the liviing dead case studies
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
pyramids of Djoser and Khufu
2600 - 2450 bce
pharaonic egypt
nile valley, modern day egypt
egyptians lavished their greatest effort and materials primarily on mortuary architecture
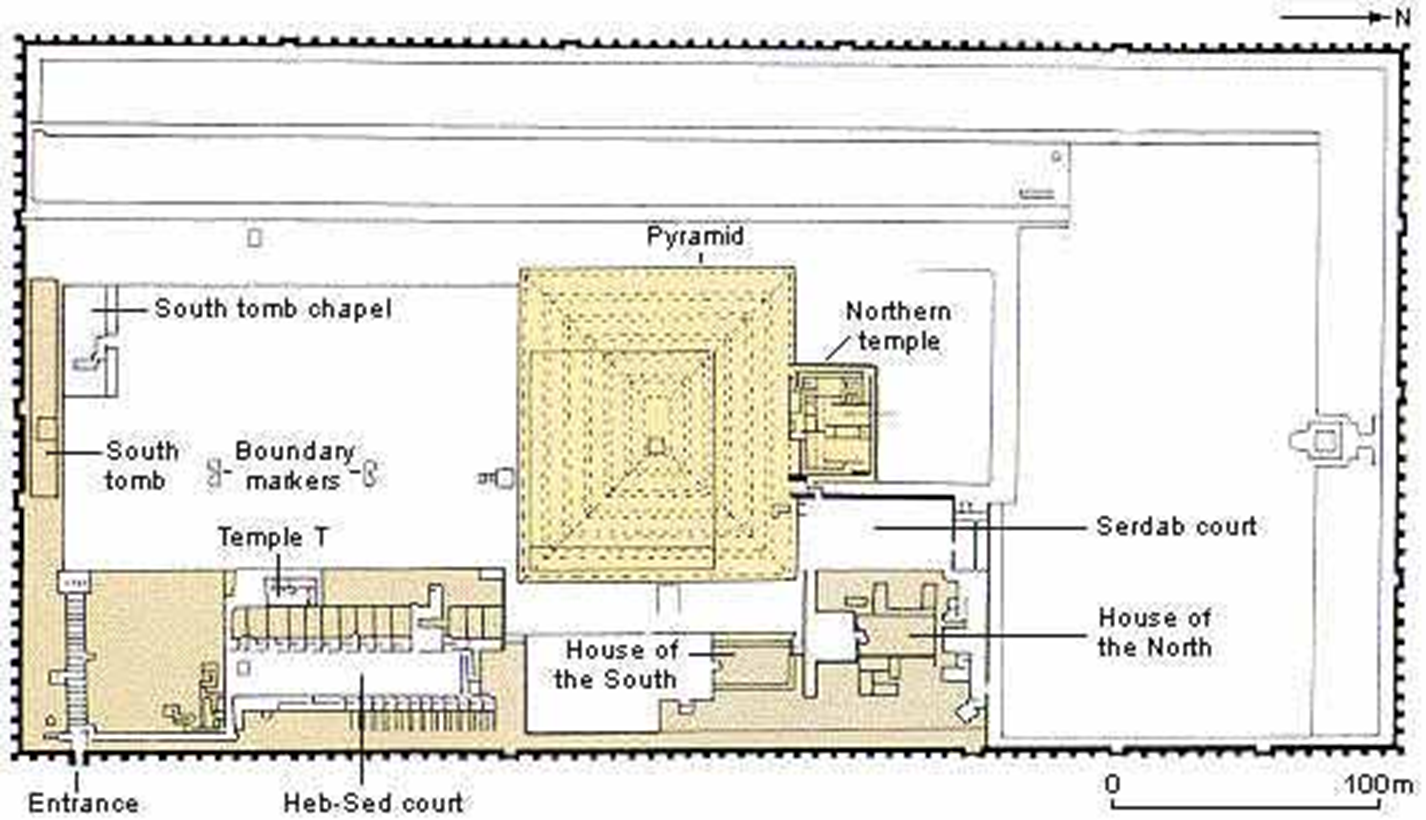
one of the first momumental stone buildings of the world and the earliest site is the monrtuary temple complex of king djoser built at saggara
King djoser
pharoah who ruled over two halves of Egypt, upper and lower
estbalish the period known as the old kingdom
stepped pyramid was his tomb
stepped pyramid is an innovative form, introducing a type that as it became more developed has come to symbolize the architecture of ancient egypt
based on a pre-existing tomb form, the mastaba
mastaba
bench-shaped tomb structures with sloped outer wall
served as above-ground markers for the tombs tunneled underground
made from stone, marking it the first monumental stone construction in Egypt
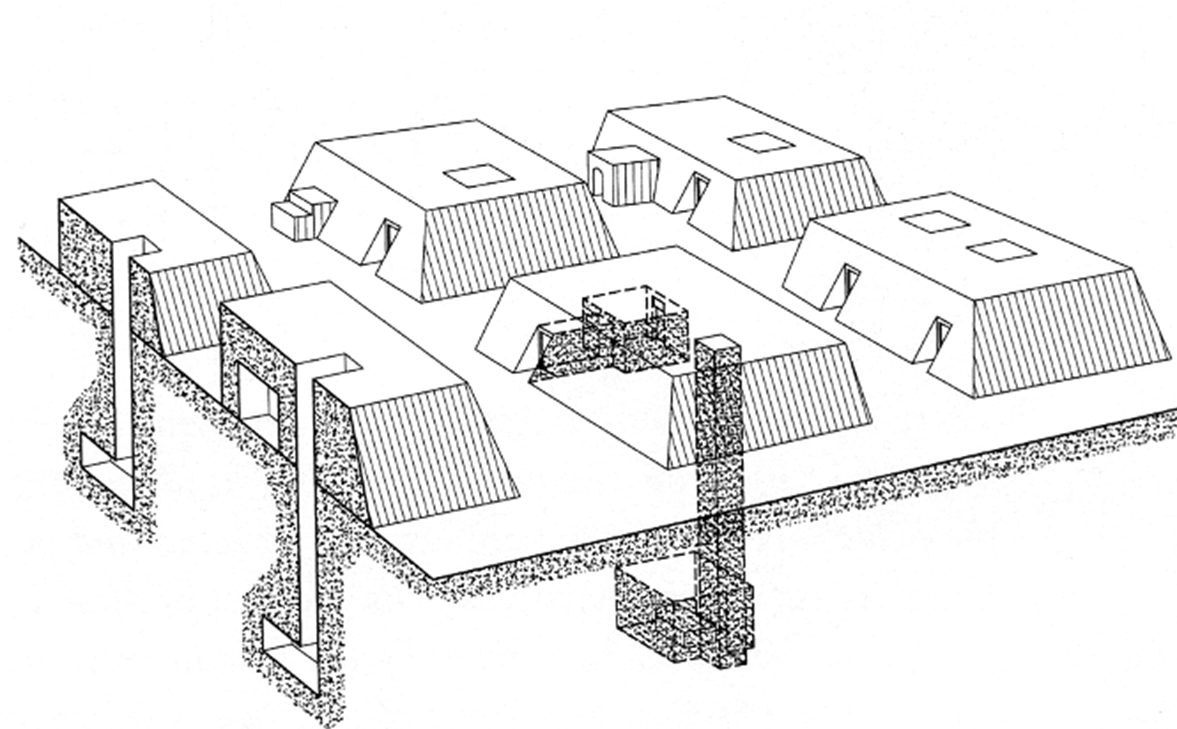
funerary complex of King djoser
tomb was the major vertical element of the site and stood wihtin a walled enclosure with additional buildings
most of the elements within the complex were doubled to represent both the north and south kingdom
Pyramid section and plan
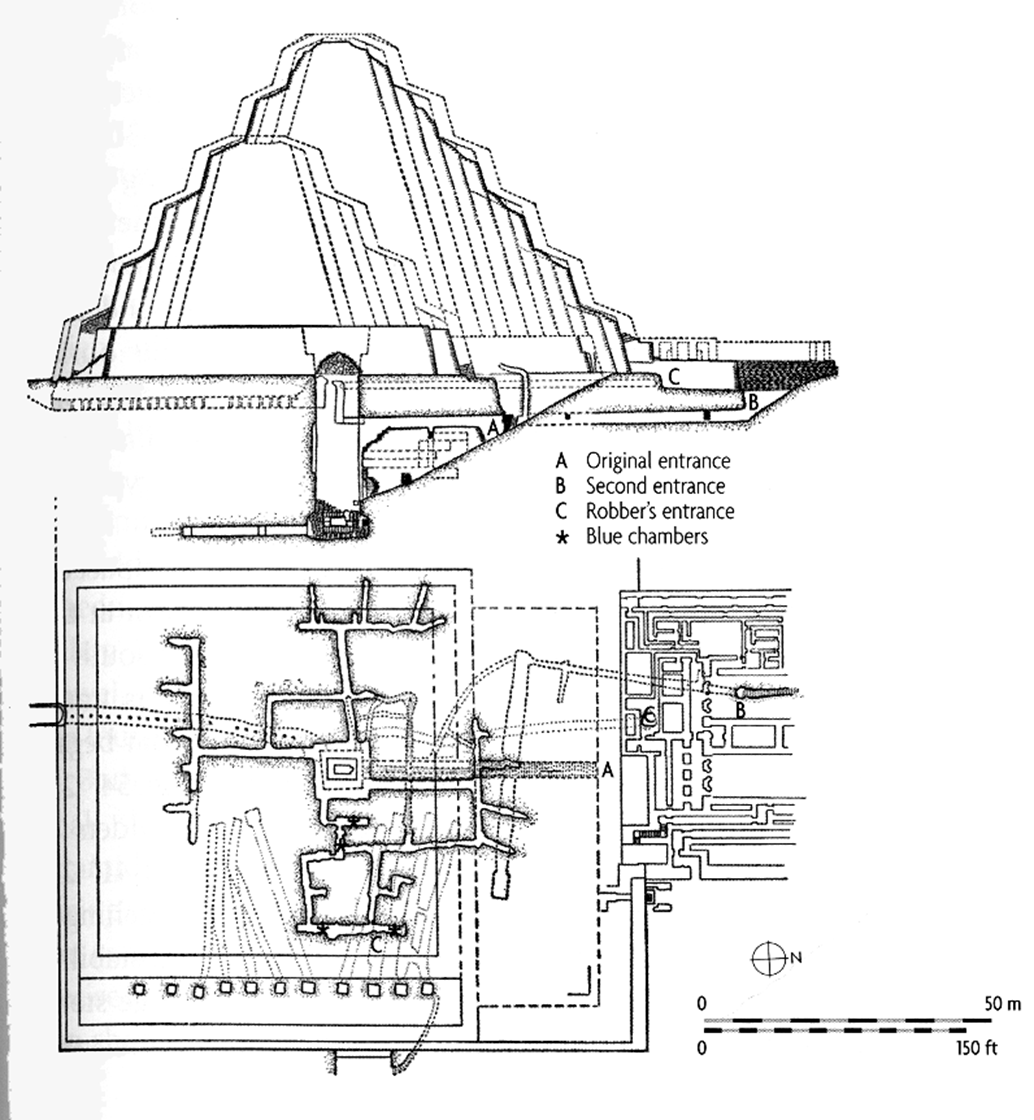
meant to be a vehicle through which he would be transported to the afterlife
- strong vertical axiality o fthe pyramid was meant to mark this journey
plan shows multiple subterraneean tunnels to protect the tomb from robbers
imhotep
first recorded architect who designed this compelx for djoser
- physician, priest, and poet
collasped pyramid, meidum, and bent pyramid
Imhotep initated a series of experiments which resulted in egypt most famous monuments
at Meidum, builders added outer layers to an existed stepped pyramid in a failed attempt to achieve a smooth-sided form, sides are too steep, though
changed the angle of the outer face midway resulting in the bent pyramid
Pyramids, Giza
Sneferu’s successors, the pharoahs Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure and built the three Pyramids at Giza, achieving a true achieving a true phyramid form
Pyramid of Khufu -455 feet tall
how are the pyramid construction
egyptians were highly skilled mathematicians for their day as several of the Great Pyramids were incredibly accurately aligned to the north star and perpendicular axis of the sun
ramps built into the interior core
the largest pyramid, workers moved 6 million tons of material including 2.3 million individual blocks of stone weighing between 2.5 and 15 tons
what is the ceremony for the funeral of a pharaoh
the pharoah’s body arrived by boat on the Nile River to a valley temple at the water
body was transported over a long causeway - long, man made ramp, to the pyramid itself
the Great Pyramids for the pharoah surrounded by burial sites for other members of his family and royal court ( buried in smaller pyramids and mastabas that surround the enormous pyramids)
Qin Emperor tomb
221-210 BCE
Qin people
modern- day China
what does confucians believe
highlights family value and venerates ancestors
mortuary archiecture
believe that “ the deceased ancestors should be treated as if they were alive”
Feng shui
wind and water
most important issue in fengshui is to find the best site that would preserve the beneolent energy while blocking the evil ones
based on practical needs of the ancient people
ideal to have shielding mountains and a relatively open field in the south
K’ung Fu Tzu ( confucianism)
The school of the Scholars
compassionate or kindhearted, just or righteous, to obey rituals or rites, wise, trustful
“ to govern by virtue, let us compare it to the North Star: it stays in its place, while the myraid stars wait upon it
He who learns but does not think is lost. he who thinks but does not learn is in great danger
what is the Qin people famous for
their great military power and efficiency
have to constantly fight the nomards, which helped to strength their military skills
location also gave them virtually endless space and resource for expansion
First emperor of Qin Empire - Qin Shihangdi, unified the langauage
Qin Dynasty ( 221-206) BCE
left us the Great Wall and the Emperor’s mausoleum along with the terrcotta army
Qin ( catch or to seize)
system of writing was standardized and language
believe that those outside the boundaries of his empire to be barbarians
how imperial capital city and garden planning in China was used as a model for making visible forms of power, hierachy, and ritual activities
it is designed with an axial emphasis, the buildings and landscape laid out with a central axis as an organization tool
built on high plinths or tai platforms
higher the tai the stronger the claim to power by the ruler
ex. Qin Shi Huangdii - between the Wei eiver and the Zhongnan mountain, able to take strength from both
known to be immense with the main room able to host 10,000 for dinner
symmetrical strcture with two wings, an earthen core that creted the image of a 3 story building of remarkable size
how long did qin empire lasted
15 years
brought down by rebellions throughout the country
group of 900 men enlisted to guard the northern frontier near modern day Beijing was behind schedule to arrive at the garrison due to heavy rain
according to Qin’s law, they are to be executed; however, they choose to revolt and the entire country follow them to rebellion
significant portion of the entire male population were enlisted to build the Great Wall and the emperor’s tomb
size of the first emperor tomb
step pyramid
350 by 345 meter surrounded by two layers of walls and gates
outer layer covers an area of 2 square km
what did the builders use to built Qin Shi Huangdi Tomb
8000 life size terra cotta figures, grouped in battle order, rank by rank
pyramidal tomb mount represented a man-made mountain, comparable inform and function to those build for the Egyptian pharaohs
builders produced an outer coffin of molten copper and a subterranean world with models of palaces, pavilions and offices
also included replicas of the major streams and rivers of China , recreated in mercury with mechanisms
Qin Shi Huangdi Tomb Mound
8000 life-size terracotta figures
there was a cross bowed soldiers at the entrance ready to kill anyone who entered
4 subterranean pits , pits containing the terracotta army had a roof of planks supported by wooden crossbeams carried by massive beams
100 variations which are repeated
2000 figures representing not an army but civil officials and scribes
brightly colored with surface paint
Taj Mahal
1632 - 1648
mughals/ mughal empire
modern-day india
associated with romance
popular myth about the taj mahal is that the mughal emperor Shah Jahan built it is a love letter in marble for his deceased wife
mausoleum, king way for islamic kings and queens to memorialize themselves
who is the patron of the Taj Mahal
Shah jahan
ruler of the Mughal empire in India
1627-1658
who is the architect
Ustad Ahmad Lahauri
served as the chief imperial architect of the Mughal empire
what is the purpose of taj mahal
construct a monumental resting place for Mumtaz Mahal, the wife of shah Jahan
favorite wife
also as an expression of Mughal identity and imperial power
history of Mughal Empire
founded in 1526 and came to a close in 1858
empire that ruled India for over 300 years
first mughal emperor came from Central Asia but his descendants would expand the empire
they would ruled over a multi-confessional, multi ethnic, and multi lingual population
major theme of Mughal art and architecture was dynastic legitimacy
Jahangir, Timur
location of Taj Mahal
located in the city of Agra in north India, one of three capitals
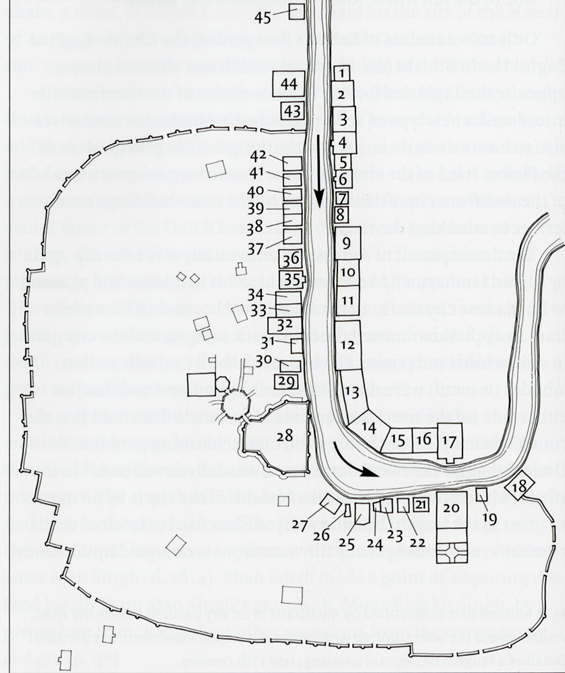
what is the 1st area of the plan
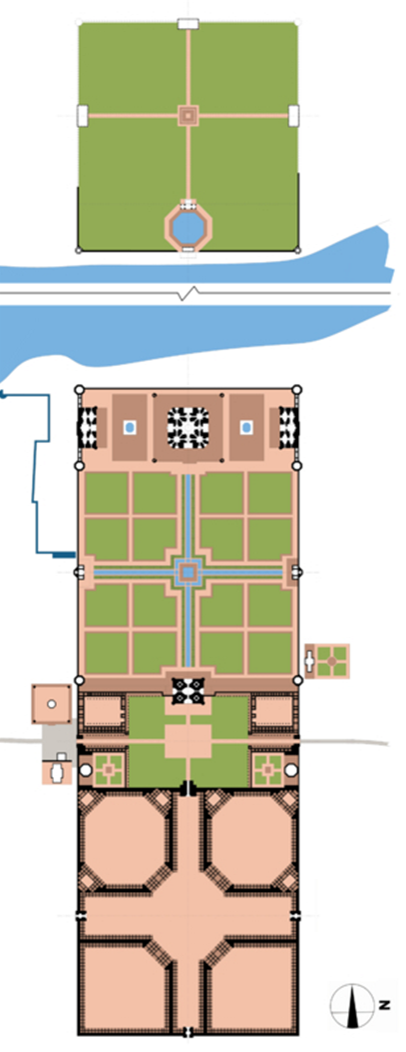
viewing garden
Taj Mahal was a place of pilgrimage, a destination for all those who wanted to honor Mumtaz Mahal
taj mahal is located at the end of this garden, on the riverfront
across the yamuna is a viewing garden
what is the second area
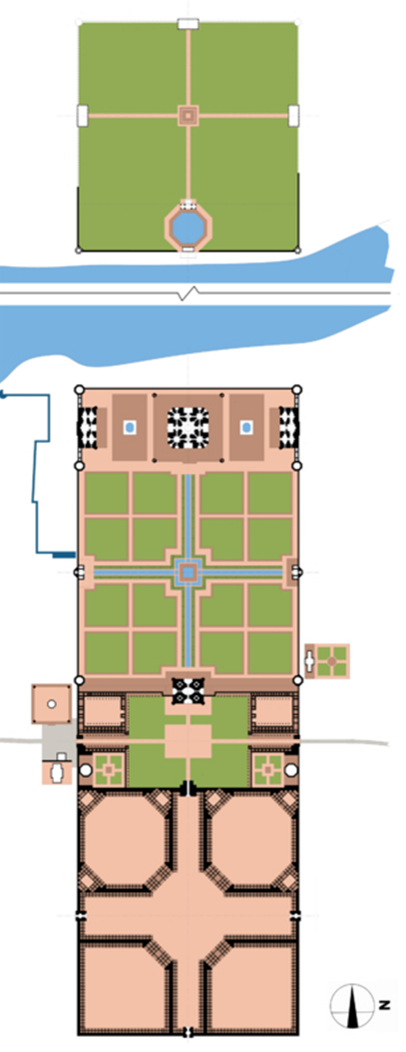
taj
what is the 3rd area
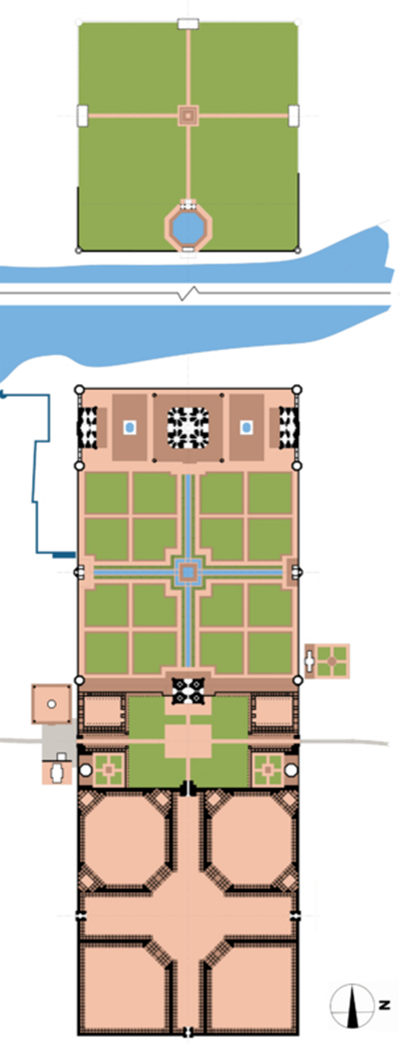
garden
monumental squares that are subdivided into smaller squares
what is the 4th area
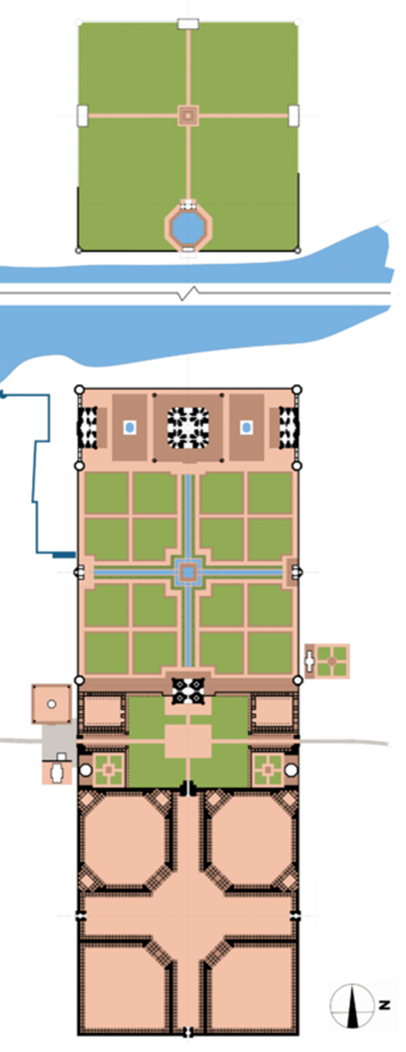
forecourt
roughly the same size as the rectangular platform that the Taj Mahal sits on
what is the last area called
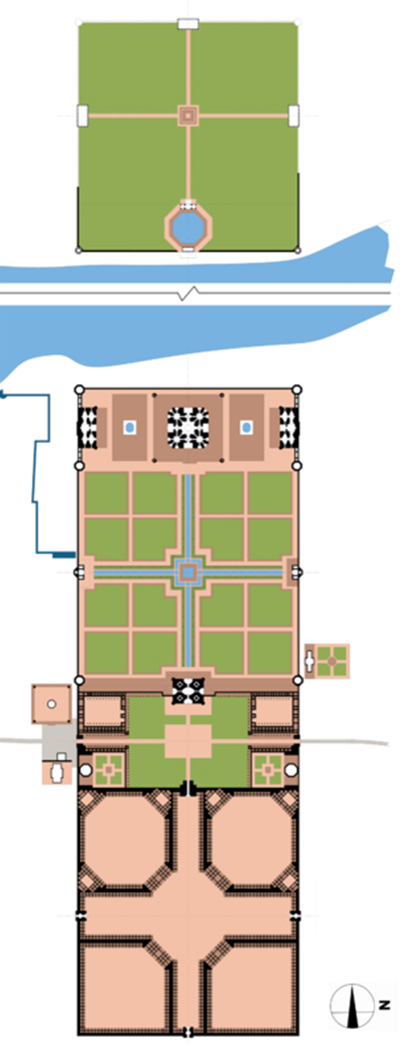
bazaar
what are the two other major structures in the complex
a mosque and a guesthouse
mosque is sandstone and marble, and topped by three marble domes, contains a single, large aisle, and a mihrab
mihrab
niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the direction of Mecca, which Muslims are supposed to face when they pray
blind arch indicating the direction of Mecca
mosque
signifies the sancitity of the Taj Mahal complex
the site of ritual commemoration at least once a year
members of the imperial family and nobility would gather to recite prayers for the dead
the design and symbolism of the char-bagh
( four partite garden)
char - four, bagh - garden
large square garden plot is bisected by two, perpendicular axes that intersect in the center, dividing the larger square into four smaller square
founder of the Mughal empire, Babur who imported this garden type from central to south asia
structure of Taj Mahal
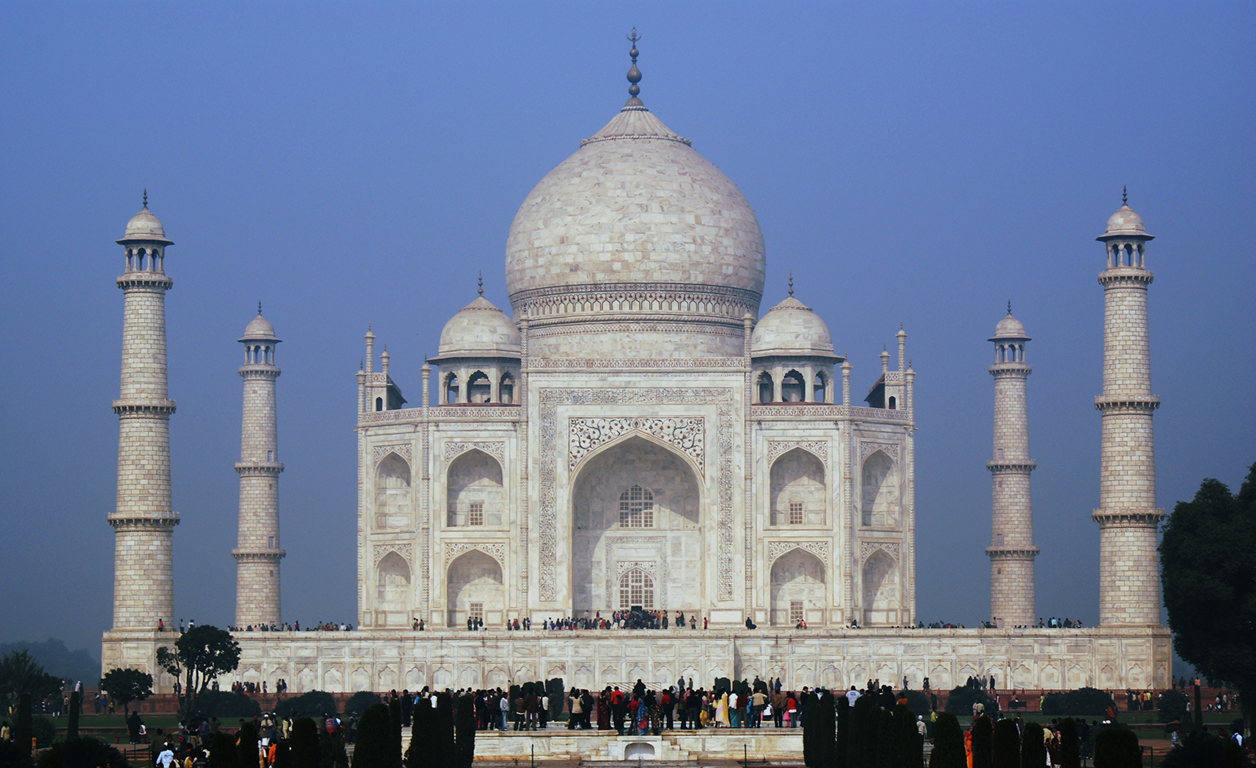

plinth - base or platform
minaret - has 4 minarets
chattri - small domed kiosks
iwan - central, two - story or pointed arch
Pietra duraas
translate “hard stone”
tone inlay technique that originated in Italy and traveled to India through merchants, diplomatic gifts and luxury goods
the longest inscripitional program in the islamic world
what does the Qur’an believed
the word of God, revealed to Muhammad through the angel Gabriel
inscriptions relate to themes that are appropriate for a mausoleum set in a funerary garden: the afterlife Day of judgement, and paradise
what is mughals fascinated by
naturalism
perfected this representational technique in their painting and sculpture
Taj mahal incorporated an elaborate garden in the char bagh tradition
what is the structure of Taj Mahal
double-dome
the plan is one that was originally developed in Iran
hasht bihisht, “ eight paradise” plan
in isiam, heaven is a garden with eight gateways and eight levels
gardens of the Taj Mahal is a british vision of what islamic and indian archiecture