AP Biology 3B
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
all living things (not just animals) experience or undergo
cellular respiration: uses food energy and produces ATP
photosynthesis
when plants convert solar energy to chemical energy (food)
occurs in plants, algae, protists, and prokaryotes
chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O > C6H12O6 + 6O2
site of photosynthesis
chloroplast (membrane bound organelle)
mesophyll
chloroplasts mainly found in these cells of leaf
stomata
pores in leaf (CO2 enters / O2 exits)
chlorophyll
green pigment in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts
essential for photosynthesis
converts sun light to electron energy
stroma
fluid filled space in the inner membrane
thylakoid
a membrane/sac
lumen
fluid filled space in the thylakoid
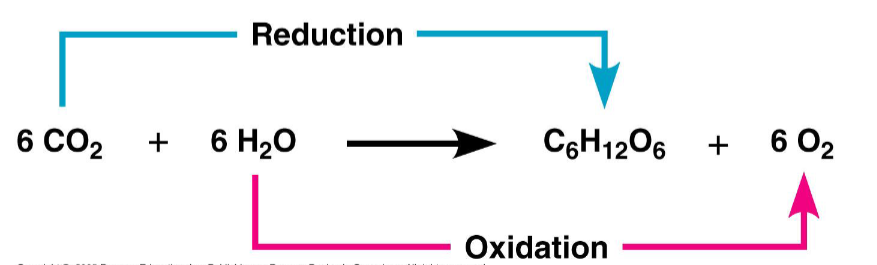
redox reaction (OIL RIG)
a process in which water is oxidized and carbon dioxide is reduced
oxidation = loss of electrons (or losing H)
reduction = gain of electrons (or gaining H)
OIL RIG meaning
Oxidation is Loss (losing H electrons)
Reduction is Gain (gaining H electrons)
stages of photosynthesis
Light dependent reaction (photo)
Calvin Cycle (synthesis)
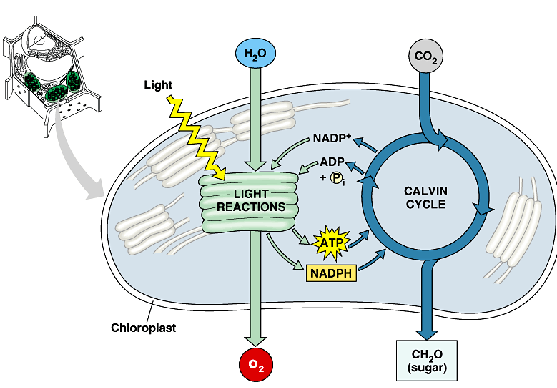
Describe the light dependent reaction (photo) stage
energy conversion reactions
convert solar energy to chemical energy
produce ATP & NADPH
two photosystems in the thylakoid membrane
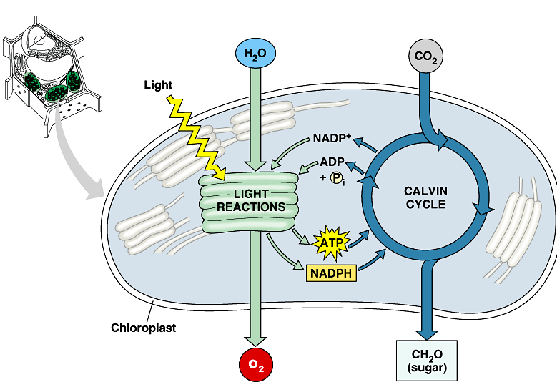
describe the calvin cycle (synthesis) stage
sugar building reaction
uses chemical energy (ATP & NADPH) to reduce CO2 & synthesizes C6H12O6
in the stroma
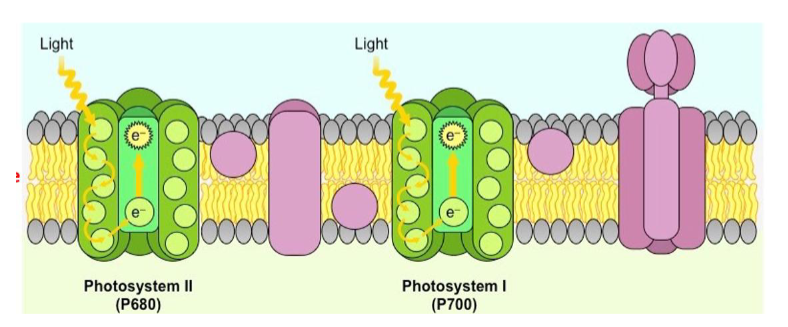
describe the two photosystems in the thylakoid membrane
a light-catching unit: large complex of proteins and pigments that capture the sunlight
collections of chlorophyll (a) molecules
transfers high energy electrons for ATP and NADPH
Name and function of Photosystem II
P680
absorbs light energy at 680nm
name and function of photosystem I
P700
absorbs light energy at 700nm
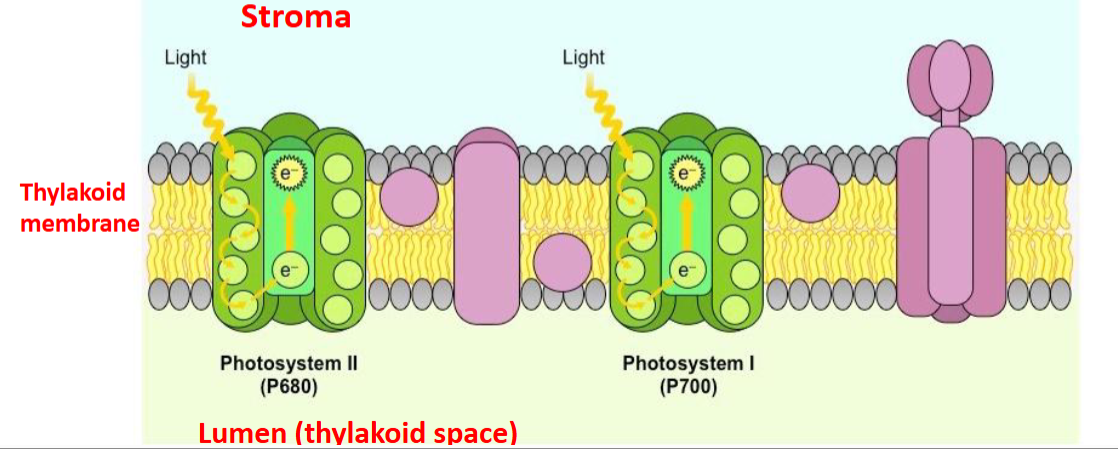
first step of a light dependent reaction
Light excites chlorophyll electrons (in photosystems) and become energized
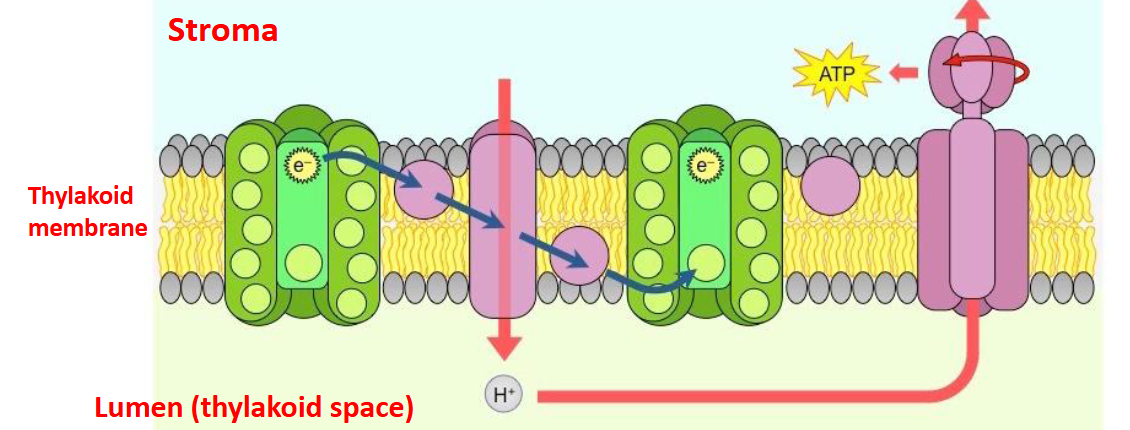
second step of a light dependent reaction
Excited electrons pass through electron transport chain (ETC), making ATP via chemiosmosis
function of the proton pump in a light reaction
pumps hydrogen from the stroma to the lumen (low to high concentration gradient)
creates a high concentration of hydrogen for the ATP Synthase to make ATP
low pH means what type of environment
acidic environment
aka. pH2
high hydrogen concentration
high pH means what type of environment
normal environment
aka. pH9
low hydrogen concentration
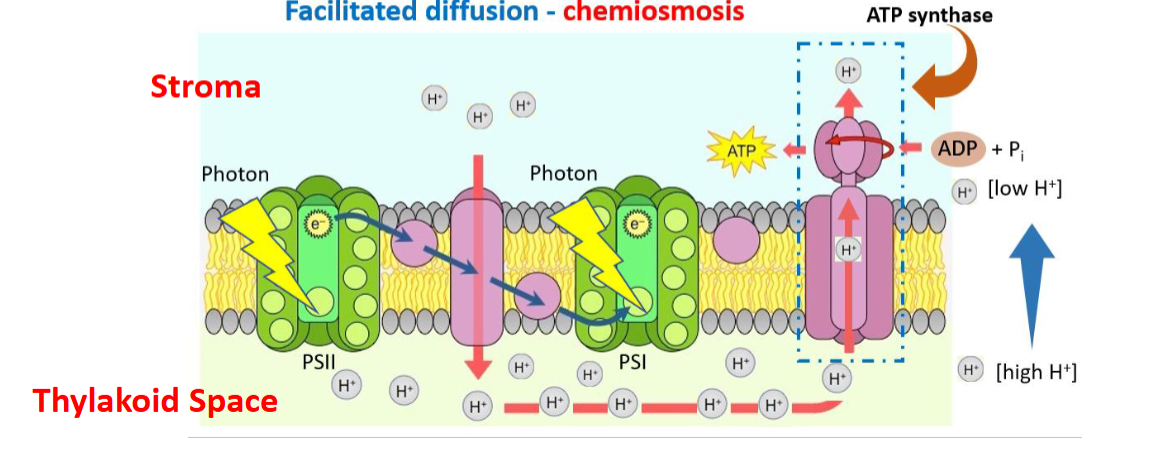
function of ATP synthase
phosphorylates ADP to ATP to make ATP energy
uses hydrogen to make ATP
Phosphorylation: adding a phosphate to diphosphate to make it triphosphate
What is the energy source of active transport in a light dependent reaction?
from the electrons traveling down the electron transport chain (ETC)
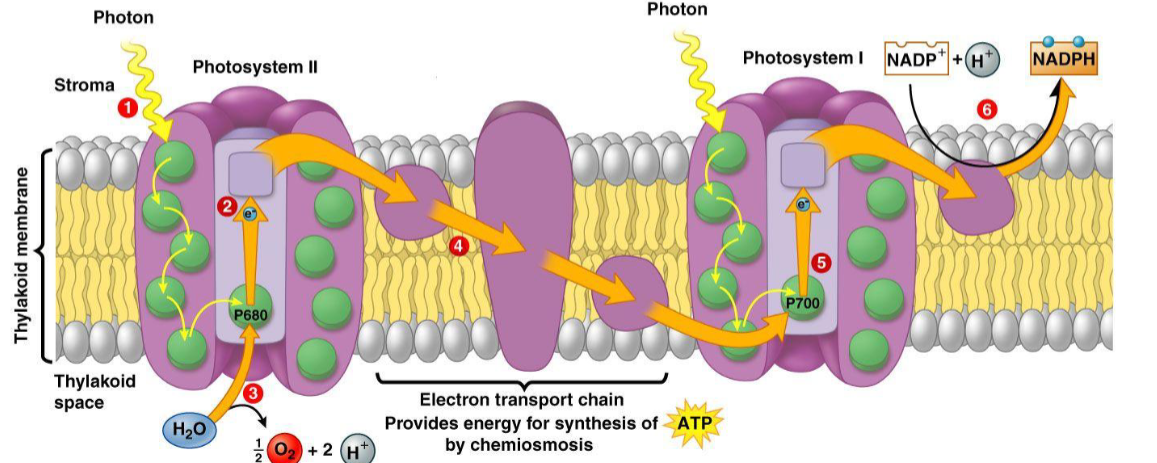
Step 3 (last step) of a light dependent reaction
electrons reduce NADP+ (to form NADPH) and are replaced by photolysis of water
NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
NADP+ is the final electron acceptor
why would the process of the light dependent reaction stop
electrons are lost to the electron transport chain and therefore will no longer create ATP / energy
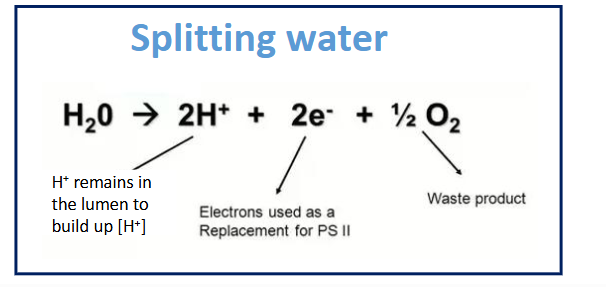
purpose of photolysis of water
water serves as an electron donor for the electron transport chain (photosystems) to compensate for the lost electrons (due to the ETC)
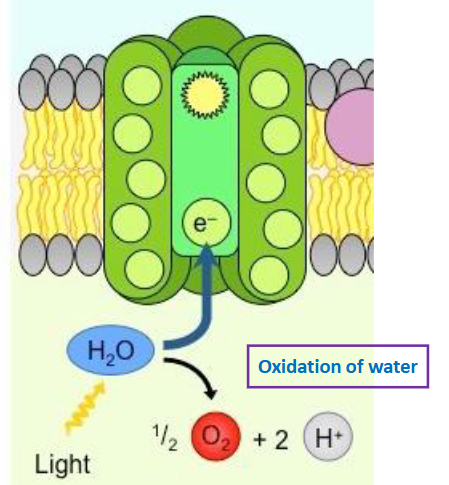
describe photolysis of water
water is in the lumen and therefore is split (by the sun) in the lumen to make 2H+ electrons
eventually creates O2 that will leave to the atmosphere via the stomata
in a light dependent reaction, when the H+ electrons are traveling to the stroma from the thylakoid space, what type of transport is it
passive transport because it moves from high to low concentration, and therefore does NOT use energy
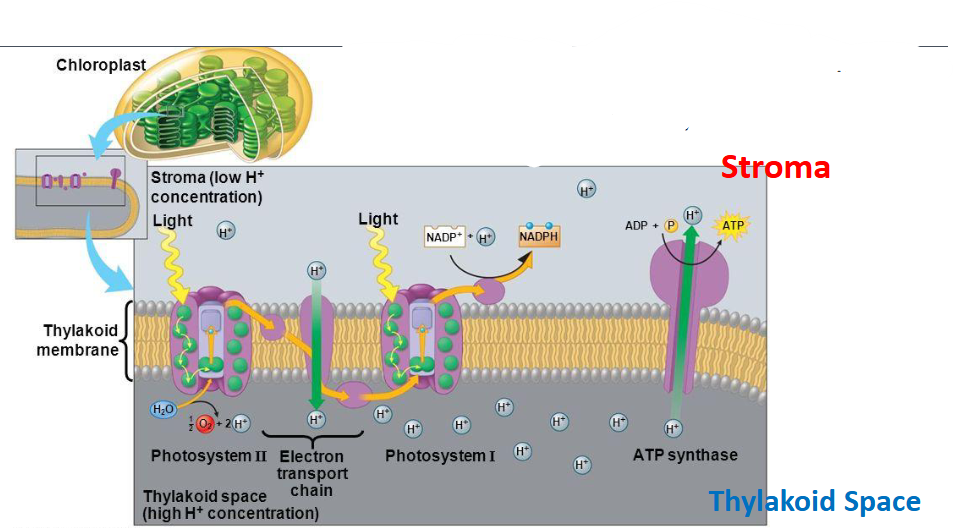
photophosphorylation is
the process of using photosystems to make ATP & ADPH via ETC and Chemiosmosis
calvin cycle occurs in the
stroma
calvin cycle requires what products
ATP & NADPH
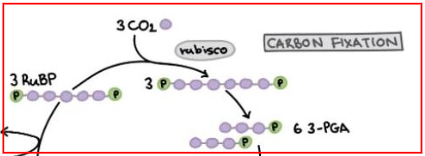
1st phase of calvin cycle
Carbon Fixation
CO2 from the air is imbedded in the cycle and combined with RuBP to make 3-Carbon compound called PGA
catalyzed by enzyme rubisco
aka. carbon fixation
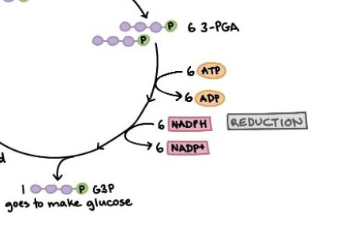
2nd phase of calvin cycle
Reduction
ATP and NADPH are used to convert PGA into G3P
PGA gains electrons (reduction)
ATP converted to ADP
ADP & NADP+ return to light dependent reaction to start process again
3rd phase of calvin cycle
Regeneration of RuBP
Some G3P make glucose, and others will be recycled to regenerate RuBP
Allows for more CO2 to be fixed in the cycle
requires ATP
describe G3P
product of the Calvin Cycle
3 carbon sugar
factors that affect photosynthesis
temperature
light intensity
more light = more reaction rate
concentration of CO2
more CO2 = more reaction rate
(experiment vocab) tissue culture
technique to grow cells in the laboratory
(experiment vocab) cell line
a type of cell grown in the lab for experiment
HeLa Cell
(experiment vocab) In Vitro
an experiment in a test tube
(experiment vocab) In Vivo
an experiment in a test tube
(experiment vocab) Nutrient medium
a liquid nutrient used to feed the cells in the lab
(experiment vocab) radioactive isotope
an isotope of an element is used to “tag” the molecules studied.
(experiment vocab) Assay
an experiment
COVID-19 PCR test
ultimate source of energy
sun
photosynthesis is
endergonic (requires energy)
cellular respiration is
exergonic (releases energy)
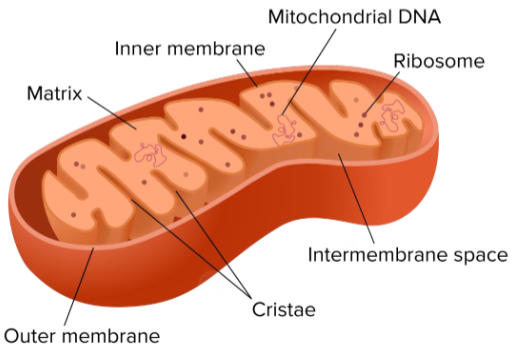
Site of cellular respiration is
mitochondria
double membrane
mtDNA
Folded inner membrane called cristae increase surface area
interior is the matrix
Two ways of making ATP are
Oxygen is available
Aerobic/cellular respiration
Oxygen is unavailable
fermentation in cytoplasm
oxidation + reduction formulas
C6H12O6 > CO2 = glucose is oxidized
O2 > H2O = oxygen is reduced
1st stage of cellular respiration
Glycolysis
breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate
2nd stage of cellular respiration
The Krebs Cycle
completes the breakdown of glucose , aka citric acid cycle
3rd stage of cellular respiration
Oxidative phosphorylation
accounts for the most ATP synthesis
Glycolysis
energy harvesting process in the cytoplasm of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
occurs in fermentation and aerobic respiration
no oxygen needed
converts glucose (6C) to 2 pyruvate (3C)
produces: 2 ATP + 2NADH + 2 pyruvate
pyruvate oxidation
pyruvate converted to acetyl CoA before the krebs cycle
pyruvate is transported from the cytosol (cytoplasm) to the matrix where oxidation occurs
NADH is produced and CO2 is released as waste
Krebs Cycle
CO2 is released, ATP synthesized, electrons transferred to NADH and FADH2
occurs in mitochondrial matrix
Electron Transport Chain
occurs in the cristae
electrons stored in NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis and Krebs cycle are transported to the ETC where oxygen is the final electron acceptor
purpose of NADH and FADH2
to deliver electrons to the ETC
without oxygen in the ETC
proton pumps stop and therefore ATP production stops
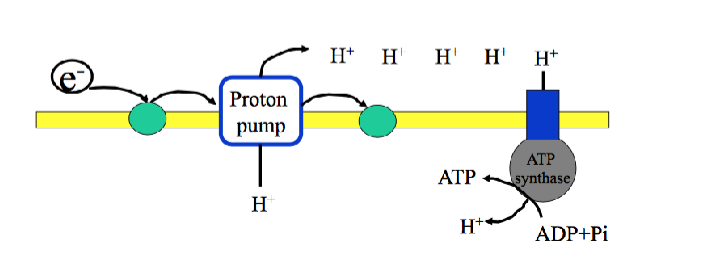
The flow of protons allow for the formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
oxidative phosphorylation (cellular respiration)
photophosphorylation (photosynthesis)
in chemiosmosis, electrons move from
intermembrane space to matrix
terminal electron acceptor in photosynthesis
NADP+
terminal electron acceptor in cellular respiration
oxygen
bacteria does not have
krebs cycle because of no mitochondria
difference between NADH vs FADH2
NADH has to travel through more protein complexes than FADH2
both have the same amount of electrons
factors that decrease ATP synthesis
poisons that block ETC or chemiosmosis
function of oligomycin (poison)
blocks the passage of H+ through ATP synthase
uncouplers such as DNP
destroy the H+ gradient by making the membrane leaky (permeable) to H+
uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation generates
heat
what type of fermentation does yeast undergo
alcohol fermentation
acetaldehyde produced
what type of fermentation do humans undergo
lactic acid fermentation
no acetaldehyde produced
plants in the dark continue to undergo
cellular respiration