BOC: Urinalysis & Body Fluids
1/255
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
256 Terms
A patient with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus will most likely have:
a. pale yellow urine with a high specific gravity
b. dark yellow urine with a high specific gravity
c. pale yellow urine with a low specific gravity
d. dark yellow urine with a low specific gravity
a. pale yellow urine with a high specific gravity
While performing an analysis of a baby's urine, the laboratorian notices the specimen has a "mousy" odor. Of the following substances that may be excreted in urine, the one that most characteristically produces this odor is:
a. phenylpyruvic acid
b. acetone
c. coliform bacilli
d. porphyrin
a. phenylpyruvic acid
An ammonia-like odor is characteristically associated with urine from patients with:
a. PKU
b. viral hepatitis
c. a bacterial infection
d. a yeast infection
c. a bacterial infection
Urine that develops a port wine or deep red color after standing may contain:
a. melanin
b. porphyrins
c. bilirubin
c. urobilinogen
b. porphyrins
Which of the following collection methods would yield the most sterile urine sample?
a. random
b. catherization
c. suprapubic aspiration
d. clean-catch midstream
c. suprapubic aspiration
Urine from a 50 year old patient with severe hepatic disease is reported as having an "amber" or dark brown color. The color of the sample is most likely caused by the presence of
a. biliverdin
b. bilirubin
c. pyridium
d. melanin
b. bilirubin
The clarity of a urine sample should be determined after:
a. the sample has been centrifuged
b. thorough mixing of the specimen
c. the addition of 3% sulfosalicylic acid
d. the specimen is heated to body temp.
b. thorough mixing of the specimen
A bright orange urine from a 24 year old patient with cystitis likely contains:
a. bilirubin
b. pyridium
c. rifampin
d. ammonia
b. pyridium
After standing, a urine sample that develops a black coloration would most likely contain:
a. bile pigments
b. porphyrinogens
c. homogentisic acid
d. RBCs
c. homogentisic acid
The yellow color of urine is primarily due to the presence of:
a. urochrome
b. melanin
c. bilirubin
d. stercobilin
a. urochrome
Following a severe crush injury, a patient is transported to the ER where a blood sample and a urine sample are collected. The patient's urine sample appears reddish-brown, which may be due to the presence of:
a. stercobilin
b. porphyrins
c. myoglobin
d. fresh blood
c. myoglobin
A random urine specimen collected shortly after the patient ate lunch appeared cloudy. Results of the reagent test strip were normal. The most likely cause of the sample's turbidity is the presence of:
a. bacteria
b. WBCs
c. amorphous urates
d. amorphous phosphates
d. amorphous phosphates
In which of the following metabolic diseases will urine turn dark brown to black upon standing?
a. phenylketonuria (PKU)
b. alkaptonuria
c. maple syrup urine disease
d. diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
b. alkaptonuria
If testing cannot be performed within one hour of collection, urine samples should be:
a. frozen
b. refrigerated
c. acidified with HCl
d. discarded down the sink
b. refrigerated
Measurement of urine specific gravity (SG) aids in the evaluation of the kidney's ability to:
a. filter the plasma
b. concentrate the urine
c. produce EPO
d. excrete waste products
b. concentrate the urine
Osmolality is a measure of:
a. all dissolved particles, including ions
b. only undissociated molecules
c. the total salt concentration
d. only ionic compoinds
a. all dissolved particles, including ions
A urine sample has a high SG by refractometry, but normal value when measured by reagent test strip. An increased presence of which of the following might explain the discrepancy between these measurement?
a. protein
b. sodium
c. hydrogen
d. ketones
a. protein
If an ambulatory, adult patient is suspected of having a UTI, which of the following collection methods would be most appropriate to obtain a urine sample?
a. random
b. catheterization
c. suprapubic aspiration
d. clean-catch midstream
d. clean-catch midstream
A urine's SG by reagent test strip is directly proportional to its:
a. color and clarity
b. ionic solutes
c. total volume
d. cellular content
b. ionic solutes
Isosthenuria is associated with a SG that is fixed around:
a. 1.001
b. 1.010
c. 1.020
d. 1.040
b. 1.010
Which of the following collection types should be performed to obtain a highly concentrated urine specimen?
a. random
b. first morning
c. post-prandial
d. 24 hour timed
b. first morning
A deficiency in arginine vasopressin (ADH) is associated with a
A. glucosuria
B. proteinuria
C. hyposthenuria
D. bilirubinuria
C. hyposthenuria
When using a refractometer to measure urine concentration, the laboratorian must correct for which of the following in their calculations?
a. temperature
b. pressure
c. glucose
d. volume
c. glucose
Which of the following collection methods would account for diurnal variation when quantitatively measuring urinary analytes?
a. random
b. first morning
c. 24 hour timed
d. two hour timed
c. 24 hour timed
The method of choice for determining urine concentration following administration of x-ray contrast dye is:
a. osmometry
b. refractometry
c. spectrophotometry
d. densitometry
a. osmometry
Which of the following urinary parameters may be measured to assess renal tubular function?
a. creatinine
b. specific gravity
c. urea nitrogen
d. total volume
b. specific gravity
Refractive index is a comparison of light:
a. velocity in solutions to light velocity in solids
b. velocity in air to light velocity in solutions
c. scattering by air to light scattering by solutions
d. scattering by particles in solution
b. velocity in air to light velocity in solids
The presence of biliverdin may cause a urine sample to appear:
a. black
b. dark-red
c. blue-green
d. bright orange
c. blue-green
A urine sample collected from a 5-day-old baby has a noticeably sweet odor reminiscent of caramel or burnt sugar. This odor is most commonly associated with:
a. cystinuria
b. alkaptonuria
c. phenylketonuria
d. maple syrup urine disease
d. maple syrup urine disease
A random urine sample from a patient with diabetes insipidus is most likely to appear
a. pale yellow
b. yellow
c. dark yellow
d. dark brown
a. pale yellow
Patients that produce more than 3000 mL (3 L) of urine in a 24-hour period are described as having:
a. anuria
b. oliguria
c. nocturia
d. polyuria
d. polyuria
A urine sample with SG of 1.003 will likely appear:
a. amber
b. yellow
c. colorless
d. dark yellow
c. colorless
After receiving a timed urine for quantitative analysis, the laboratorian must first:
a. subculture the urine for bacteria
b. add the appropriate preservative
c. screen for albumin using a dipstick
d. measure and record the total volume
d. measure and record the total volume
A falsely low result for urobilinogen may occur if the urine specimen is:
a. exposed to light
b. adjusted to a neutral pH
c. cooled to room temperature
d. collected in a nonsterile container
a. exposed to light
Which of the following urine results is most likely to be affected by prolonged light exposure?
a. pH
b. protein
c. ketones
d. bilirubin
d. bilirubin
The results in the table are obtained on a urine specimen collected at 8:00 am.
If the sample is stored unrefrigerated and retested at 12:00 pm, which of the following test results would likely be decreased due to the storage conditions?
a. protein
b. glucose
c. ketones
d. nitrite
b. glucose
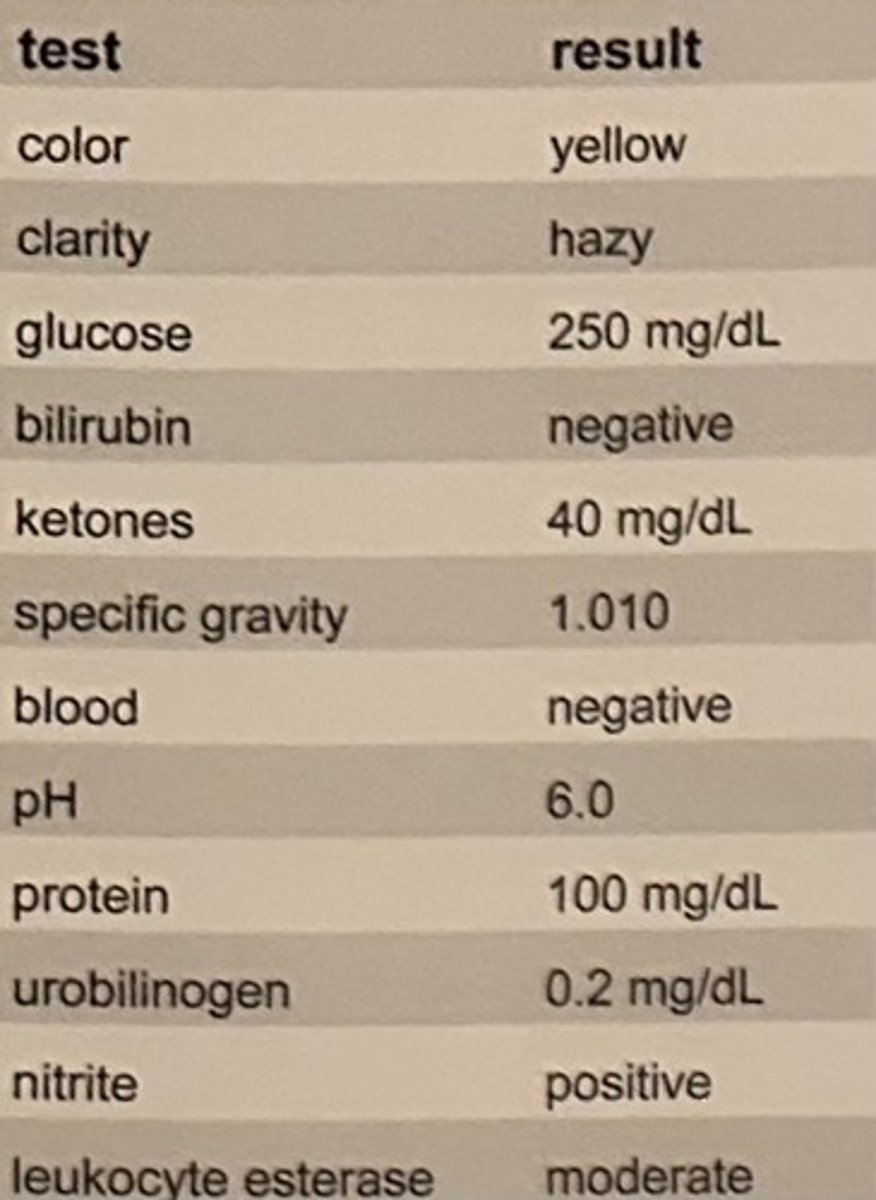
Which of the following would be affected by allowing a urine specimen to remain at room temperature for 3 hours before analysis?
a. pH
b. protein
c. occult blood
d. SG
a. pH
The glucose test pad on a test strip may yield a false-positive result in the presence of:
a. bleach
b. lactose
c. galactose
d. ascorbic acid
a. bleach
Which of the following confirmatory tests has historically been used to semi-quantitatively determine the presence of urinary ketones?
a. SSA
b. Ictotest
c. Acetest
d. Clinitest
c. Acetest
The occult blood test pad on a test strip may yield a false-positive result in the presence of:
a. bleach
b. protein
c. hemoglobin
d. ascorbic acid
a. bleach
Which of the following can lead to a false-negative urine protein reading?
a. presence of albumin
b. presence of mucus
c. a concentrated urine
d. a dilute urine
d. a dilute urine
The pH of a urine specimen is related to its concentration of free:
a. sodium ions
b. hydrogen ions
c. calcium ions
d. magnesium ions
b. hydrogen ions
After standing at room temperature, a urine pH will typically increase due to bacterial production of:
a. nitrite
b. urease
c. esterase
d. nitrate
b. urease
Urine reagent test strips should be stored in a tightly-sealed container in/on the:
A. freezer (-20 C)
B. refrigerator (5 C)
C. benchtop (20 C)
D. incubator (37 C)
c. benchtop
The principle of the reagent test strip for urine protein depends on:
a. reduction of copper sulfate
b. the protein error of indicators
c. reaction with Ehrlich reagent
d. a double-sequential enzyme reaction
b. the protein error of indicators
The urine reagent test strip pad for protein is most sensitive to:
a. albumin
b. Hgb
c. paraproteins
d. mucoproteins
a. albumin
Patients that take high doses of vitamin C may have a false-negative result for which of the following urine reagent test strip analytes?
a. pH
b. ketones
c. bilirubin
d. SG
c. bilirubin
Which of the following reagents is embedded on the reagent test strip pad for ketones?
a. p-arsanilic acid
b. acetoacetic acid
c. Ehrlich reagent
d. sodium nitroprusside
d. sodium nitroprusside
Which of the following reagents is used to enhance the reaction of acetone with sodium nitroprusside in the table test for ketones?
a. lactose
b. galactose
c. ascorbic acid
d. glacial acetic acid
a. lactose
A reagent test strip pad impregnated with a stabilized diazonium salt, such as diazonium salt, such as diazotized 2, 4-dichloroaniline, will yield a positive reaction in an acid medium with:
a. bilirubin
b. ketones
c. Hgb
d. urobilinogen
a. bilirubin
Which of the following substances may interfere with the reagent test strip pad for leukocyte esterase and yield a false-negative result when present in high concentrations?
a. lactose
b. ketones
c. protein
d. bilirubin
c. protein
The principle of the reagent test strip for urobilinogen is based on its reaction with:
a. p-arsanilic acid
b. sodium nitroprusside
c. diazotized 2,4-dichloroaniline
d. p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde
d. p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde
When employing the urine reagent test strip method for protein, a false-positive result may occur in the presence of:
a. large amounts of glucose
b. x-ray contrast media
c. Bence Jones proteins
d. a highly alkaline urine
d. a highly alkaline urine
Which of the following substances would most likely be found in the urine of a patient with anorexia nervosa?
a. protein
b. ketones
c. glucose
d. bilirubin
b. ketones
The presence of ketones in a random urine sample from a 2-year-old child would most likely be associated with:
a. prolonged vomiting
b. a hemolytic event
c. a UTI
d. biliary tract obstruction
a. prolonged vomiting
A patient's urinalysis revealed a positive bilirubin and a decreased urobilinogen level. These results are associated with:
A. Hemolytic disease
B. Biliary tract obstruction
C. Hepatic disease
D. Urinary tract infection
b. biliary tract obstruction
A urine specimen with an elevated urobilinogen concentration but a negative bilirubin result may indicate the patient has:
a. gallstones
b. viral hepatitis
c. hemolytic anemia
d. liver cirrhosis
c. hemolytic anemia
Microscopic analysis of a urine specimen yields a moderate amount of RBCs in spite of a negative result for occult blood using a reagent strip. The presence of which of the following may explain this discrepancy?
a. bleach
b. vitamin C
c. salicylates
d. Hgb
b. vitamin C
The principle of the reagent test strip for microalbumin is based on:
a. reaction with a diazonium salt
b. the protein error of indicators
c. an immunochemical reaction
d. reaction with p-arsanilic acid
c. an immunochemical reaction
Measurement of which of the following may be performed to account for the patient's hydration status and renal function?
a. creatinine
b. hydrogen
c. sodium
d. glucose
a. creatinine
The reagent test pad for pH contains which of the following?
a. diazotized 2, 4-dichloroaniline
b. methyl red and bromthymol blue
c. glucose oxidase and peroxidase
d. tetrabromphenol blue and a buffer
b. methyl red and bromthymol blue
Which of the following tablet tests has historically been used to rule out a false-positive bilirubin result achieved by reagent test strip?
a. Acetest
b. Clinitest
c. Ictotest
d. guaiac test
c. Ictotest
A clear, red-brown urine specimen resulted in a positive reaction for blood on the reagent test strip, but no RBCs were seen on microscopic examination. These results most likely indicate the presence of
A. nitrates
B. pyridium
C. porphyrins
D. myoglobin
d. myoglobin
A double sequential enzyme reaction employing glucose oxidase and peroxidase is used to measure which of the following urinary analytes by reagent test strip?
a. pH
b. nitrites
c. glucose
d. ketones
c. glucose
Development of a pink color on the absorbent mat surrounding an Ictotest tablet should be reported as:
a. invalid
b. positive
c. negative
d. nonreactive
c. negative
The absorbent mat surrounding an Ictotest tablet develops a dark purple color. This reaction indicates the presence of which of the following?
a. protein
b. glucose
c. ketones
d. bilirubin
d. bilirubin
A urine specimen analyzed for glucose by a glucose oxidase reagent test strip may yield a falsely low or negative value in the presence of:
a. bleach
b. galactose
c. ascorbic acid
d. hydrogen peroxide
c. ascorbic acid
The surface of an Acetest tablet develops a dark purple color. This reaction indicates a large presence of which of the following in the patient's urine sample?
a. protein
b. glucose
c. ketones
d. bilirubin
c. ketones
A urinalysis performed on a sample from a 2-week-old infant with diarrhea showed a negative reaction with the glucose oxidase reagent test strip. Historically, a copper reduction tablet test would have been performed to check the urine sample for the presence of:
a. glucose
b. galactose
c. bilirubin
d. ketones
b. galactose
A patient suspected of having recurrent UTIs provides a clean-catch midstream urine sample. A positive value for which of the following reagent test strip results would best support this diagnosis?
a. glucose
b. occult blood
c. urobilinogen
d. leukocyte esterase
d. leukocyte esterase
The occult blood pad of a reagent test strip yields an orange background with several green spots. This indicates the specimen likely contains:
a. myoglobin
b. intact RBCs
c. Hgb
d. ascorbic acid
b. myoglobin
A reagent test strip pad for occult blood is reported as positive, but microscopic examination did not reveal the presence of RBCs. This patient's condition can be termed:
a. oliguria
b. hematuria
c. hemoglobinuria
d. hemosiderinuria
c. hemoglobinuria
A patient seen at an urgent care facility for lower back pain and a fever has the urinalysis shown in the table.
Microscopic examination shows the presence of 15-20 RBC/HPF, 30-40 WBC/HPF, 3+ bacteria, and 2-3 renal tubular epithelial cells/HPF. The discrepancy between the "negative" result for nitrite on the reagent test strip and the presence of bacteria on microscopy may be best explained by:
a. failure to mix the specimen before centrifuging
b. failure to test the sample within 1 hour of collection
c. presence of an oxidizing detergent in the specimen container
d. the presence of a non-nitrate-reducing organism
d. the presence of a non-nitrate-reducing organism

Which of the following reagent test strip pads will yield a positive reaction when the sample contains hemoglobin or myoglobin?
a. protein
b. ketones
c. occult blood
d. leukocyte esterase
c. occult blood
The results of a urinalysis on a first morning specimen are shown in the table.
After viewing uric acid crystals in the centrifuged urine sediment, the laboratorian should question which of the results?
a. pH
b. protein
c. glucose
d. specific gravity
a. pH

A false-negative result may occur for the nitrite reagent test strip pad if the sample:
a. contains a nitrate-reducer
b. is contaminated with skin flora
c. is contaminated with a cleaning agent
d. does not incubate in the bladder long enough
d. does not incubate in the bladder long enough
The nitrite reagent test strip pad is most useful in the identification of a bacterial UTI when evaluated in combination with which of the following test pads?
a. pH
b. occult blood
c. SG
d. leukocyte esterase
d. leukocyte esterase
Despite their presence in a sample, the leukocyte esterase reagent test strip pad would yield a negative result for which of the following types of WBCs?
a. monocytes
b. eosinophils
c. lymphocytes
d. neutrophils
c. lymphocytes
Reagent test strip pads for ketones primarily measure:
a. acetone
b. cholesterol
c. acetoacetic acid
d. beta-hydroxybutyric acid
c. acetoacetic acid
Microscopic examination of cellular elements in a urine sediment, such as RBCs, WBCs, bacteria, and epithelial cells, should be enumerated using:
a. low power (10x objective)
b. high dry power (40x objective)
c. oil immersion (100x objective)
d. phase contrast microscopy
b. high dry power (40x objective)
The centrifuged sediment for a random urine sample collected from a 17-year-old female patient is shown in the photomicrograph.
The reagent test strip is negative for leukocyte esterase and nitrite. The elements seen in the sediment are most likely the result of:
a. contamination
b. improper preservation
c. a UTI
d. chronic glomerulonephritis
a. contamination
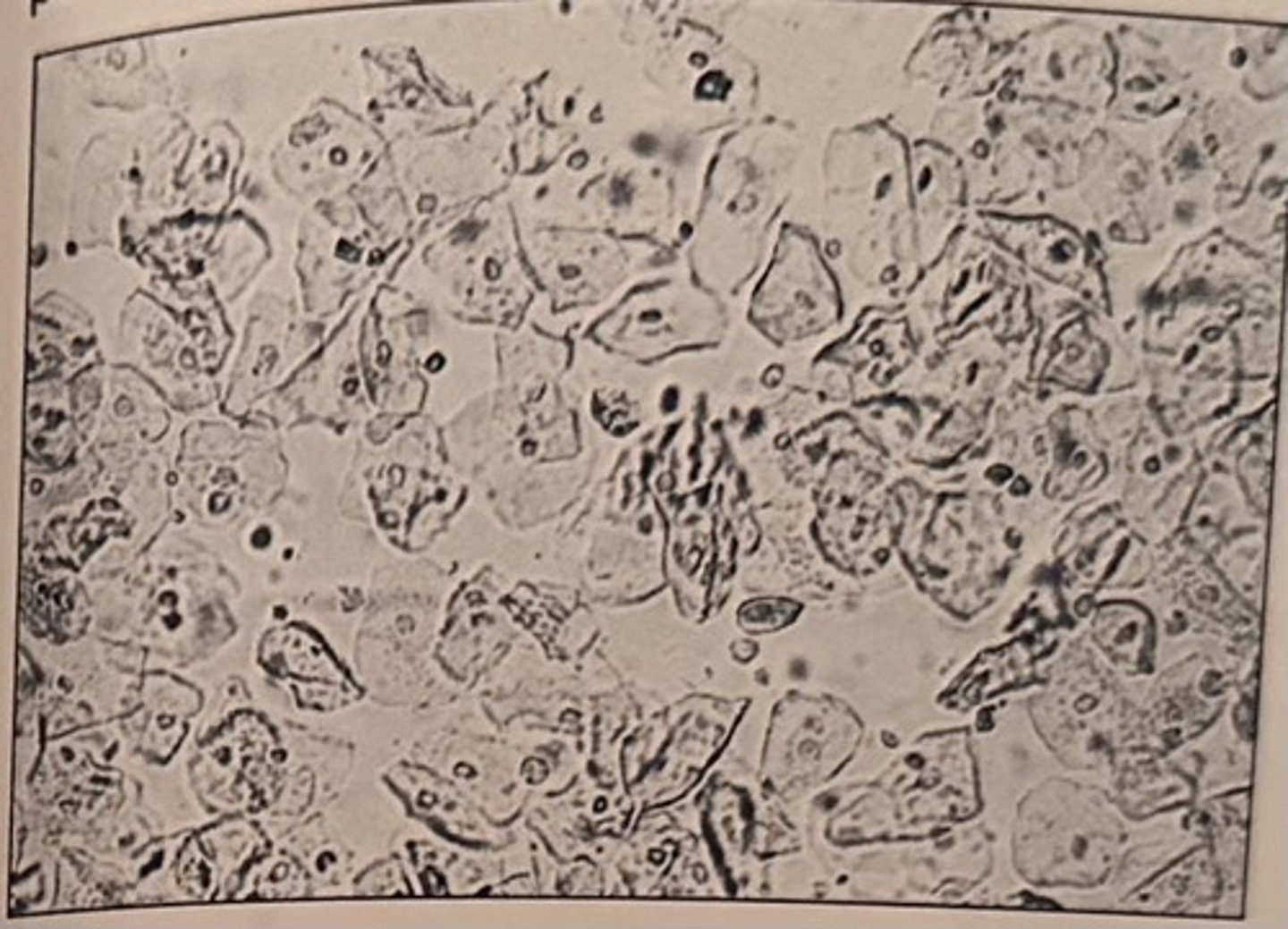
Oval fat bodies are:
a. hyaline casts that contain lipids
b. squamous epithelial cells that contain lipids
c. transitional epithelial cells that contain lipids
d. renal tubular epithelial cells that contain lipids
d. renal tubular epithelial cells that contain lipids
Microscopic examination of a urine sediment reveals the presence of ghost cells which would most likely be associated with a:
a. pH of 6.5
b. SG 1.000
c. ketone concentration of 5 mg/dL
d. glucose concentration of 1000 mg/dL
b. SG 1.000
Glitter cells are a microscopic finding of:
A. red blood cells in hypertonic urine
B. red blood cells in hypotonic urine
C. white blood cells in hypertonic urine
D. white blood cells in hypotonic urine
D. white blood cells in hypotonic urine
Which of the following cells is most commonly associated with a non-clean-catch specimen and/or vaginal contamination?
a. WBC
b. renal epithelial cells
c. squamous epithelial cells
d. transitional epithelial cells
c. squamous epithelial cells
Identify the elements indicated by the arrows in the photomicrograph:
a. clue cells
b. ghost cells
c. glitter cells
d. oval fat bodies
b. ghost cells
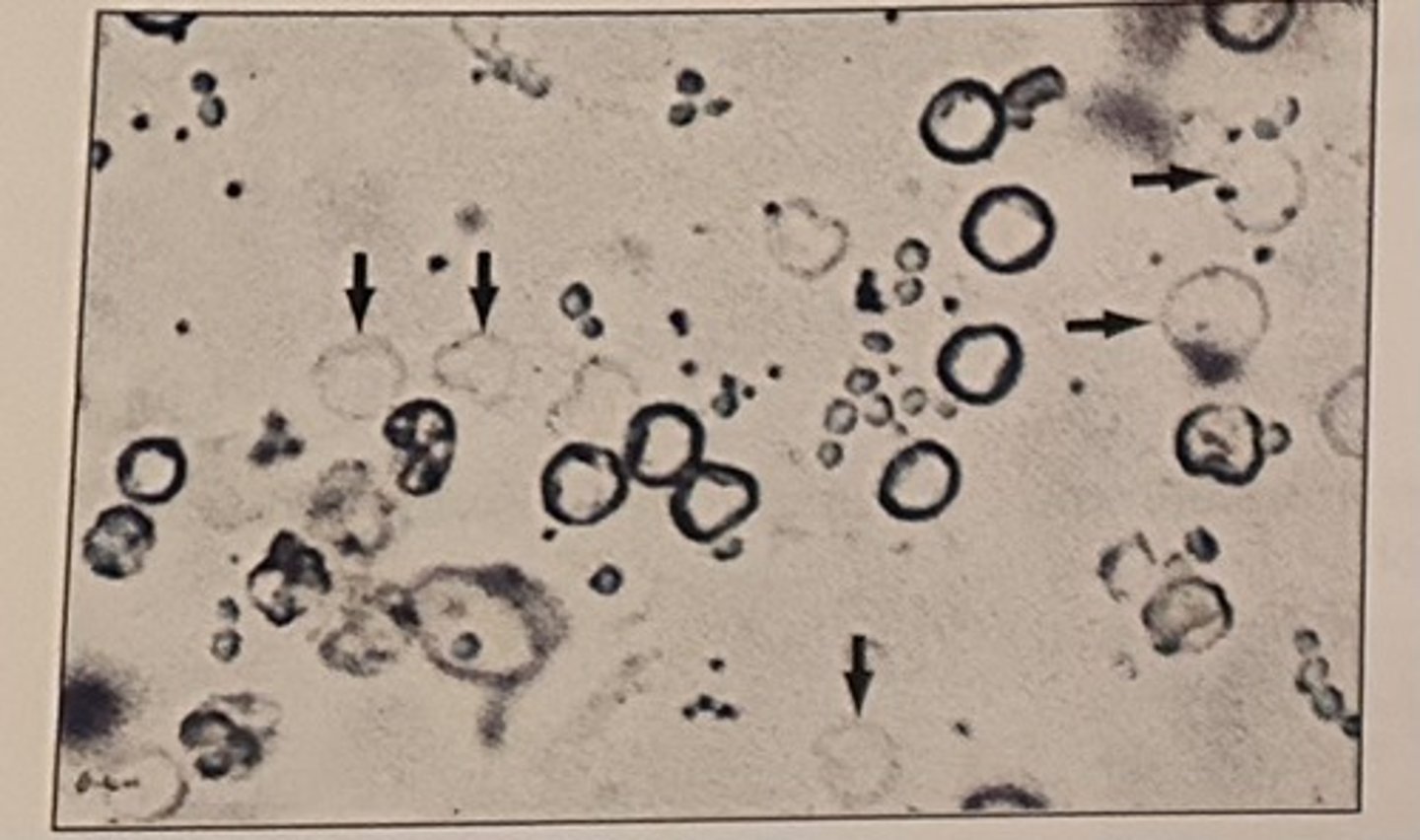
Identify the types of cast seen photomicrograph:
a. broad
b. hyaline
c. cellular
d. granular
d. granular
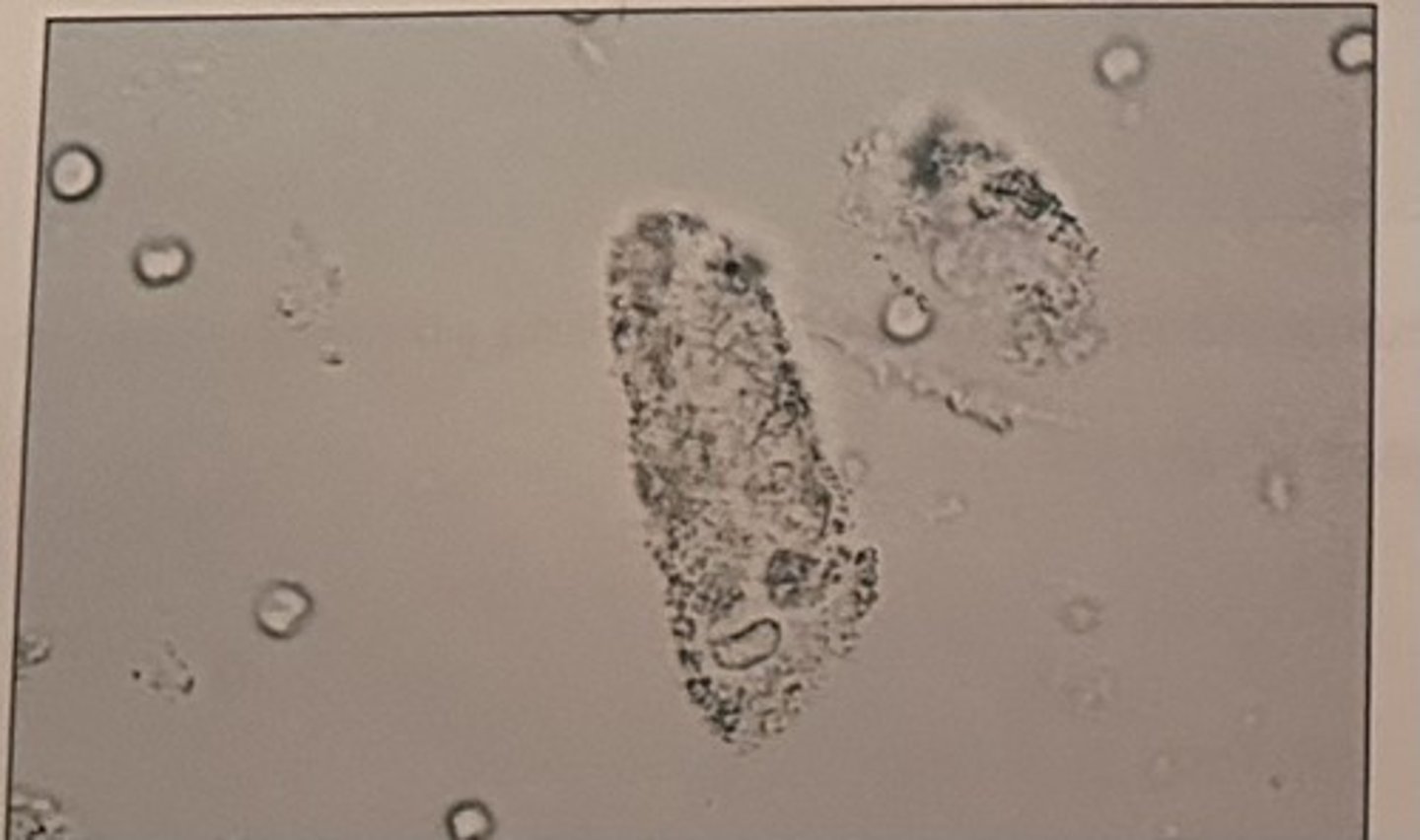
The presence of which of the following is associated with bacterial vaginosis?
a. clue cells
b. hyaline
c. cellular
d. granular
a. clue cells
Which of the following elements is most likely to be seen in a urine sediment as a result of catheterization?
a. hyaline casts
b. oval fat bodies
c. transitional epithelial cells
d. renal tubular epithelial cells
c. transitional epithelial cells
What is the most likely diagnosis given the microscopic finding?
a. cystitis
b. pyelonephritis
c. glomerulonephritis
d. nephrotic syndrome
a. cystitis
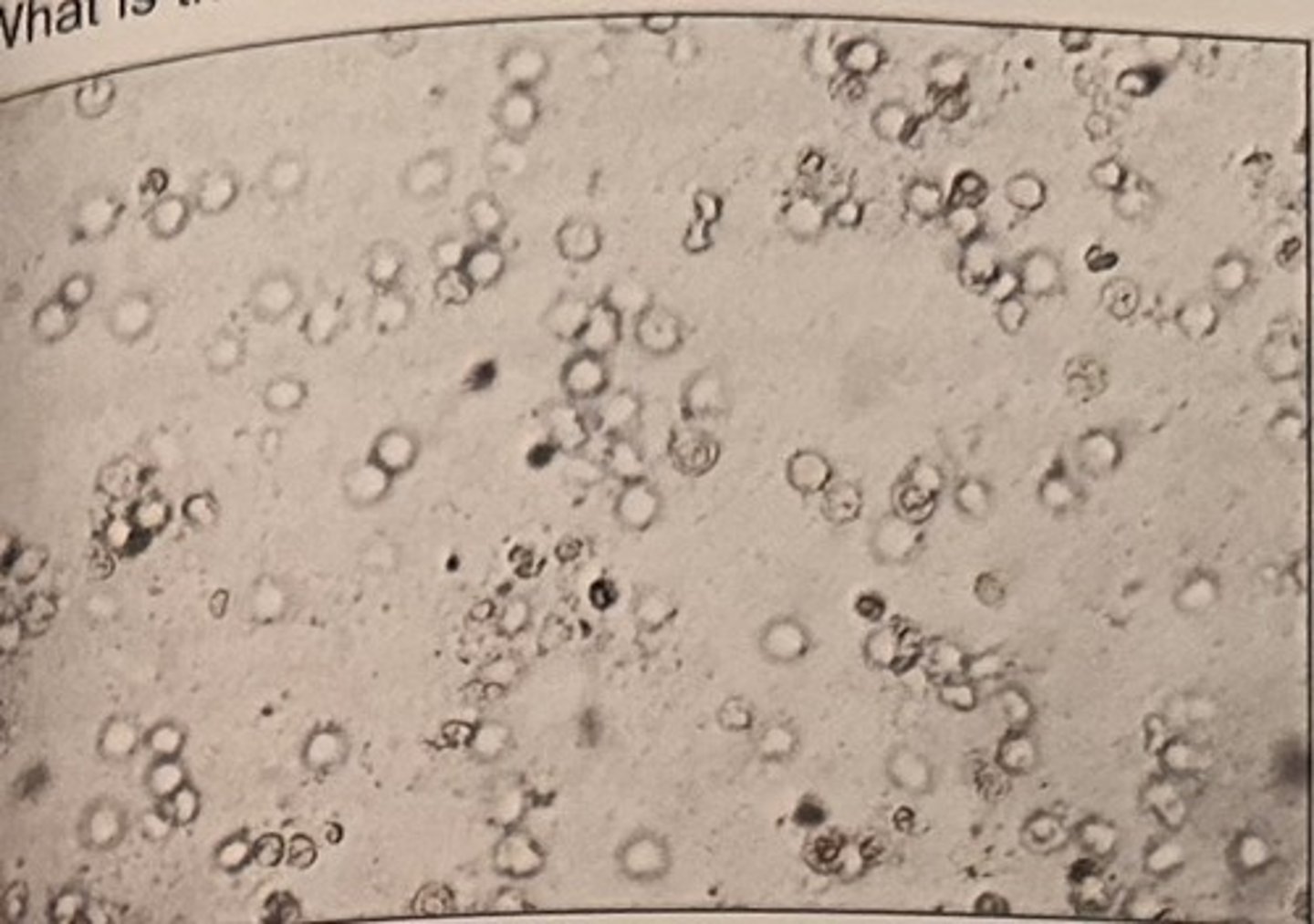
Identify the elements seen in the photomicrograph:
a. RBC
b. urothelial cells
c. WBCs
d. tyrosine crystals
a. RBC
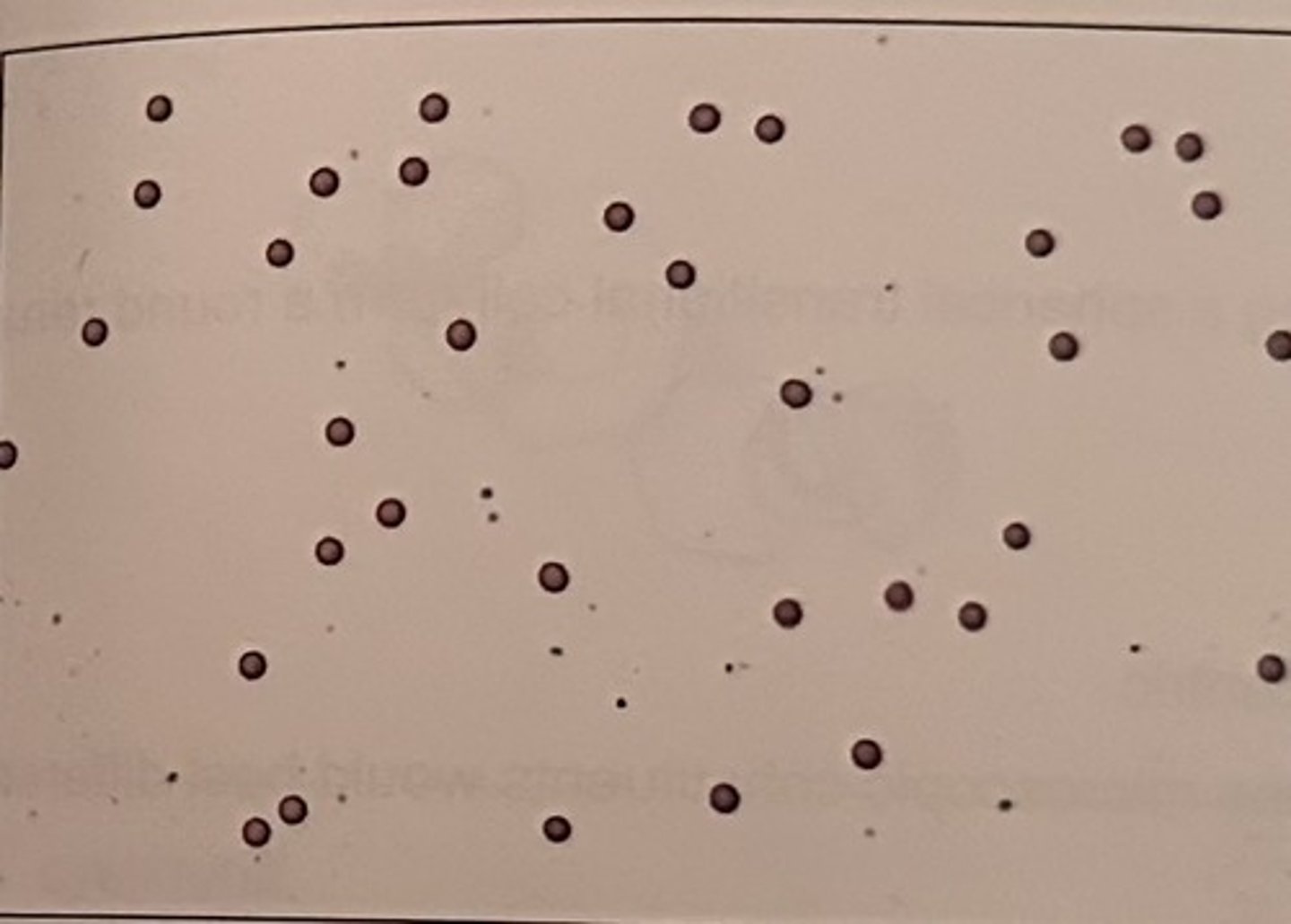

Urinary casts are primarily composed of:
a. albumin
b. globulins
c. paraprotein
d. uromodulin
d. uromodulin
Examination for casts should be performed:
a. after adding glacial acetic acid to the sediment
b. under high dry power (40x obj.) with bright light
c. after adding Sternheimer-Malbin stain to the supernatant
d. using subdued lighting and low power (10x obj.) magnification
d. using subdued lighting and low power (10x obj.) magnification
Which of the following casts is most likely to be found in a urine sample from an apparently healthy person?
a. fatty
b. waxy
c. hyaline
d. granular
c. hyaline
Which of the following casts is most indicative of renal failure/end stage renal disease?
a. waxy
b. cellular
c. granular
d. hyaline
a. waxy
Shortly after collection of a random urine sample, the laboratorian performed a microscopic urinalysis and reported the results shown in the table.
The urine sediment is reevaluated by a trainee 2 hours later and similar values were reported for the WBC, RBC, and bacteria, but they found no hyaline cast. The most probable explanation for this discrepancy is that the casts dissolved due to a(n):
a. increase in urine pH
b. decrease in urine pH
c. increased in specimen temperature
d. decrease in specimen temperature
a. increase in urine pH

Which of the following aids in differentiating a spherical transitional cell from a round renal tubular cell?
a. round renal tubular cells are larger
b. spherical transitional cells are larger
c. renal tubular cell nuclei are eccentric
d. spherical transitional cell nuclei are eccentric
c. renal tubular cell nuclei are eccentric
The presence of which of the following urine microscopic constituents would best differentiate between cystitis and pyelonephritis?
a. WBCs
b. RBCs
c. bacteria
d. WBC casts
d. WBC casts
Renal tubular epithelial cell casts are most indicative of:
a. pyelonephritis
b. tubular necrosis
c. glomerulonephritis
d. nephrotic syndrome
b. tubular necrosis
Hyaline casts found in the urine of a football player admitted to the hospital following a concussion are most likely the result of:
a. dehydration and urinary stasis
b. trauma to the blood brain barrir
c. significant trauma to the kidneys
d. excessive ingestion of electrolytes
a. dehydration and urinary stasis