L3-4 Social Development
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to social development from lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Imprinting
Process by which mother-offspring attachments are formed in many species of birds where they follow the first moving object they encounter after hatching, influencing sexual preference and mate selection with long-lasting effects.
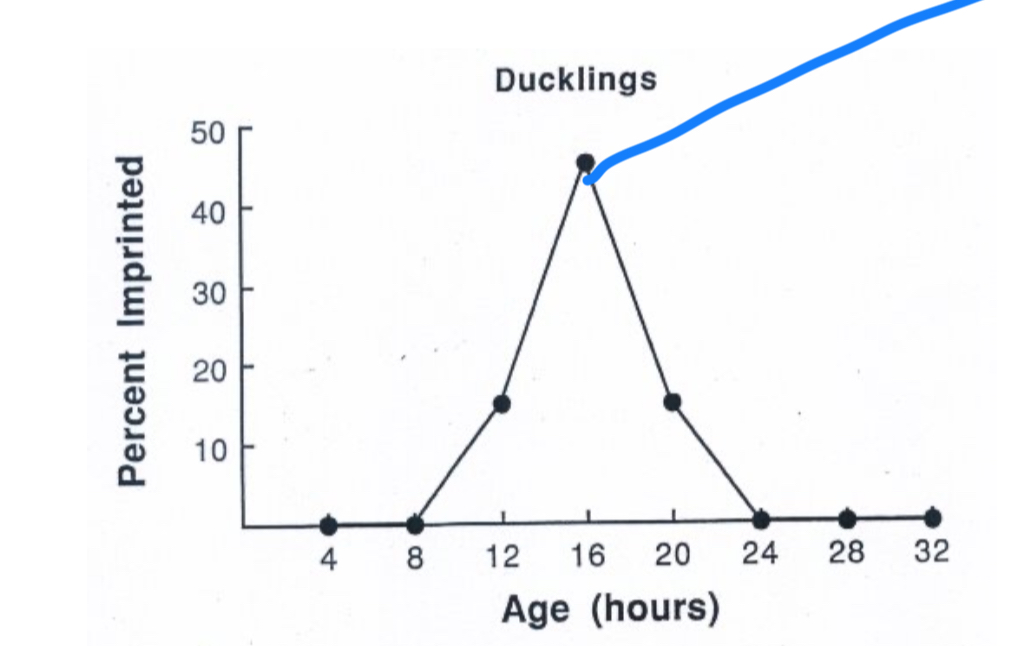
Critical Period
A time frame where the birds need to be exposed to moving object (mother), if not imprinting doesn’t occur.
Konrad Lorenz
Showed that greylag geese would imprint on the first moving being they encountered during a critical period (13-16 hours after birth)
Henry Harlow Experiments 1957-1963
Series of experiments challenging the dominant belief that physical contact would spoil a child and emotions were of negligible importance.
Partial Isolation (Harlow)
Rhesus monkeys raised in bare wire cages, able to see and smell other monkeys but not touch them, resulting in blank staring, repetitive circling, and self-mutilation.
Outcome of partial isolation
Blank staring, repetitive circling, self mutilation.
Total Isolation (Harlow)
Monkeys isolated in chambers where they couldn’t see other monkeys, led to emotional shock, self-clutching, rocking (stereotypy), and in some cases, death due to emotional anorexia. By 12 months in isolation monkeys were socially obliterated.
Effects of Social Isolation (Harlow)
Increases self-directed and stereotypic behavior (rocking, biting), causes deficits in social behavior directed at others (social play with peers, maternal behavior), cognitive ability unaffected.
isolated monkeys exposed to older or same age monkeys
Other monkeys attack isolates, isolates do not defend themselves, but later become aggressive under inappropriate circumstances.
Isolates exposed to younger monkeys
6 month isolates and 3 month “therapist” monkeys interact 8 hours a week. Isolate becomes as social as “therapist” over course of 18 weeks therapy.
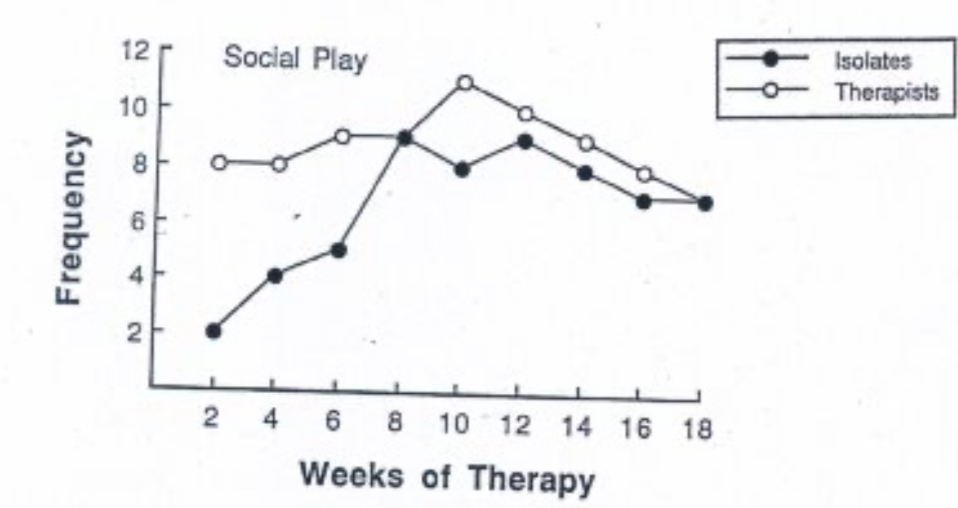
Can isolates be rehabilitated?
Yes, even at 12 months of isolation. They can recover substantially when exposed to younger monkeys, this argues against a critical period for social behaviour, or that it is longer than the first 12 months.
cloth surrogate vs wire surrogate
Wire gave young monkey food, but monkey always chose cloth surrogate. If frightening stimulus entered cage it would run to cloth, when it was removed infant froze, cried, etc.
Brain developement
Genetics is like the hardwiring and experiences is the soft wiring. During growthspurts dendrites that are often fired stay, and ones that aren’t are pruned back. So early experience is important.
Oxana Malaya
Lived in a dog kennel discovered at age 8, had dog-like behaviors, later remedied but still unable to be “normal”. Shows extreme behaviours can still be overcome.
Immitation and observation
Fundamental mechanisms for learning, common in many species including humans.
Residental nursery and Hospital Care (1800-1900)
Deprivation from parents (attention) and a primary caregiver was common, psychoanalysts (John Bowlby) concerened this could cripple ability to form relationships.
Outcome of childrens behaviours in foster homes
Increased attention-seeking, apathy, indifference to people, withdrawal, and cognitive and language impairments.
Harold Skeels (1930s)
Adequate nutrition, warmth, and cleanliness provided to infants, with 13/25 infants moved to an institution for intellectually disabled women and “adopted” by one woman at 19 months of age.
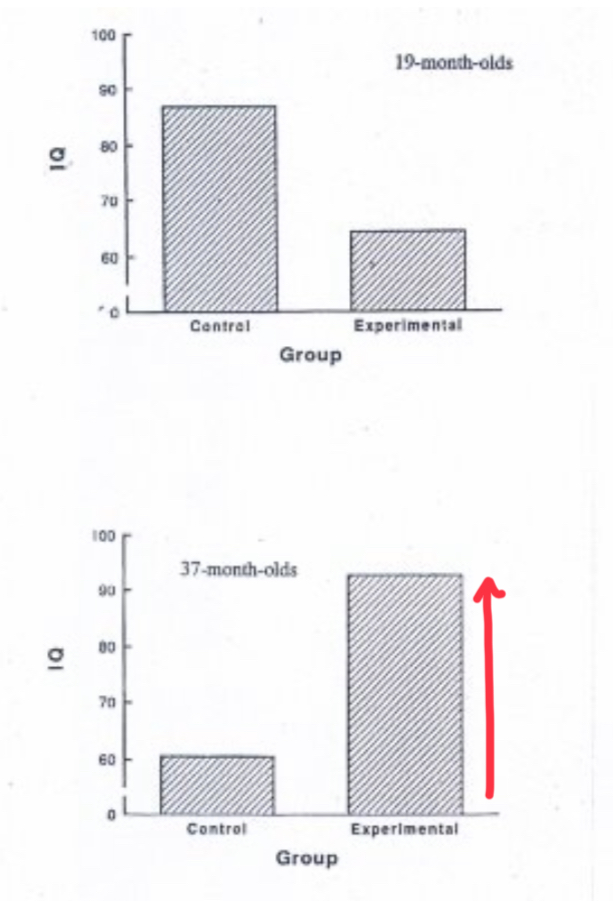
Long-Term Follow-Up (Skeels) 30 years
11/13 Self-supporting, married with children, and with normal IQs, compared to controls, where 6 received a primary school education and 4/12 remained in an institution. Showing importance of early experience.
Dennis (1973)
Studied 89 children who were intilectually disabled (IQ of 53) aged 1-6. IQ was tested two years later after adoption. Earlier age of adoption better the outcome.
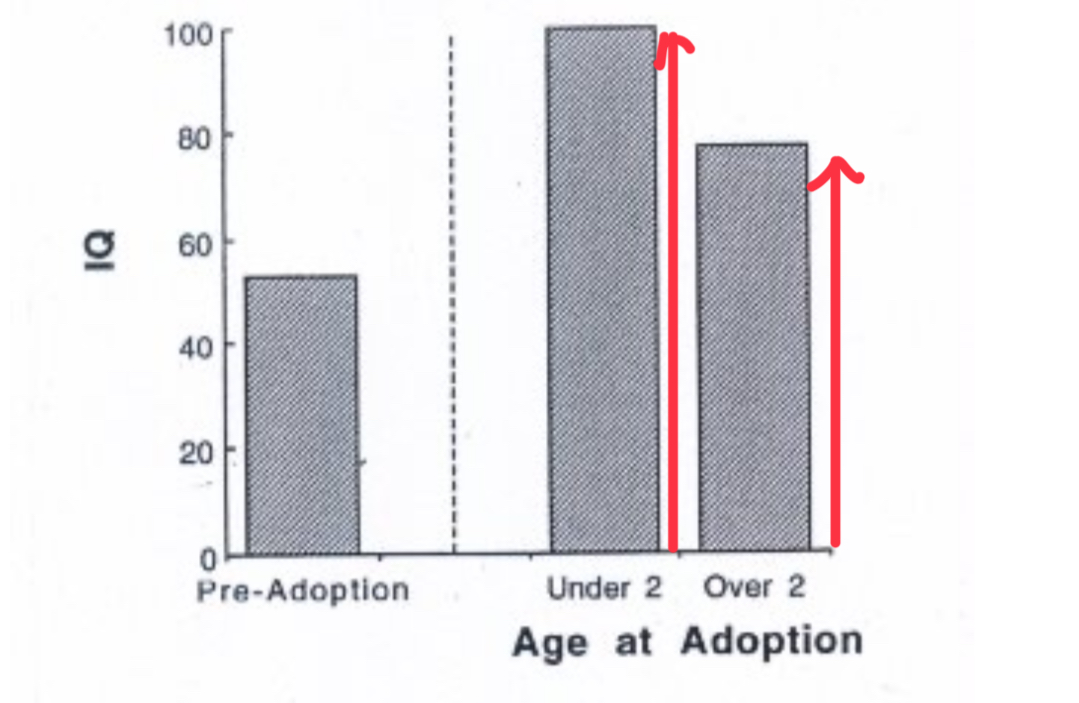
Critical Period
When the organism is susceptible to the effects of a particular experience; effects are dramatic and irreversible, sharp onset and offset points. eg prenatal developement (teratogens and testosterone) and imprinting (birds)
Sensitive Period
When the organism susceptible to the effects of a particular experience; harmful effects can be altered by later events, effects are less dramatic, and begins and ends gradually. eg social developement in primates and humans.
Perry (2002) - Neglected Children
Early removal from a neglecting environment leads to bigger brain volume.
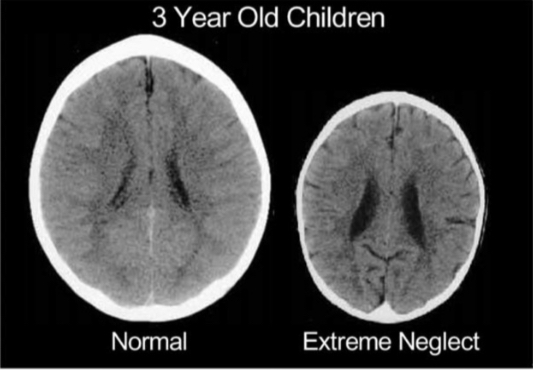
Social developement Conclusions
Social deprivation in infants and children leads to dramatic behavioral and cognitive deficits, brain damage, but development can be modified by exposure to a nurturing environment, most effective during the first 2-3 years of life, reflecting a sensitive period.