PAINTS AND PIGMENTS 2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
whats a major factor in the comparison of paints and pigments
colour perception
what does perception of colour rely on
simultaneous contrast
what are colours refered to as
RGB
what is RBG
stanardised digital space in identification of colour
what is microspectrophotometry
microscope and spectrometer combined
what does microspectrophotometry do
charateristics of distribution wavelengths
what does microspectrophotometry capture
magnified visual and spectroscopic patterns
what does microspectrophotometry combine
IV visible NR digital imaging with colorimetry
what is the most common paint evidence
automotive
what does a comparison microscope make a note of with paint
colour
texture
layer sequence
relative layer thickness
pigment size and distrivution
defects
what are some defects that can be seen in pain
weathering dirt and solvent traps
what are the 4 ways paint can be observed under comparison micro
cross section
thin peels
wedge cut
stair step exposure
what is the secodn most essential tool in forensic paint analysis
IR spec
why is IR spec good
quick
minimal destruction
little sample prep
how is IR spec run
in transmitted or ATR
what is ATR
attenuated total reflection
what is a limitation for IR
pigments below cut off and LOD cant be seen
what can raman do that IR cant
discriminate crystalline polymorphs
what does fluorescence mean
absorbance of radiation at one energy and remission at a different
what is created when a electron from the inner K shell is ekected from the atoms due to being excited
a vacancy
what happens once a vacancy is created
atoms from L or M shell fills it
what deos XRF stand for
xray fluoresence
what are 3 advantages of using XRF
handheld, non destructive, no sample prep
how is nano structure characterised
studying chemical and physical properties
what are the 2 techniques useed to asses nano structure
microscopy and diffraction
what are 3 examples of microscopy
scanning electron, transmission electron and atomic force
what method can you use to achieve a higher resolution
electron microscopy
when does beam damage occur
with sensitive samples
what does electron microscopy show
elemental com
what does combing electron micro and XRF increase
discirminating power
what scattering is used in TEM
elastic diffraction
what scattering is used in SEM
inelastic backscattering
what scattering is used in spectroscopy
inelastic energy loss
does sem or xrf require a larger sample size
xrf
does sem or xrf have a lower lod
xrf

what does this represent
braggs law
what is braggs law for
understanding conditions required for diffraction
what does braggs law show
arrangements of atoms in crystal structure and how they stack
what is n in braggs law
integer (1)
what is d in braggs law
interplanar spacing
what is theta in braggs law
angle between plane and beam
what can be controlled in braggs law
theta and lambda
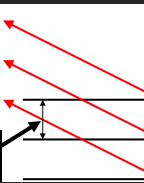
what does this spacing show us
interplanar spacing
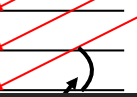
what does this angle show us
angle between plane and beam
what can diffraction determine (4)
lattice parameters
phase composition
crystal structure
crystallite size
how does diffraction determine lattice parameters
indexing position of peaks
how does diffraction determine phase compostion
given relative amount of voerlayed diffraction
how does diffraction determine crystal strcuture
redefining whole diffraction pattern
how does diffraction determine crystallite size
looking at peak broadening