TV4101 - Cytology Part 2 - Lymph Nodes
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Top 5 cytological findings?
1. Reactive or hyperplastic lymph node
2. Lymphoma
3. Lymphadenitis
4. Metastatic disease
5. Accidental salivary gland aspirate
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Reactive or hyperplastic lymph node
Occurs when?
Cell Features?
With local or systemic immune stimulation
Cells
Small Lymphocytes predom
15 - 25% inc in medium & large lymphocytes
Reactive class- if inc plasma cell numbers
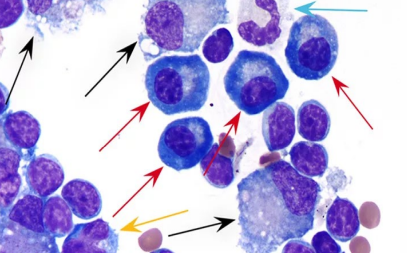
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Reactive or hyperplastic lymph node
What is the red arrow? Features of each?
Blue arrow?
Red -Plasma cell
<5%
Eccentric nuclei
Condensed chromatin
Abundant deeply basophilic cytoplasm with a perinuclear clear area (golgi region)
Similar size to neutrophil
Blue arrow - Neutrophil
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Lymphoma
Features of this?
Most common haemopoietic tumour in dogs & cats
Neoplastic malignant proliferation of lymphoid cells arising in peripheral lymphoid tissue (e.g. lymph nodes & spleen)
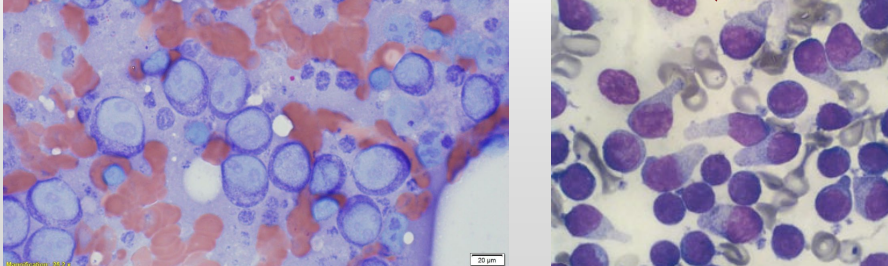
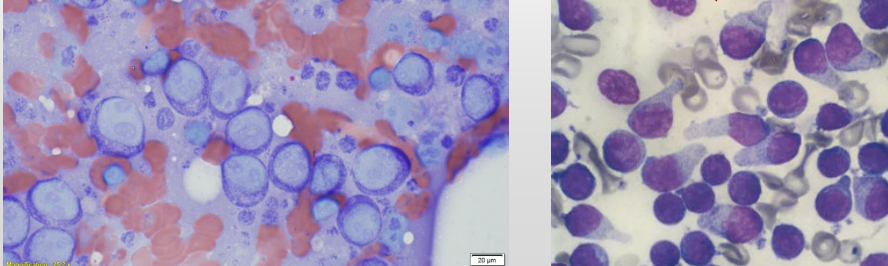
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Lymphoma
Cyto Dx?
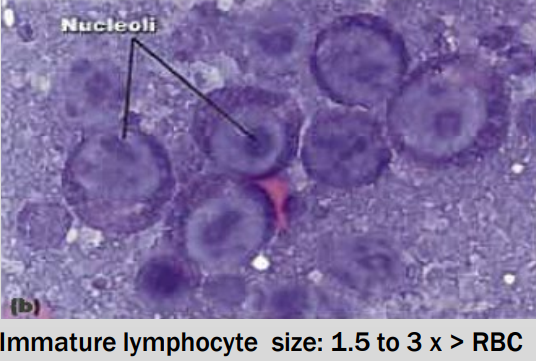
Majority ( > 50%) of lymphocytes are immature (lymphocytes are intermediate or large)
Easier if lymphocytes contain prominent nucleoli
(finely granular to dispersed chromatin)
Small cell lymphoma difficult to DX
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Lymphoma
Classification
Main principles include?
Main principles:
Anatomic location
Cellular morphology
Tissue architecture,
Immunophenotype and genetics
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Lymphoma
Classification and cytology aspect?
Cytology: use morphology to classify into high – grade and low grade & then distinguished by phenotype (T or B cell)
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Lymphoma
Classifications - Important Parameters and Lymphoma types
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Lymphoma
How it Mitotic Index determined?
Counting the number of mitoses in 5 HPF (on 50x objective)
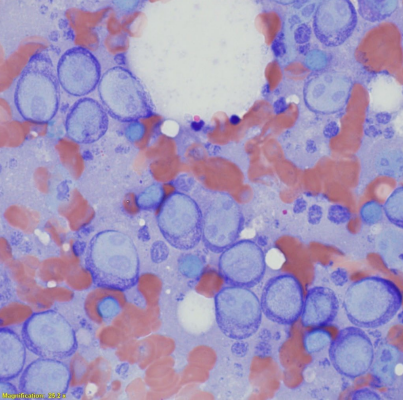
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
What is this?
Large cell high grade lymphoma
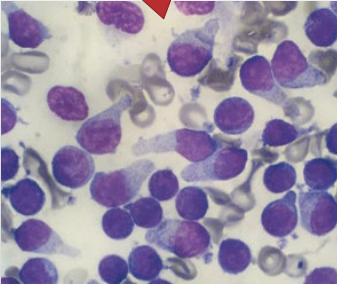
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
What is this?
Small cell low grade lymphoma
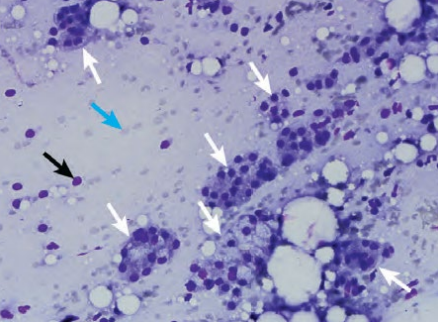
Lymph node cytology
Enlarged lymph nodes - disease
Submandibular lymph node was enlarged and underwent FNA - what can we see here?
DX?
White arrows - Cohesive clusters of vacuolated, secretory epithelial cells from salivary gland
Blue - RBCs
Black - Nuclear remnants of ruptured cells
Accidental salivary gland aspiration
What is this?
Describe what we can see?
DX?
Windrowing
Lining up of RBCs in a linear array due to the viscosity of saliva (eosinophilic material in the background)
Accidental salivary gland aspiration

Lymph node cytology
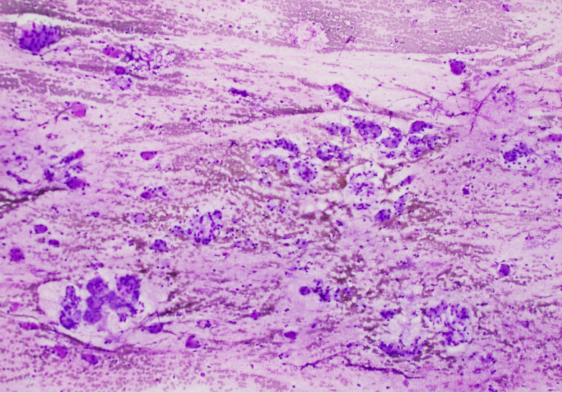
Metastatic disease
What do we see?
A marked increase in cells ( & clustering) found in lymph nodes (e.g. mast cells)
Presence of cells not expected in a lymph node (e.g. epithelial cells – raise suspicion)
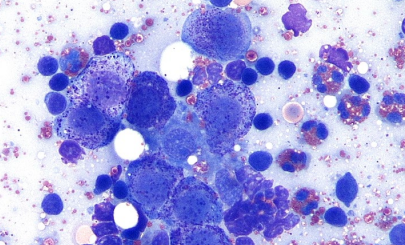
What is this?
Metastatic Dz
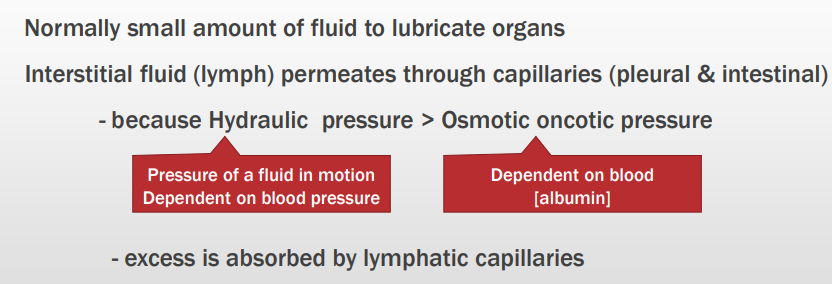
Body cavity effusions
Health (canine & feline)
Normal features?
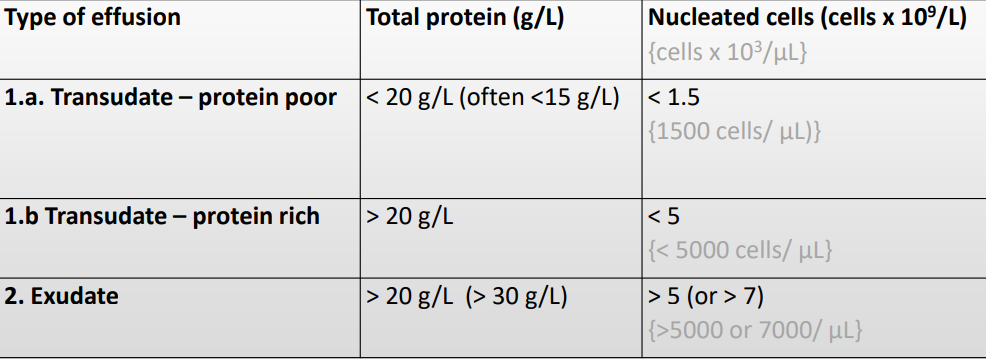
Body cavity effusions
“Simplified” laboratory criteria for classification
Need to know detail:
Step 1 [protein]
Step 2 [cell]
Body cavity effusions
What should we observe to help dx?
1. Macroscopic appearance of fluid (colour – yellow, red; smell – urine)
2. Measure protein (g/L) concentration
3. Determine automated total nucleated cell count (x 109/L)
4. Cytology – evaluate direct and cytocentrifuged preparations
Body cavity effusions
Transudative effusions
Colour?
Protein?
Nucleated cells?
Cell Characterisitcs?
Body cavity effusions
Exudative effusions
Predominantly characterised by? Why? Steps involved?
High cellularity and high protein concentration because they are formed due to an inflammatory process


Body cavity effusions
What is this? Why?
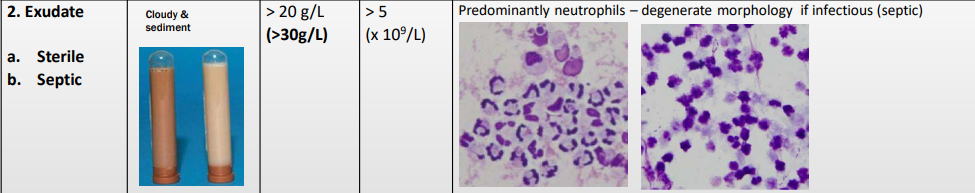
Exudate - sterile or septic
Cloudy & sediment
Body cavity effusions
What is this?
Why?
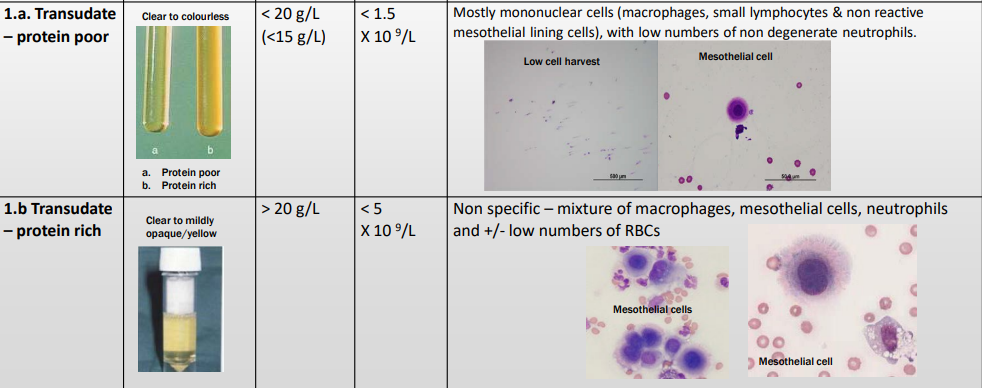
Sterile or Septic Exudative Effusion
Predominantly neutrophils – degenerate morphology if infectious (septic)
Body cavity effusions
What is this?
Why?
Exudate viral – FIP
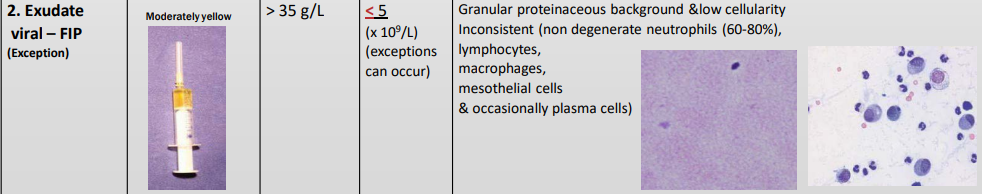
Moderately Yellow
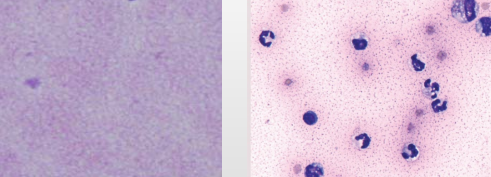
Body cavity effusions
What is this?
Why?
Granular proteinaceous (high protein) background & low cellularity
Exudative effusion – FIP
Body cavity effusions
Haemorrage - trauma, coagulopathy, neoplasia
Acute version
Colour?
Nucleated characteristics/ Microscopy?
Body cavity effusions
Haemorrage - trauma, coagulopathy, neoplasia
Chronic version
Colour?
Nucleated characteristics/ Microscopy?
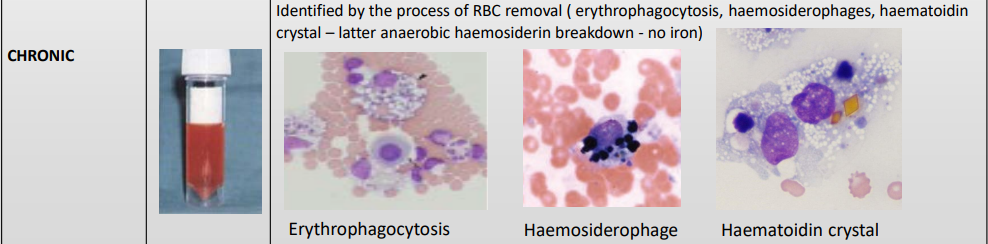
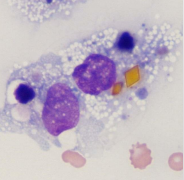
Body cavity effusions
What is this?
DX?
Haematoidin crystal
Chronic Haemorrage
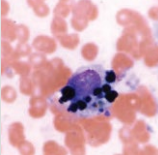
Body cavity effusions
What is this?
DX?
Haemosiderophage
Chronic Haemorrage
Body cavity effusions
What is this?
DX?
Erythrophagocytosis
Chronic Haemorrage
Body cavity effusions
Lymphorrhage - means what?
How does it occur? Result?
Lymphatic Effusion from obstruction (physical or functional) to lymphatic flow (thoracic duct into venous system) → Increased pressure and dilation of lymphatics (lymphangiectasia)
Body cavity effusions
Lymphorrhage
Specific ways it occurs?

Body cavity effusions
Lymphorrhage
Types of effusion?
Chylous effusion and Nonchylous lymphatic effusion
Body cavity effusions
Lymphorrhage - Chylous effusion
Features (general)
Lymphatic vessel btw SI and thoracic VC is affected
Effusion from damaged lymphatic vessel or 2ndary to inc hydraulic psi in cranial or CVC
Chylothorax more common in cats (cardiac disease, neoplasia, trauma, idiopathic)
Chyloabdomen rare
Body cavity effusions
Lymphorrhage - Chylous effusion
Colour, Protein, MS?
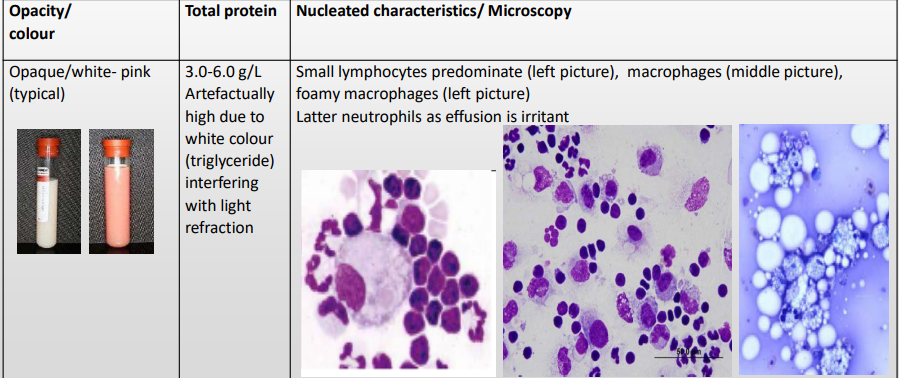
Body cavity effusions
Lymphorrhage - Chylous effusion
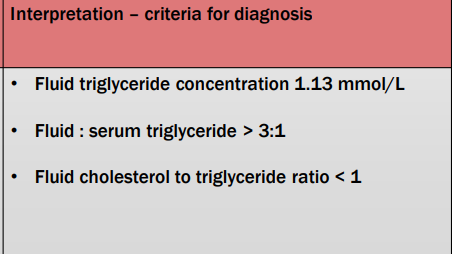
Unique chemical characteristics in chyle?
What tests are done?
Criteria for DX?
Effusion is high in triglyceride & low in cholesterol
Biochemical test on effusion & blood
• Triglycerides
• Cholesterol
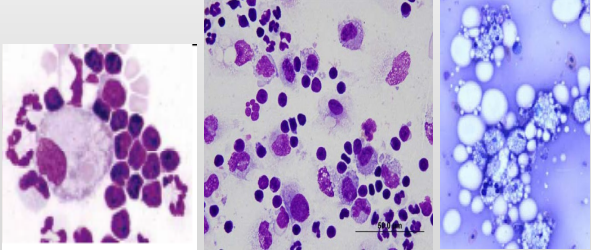
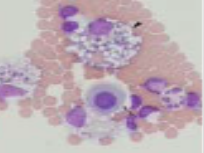
What is this? Describe why
Small lymphocytes predominate (left picture), macrophages (middle picture), foamy macrophages (left picture)
Latter neutrophils as effusion is irritant
Body cavity effusions
Lymphorrhage - Non-chylous effusion
Features (general)
(other lymphatics, not triglyceride rich lymph just high in lymphocytes)
(lymphatics not in the drainage path from intestine to thoracic duct)
Body cavity effusions
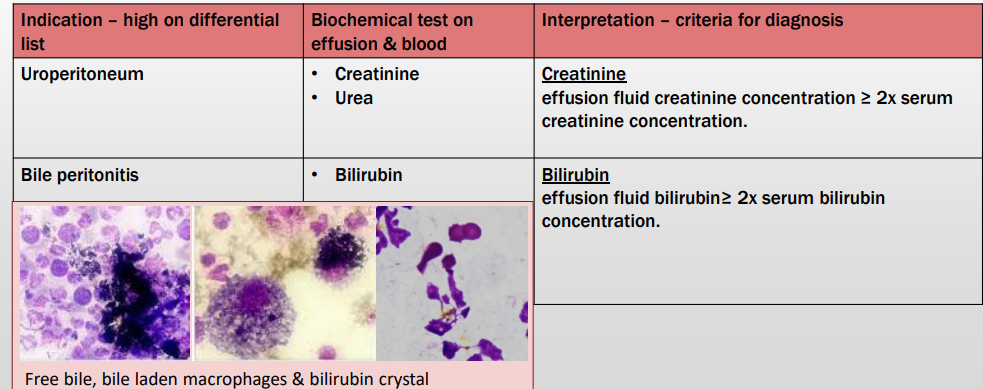
Rupture of hollow organ or viscous (e.g. bladder or biliary tract)
Indications? Tests for each? Criteria for DX?

Body cavity effusions
What is this? Why?
Lymphorrage - Chylous effusion
Opaque/white- pink (typical)
Exudative effusion – FIP (exception)
Ratio aspect?

Exudative effusion - FIP Exception
Colour/opacity?
Total protein?
Nucelated cells?
MS fx?
Exudative effusion - Sterile or Septic versions
Colour/opacity?
Total protein?
Nucelated cells?
MS fx?
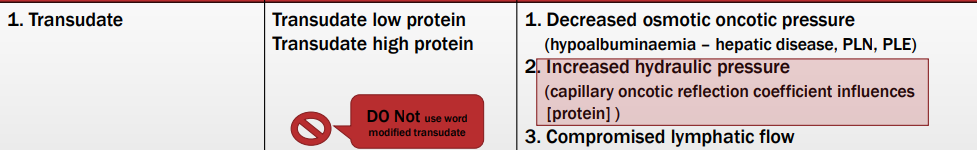
Body cavity effusions
Transudate
Sub classes?
Pathogenesis?
Body cavity effusions
Exudate
Sub classes?
Pathogenesis?

Body cavity effusions
Lymphorrhage and haemorrage
Sub classes?
Pathogenesis?

Body cavity effusions
Transudate low protein & Transudate high protein effusions
The fluid that leaks from the vessels depends on the blood vessels X?
(Previous X) is an indication of X?
This can be roughly determined by?

Body cavity effusions
Transudate low protein & Transudate high protein effusions
Common causes for each?

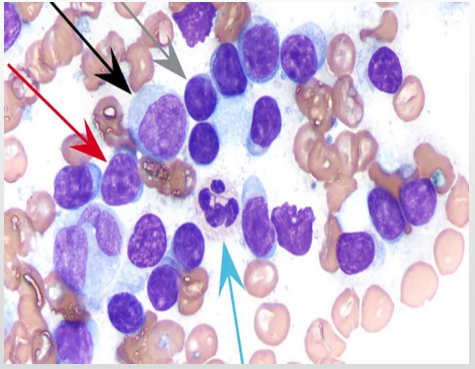
Normal lymph node morphological features
Look at the arrows, features for each?
90% small well differentiated lymphocytes (grey arrow)
10% of nucleated cells are composed of medium sized lymphocytes (red arrow) scant large lymphoblast (black arrow)
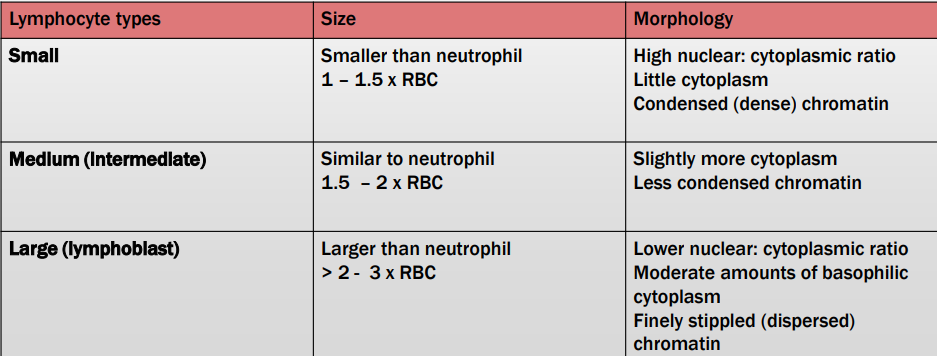
Normal lymph node morphological features
Lymphocyte Types and Features?
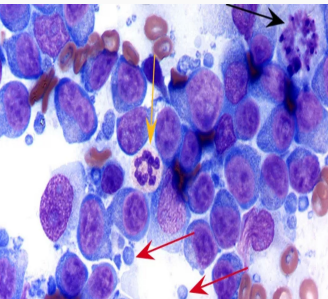
lymph node morphological features
What are the red arrows?
Lymphoglandular bodies – basophilic cytoplasmic fragments of lymphocytes (red arrow)
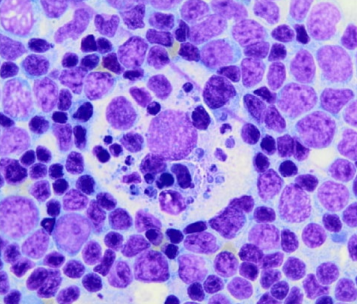
lymph node morphological features
What is this?
Tingible body macrophages – contain phagocytosed apoptotic lymphocytes