Cellular Respiration
1/15
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
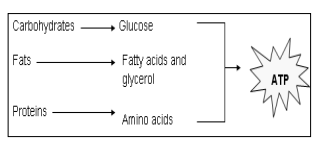
heterotrophic organisms
have to obtain food in the form of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to survive
food stuffs are digested to simplest forms and absorbed into the body
breakdown product of food is utilized to form ATP
cellular respiration
goal is to oxideize organic compunds to produce ATP
cellular respiration
glucose + O2 → CO2 + H20 +ATP
glucose; fats; proteins
the ___ is themain source of ATP. In its absence, ___ is utilized to form ATP. If it used up, the last source of ATP are the ___ from the muscles.
STAGES OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION
does not utilize oxygen
Anaerobic Respiration
does not utilize oxygen
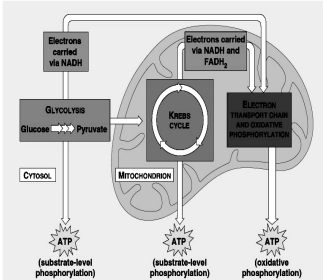
Glycolysis
Refers to the breakdown of glucose to 3-C compound pyruvate. This occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell
Produces 4 ATP with a net of 2 ATP
Skeletal muscles shift to anaerobic respiration when oxygen available to muscles is depleted as a result of a strenuous physical activity.
Aerobic Respiration
utilizes oxygen and occurs in the
mitochondria
produces 30 ATP
Parts of Aerobic Respiration:
Intermediate Step
Krebs Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Intermediate Step
conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
Krebs Cycle
produces reducing equivalents nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH2)
Electron Transport Chain
set of proteins that receive electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP
oxygen
Final electron acceptor
CHEMIOSMOTIC THEORY
States that the movement of electrons through a series of transporters creates a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This is coupled to formation of ATP
Calculation of ATP produced from glucose
Glycolysis: 7 ATP
Intermediate Step: 5 ATP
Krebs Cycle: 20 ATP
Total ATP 32 ATP
FERMENTATION
Anaerobic conversion of organic compounds to produce ATP
Pyruvate is converted to lactic acid or ethanol
Ex. This process is used in production of beer
using yeasts.
Complete Oxidation of Glucose = 32 ATP