Week 5 - LTM
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Different types of LTM
Declarative (knowing that) and procedural (knowing how). Within declarative there is episodic (memories) and semantic whereas procedural encompasses skills mostly
Complementary learning systems - Kumaran et al 2016
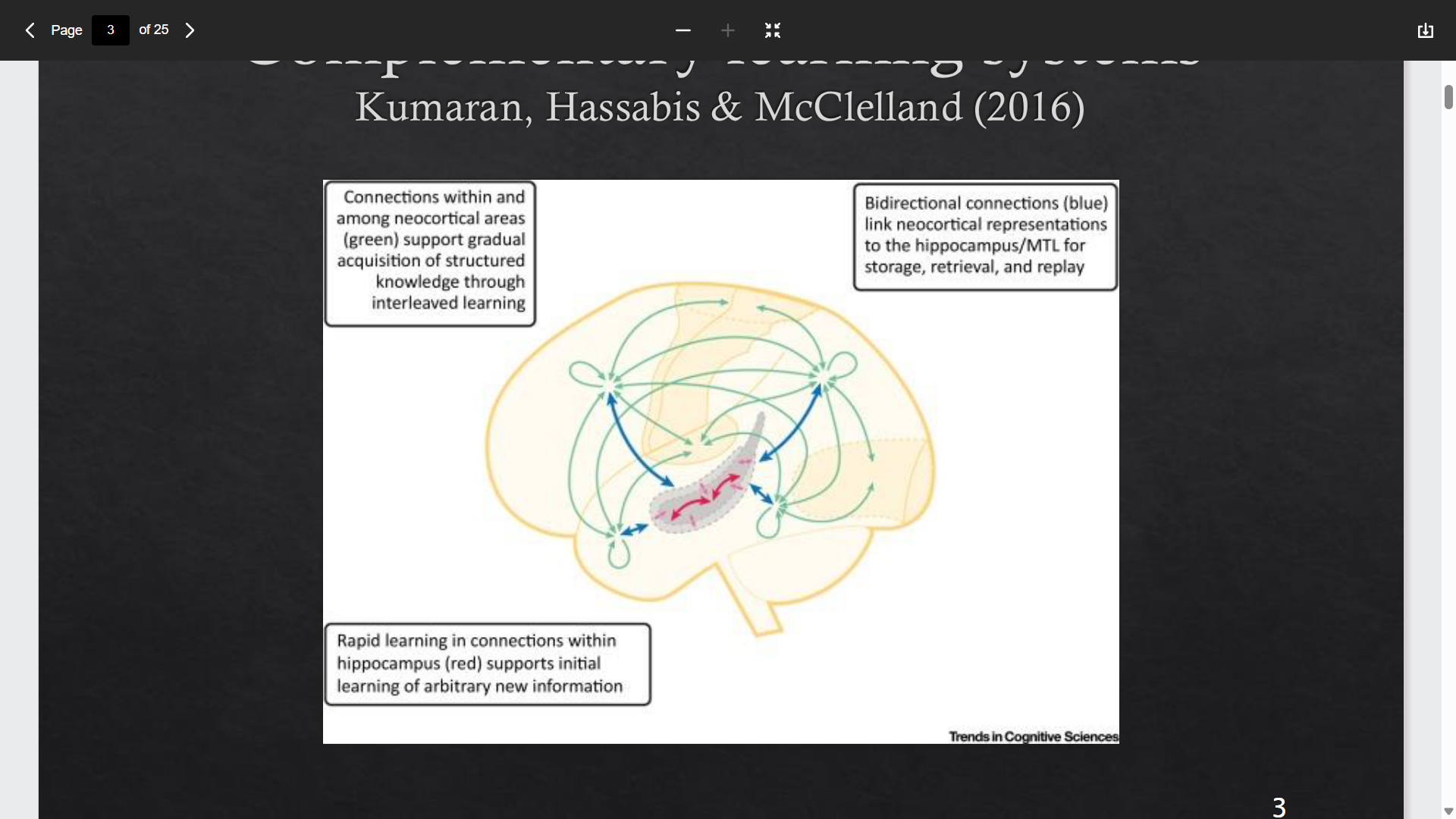
Damage to the hippocampus
Impairs learning of new associations (found in case of HM)
Causes problems retrieving earlier memories, particularly recent ones - Squire 1992
Preserves ability to recall more distant memories, performance on intelligence tests and normal conversation
Preserves ability to understand general meaning - Knowlton et al 1992
Semantic memory
General knowledge of the world, abstracted from individual experiences. Used to make inferences and predictions about the world. (for example hear something bark, assume it is a dog, might bite, might be chasing a cat, could be a cavachon)
Schemes and scripts in semantic memory
Types of knowledge structures used to organise and understand information - Bartlett
Symbolic approach to semantic memory
Knowledge represented in a mental language consisting of propositions. propositions made up of concepts and relations. Semantic networks represent knowledge spatially as units linked by relations
Semantic network - Collins and Quillian
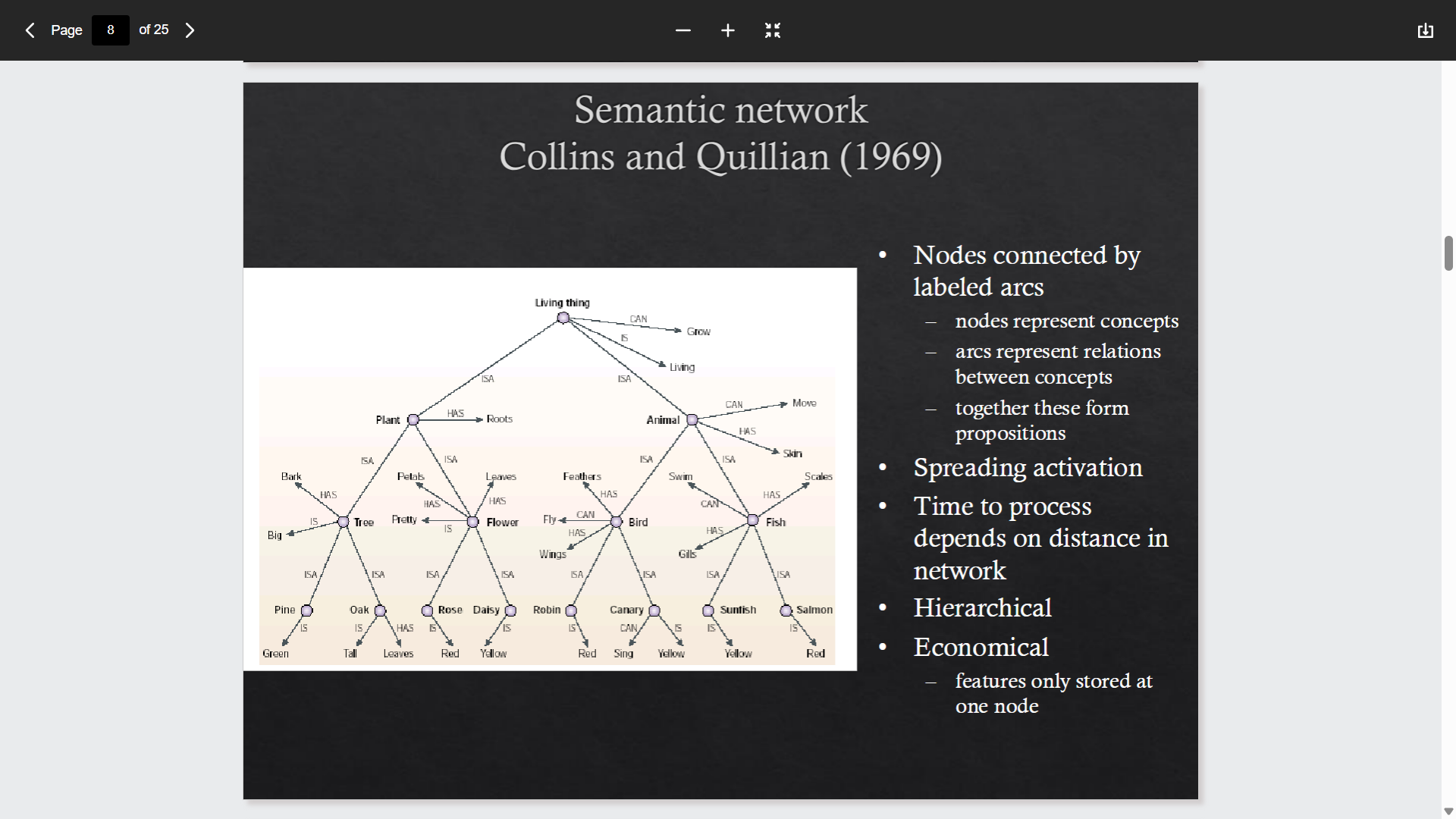
Problems with symbolic approach
Typicality effects (Rosch 1973)- Some instances are more typical of a categpry than others for example a robin is more typically a bird than a penguin
Rosch 1976 - Some levels are more salient than others - Intermediate level categories are associated with more attributes - basic level categories. For example contrast furniture with a chair
More problems with symbolic approach
Concepts vary with context - what attributes does a frog have changes if they are in a French restaurant
Concepts are theory dependent - unclean animals vs clean animals
No mechanism for learning - how can these networks change as we learn
Parallel distributed processing - PDP
Information represented by ‘dumb’ neurons which just add activation and pass it on
Information is distributed as patterns of activation across many units
Learning is accomplished by changing the strength of connections
between units
Learning in PDP networks - backpropagation of error
Input: Patterns corresponding to various examples of cats and dogs
Required output: CAT or DOG
Each input pattern is presented
Activation is passed through the network
Output is compared to target (error)
Weights are adjusted to reduce error
Next example is processed, and so on until all
patterns are classified correctly
Distributed representations in the brain - Kiani et al 2007
we examine responses of a large number (>600) of neurons in monkey inferior temporal (IT) cortex with a large number (>1,000) of natural and artificial object images. During the recordings, the monkeys performed a passive fixation task. We found that the categorical structure of objects is represented by the pattern of activity distributed over the cell population. Animate and inanimate objects created distinguishable clusters in the population code. The global category of animate objects was divided into bodies, hands, and faces. Faces were divided into primate and nonprimate faces, and the primate-face group was divided into human and monkey faces. Bodies of human, birds, and four-limb animals clustered together, whereas lower animals such as fish, reptile, and insects made another cluster.
Semantic dementia
Gradual loss of semantic distinctions - reverse of early development, move from specific to general such as dog used for different animals
