BSCI330: Central Dogma (pt.2)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is protein translation?
mRNA translated to protein by ribosome
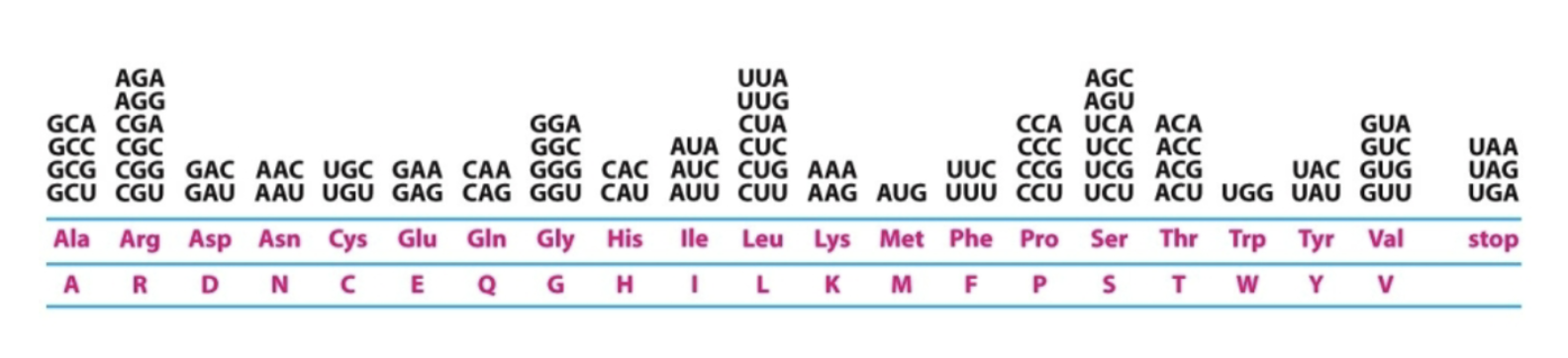
What is a codon?
A set of three nucleotides!
What is the result of the “degenerate” nature of the genetic code?
For a given protein sequence, there may be more than one RNA sequence (more than one codon codes for an amino acid)
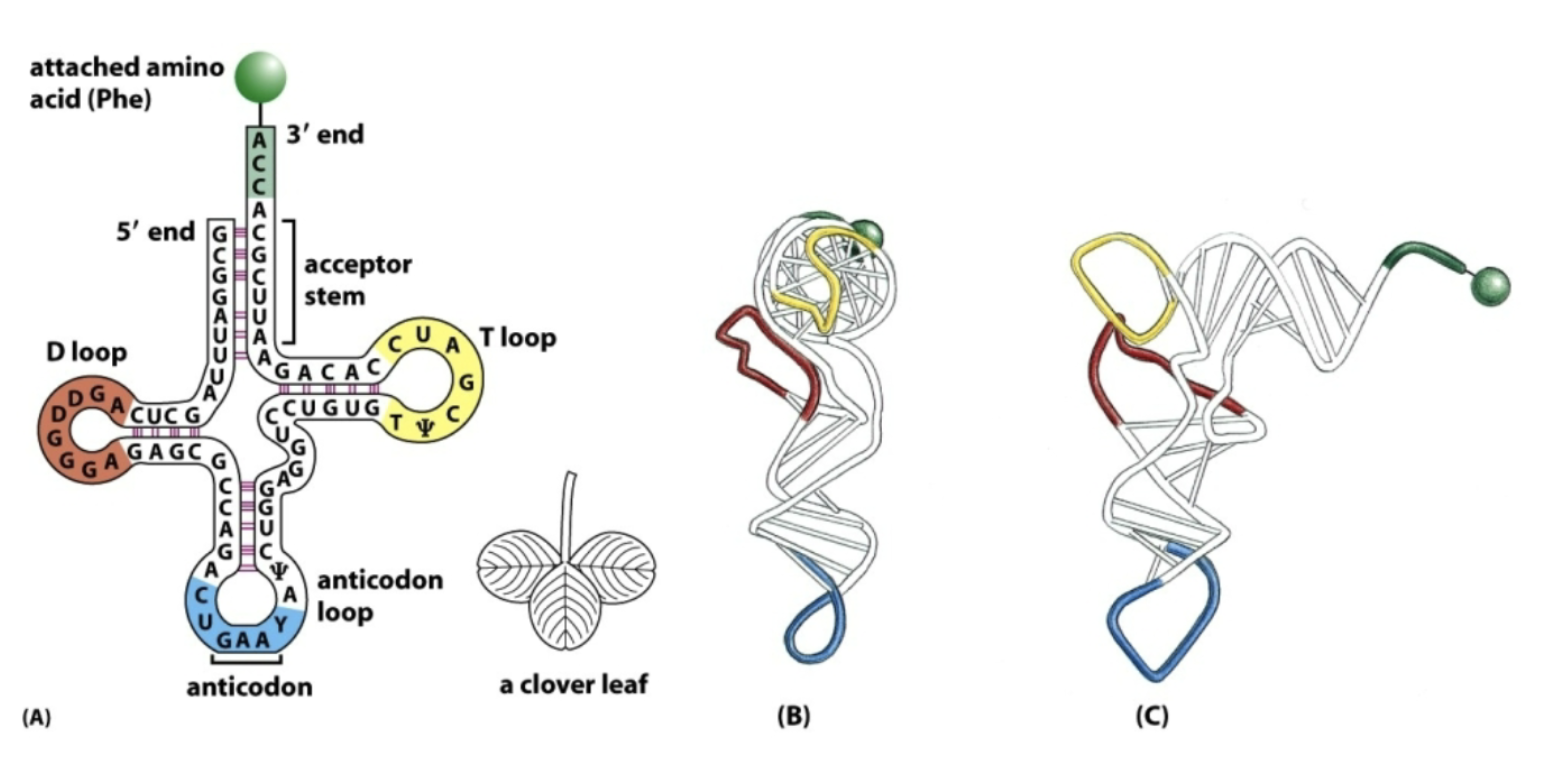
What’s tRNA’s role?
Matches amino acids with codons
Where are amino acids attached to (which end of tRNA)?
3’
How does tRNA work?
Each tRNA contains a loop with an “anticodon”, complementary to the appropriate amino acid’s codon
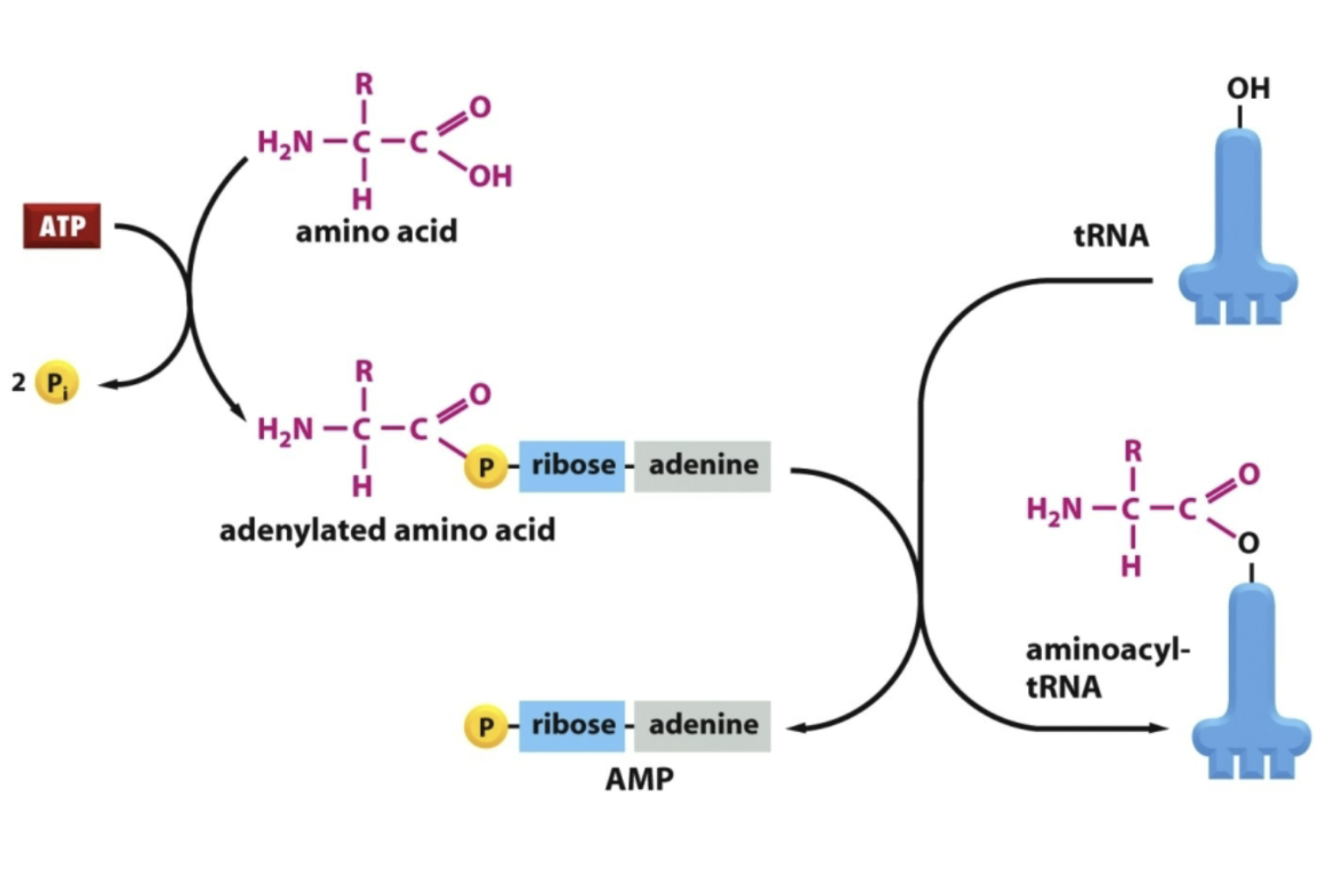
What couples the amino acid to the tRNA?
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase!
Each amino acid has a distinct synthetase
How does the attachment to rRNA occur (MUST KNOW) ?
Amino acid is first activated by conjugation to AMP
Then, it is transferred from AMP to tRNA
Proofreads for accuracy
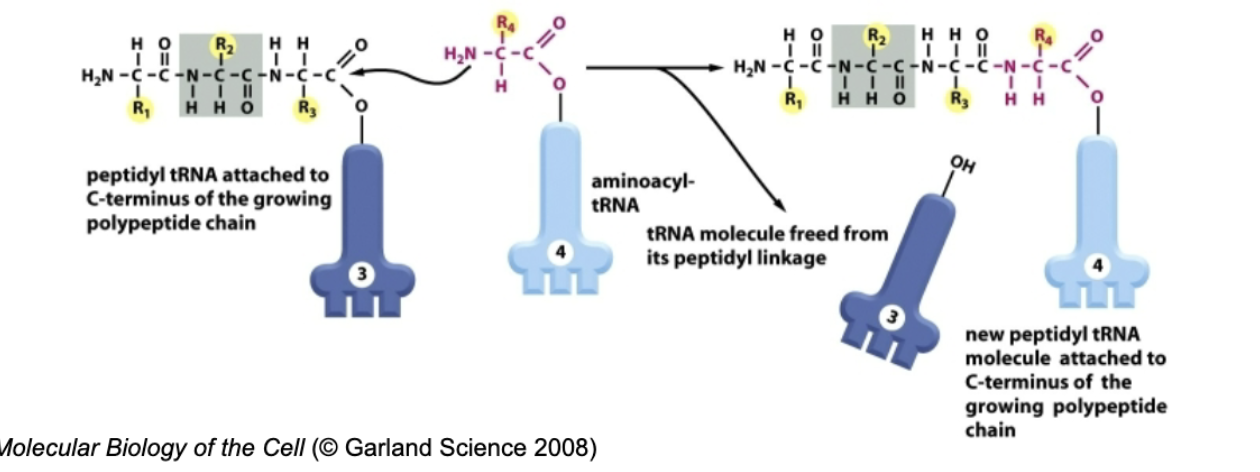
What is the direction of protein synthesis?
N-terminal → C-terminal direction
New amino acids are added to the C-terminal end
How does protein synthesis work?
New aminoacyl tRNA replaces old tRNA
What are ribozymes?
Function as part of the large subunit ribosomal RNA to link amino acids during protein synthesis.
How do ribosomes read mRNA?
From 5’ to 3’, reading 3 bases at a time (i.e. one codon at a time)
Translation begins with the codon…
AUG (Met), the start codon which is special “initiator” tRNA
small and large subunits come to form the ribosome
What is translation elongation facilitated by (MUST KNOW)?
Elongation factors, which use GTPase activity to allow proofreading.
Ef-Tu/Ef-G in PROKARYOTES
EF1/EF2 in EUKARYOTES
When does protein translation terminate?
Protein translation terminates when the ribosome encounters a “stop” codon (UAA, UAG, UGA)
How is the complete protein released?
A release factor binds to the ribosome causing hydrolysis of the peptidyl tRNA (lets go of protein)
What happens when protein synthesis is done?
The ribosome dissociates into separate small and large subunits, releasing mRNA, release factor, and remaining tRNA
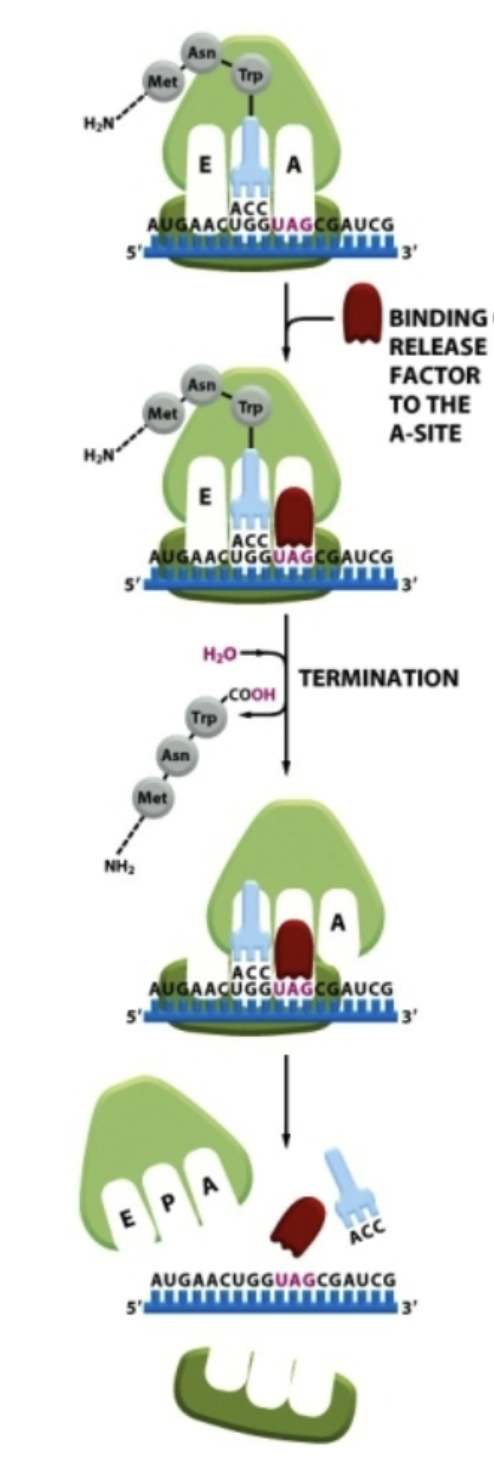
Does an in-frame stop codon always terminate translation?
NO
There are circumstances when a stop codon is translated to insert an amino acid (ex. celinocysteine uses a STOP codon)
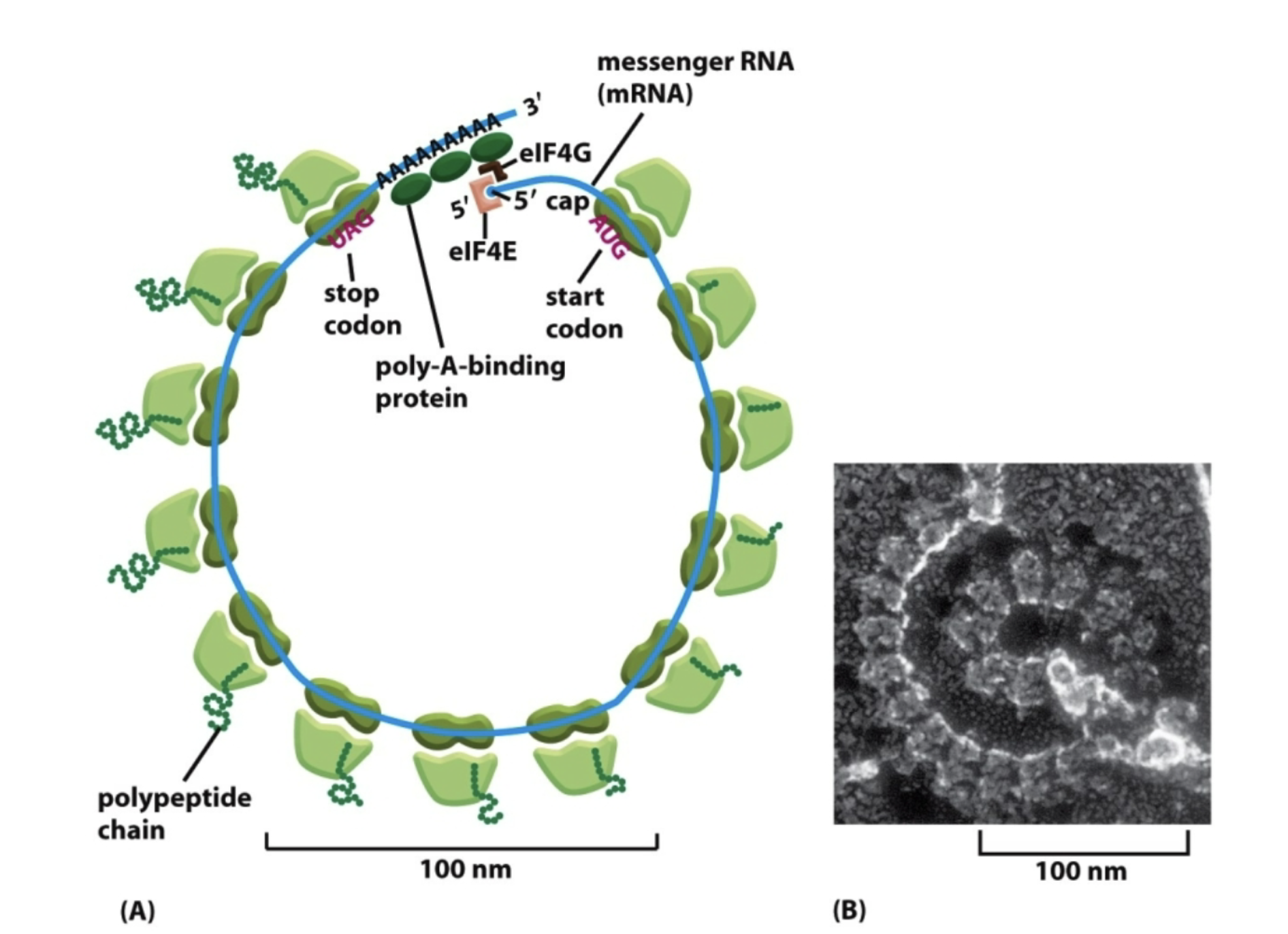
What’s a polyribosome?
When a single mRNA has several ribosomes translating simultaneously.
What do antibiotics do to protein synthesis?
They inhibit, but mostly in prokaryotes.
Few exceptions for blockage of eukaryotic ribosomes is cycloheximide and puromycin.
Why is RNA and protein synthesis costly?
Each additional subunit requires conversion of an NTP into an NMP (2 ATPs REQUIRED)
Elongation = multiple ATP/GTP molecules
mRNA splicing and protein proofreading = more ATP/GTP molecules
What is the information at each level?
Protein sequence: 3D structure, cellular location, protein function
mRNA: same as protein + initiation and termination of translation
DNA: same as mRNA + initation and termination of transcription + splicing