Structures of the Thoracic Wall
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Thoracic wall anteriorly: ________ & _____ ______
Sternum, costal cartilage
Thoracic wall posteriorly: ________ column from __ - __.
Vertebral, T1, T12
Thoracic wall laterally: ________
Costal spaces
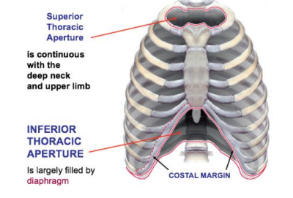
Thoracic wall superiorly: _____________ bordered by __ and ___, ______ of sternum
Superior thoracic aperture, T1, rib 1, manubrium
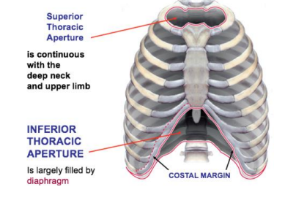
Thoracic wall inferior: ____________ bordered by T__, rib __ and end of rib ___, costal ______ and _______ process of the sternum is separated from abdomen by the _________.
Inferior thoracic aperture, 12, 12, 11, margin, xiphoid, diaphragm
_______ is the medial plane over the sternum.
Midsternal line
_____ is vertical down on _______ wall of thorax passing the ______ angle of scapula
Scapular line, posterior, inferior
What is the space above and below the clavicle?….
Supraclavicular, infraclavicular
_______ is the space overlying the stomach..
Traube’s
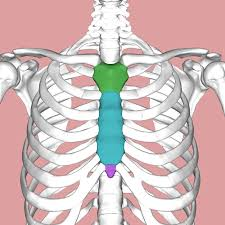
Parts of the sternum.
Green: ______
Blue:_______
Pink: _______
Manubrium, body, xiphoid
What is the space in between the scapula, above and below?….
Interscapular, suprascapular, infrascapular
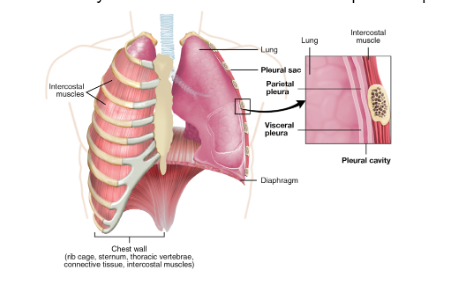
_______ is the thin membrane covering the lungs.
Visceral pleura
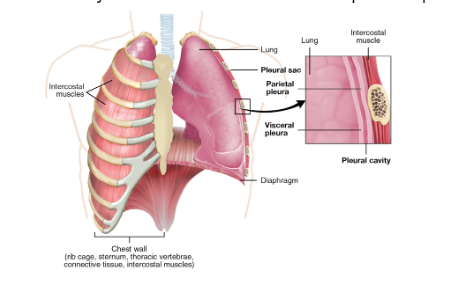
_______ is the inner surface of the chest wall.
Parietal pleura
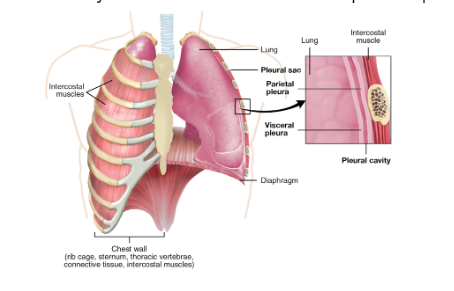
_______ is the sac between the parietal and visceral pleura…
Pleural cavity
The manbrium attaches to the ___ and 1st upper _______ cartilages, it is also opposite of __ and __
Clavicle, costal, T3, T4
The thoracic cavity is divided into two parts: the ______ (median portion) and _______ & ____.
Mediastinum, plurae, lungs
The body of the sternum articulates with ___ to ___ costal cartilages
2nd, 7th
True or False: The xiphoid process does not ossify in children
True
________ is where the 2nd rib is attached, opposite intervertebral disc of T_- T_
Sternal angle of Louis, 4, 5
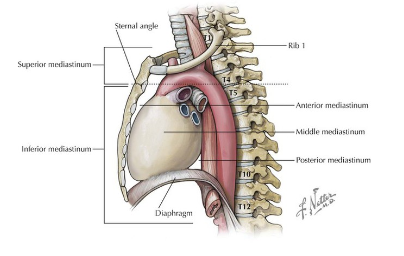
The _____ marks the plane separating the superior and inferior mediastinum.
Sternal Angle of Louis
In the Sternal angle of Louis, the ______ aorta ends, ____ of aorta starts and ends and ______ aorta begins at this level…
ascending, arch, descending
In the Sternal angle of Louis, _____ divides into 2 principal bronchi
trachea
_____ arches over the roof of the ____ lung and open in _____ vena cava.
Azygos vein, right, superior
Pulmonary _____ divides into 2 pulmonary ______ below the level of the sternal angle of louis.
trunk, arteries
________ crosses from _____ to ____ side and reaches left side at the level of sternal angle
Thoracic duct, right, left
More statements about the Sternal Angle of Louis:
Marks the ______ limit of the base of the ____.
_______ _____ are situated at the same level
Upper, heart, cardiac plexus
_______ joint is opposite __ vertebral body…
Xiphisternal, T9
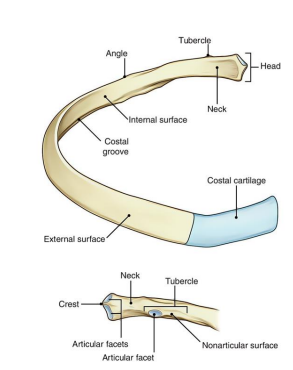
Ribs are ___, _____ & ____.
Long, twisted, flat
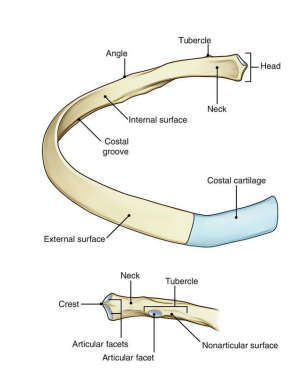
Characteristics of ribs:
1. Superior: ______ & _____.
2. Inferior: _____ & ____ with ______ groove for intercostal nerves and vessels.
Round, smooth, sharp, thin, costal
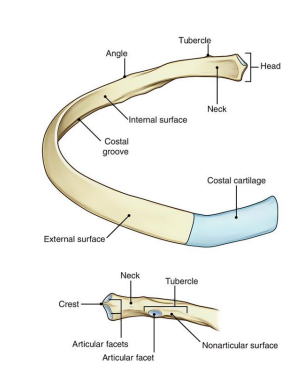
Ribs _ to _ are attached to the sternum called “True” ribs.
1,7
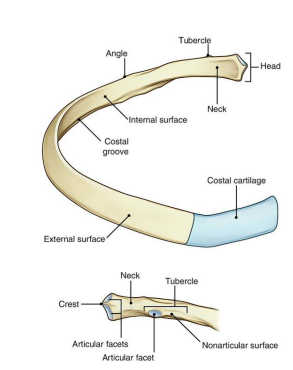
“False” Ribs __ to __ are attached to the __ costal cartilage not the sternum and anteriorly to each other
8, 10, 7th
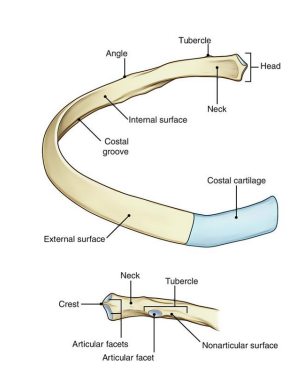
“Floating” Ribs __ to __ have no attachment at all…
11, 12
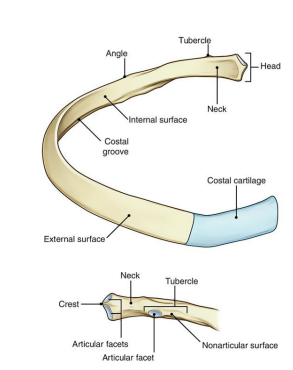
Superior surface: Articulates with ____ costal facet
Inferior surface: Articulates with ____ costal facet
Inferior, superior
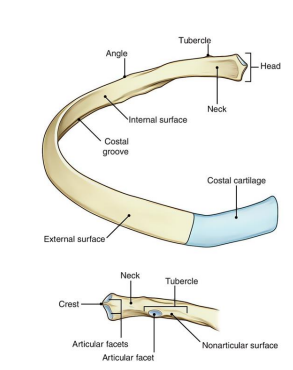
____ is the flat slightly constricted region separating head from tubercle
Neck
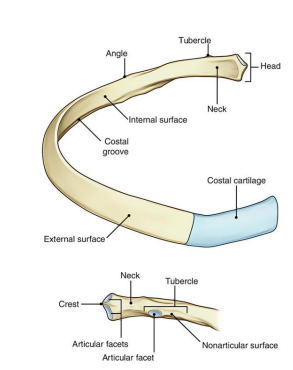
_____ is the prominence in the outer posterior surface at junction of the neck and body
Tubercle
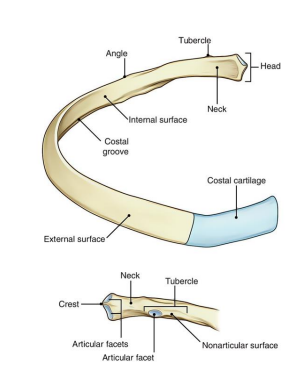
2 parts of the Tubercle of the rib:
______ - medial oval facet for articulation of transverse process of associated vertebrae
______ - roughened by attachment of ligament
Articular, non-articular
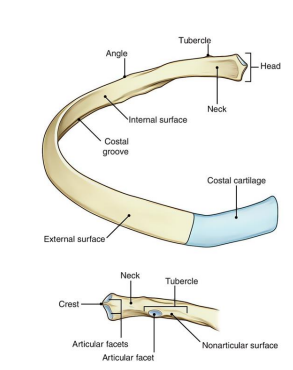
_______ where body sharply turns; most common site of fracture
Angle
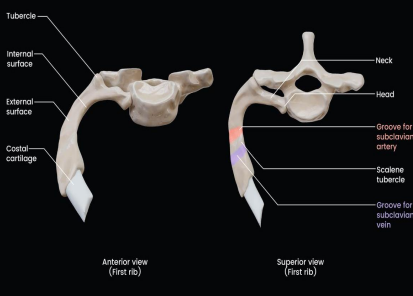
_______ important because of its relation to the lower nerves of brachial plexus and _______ artery and vein
First rib, subclavian
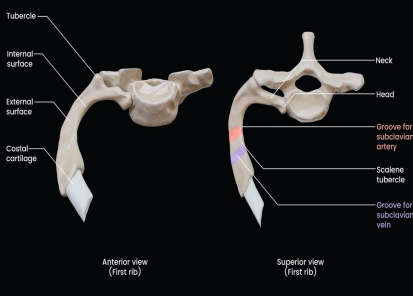
The anterior groove house the _____ while the posterior groove houses the _______& _______.
Subclavian vein, brachial plexus, subclavian artery
True or False: Both ribs 11-12 have their own tubercles and necks.
False
Costal cartilage is made of ________ cartilage and connects the upper seven ribs to the lateral edge of the sternum.
Hyaline
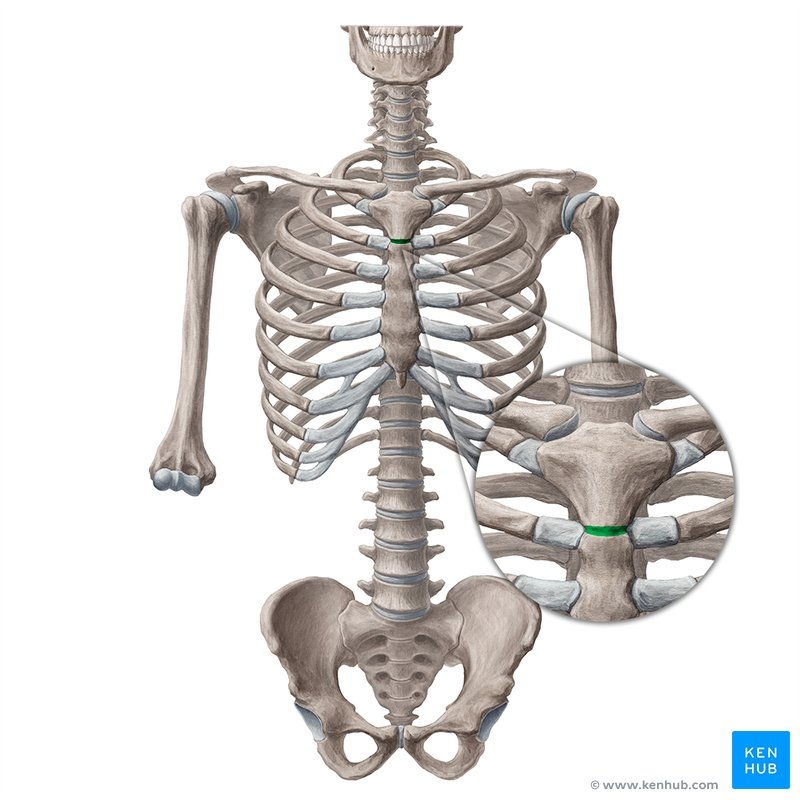
__________ joint is a ___________ joint that is opposite to __ IV disc, plane separation between superior and inferior mediastinum
Manubriosternal, cartilaginous, T4
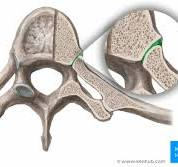
Name this joint & its type.
Costovertebral joint, plane
What type of joint is the one between the body of the sternum and manubrium?…
Cartilaginous joint
What type of joint is the one between the sternum and Xiphoid process?..
Cartilaginous joint
What type of joint is the one between the 1st rib and the manubrium?.
Cartilaginous joint
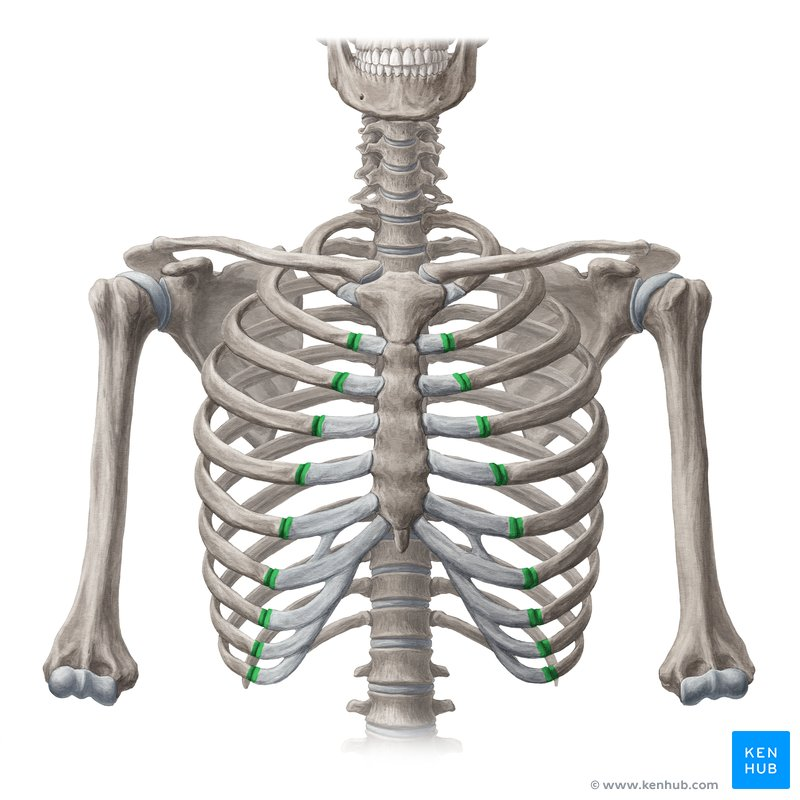
Name this joint & its type.
Costochondral joint, cartilaginous
Joints between costal cartilage & sternum…
1st rib to sternum - ____________
2nd to 7th - ____________
6th-10th (costal cartilage articulates with one another) - ____________
Cartaliginous, plane, plane
True or False: Ribs 11 and 12 have a synovial plane joint of the tubercle and rib with the costal facet
False
A.K.A superior aperture that communicates with the roots of the neck…
Thoracic outlet
Name the 4 Structures that pass the thoracic outlet:
______
______
______ & _____
______
Esophagus, Trachea, Vessels and nerves, Apices of the lungs and pleura
______ TA communicates with the root of the neck while the _______ TA is the communication with abdomen..
Superior, Inferior
______ is the compression of the brachial plexus nerves, subclavian artery and vein as it exits between first rib and clavicle
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Swelling or puffiness in the arm or hand
bluish discoloration of the hand
feeling of heaviness in the arm or hand
pulsating lump above the clavicle
deep, boring toothache-like pain in the neck and shoulder region which seems to increase at night
easily fatigued arms and hands
superficial vein distention in the hand
Vascular symptoms
Paresthesia along the inside forearm and the palm (C8, TQ dermatome)
muscle weakness and atrophy of the gripping muscles (long finger flexors) and small muscles of the hand (thenar and intrinsics)
difficulty with fine motor tasks of the hand
cramps of the muscles on the inner forearm (long finger flexors)
pain in the arm and hand
tingling and numbness in the neck, shoulder region, arm and hand
Neurological symptoms
_____ rib - 13 ribs; 7th rib had a rib
______ syndrome - between the anterior and middle scalene
_______ syndrome - between clavicle and 1st rib
_______ syndrome - beneath pectoralis minor
Cervical, scalene, costoclavicular, hyperabduction

The examiner flexes tha patient's elbow to 90 degrees while the shoulder is extended horizontally and rotated laterally. The patient is asked to turn their head away from the tested arm. The radial pulse is palpated and if it disappears as the patient's head is rotated the test is considered positive
Allen test

The examiner palpates the radial pulse while moving the UE in abduction, extension and ER. The patient then is asked to rotate her head toward the involved side while taking a deep breath and holding it. A positive exam will result in a diminished or absent radial pulse
Adson’s test
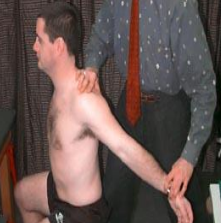
The examiner locates the radial pulse and draws the patient's shoulder down and back as the patient lifts their chest in an exaggerated “at attention” posture. A positive test is indicated by an absence of a pulse. This test is particularly effective in patients who complain of symptoms while wearing a back-pain or a heavy jacket
Costoclavicular maneuver
______ is the space between adjacent ribs..
Intercostal space
_______ lies the intercostal nerves, arteries and vein
Costal groove
Name all 7 layers of the Intercostal space.
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
Skin, superficial fascia, deep fascia, intercostal membrane, endothoracic fascia, extrapleural fatty layer, parietal pleura
The _______ intercostal is the most superficial layer and its fibers are directed downward and _____
External, forward
The _______ intercostal is in the intermediate layer and its fibers are directed downward and _____
Internal, backward
_______ is when the __ rib is fixed by the ______ muscle and the ______ muscles raise the __ to __ rib towards ____ rib
Inspiration, 1st, scaleni, intercostal, 2nd , 12th, first
______ is when ____ rib is fixed by _______ and the _____ muscle of the abdomen; the ___ to __ ribs will be lowered by the contraction of the _______ muscles
Expiration, quadratus lumborum, oblique, 1st, 11th, intercostal