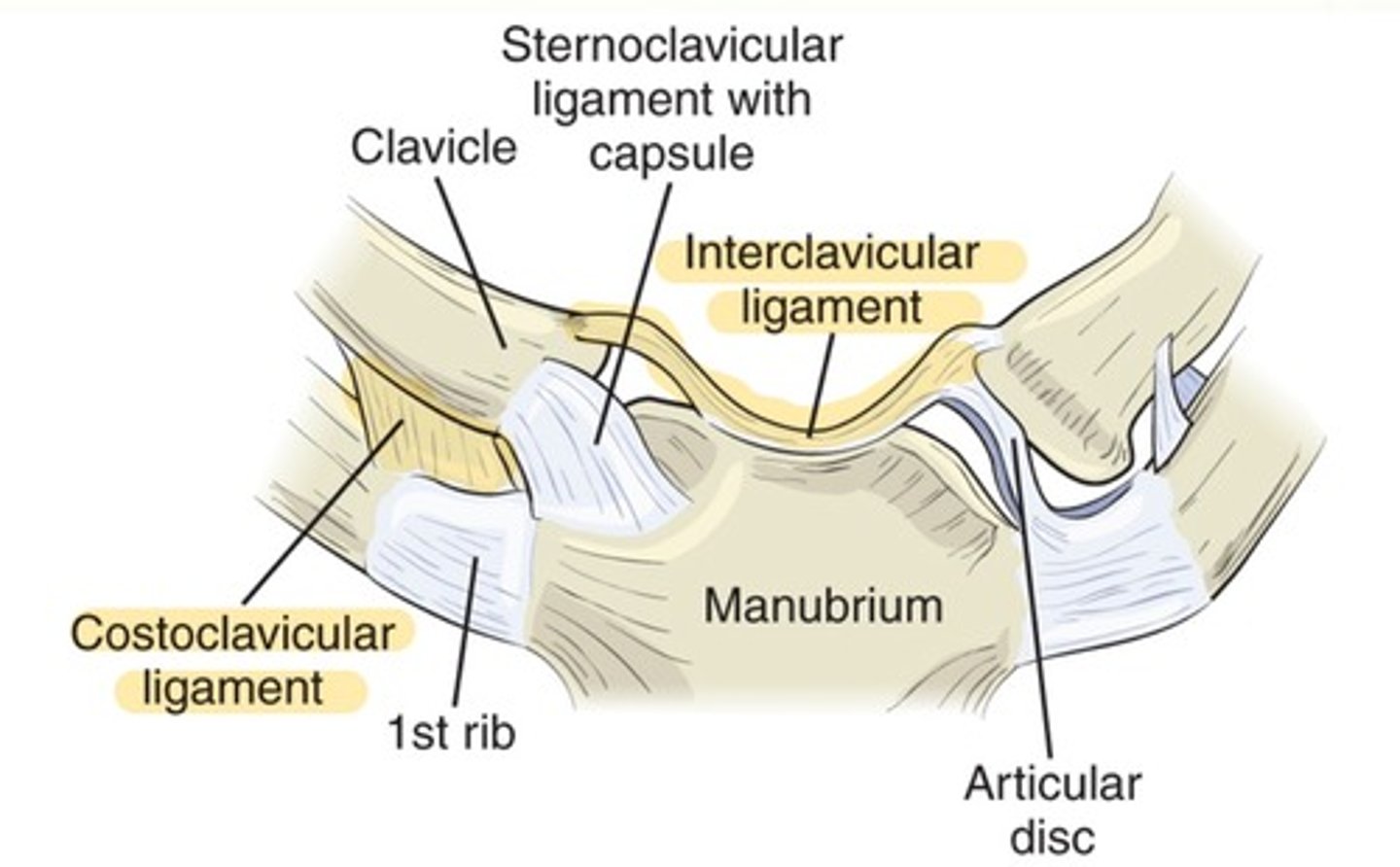
SC joint classification
synarthrodial classification
SC joint movement anteriorly
15 degrees with scapular protraction
SC joint movement posteriorly
15 degrees with scapular retraction
SC joint movement superiorly
45 degrees with elevation
SC joint movement inferiorly
5 degrees with depression
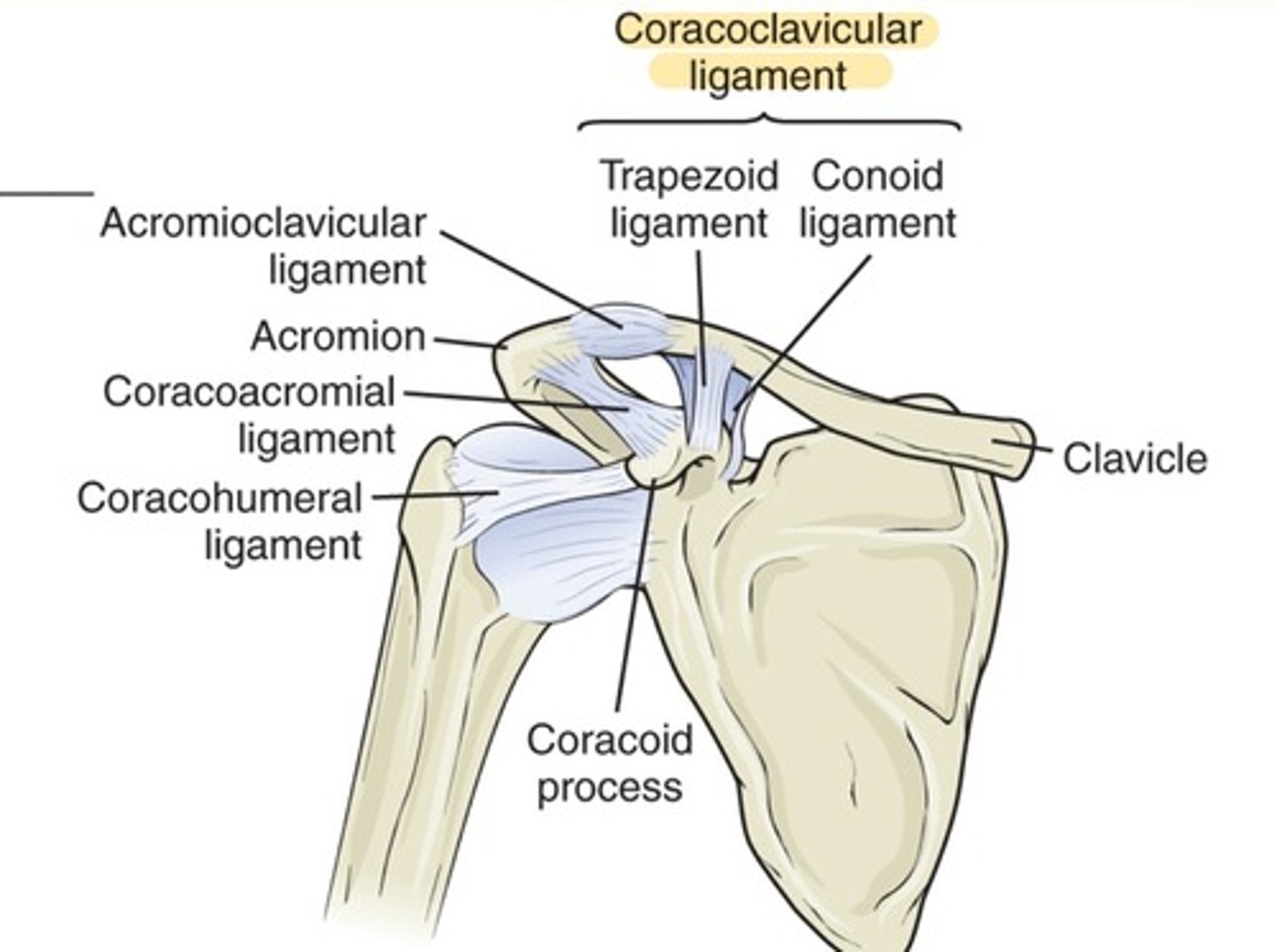
AC joint
arthrodial classification, 20-30 degree rotational/gliding motion
AC joint supported by
coracoclavicular, superior ac, and inferior ac ligaments
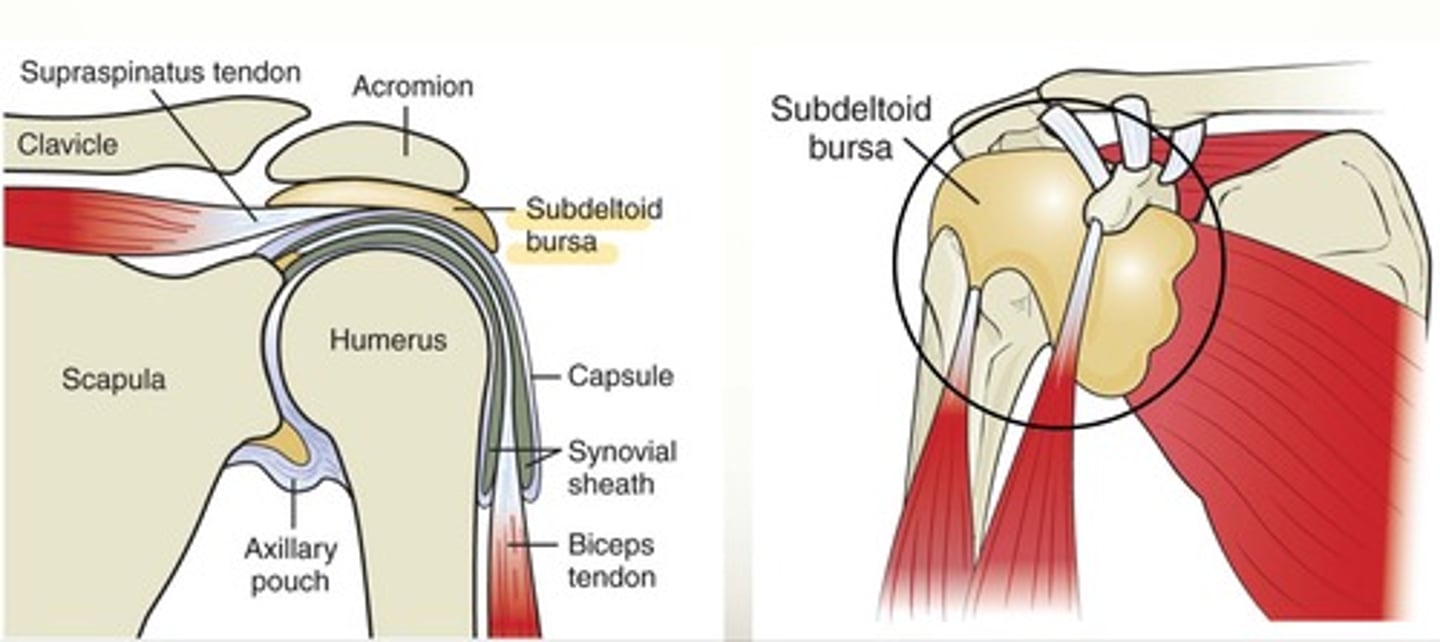
Subdeltoid bursa
large, located between deltoid muscle and joint capsule
Scapulothoracic joint (ST joint)
scapular moves on the rib cage
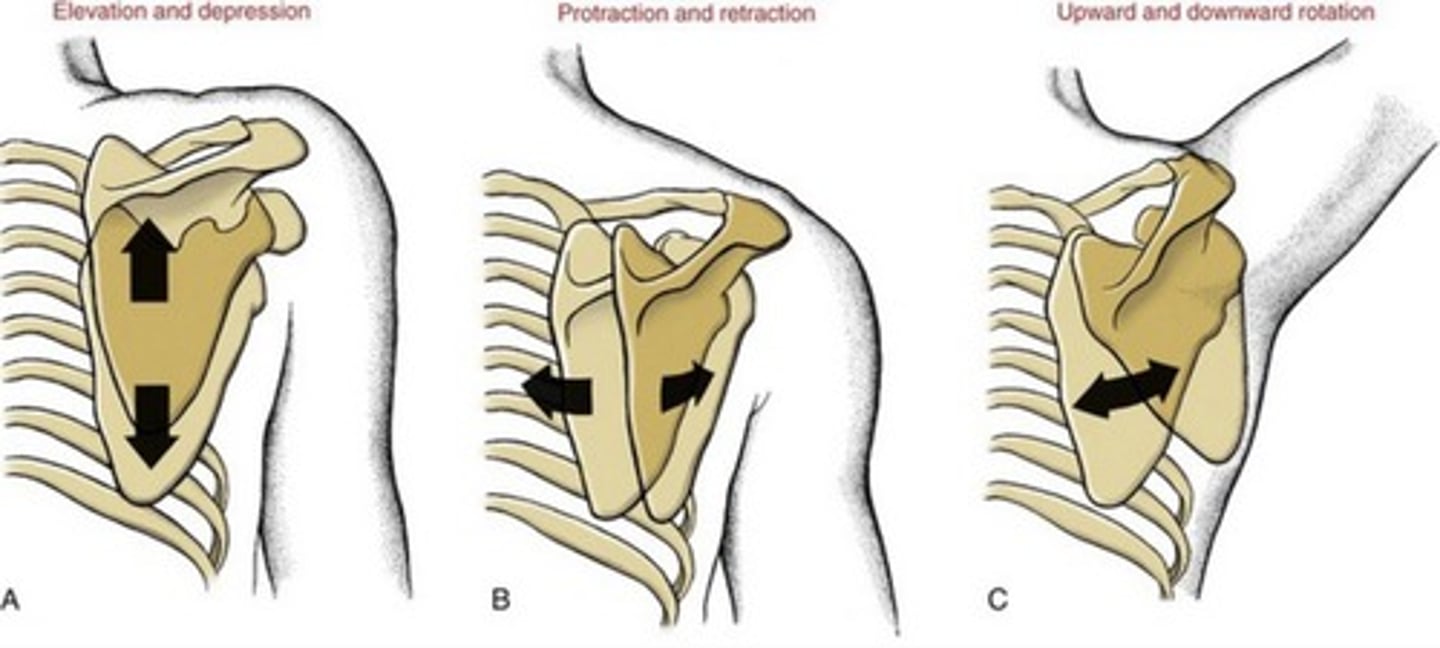
Scapula moves 25 degrees with
abduction-adduction
Scapula moves 60 degrees with
upward-downward rotation
Scapula moves 55 degrees with
elevation-depression
Scapula muscles...
stabilize scapula, provide stable base to exert forces
Scapula remains in a _______ position during shoulder joint actions
static
5 muscles primarily involved in shoulder girdle movements
upper and lower traps, serratus anterior, rhomboids, and pec minor
The 5 muscles primarily involved in shoulder girdle movements provide what type of stability for the shoulder?
dynamic stability
Scapula muscles are important in...
spinal posture
Scapula muscles contribute to what lumbar deformity
kyphosis
Scapula muscles maintain what in the spine?
Lumbar lordosis and keep head over trunk in balanced position
Good posture aids in easier...
breathing
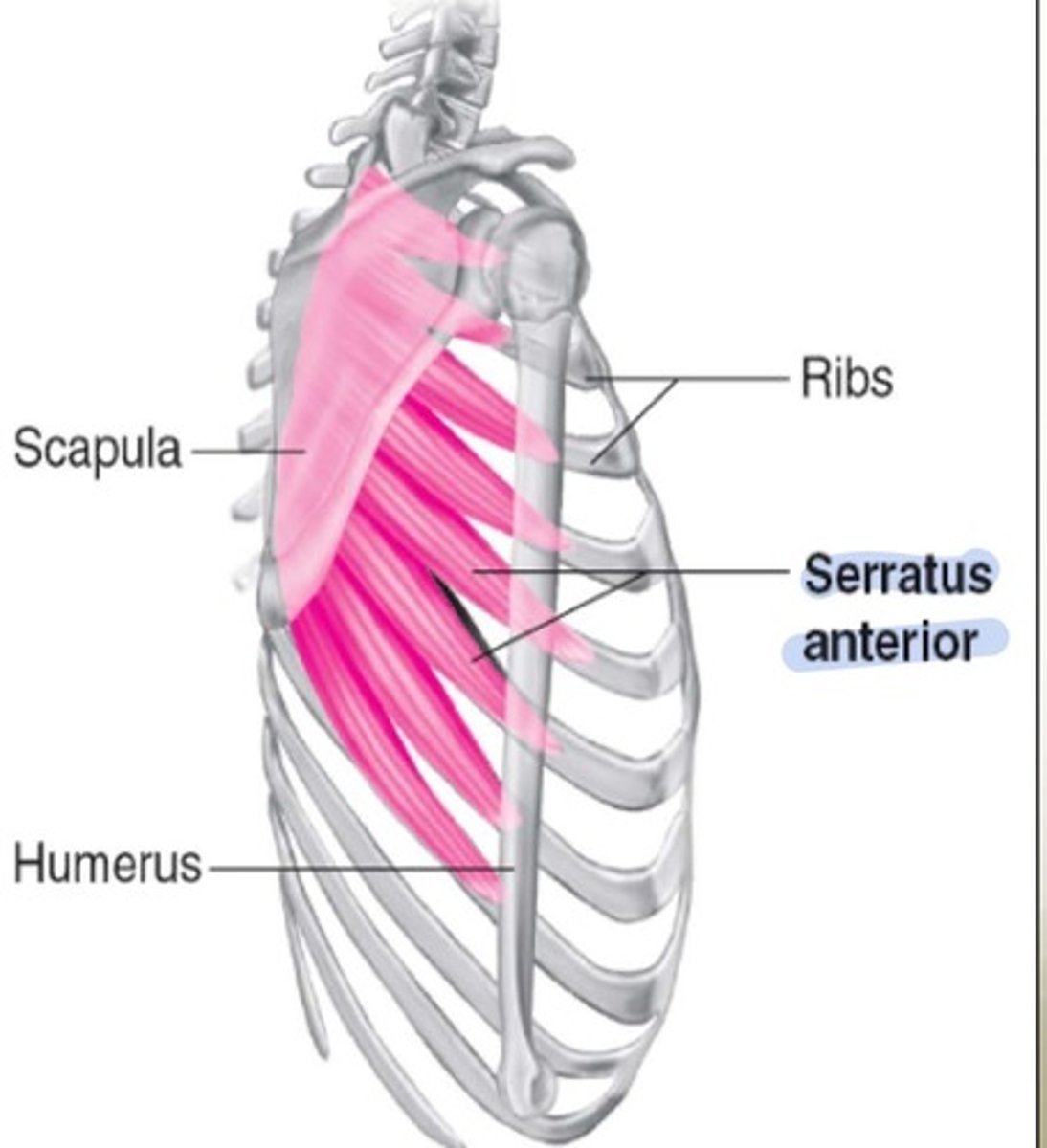
Scapula winging affects which muscle
serratus anterior
Serratus is located where and does what actions
posterior and laterally, abduction and upward rotation
Pec minor is located where and does what action
anterior, abduction, downward rotation, and depression
Subclavius is located where and does what action
anterior, depression
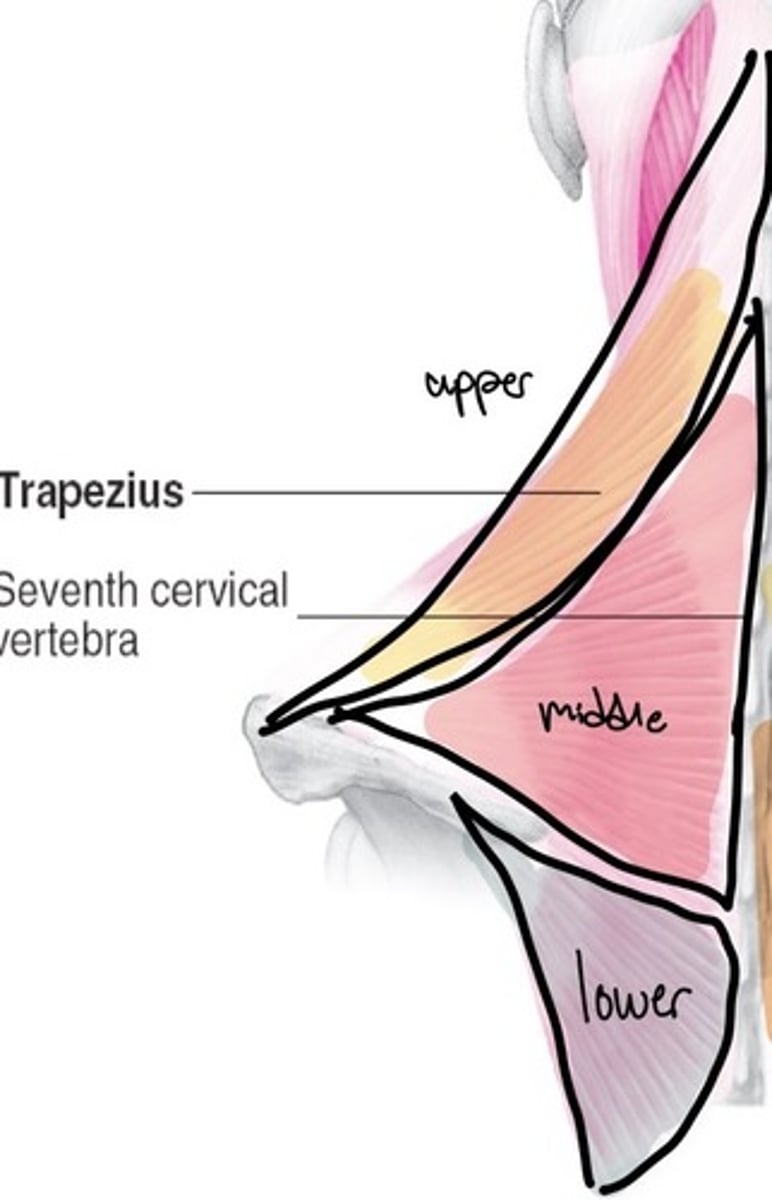
Trap upper fibers action
elevation and extension of the head
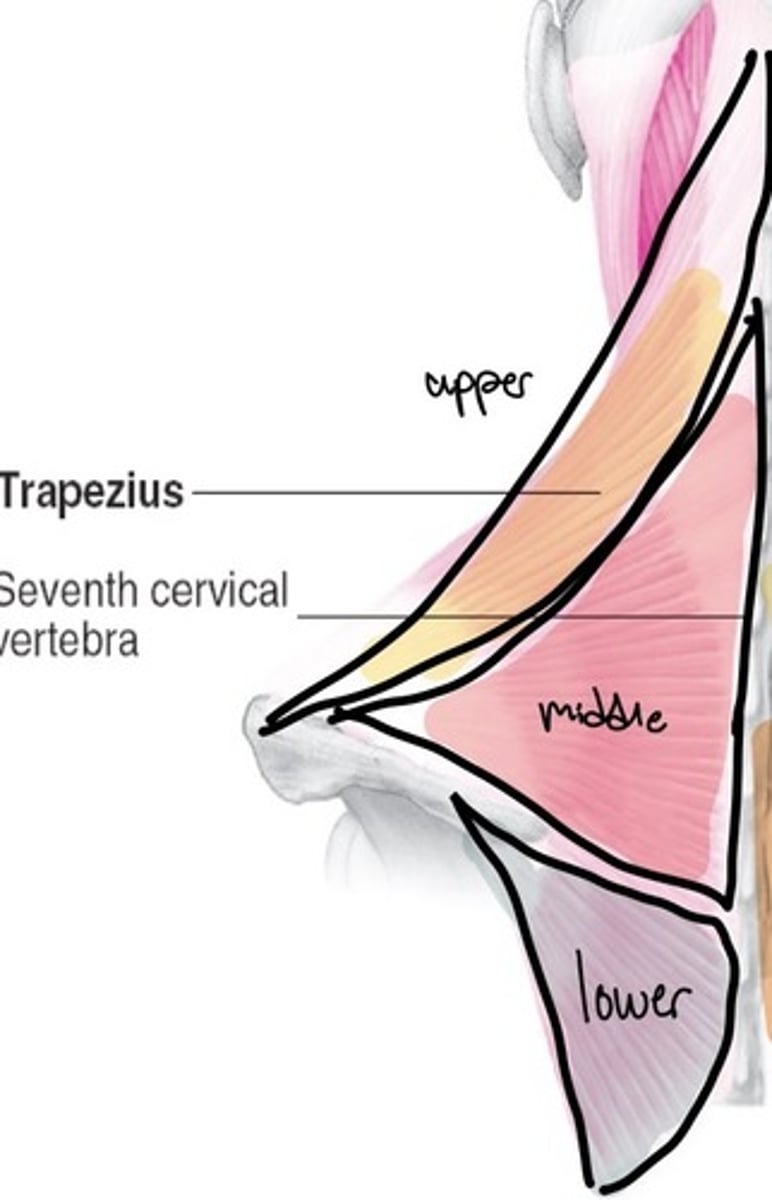
Trap middle fibers action
elevation, adduction, and upper rotation
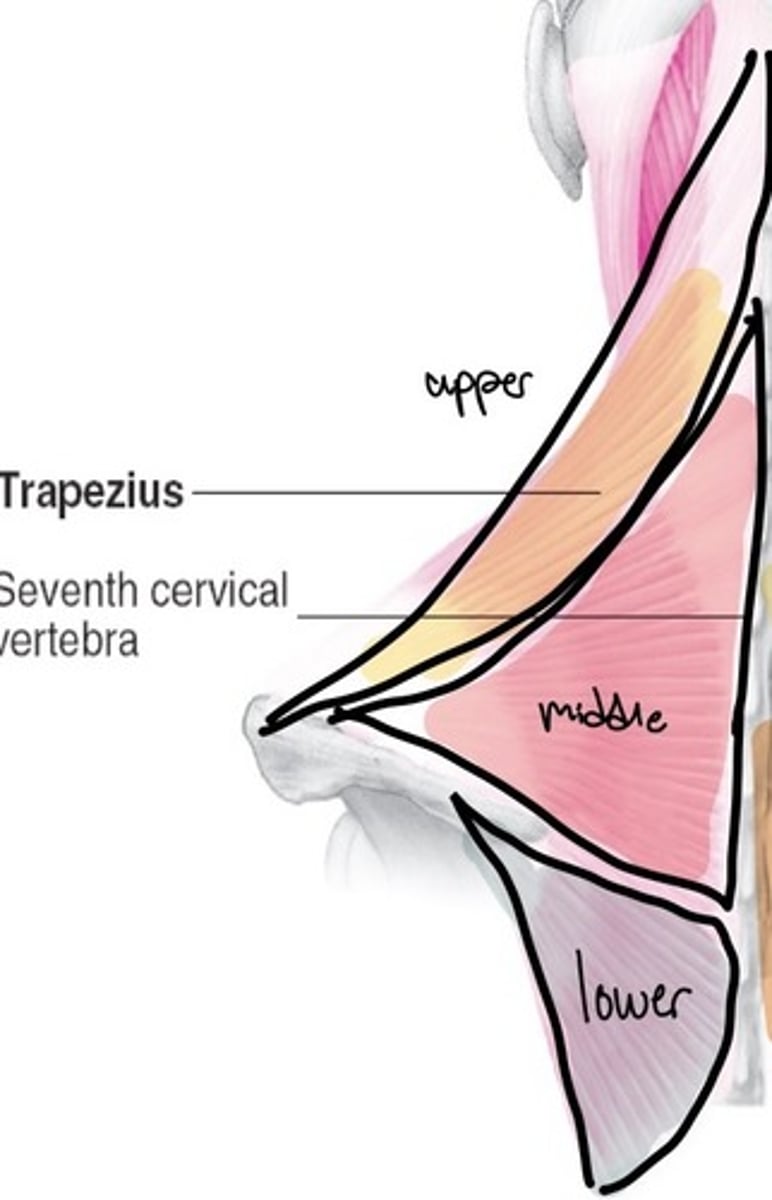
Trap lower fibers
adduction, depression, upward rotation
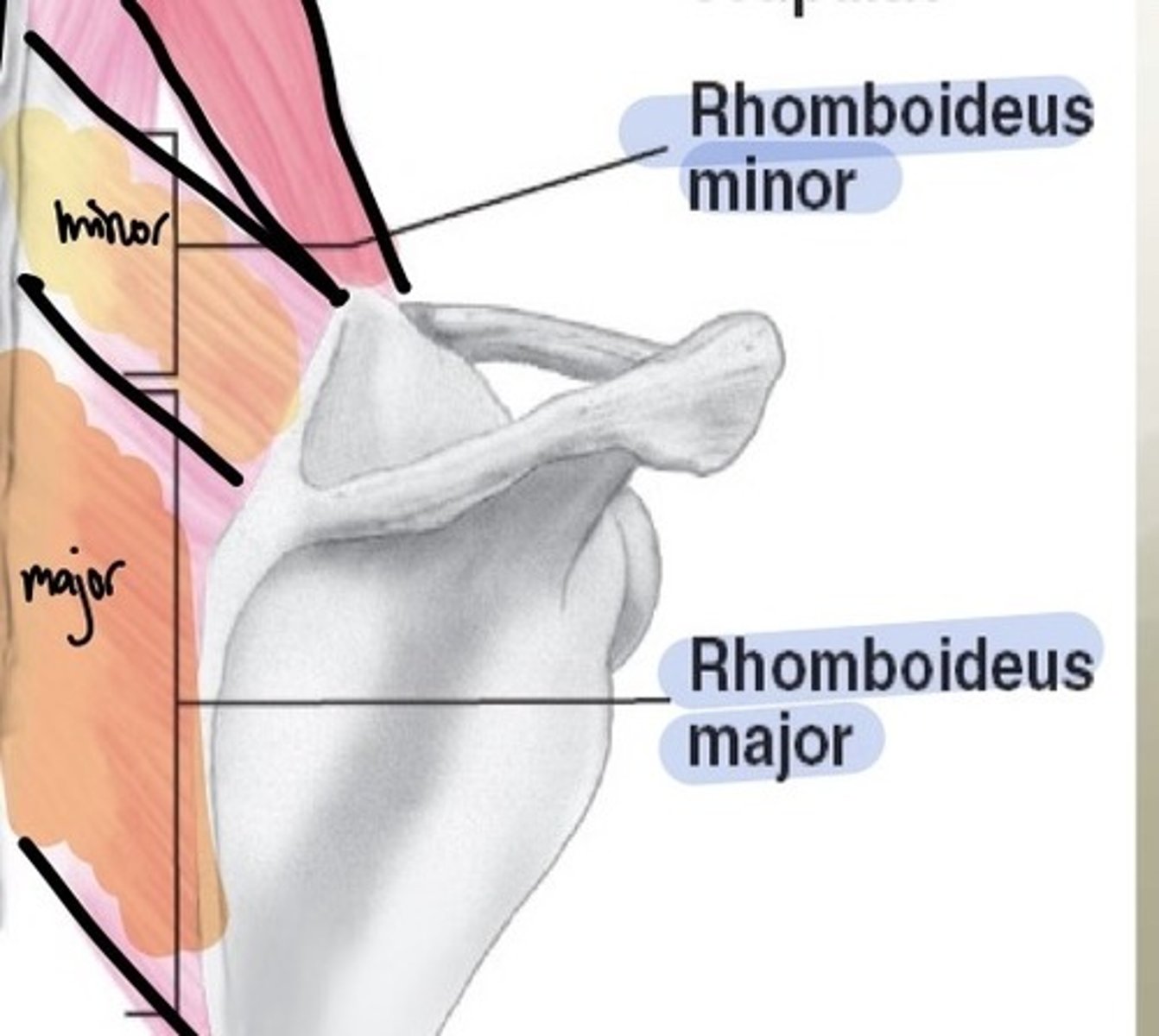
rhomboid action
adduction, downward rotation, and elevation
levator scapulae action
elevation