bb
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
--
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Give rise to ear
otic placodes
is an inner ear organ located within the cochlea that contributes to audition.
Organ of Corti
otolith organs
saccule, utricle
saccule, utricle
otolith organs
head movement stable reflex
vestibulo-ocular reflex
rapid movement of eye
nystagmus
record electrical activity in the brain, cortical
electroencephalogram
Origin: CNS//PNS
neural plate//neural crest
imcomplete closure of neural tube
spina bifida
failure closure of neural tube
anencephaly
axon guidance, Angiogenesis (血管新生)
ephrin
mimic alzheimer’s symptoms dur to CSF buildup
normal pressure hydrocephalus
unprovoked seizures
epilepsy
immune system (autoimmune) attack myelin
multiple sclerosis
early sign of MS
optic neuritis
2 stroke
ischemic, hemorrhagic
inflammation of membrane//brain
meningitis//encephalitis
TBI : brain jolt
traumatic brain injury
mild TBI
concussion
blood bleed
hematomas
accumulate CSF
cerebral edema
cant [speak,purposeful movement, process sensory info]
aphasia, apraxia, agnosia
cant [coordination,move]
ataxia, persistent vegetative state
alzheimer’s … accumulate
beta-amyloid, neurofibrillary tangle
neurofibrillary tangle
hyperphosphorylated
Delusion, hallucination 思覺失調 ~ dopamine
schizophrenia
copper acc
wilson’s disease
decrease/inc appetite
leptin, ghrelin
Ca2+ —> bone (vv)
calcitonin, parathyroid hormone
milk production
prolactin
painkiller
endorphin
[inhibit reuptake of dopamine (毒品), alcohol inc effect of ]
cocaine, GABA
[make CSF, support in PNS] cell
ependymal, satellite
damage to posterior parietal (associate)
hemispatial neglect
Produce histamine (hypothalamus)
tuberomammillary nucleus
produced by cells in the lateral hypothalamus —> narcolepsy
orexin
is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. Attention, reward
nucleus accumbens
enter hippocampus
entohinal cortex
a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system
locus coeruleus
connect LR temporal lobe
anterior commissure
—>glycine
serine
Light bleaches
rhodopsin
a local anaesthetic
Lidocaine
hippothalamus — pituitary gland
infundibular stalk
Test min distance b&/ 2 stimulii [-test]
two-point discrimination
antipressant
fluoxetine, paroxetine
stretching
ruffini’s end organ
pathway (DCML) carries the sensory modalities of fine touch (tactile sensation), vibration and proprioception.
dorsal column-medial lemniscal
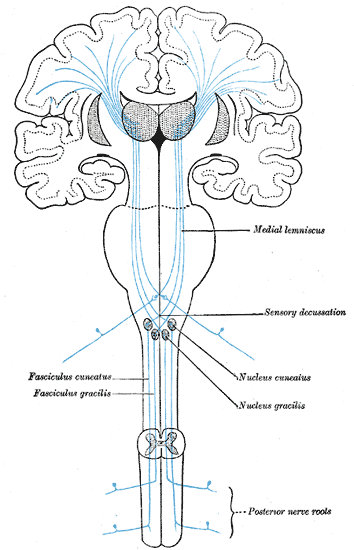
substantia gelatinosa —> thalamus
Anterior __ tract – carries the sensory modalities of crude touch and pressure.
Lateral __ tract – carries the sensory modalities of pain and temperature.
spinothalamic
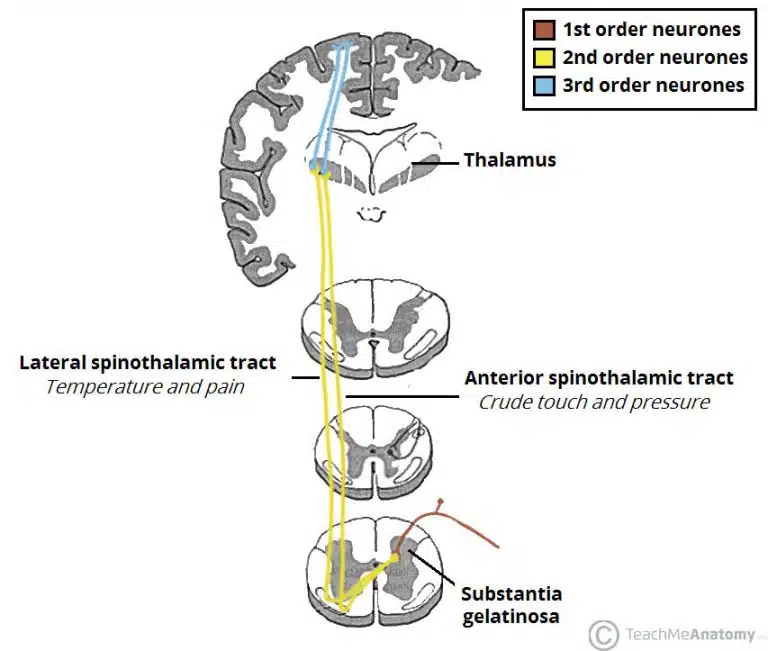
All ipsilateral
Posterior __ tract – proprioceptive from the lower limbs
Anterior __ tract – proprioceptive information from the lower limbs. The fibres decussate twice
Rostral __ tract – Carries proprioceptive information from the upper limbs
unconcious
spinocerebellar
__ Pathway: Associated with detecting motion and contrast; important for identifying the location of visual images.
Magnocellular
__ Pathway: Associated with color perception and fine detail (form).
Parvocellular
__ Tract: Influences automatic movements and muscle tone
Reticulospinal
cluster of interconnected nuclei that form a part of the basal ganglia. It is involved in decision making functions, such as motor control, emotion, habit formation, and reward.
striatum
are a bruising or swelling of the brain
when blood vessels bleed into brain tissue.
Contusion
primarily dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Our body uses an enzyme called __ (MAO)
monoamine oxidase
Modulate / descending pain
Periaqueductal Gray
The __ is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway
inferior colliculus
________ is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired social interaction, communication difficulties, and repetitive behaviors.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
The Serotonergic System includes the __ and is involved in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite.
raphe nuclei
________ is a type of epilepsy characterized by sudden, brief lapses in muscle tone, often triggered by strong emotions.
cataplexy
________ is a type of neurodegenerative disease characterized by the progressive loss of motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
The ________ is a structure in the brain that is involved in the regulation of circadian rhythms and is synchronized by light input from the retina.
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
__ means that different parts of the _ gyrus are associated with distinct parts of the body.
somatotopic, precentral
The gyrus is the primary receiving area for _ (i.e: kinesthetic, tactile)
postcentral, somesthetic
__ sulcus divide parietal lobe to superior and inferior, inferior consists of _ gyrus and _ gyrus.
interparietal, supramarginal, angular
The superior surface of the superior temporal gyrus lie the transverse gyri of _, which constitute the primary auditory receiving area.
Heschl