CCBPE Lec 3: Cell Culture Maintenance & Bicarbonate
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Culture environment of CO2 Incubator
1) Temperature: maintained within limits of natural habitat of animals (i.e. 37oC)
2) Oxygen: 1-10%
3) CO2: get dissolved in the mdium and remains in equillibrium with Bicarbonate Ions HCO3- → Lower pH
Why should antibiotics not be used for routine culture of cell?
Toxicity effect
Mask the presence of low levels of microbial contamination
Why is serum added to basal medium?
contains factors for cell proliferation & maintenance
buffer against perturbations and toxic effects (like pH/presence of heavy metal ions/endotoxins)
Disadvantages of Serum-containing medium
Lack of standardisaion (variation in serum effects)
Risk of viral/prion/mycoplasma contamination
Availability and cost (expensive)
Make purification of proteins (in serum) more difficult in downstream processing
Serum Ab → Potential cytotoxicity
Challenges of Serum-free medium
Chemical contaminants in serum-free medium may be more toxic to cells
More specific to certain cell types
Adaptation to serum-freee medium takes time
Serum-Free Adaptation
Have cells in logarithmic phase of growth
Consistently monitor cells
Methods:
1) Sequential adaptation
→ Slowly increasing serum conc.
2) Starve and save adaptation
When to use Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)?
Serum supplementation for high cell growth
When to use Ham’s F12 or F10 and the MCDB media series?
Growing specific cell types at low density with minimal amount of serum
Methods to adapt adherent cells to a suspension culture
1) Incubate cells in serum-free medium (using Sequential adaptation)
2) Coat surface with anti-sticking agent (e.g. Teflon)
Partial pressure and Henry’s law constant
H = 29.4 atm/M
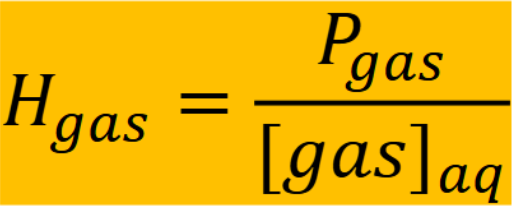
Henderson-Hasselback Equation (determine pH)
Note: The concentrations of the base/acid must be in moles/L
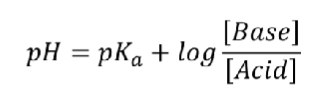
Importance of Bicarbonate buffer
Maintaining pH is Human body and Cell culture
Counters CO2 to create an equillibrium
What are some factors to look out for when Observing a Cell Culture?
Drop in pH → Colour change
Cell concentration (Higher conc → Medium used up faster)
Morphological deterioaration
What method can be used for Protein determination?
Bradford Assay
Specific enzyme activity
What methods can be used for DNA determination?
Staining of cells with fluorescent that bind to DNa
DAPI
Hoescht 33258
What factors can be used indirect monitoring of Metabolic assessment?
Glucose concentrations
Lactic Acid production
Oxygen Consumption
Name at least 3 Cell Viability Assays
(name at least one of the 3)
Dye exclusion (e.g. Trypan Blue)
MTT Assay
Lactate Dehydrogrenase (LDH) Determination
Colony forming assay → Calculate plating efficiency
Rate of protein and nucleic acid synthesis
Energy level: intracellulcar energy charge
Limitation of Dye Exclusion assay
Cannot distinguish between healthy viable cells and unhealthy viable cells
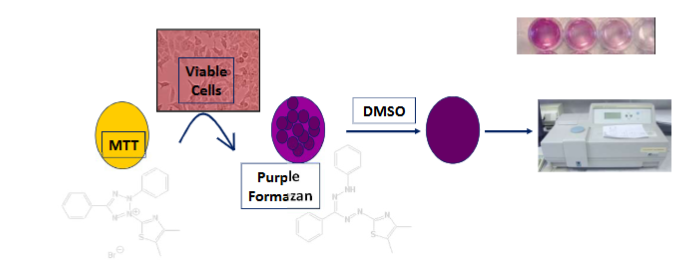
Describe the concept of the MTT Assay in indirect monitoring of cell viability
MTT added to culture medium and taken in by the cells
MTT (yellow) is reduced by NAD(P)H dehydrogenase in mitochondria to purple formazan derivative
Upon, solubilisation, purple formazan quantified colorimetrically by UV-Vis spectrophotometer
Strength of purple colour directly proportional to the metabolically active cells
Describe the concept of the LDH Dehydroogenase Determination Assay in indirect monitoring of cell viability
When a cell is damaged, LDH is produced
More lactate → pyruvate via NAD+ reduction to NADH
Diaphorase uses NADH to convert INT to Red Formazan
More cell damaged (cytotoxicty)→ More LDH released → More Red Formazan formation
Describe the concept of the Colony forming Assay in indirect monitoring of cell viability
Known no. of cells at LOW density seeded and grown in wells
Each cell will produce a cell colony
Count no. of cell colonies
PE = No. of colonies/cells plated * 100%
Describe the concept of the Rate of protein and nucleic Assay in indirect monitoring of cell viability
Use radio-labelled amino acids/nucleotides
Add to log phase cultures
Rate of protein synthesis measured by scintillation counter
More protein content → More cell growth
What radio-labelled amino acids/nucleotides usually used in rate of protein nucleic acid determination?
3H-leucine
35S-menthionine
Intracellular energy charge caluclation
Energy=ATP+\frac{0.5\left(ADP\right)}{ATP+ADP+AMP}
Lower values → Lower viability
Normal cells have 0.7 - 0.9