Chapter 3 - Neurones
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
typical neurone transmission pathway - transmits electrical and chemical signals
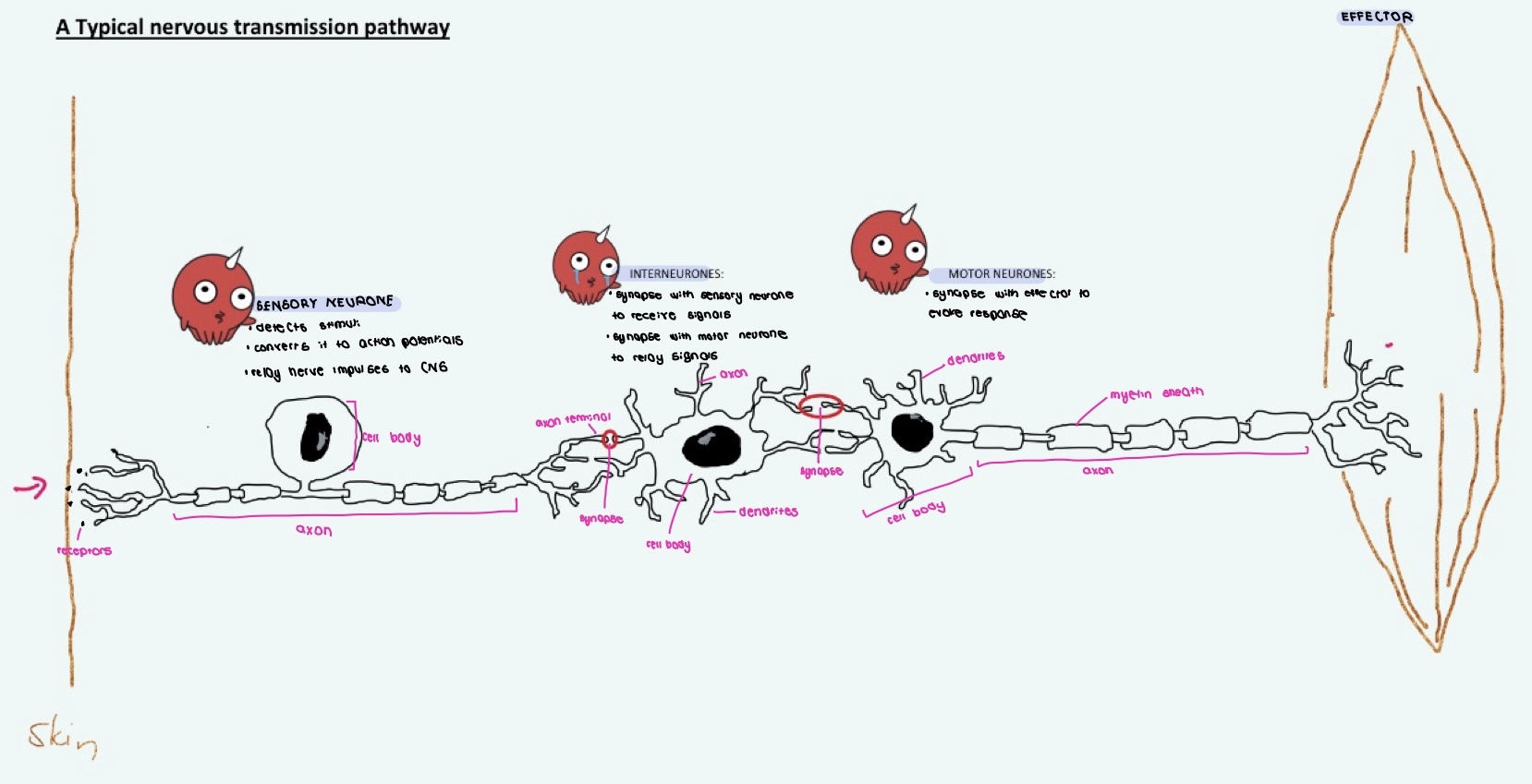
synapse
junction between the axon terminal of one neurone with dendrite of another adjacent neurone
dendrites VS axon
dendrites carry nerve impulses TOWARDS cell body
axons carry nerve impulses AWAY from cell body
types of neurone - multipolar
one axon and multiple dendrites extending from cell body
structure for most motor and interneurones
type of neurone - bipolar
one axon and one dendrite extending from cell body
structure occurs in eye, ear and nose

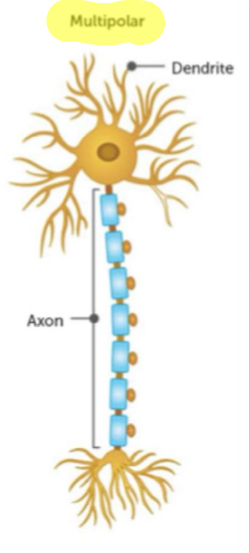
type or neurone - unipolar
one extension from cell body which is the axon
structure typically found in invertebrates
type of neurone - pseudounipolar
one axon extending from cell body
most sensory neurones are this type

generation of action potential
1) resting potential
2) depolarisation
3) repolarisation
4) hyperpolarisation
5) recovery
resting potential
membrane potential maintained at -70mV
sodium potassium pump pumps 3 sodium ions out axon while somultaneously pumping 2 potassium ions into axon, by active transport
both voltage gated sodium and potassium ion channels CLOSED
depolarisation
when stimulus strong enougn, membrane potential reach threshold value of 55mV, and initiate action potential
voltage gated sodium ion channels open, sodium ions diffuse into axon down conc gradient
membrane potential become more positive
repolarisation
when membrane potential reach 30mV, membrane repolarise
voltage gated sodium ion channels close
voltage gated potassium ion channels open, potassium ions diffuse out of axon into extracellular fluid, down conc gradient
membrane potential become more negative
hyperpolarisation
voltage gated potassium ion channel close
membrane potential more negative than resting potential
recovery
sodium potassium pump pumps 3 sodium ions out of axon, while simultaneously pumping 2 potassium ions into axon, by active transport
voltage gated sodium and potassium channels CLOSED
how is resting potential maintained?
sodium potassium pump
cell membrane HIGHYL permeable to K+ and Cl- ions, SLIGHTLY permeable to Na+ and IMPERMEABLE to large negatively charged organic ions
what type of response are action potentials
ALL OR NOTHING
size of nerve impulse is always same, regardless of stimulus
BUT stronger stimulus stimulate greater freq of nerve impulse THUS MORE RECEPTORS ACTIVATED
why nerve cell membrance ONLY relay signals in ONE direction
when action potential is generated, section of membrane behind the action potential is in its refractory period, thus membrane potential not at -70mv(resting potential)
transmission of impulses along MYELINATED axon - saltatory conduction
cause action potentials to jump from one node of ranvier to another
local current flow distance is longer
trnamsission of impulses along UNMYELINATED axon - continuous propagation
depolarization of one area on membrance causes a local current flow between neighbouring areas on the membrane immediately adjacent to the site of the original stimulus
each action potential generates another action potential just infront of it
local current flow distance is shorter
role or myelin sheath
fatty layer wrapping around axon to insulate the axon to speed up nerve impulse transmission
WHY local current flow distance longer but nerve impulse transmission faster?
allows electrical signals to jump farther along axon before needing to regenerate at another ion channel
synaptic transmission
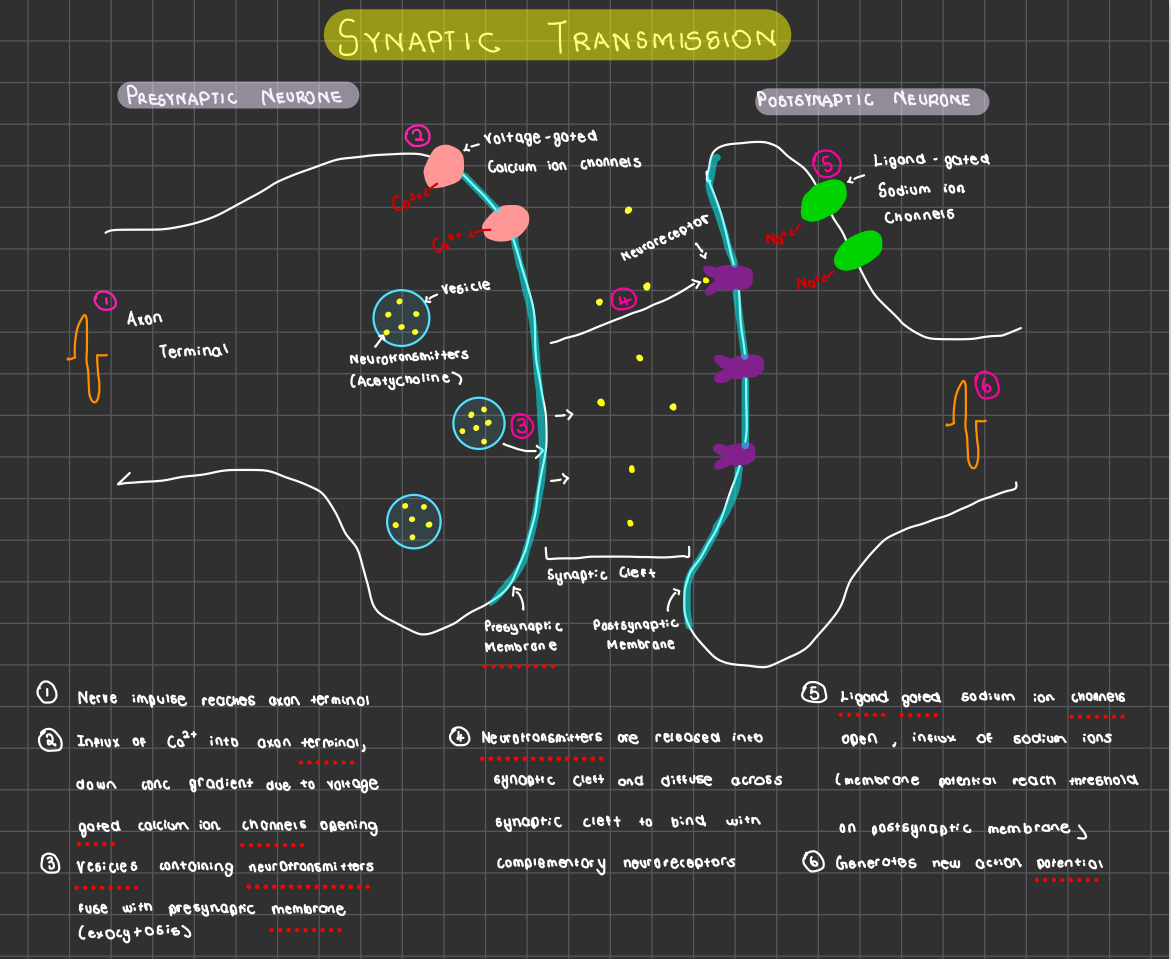
receptor
detects stimuli
similar receptor cells are grouped together in a sense organ
provides SOMATIC and SPECIAL sensation
somatic sensation - originate from receptors found in more than 1 location in body, EG: touch, pain
special sensation - originate from receptors restricted to a particular area of the body. EG: sight, taste
reflexes
rapid, automatic response to a change in the external or internal environment
mostly coordinated by spinal cord
4 properties of reflexes
1) stimulus is required, not spontaneous
2) reflex is involuntary, occur without consious thought
3) response is rapid, only small number of neurones involved
4) response is stereotyped, occurs in same way every time
purpose of reflexes
rapid and involuntary to prevent further or long term injury to body
innate vs acquired reflexes
innate: present from birth, determined genetically
acquired reflexes: learnt through constant repetition