DMS unit 10 study guide
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
most common renal lesion
simple renal cyst
US criteria for simple cyst
1. thin well defined walls
2. anechoic
3. post enhacement
4. edge artifact
5. no color flow
simple renal cysts may occur
anywhere
-arise from obstructed ducts or tubules
complex cyst
if cyst does not meet all criteria for simple it is complex.
-may contain septations, thick walls, calcifications, internal echos, and mural nodularity
category 1 for cysts
-simple/benign
-anechoic
-thin walls
-no calcifications or septations
-no further eval needed
category II for cysts
-cystic with 1 or 2 thin (<1mm) septations
-fine calcifications in walls or septa
-must be 3cm or less in diameter
-must have 1/4 of wall extending outside kidney
-no vascularity
category IIF for cysts
-minimally complicated cysts that need FU
-do not fall neatly into category II
-most likely benign
-6mo to 1y FU
category III for cysts
-intermediate cystic masses
-uniform wall thickening/nodularity
-thick irregular calcification
-multilocular nature
-require biopsy or surgery
category IV for cysts
-diffuse wall thickening
-may include areas of high vascularity or large nodules in wall
-all features strongly suggest malignancy
parapelvic cysts US
-well defined mass
-no internal septations
-can have irregular borders
-may cause obstruction
parapelvic cysts location
at renal hilum or sinus
-do not communicate with collecting system
von hippel Lindau disease
a hereditary disease that includes the development of cysts within the pancreas and other organs
tuberous sclerosis
a systemic disorder that leads to the development of tumors within various organs
tuberous sclerosis US
-multiple renal cysts
-angiomyolipoma
-may become large
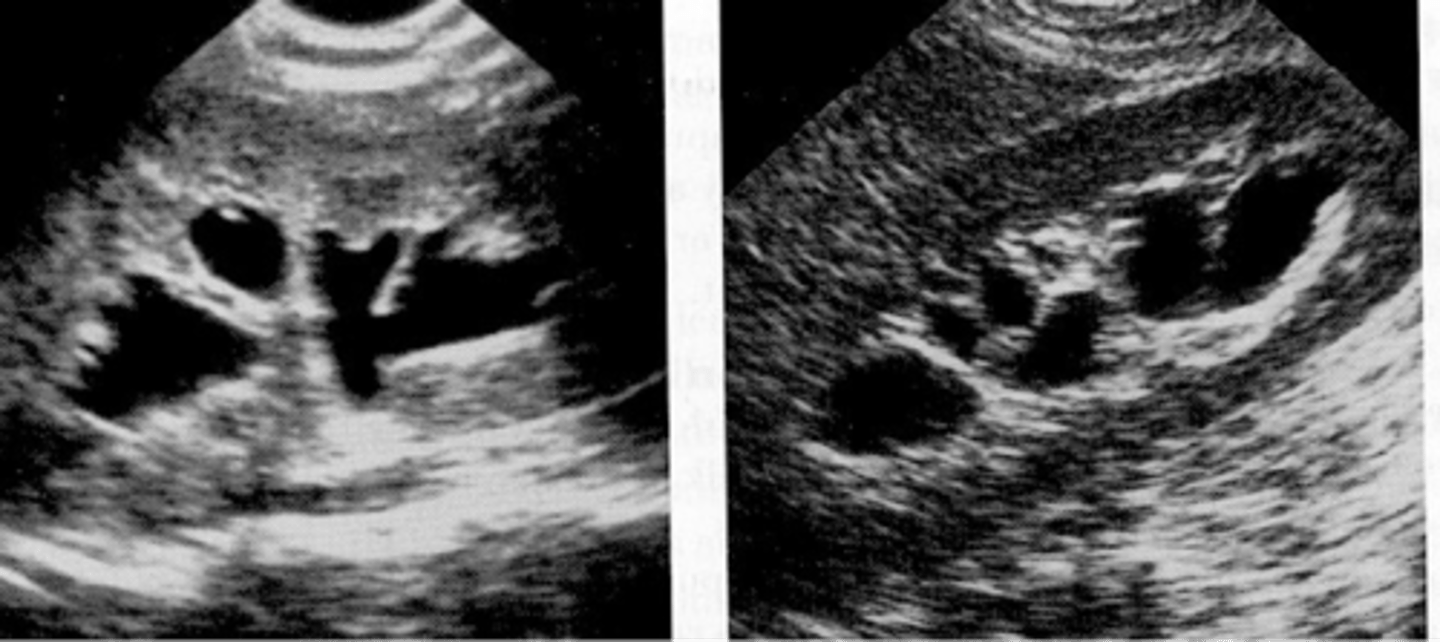
acquired cystic kidney disease (from dialysis) US
-native kidneys are small and echogenic with several small cysts
ARPKD categories
perinatal, neonatal, infantile, juvenile
ARPKD juvenile US
-large kidneys replaced by multiple small cysts
-echogenic cortex
ARPKD infantile US
large echogenic kidneys
ADPKD associated abnormalities include cysts in
-liver
-pancreas
-spleen
-thyroid
-testes
-breast
most common hereditary disorder
ADPKD
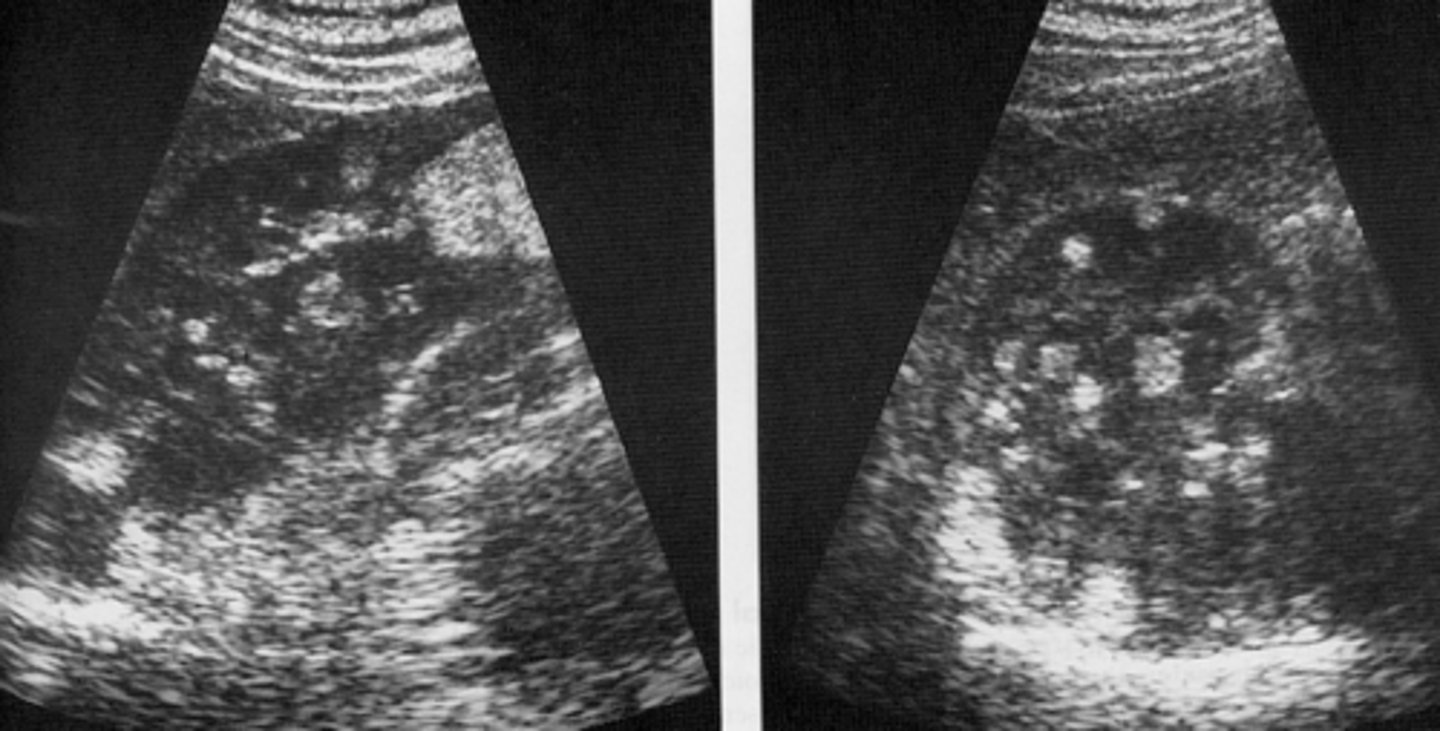
ADPKD US
-large kidneys with multiple asymmetrical cysts varying in size and location in the cortex and medulla
-sinus obliterated
most common palpable abdominal mass in neonates
multi cystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK)
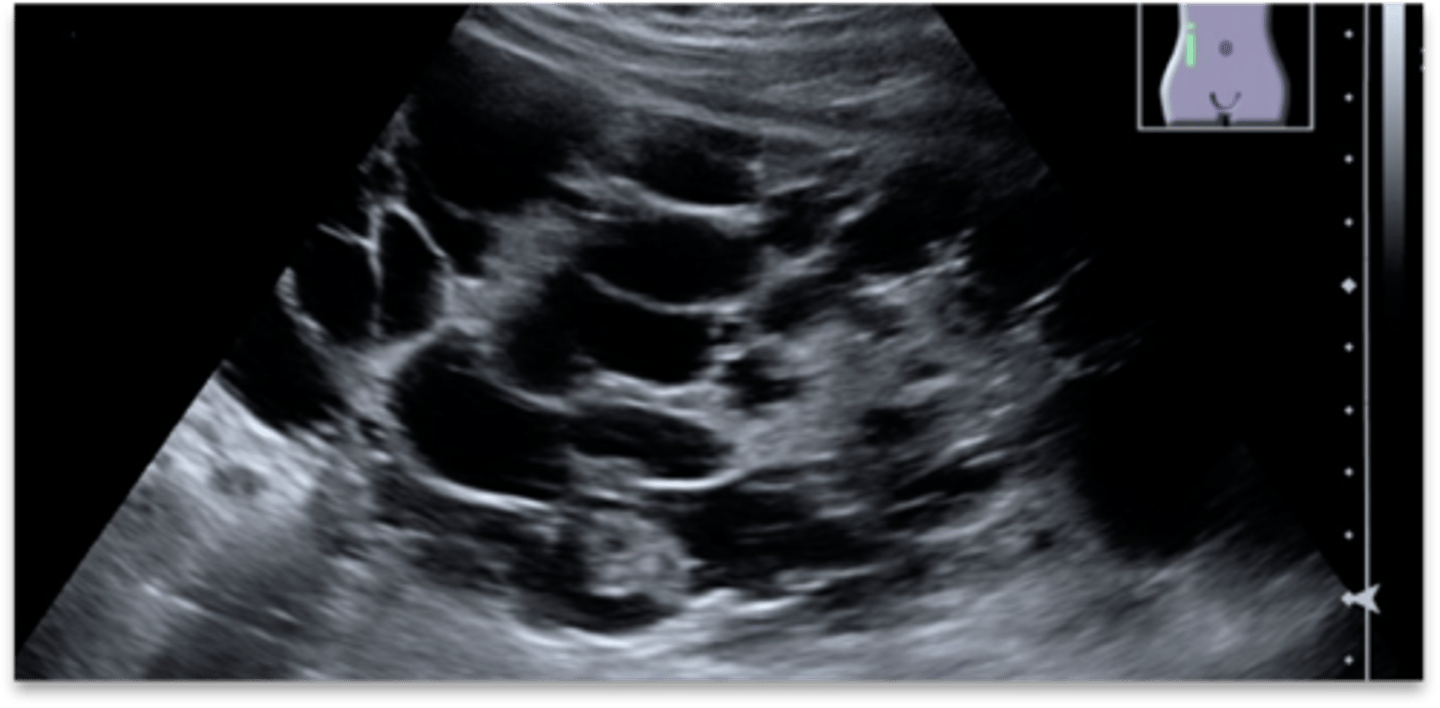
MCDK US neonates and children
-kidneys enlarged
-multicystic and non functioning
-absence of renal parenchyma, sinus, and RA
MCDK US adults
may be small and calcified
medullary sponge disease
-development anomaly that occurs in the pyramids
medullary sponge disease causes
urine stasis and stone formation
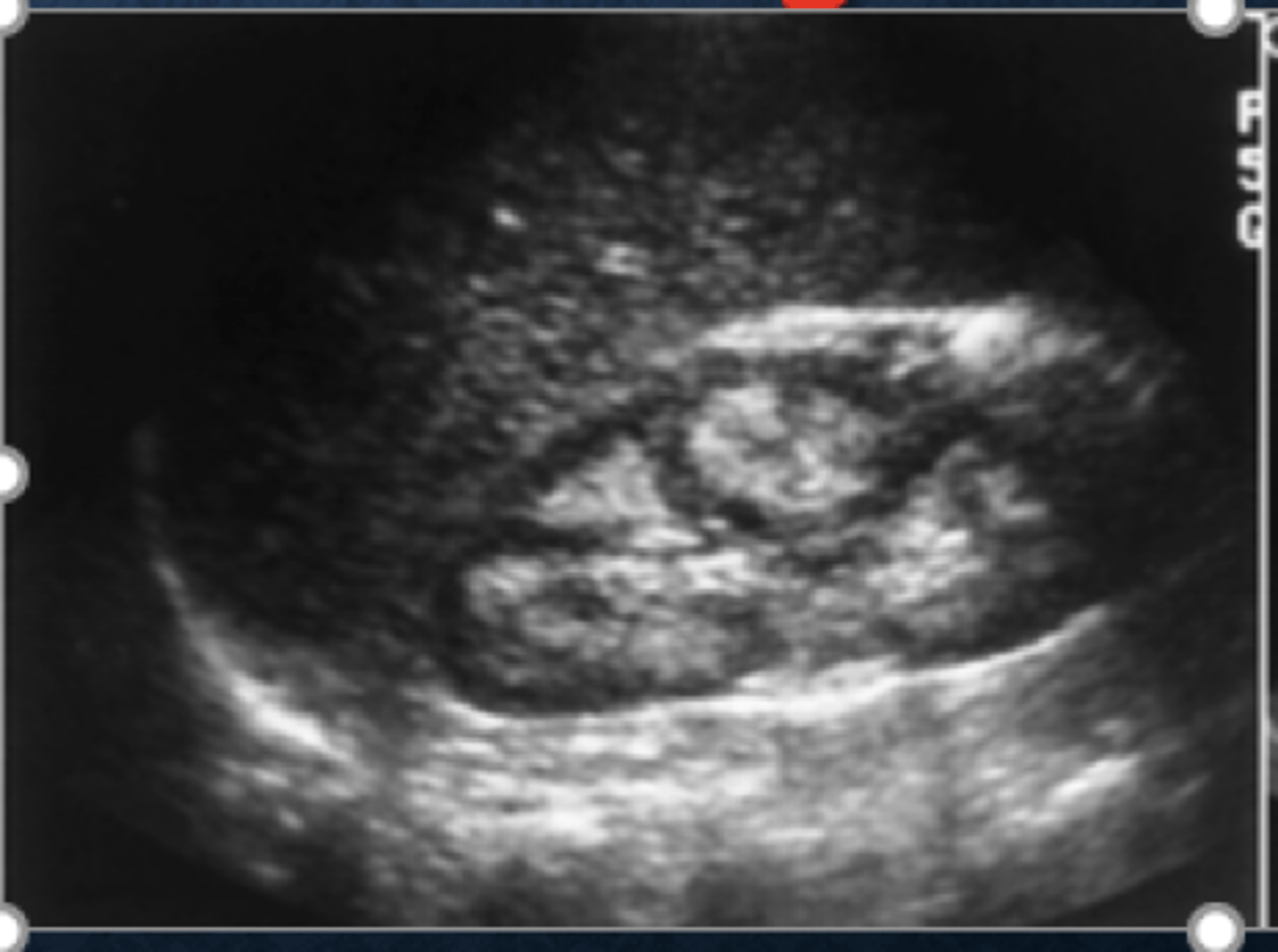
medullary sponge US
-normal or small kidneys
-echogenic parenchyma
-small cysts in medulla
-hyperechoic calyces w/wo shadowing
most common of all renal tumors
RCC
RCC has an increased incidence with
-von hippel-lindau
-dialysis
-tuberous sclerosis
other name for RCC
hypernephroma
RCC symptoms
-hematuria
-weight loss
-fatigue
-flank pain
-fever
-HTN
-palpable mass
RCC most common of all renal tumors and represents ________ % of all kidney tumors
85
RCC less than _________ cm in diameter are always ________
2-3; hyperechoic
bigger the tumor, the more _________ in echo texture
heterogenous
RCC US
-hypoechoic rim represents vascular psuedocapsule
-basket sign
where does RCC invade
invasion of the RV or IVC occurs in 5-24% of cases
where does RCC met from
lungs, mediastinum, other nodes, liver, bone, adrenal and contralateral kidney
stage 1 of Robson staging of RCC
tumor confined within kidney/capsule (67%)
stage 2 of Robson staging of RCC
tumor invasion to perinephratic fat (52%)
stage 3 of Robson staging of RCC
tumor invasion to vein, IVC, lymph nodes (33.5%)
stage 4 of Robson staging of RCC
tumor invasion of adjacent organs, distal mets
(palliative treatment only)
most common tumor of the renal collecting system
TCC
locations of TCC
pelvis, ureters, bladder
TCC US
-mass in renal pelvis w/ low level echos
-widening of central sinus
-hypoechoic mass in collecting system
TCC symptoms
-hematuria
-weight loss
-fatigue
-fever
-flank pain
can TCC cause obstruction of the collecting system
no
squamous cell carcinoma
-highly invasive
-poor prognosis
-history of chronic irritation and gross hematuria
-palpable kidney secondary to hydronephrosis
squamous cell carcinoma US
-large mass in renal pelvis
-obstruction from kidney stones may be present
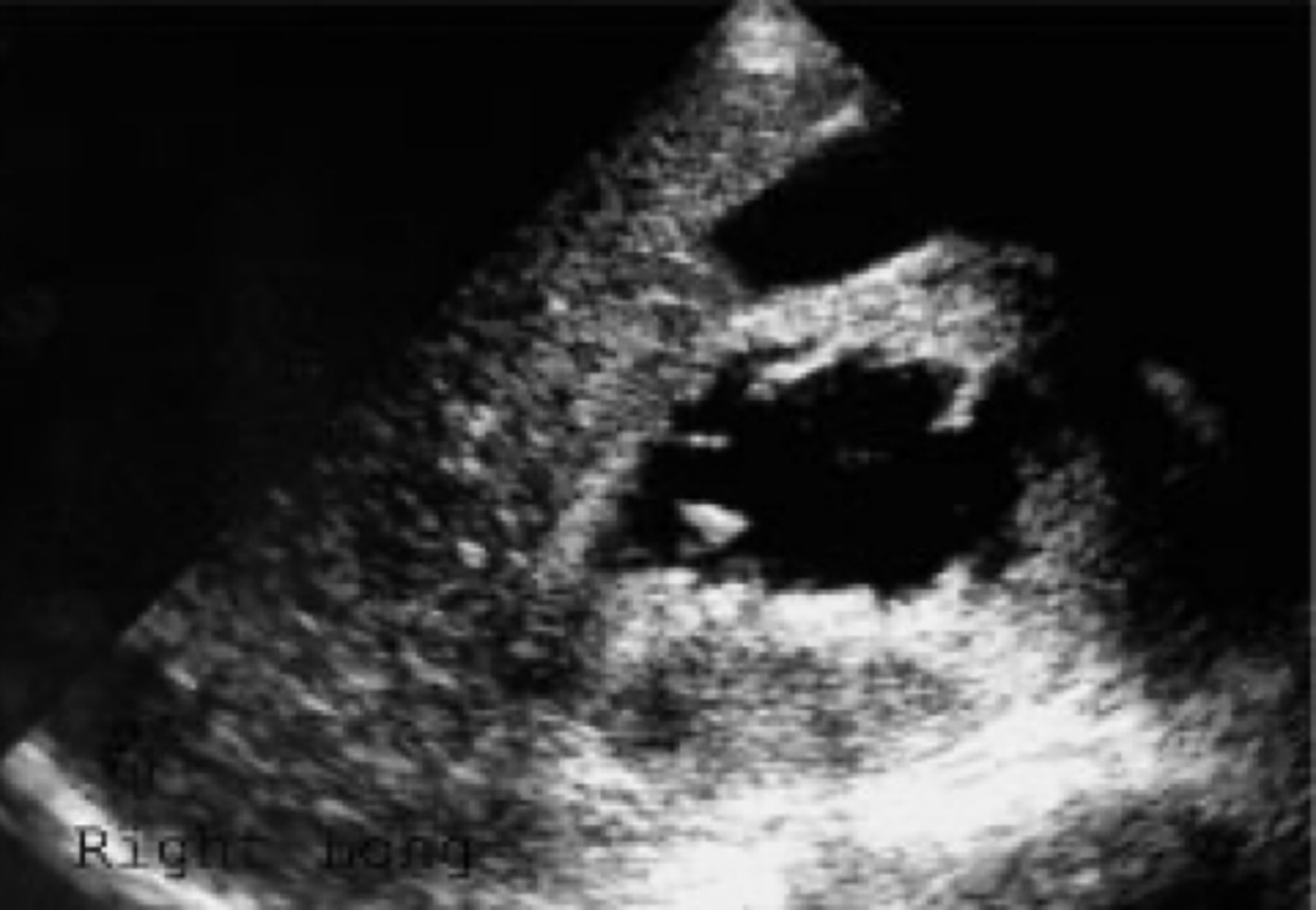
renal lymphoma
-secondary form more common
-non Hodgkins mor common than Hodgkins
renal lymphoma US
-enlarged hypoechoic kidneys
-mass may stimulate a cyst wo post enhancement
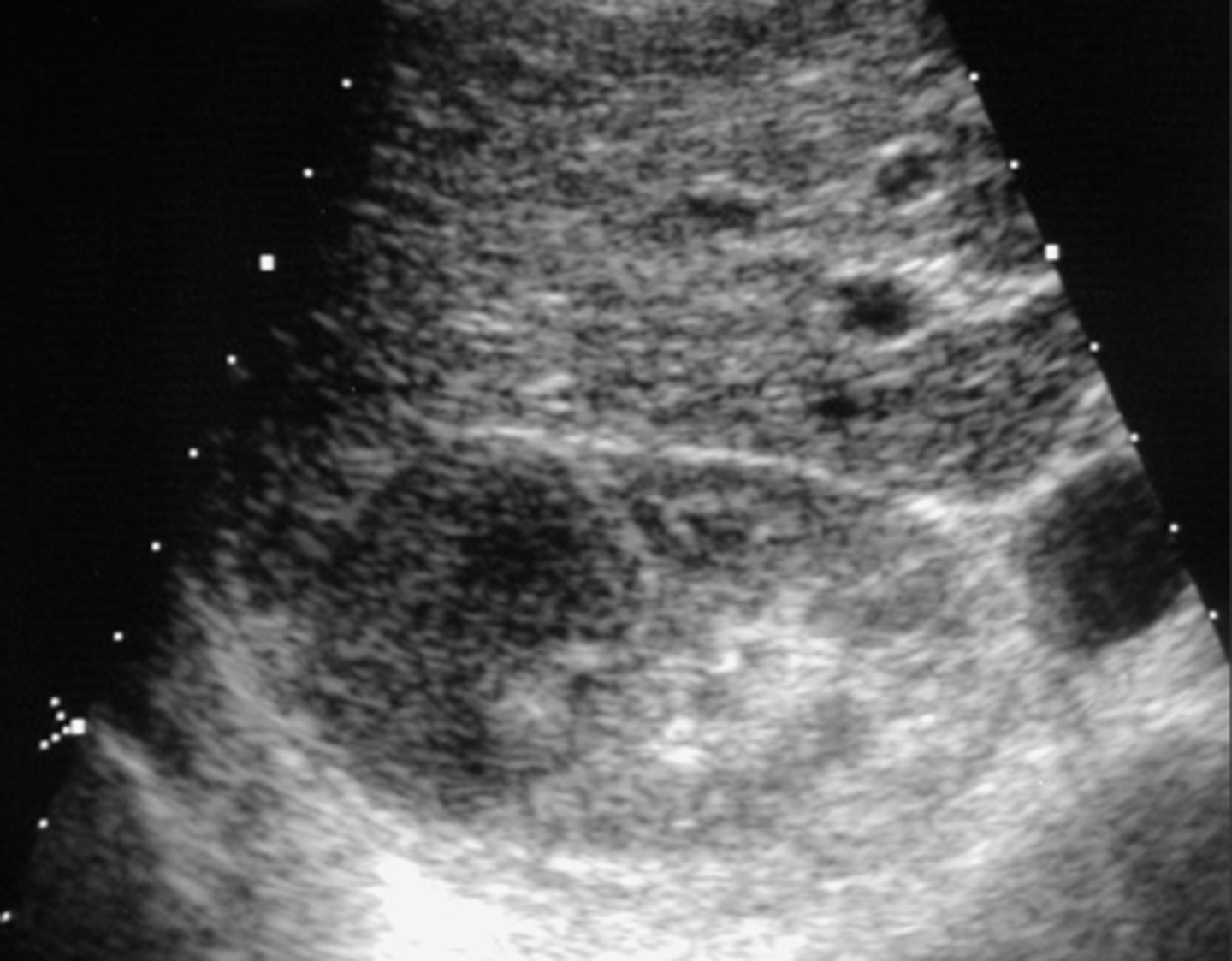
mats to kidneys occurs in _______ of disease
late course
most common primaries of mets
carcinoma of lung/breast, RCC of contralateral kidney
Mets US
-multiple poorly marginated hypoechic masses
-tumor may spread to renal capsule -> RV -> IVC -> right atrium ->lung
most common abdominal malignancy in children
wilm's tumor/nephroblastoma
most common solid renal tumor in peds 1 to 8yo
wilm's tumor/nephroblastoma
what age group most affected by nephroblastoma
-peak incidence is seen at 2.5 to 3yo
-90% are younger than 5
-70% are younger than 3
nephroblastoma US
-hypoechoic to moderately echogenic
-large bulky tumor
-may spread beyond capsule
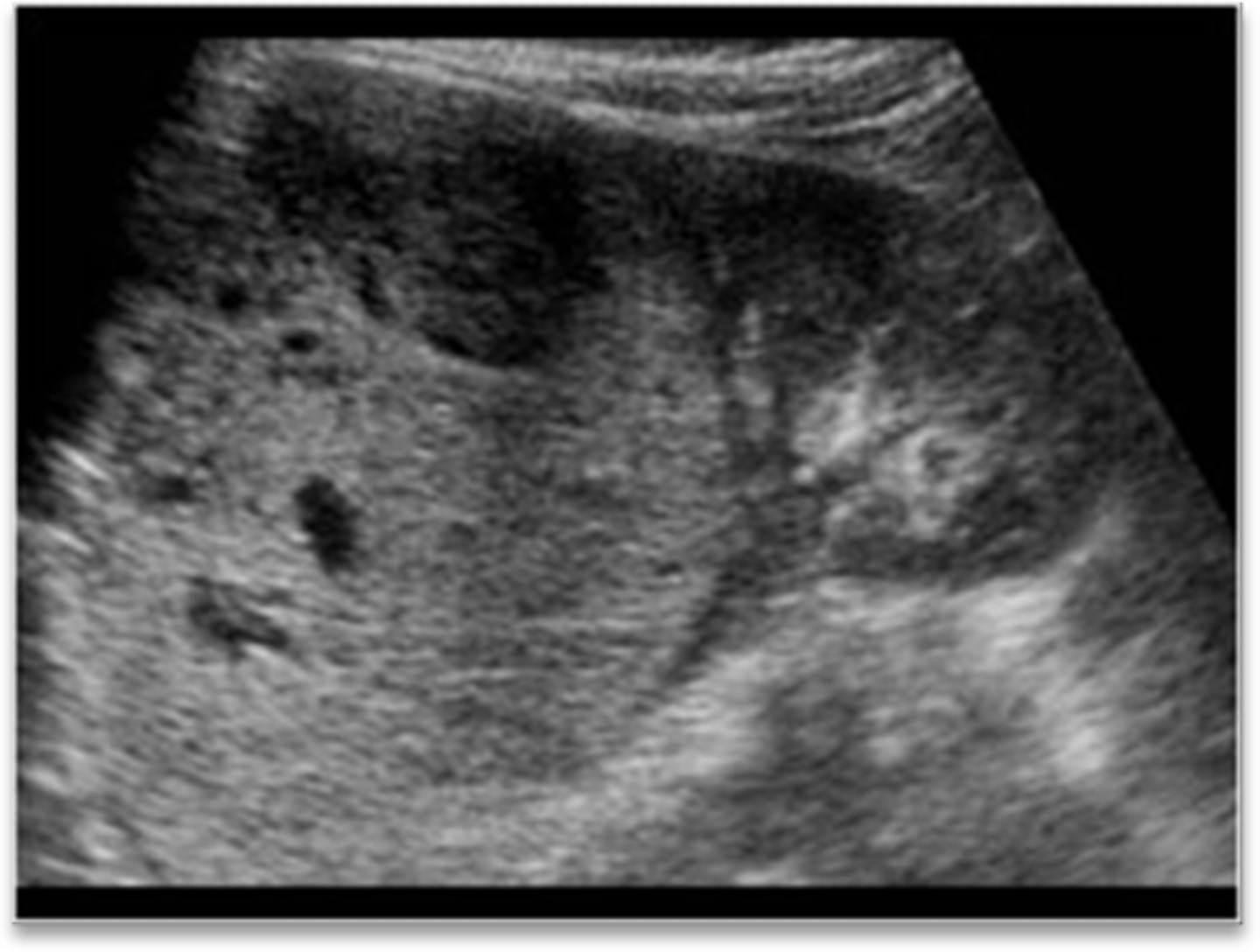
What else would you look for when you find this tumor
Eval of both kidneys for tumors, RV thrombosis, leg edema, varicocele, budd-chiari syndrome
nephroblastoma diff DX
neuroblastoma
Angiomyolipoma US
-hyperechoic
-well defined borders
-post enhancement
-usually solitary
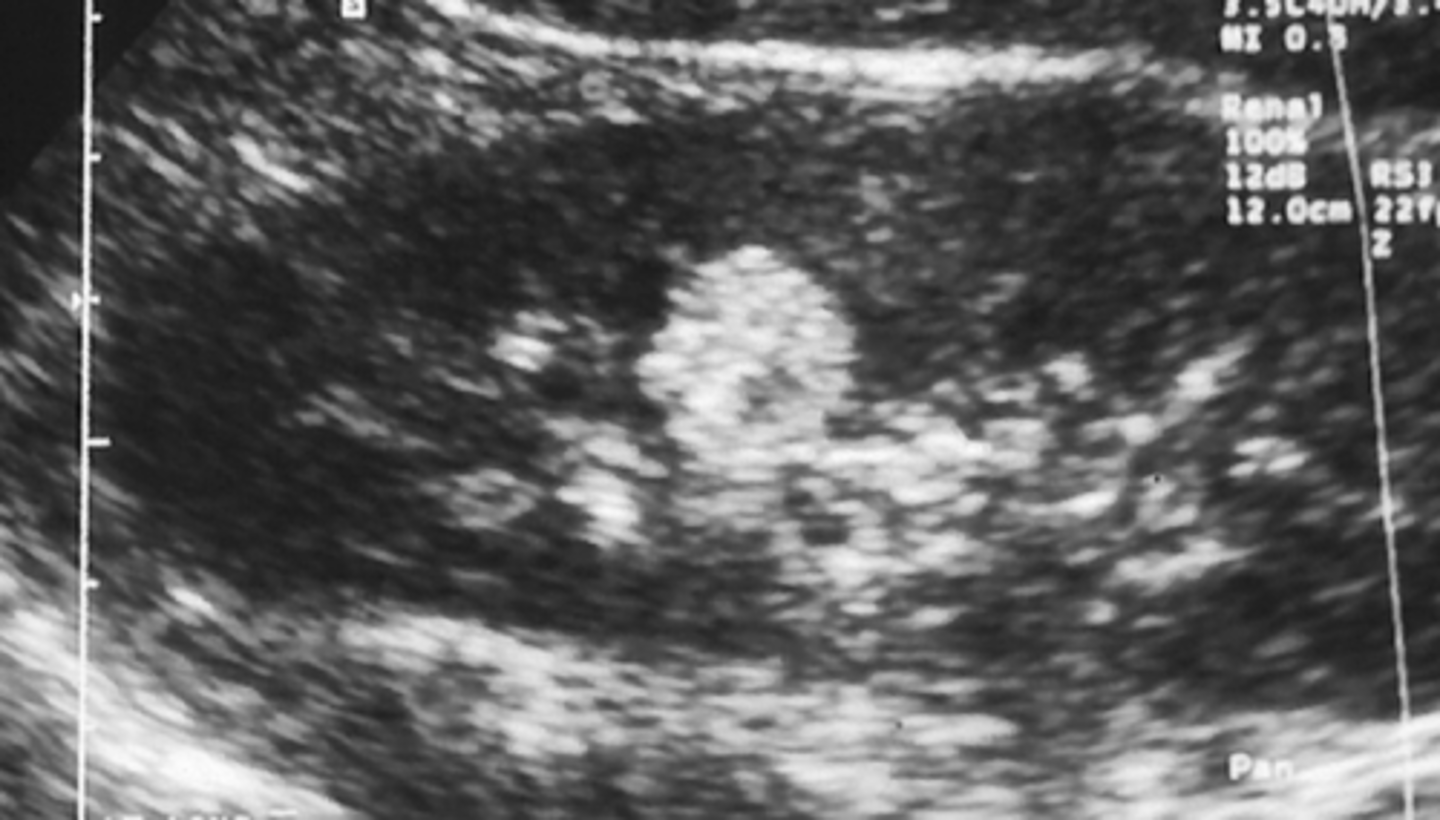
adenoma US
-well defined
-hyper to hypoechoic
-calcifications in cortex
-hypovascular
angiomyolipoma
-contains fat, muscles, vessels,
females >
most common benign renal tumor
angiomyolipoma
Oncocytoma US
-well defined mass
-hypoechoic
-homogenous
-spoke wheel pattern with scar
lipoma US
-well defined
-echogenic
group 1 classification of renal disease
generalized increase in cortical echos results from deposition of collagen and fibrous tissue
group 2 classifications of renal disease
loss of anatomic detail cortex and medullary regions indistinguishable
acute glomerulonephritis US
-increased cortical echoes
-result from changes in the glomeruli, interstitium, tubules, vessels
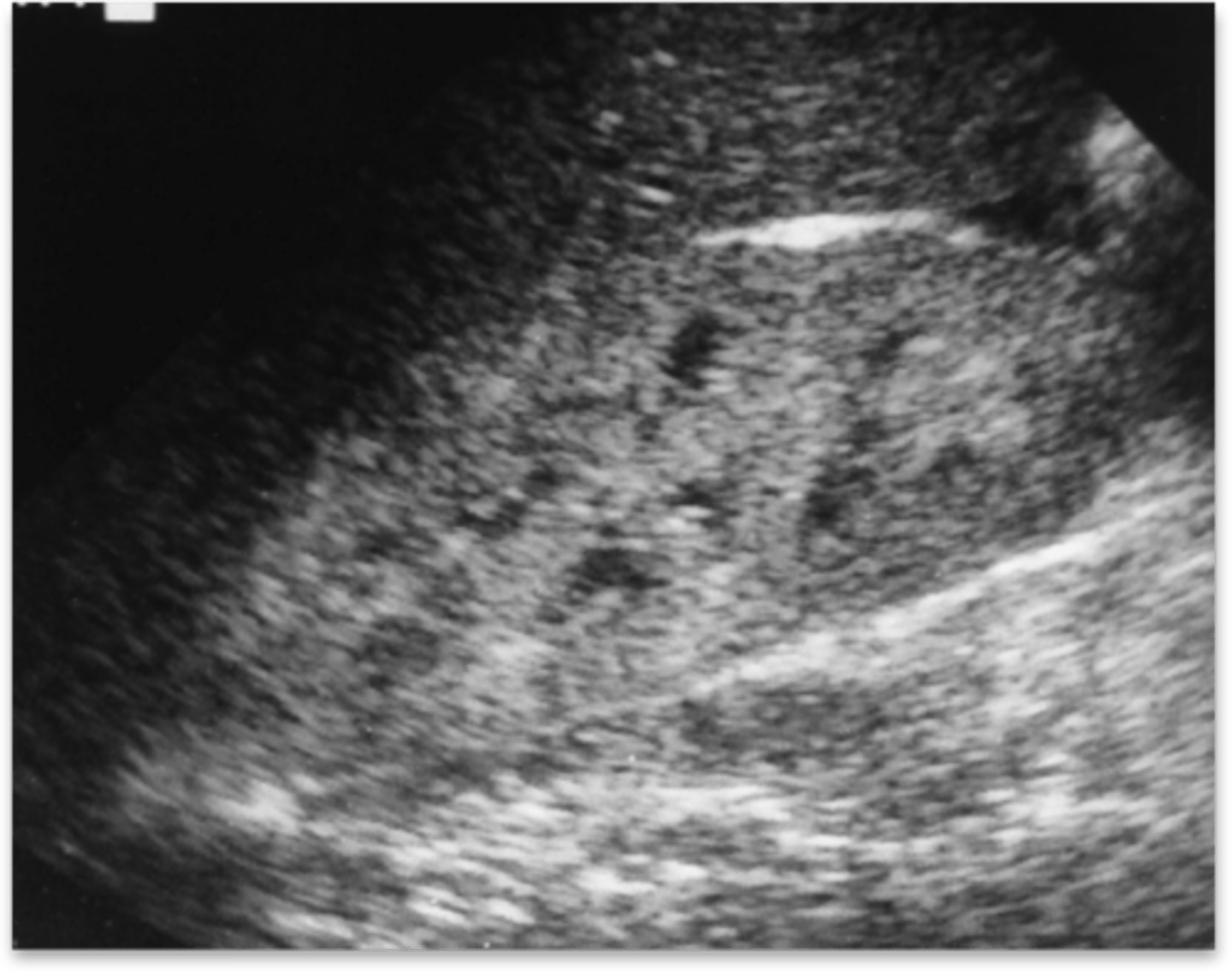
acute interstitial nephritis US
-enlarged and mottled kidneys
-increased cortical echogenicity
lupus nephritis US
-increased cortical echogenicity
-renal atrophy
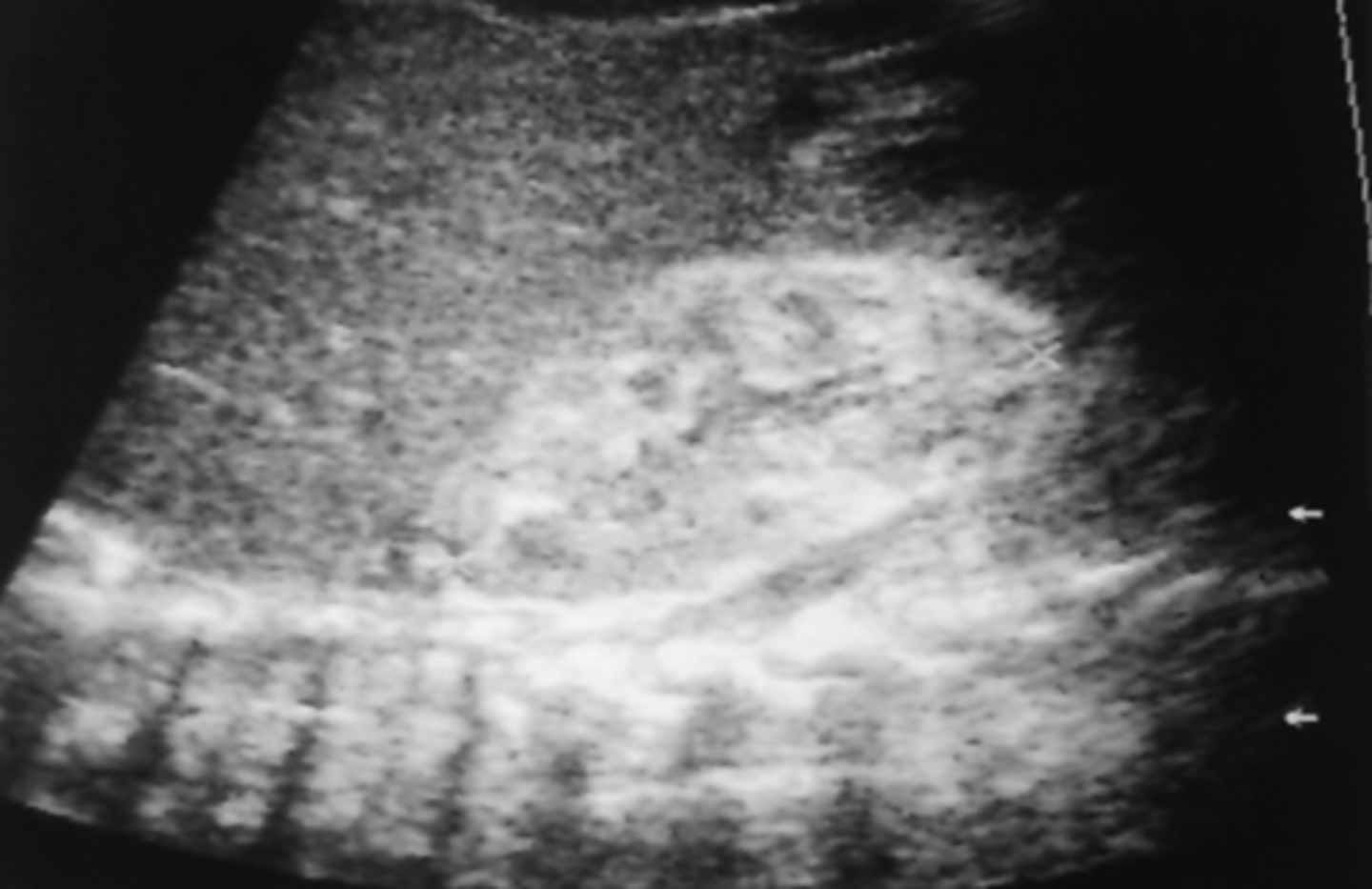
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) US
-kidneys normal to large
-echogenic parenchyma
-increased cortical echogenicity
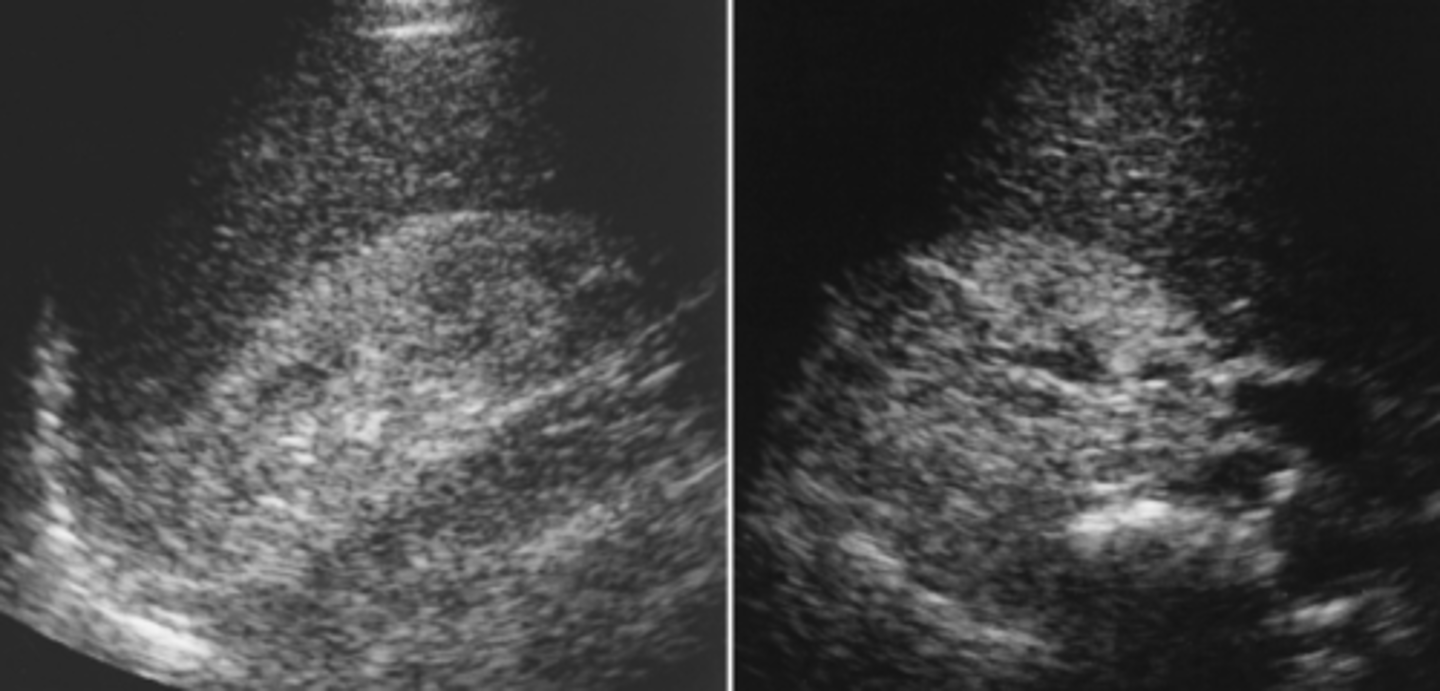
diagnosis is specific in sickle cell nephropathy if _________ is seen
thrombosis
acute sickle cell nephropaty
- 0-4 days
-renal vein thrombosis = enlarged kidneys and decreased echo
subacute sickle cell nephropathy
- 4-14 days
-thrombosis = enlarged kidneys and increased cortical echo
hypertensive nephropathy US
-small kidneys with smooth borders
-scarring
-lobar infarction
papillary necrosis US
-fluid spaces at coritical medullary junction corresponding to pyramid distribution
-round or triangular shaped
-mimic calculi
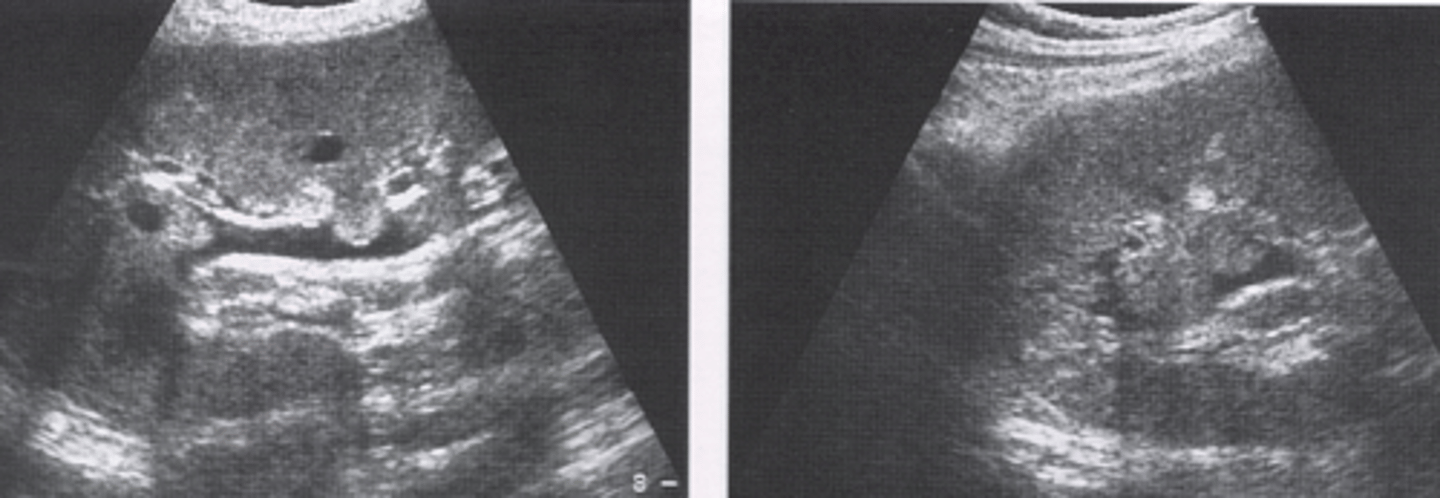
renal atrophy US
-smaller kidneys
-highly echogenic enlarged renal sinus
-thin cortical rim (<5mm) is abnormal
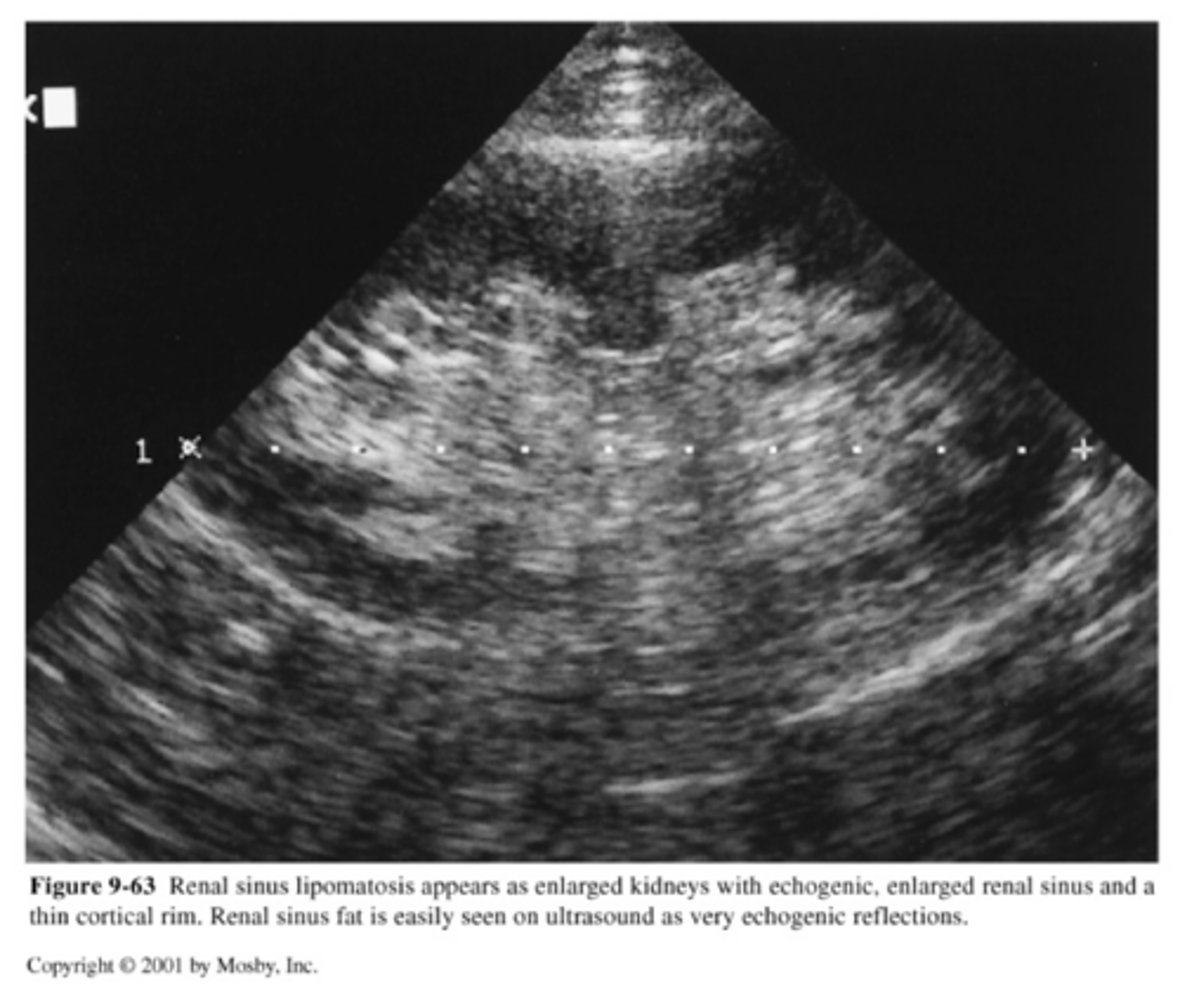
renal failure 3 categories
-prerenal- decreased perfusion
-renal- intrinsic renal disease
-postrenal- obstructive process (reversible)
prerenal failure causes
-hypoperfusion
-hypotension
-CHF
renal failure causes
-infection
-nephrotoxicity
-RA occlusion
-renal mass or cyst
postrenal failure causes
-lower urinary tact obstruction
(ureter, bladder, retroperitoneal fibrosis)
Most common medical renal disease to produce acute renal failure.
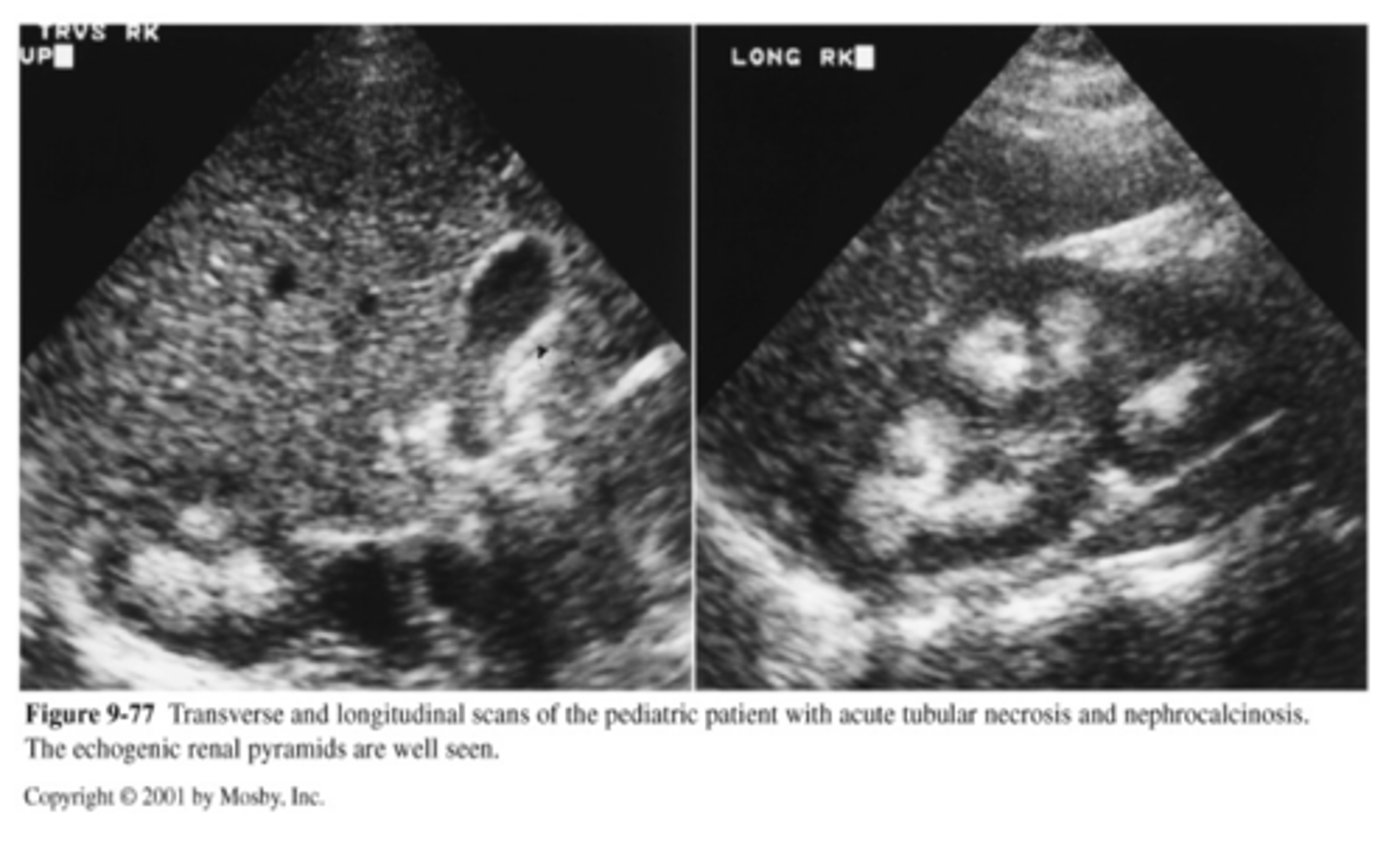
acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
acute tubular necrosis US
-enlarged kidneys
-hyperechoic pyramids
-can be reversed with medical treatment
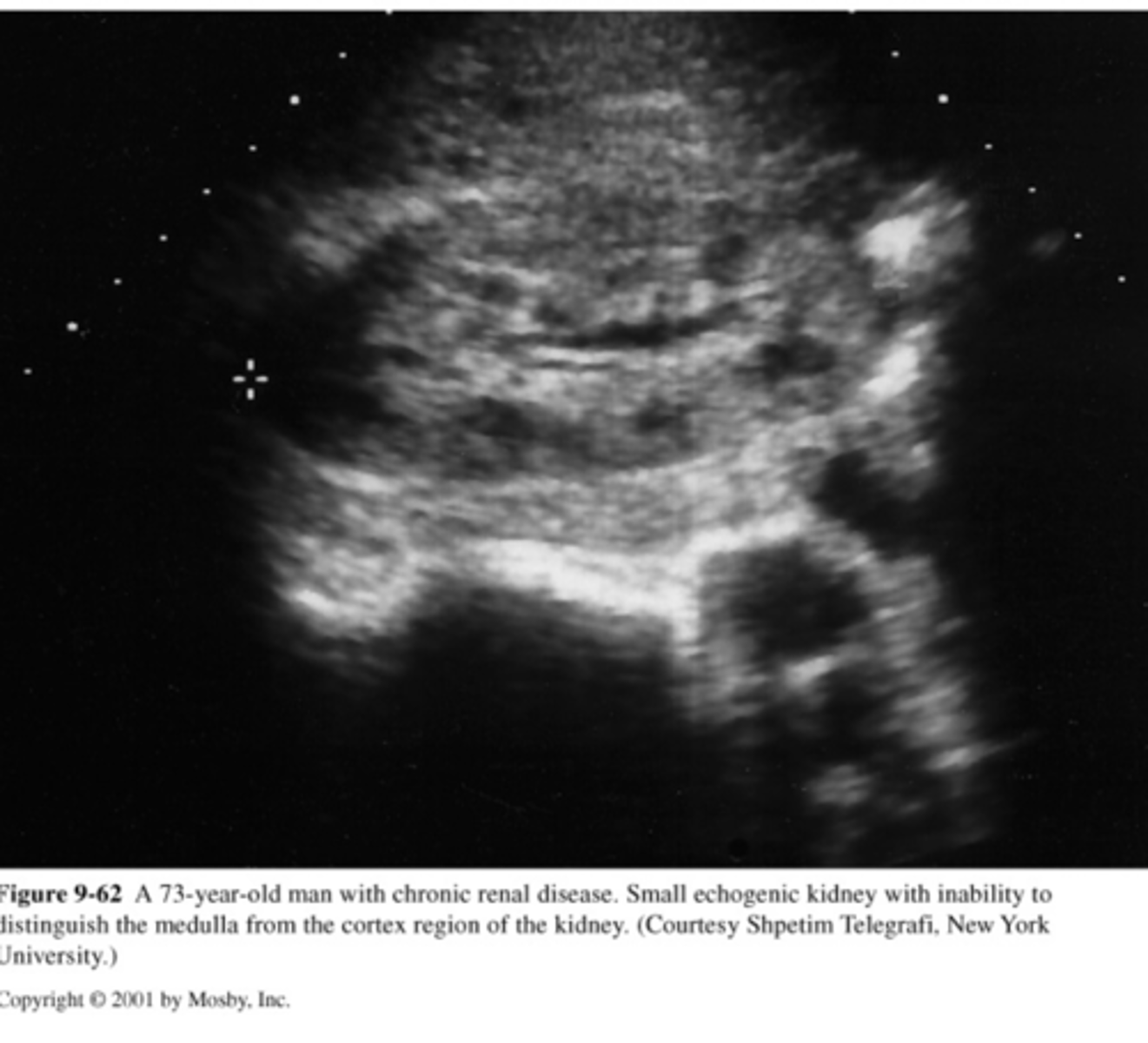
chronic renal disease
-loss of renal function because of disease (most likely parenchymal)
-3 types: nephron, vascular, interstitial
chronic renal disease US
-diffusely echogenic kidney
-loss of normal anatomy
-small
-may be bilateral
what individuals are more predisposed to chronic renal failure
patients with diabetes, HTN, and related nephropathies
hydronephrosis grade 1
Small, fluid-filled separation of the renal pelvis "splaying"
hydronephrosis grade 2
extension into some but not all major and minor calyces "bear claw"
hydronephrosis grade 3
Complete pelvocaliectasis; echogenic line separating collecting system from renal parenchyma
hydronephrosis grade 4
massive dilation of collecting system; loss of renal parenchyma
obstructive hydronephrosis US
-fluid filled collecting system
-thin parenchyma
-hydroureter
-decreased or absent ureteral jet
obstructive hydronephrosis RI values
-increased for 48-72 hours
- > .7 then returns to normal
-compare with contralateral side
other name for transient hydronephrosis
pseudohydronephrosis
transient hydronephrosis from
over distended urinary bladder
false positive hydronephrosis
-extra renal pelvis
-parapelvic cyst
-reflux
-multicystic kidney
-central renal cyst
false negative for hydronephrosis (3)
-dilated renal pelvis
-polycystic kidney disease
-transient obstructive process
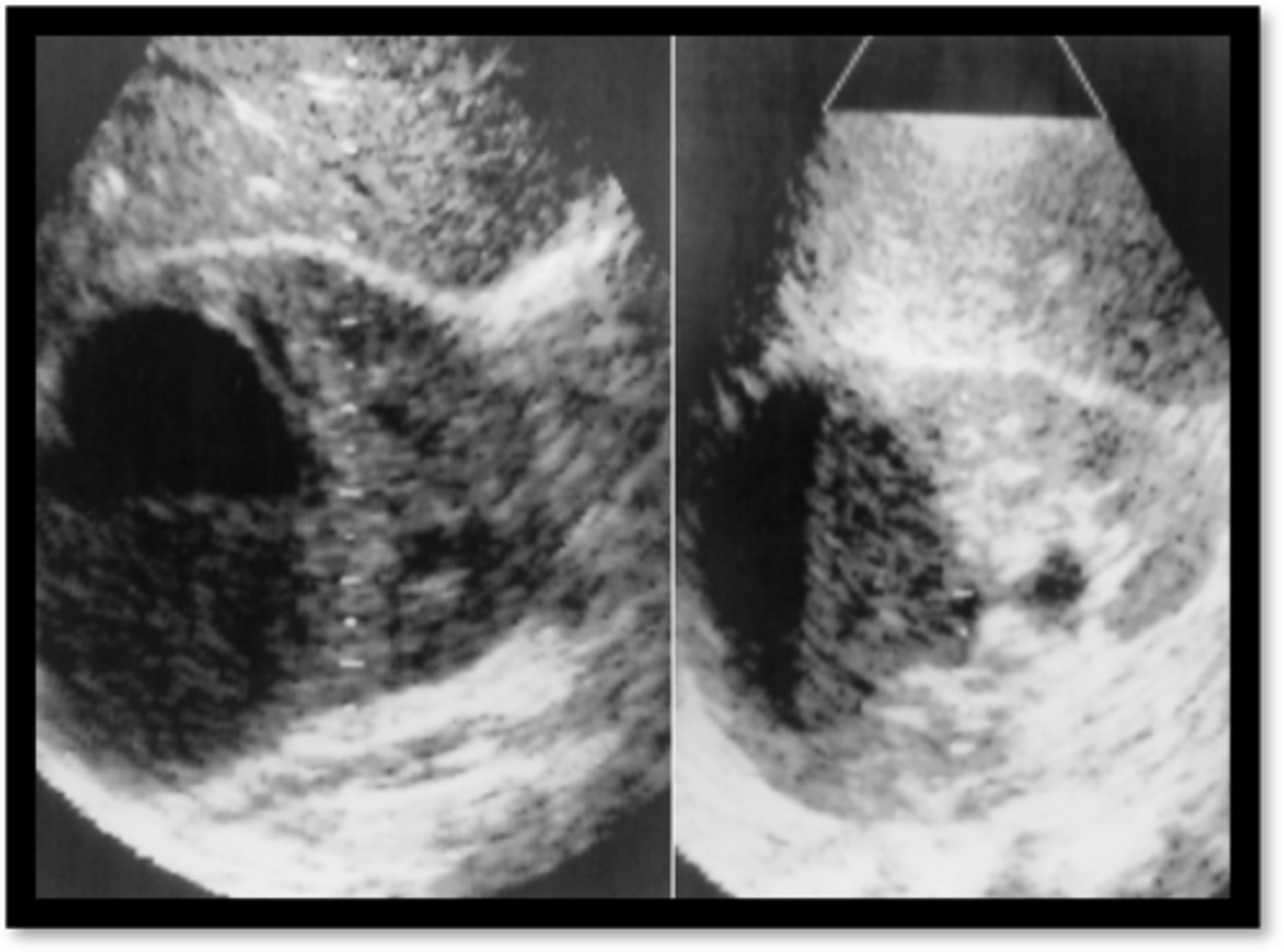
pyonephrosis
-pus in collecting system
-urologic emergency
-percutaneous drainage required
pyonephrosis US
-low level echos
-fluid=debris level
-anechoic dilation may occur
acute pyelonephritis
-Bacterial infection in the Kidney or Renal Pelvis
-(UTI): E. coli,
-females >
Emphysematous pyelonephritis
gas in parenchyma
-e-coli