Test 1 for C.S. Lewis
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
When was C.S. Lewis Born and when did he die?
Born November 29, 1898
Died November 22, 1963, the same day as JFKs assassination
What does C.S. stand for and why does he rename himself
Clive Staples
He renamed himself Jacksie or jack because he didn’t like his name and due to the death of his family dog named jackie
Where did he grow up? Name city, country
Belfast, Ireland - the emerald isle - Europe
The influence of his family upon his upbringing
being born into a bookish family
after his mother’s death his father didn’t comport him, so he had to engage with books
His relationship with Warren was really close and they co-created imaginary worlds like boxen and supported each other when their mother died
What is Joy? Define and give examples from the life of Lewis
a profound and complex experience that is not merely pleasure
often accompanied by a sense of longing for that is out of reach
when we are not fixated on ourselves but are fully present in the moment
he felt the sense of joy when he was flowing a currant bush in full bloom
his journey from atheism to Christianity
being able to study the subjects he loved without the fear of torment
The effect of his mother’s death on his life; on his faith
When the happy days in the new house ended
he prayed for God to perform a miracle to heal her, but she died
after she died, he then prayed for her to come back to life
when he wrote the magicians nephew it took him years to finish, and he made Digory’s mom heal and be better
His faith took a big hit and he began doubting his belief in god
School life: early years at boarding school with Oldie
Oldie was a cruel man that treated students horribly by beating them with his cane
Groups of boys would walk around his rough up smaller boys
rarely Lewis
What is “Belsen”?
a term C.S. Lewis uses to describe how terrible his experience with oldies school was
Comparing his time at that school to the Belsen concentration camp
What is “fagging”?
when younger students act like servants to older boys and was forced to trivial or menial jobs
was also associated with the older boys sexually assaulting the younger boys
The Great Knock (Kirk/Kirkpatrick)
nickname for Kirkpatrick when he was C.S. Lewis tutors
teaching him how to think critically and express himself logically
the great knock symbolized his significant impact on Lewis’s intellectual development
represented by the professor in the lion, the witch, and the wardrobe
WWI; Paddy Moore; Jane Moore
meets Paddy in Oxford
Paddy was killed in WW1 and Lewis takes care on his mom and sister for the rest of his life
what was his first real job at Magdalen college, Oxford where he remained most of his career.
in 1924 he takes a low paying job as a philosophy major tutor
Then in 1925 he is elected as a fellow of magdalen
he tutors and does lectures
what is myths appeal to Lewis
(Balder the beautiful, is dead, is dead) to his shared love of mythology with Arthur Greeves
the ability to convey universal truths and enchantment
Looking at/along the beam for Enjoyment
Internal:
Observer participates inside the phenomenon, participating in it
Experience along a Beam:
moving into the sunbeam, one sees the tree outside, the leaves, the sky,
experience the world through the beam
Meditation in a Toolshed
Explores the distinction between experimental knowledge and observational knowledge
Lewis personal experience in a dark toolshed where a beam of sunlight enters a crack in the door.
serves as a metaphor of two different ways of perceiving reality
looking at something
looking along something
Joy Davidman Gresham Lewis: her background, courtship with Lewis, death
previously married with two children
worked with C.S. Lewis as a secretary at Cambridge
had a civil marriage with C.S. Lewis due to her dying of cancer and Lewis wanting to take care of her kids
She miraculously recovers from her cancer, and they go on trips until going to Greece and dying shortly after returning
What is allegory?
The use of symbols in a story, picture, etc., to convey a hidden or ulterior meaning, typically a moral or political one; symbolic representation.
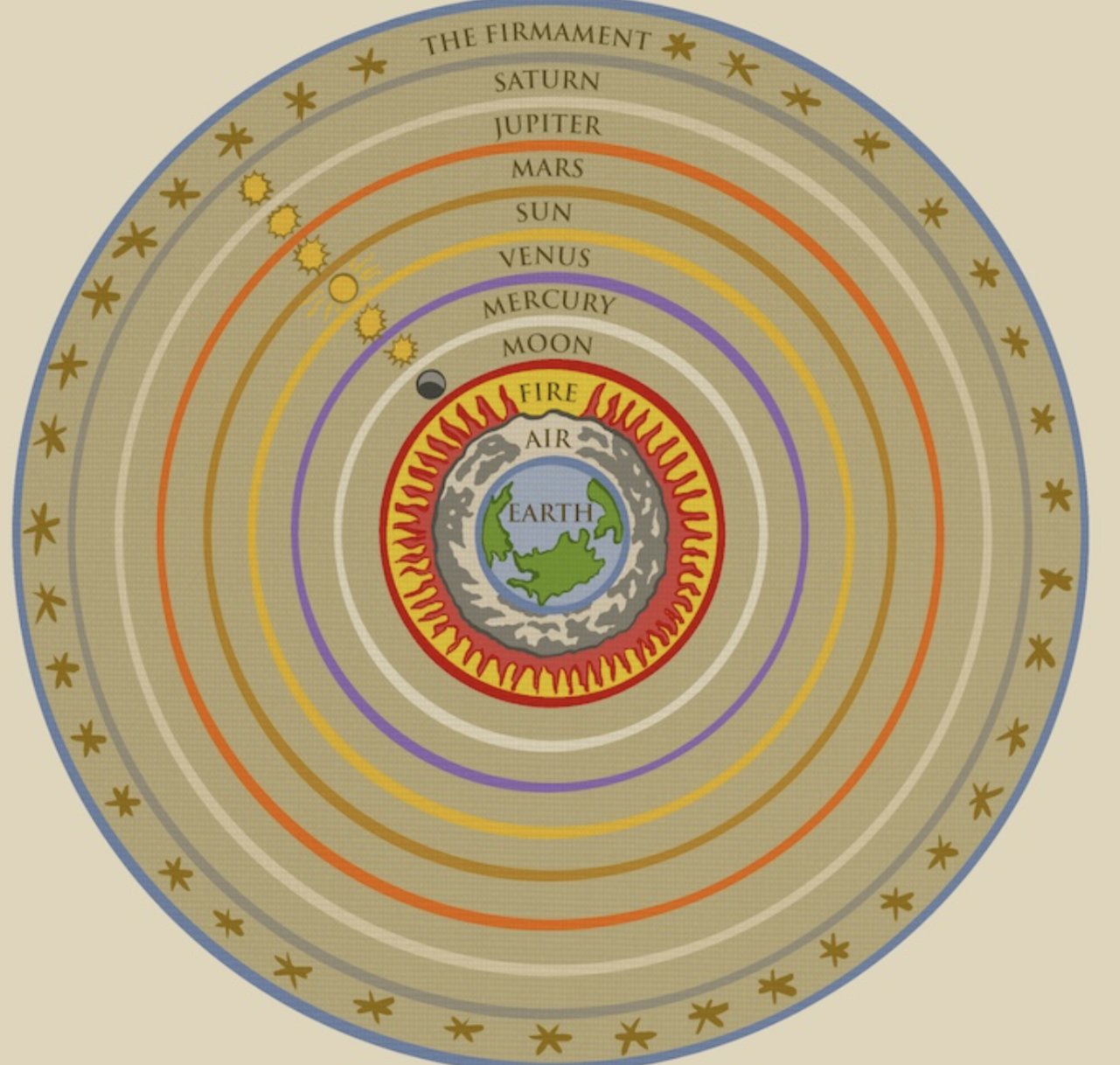
Ptolemaic cosmology
The belief that the earth is stationary and is at the center of the universe
all rest of the planets revolve around the earth
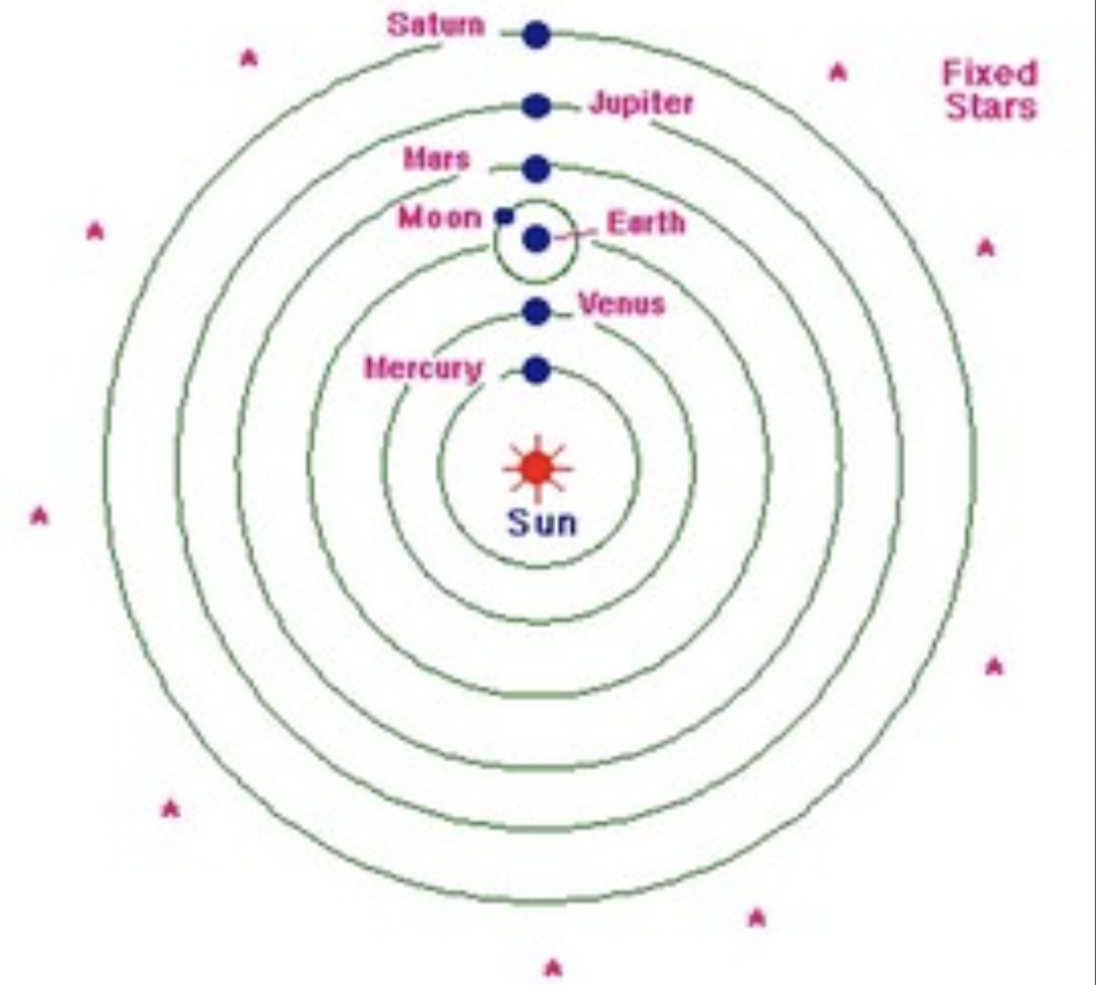
Copernican cosmology
a model that the sun is stationary and the earth and the other planets orbit around it
it was radical and challenged the long-held belief that the Ptolemaic cosmology system had on science and religion
significance of influence
Literary and Narrative Influence
Integration of myth and folklore: Greek, Norse, Roman, Christianity
Influence of prior authors
Story telling as a transformative medium
Philosophical and Theological Influence
Christian allegory
moral and ethical framework
Universal themes beyond religion
significance of tingle
deeply rooted in themes of faith, redemption, and the power of love
the voice of Alsan bringing life into Narnia making the blood of the children bodies tingle
a metaphor of awakening faith and the recognition of the divine
significance of disaster
its role as a catalyst for transformation and revelation for these characters to deepen their understanding of faith and actions
Highlights the consequences of the choices these characters make and the importance of loyalty
example: the final battle because of its themes of loyalty, and resolution as Narnia comes to an end
the meanings of “liberal in Narnia
Theological/Literary
being generous or open-hearted, highlighting grace and moral inclusivity.
Narnia’s moral universe rewards courage, faith, and repentance rather than social status or rigid orthodoxy
Moral and Ethical
self-determined action and moral choice
individual conscience and personal virtue matter
Political/Cultural
utopia within a political sense, where hierarchical or authoritarian structures (like the White Witch’s tyranny) are challenged by inclusive coalitions of humans and magical beings.
Intellectual/Interpretative
allowing multiple simultaneous readings
Christian allegory (Aslan as Christ, Edmund as repentance)
Astrological/cosmological symbolism (Seven Heavens theory)
Boethius and his wheel
The wheel of fortune is an allegorical device that represents the ever-changing nature of fate
fortune is inherently just or unjust, a tool in a larger divine order
Represented in the voyage of the dawn treader with Reepicheep talking to dragon Eustace about the wheel of fortune
Reepicheep reminds Eustance that kings, knights have fallen from prosperity and those who have recovered and lived happily
Feuerbach and his theories of religion
The belief that religion is a human-made and is redundant since it does not reflect the true relationship between thought and being
True religion is the relationship between oneself or his true nature
god is manifested inward nature of man
Docetism
The Greek word to seem
Christians that said that Jesus only seems to have a human body
Relates to the boy and his horse when Aslan is doubted to be a real lion
apophatic theology
Prayer without words is best
Not trying to put god into words
theosis
It is the process of a worshiper becoming united with God, beginning in this life and culminating in bodily resurrection.
Connected with east orthodoxy
Theo = God
rightly ordered love
Represents a hierarchical and morally organized Ordering of affections where the proper direction and intensity of love determine virtue and moral flourishing
Primary orientation toward God
Love for neighbor and self
integration with virtue and moral life
connection to moral knowledge and will
Are the Chronicles allegory? Why or why not?
The Chronicles are not an allegory!!
C.S. Lewis was very adamant that his stories were not allegories
the importance of books in his life
His childhood home was filled with books
His parents greatly pushed a love of books in him
exposure to classical and mythological literature that instilled his passion for imaginative exploration
his academic pursuits in Oxford that improved his critical thinking and philosophical ideas
the significance of consider
Faith and spiritual growth
encourages the reader to consider their faith and the transformative power it holds
Good vs Evil
Consider the implications of their choices in this moral landscape
What is the planet, God, metal and characteristics of The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe?
Jupiter
Jesus Christ / Father Christmas
Tin
Themes
good vs evil: Alsan and the white witch
Sacrifice and redemption: Aslan’s sacrifice for Edmund highlights forgiveness and the importance of selflessness
courage and friendship: The siblings learn about bravery, loyalty and the strength of their bond to face challenges
power of belief: the importance of faith and belief like with Lucys unwavering faith in Aslan
What is the planet, God, metal and characteristics of Prince Caspian
Mars
mars Silvanus - God of war
iron
Themes
nobility and bravery - Caspian’s sense of justice and fairness
idealism and imagination - Caspians imagination and idealistic nature
What is the planet, God, metal and characteristics of The Voyage of the Dawn Treader
The sun or sol
Apollo
gold
Themes
Spiritual growth and redemption - Eustace for Aslan
courage and honor - reepicheep and Caspian leadership
Temptation and moral choices: Goldwater Island and dark island testing greed, vanity and morality
fate and divine guidance: divine intervention from Aslan’s influence
What is the planet, God, metal and characteristics of The Silver Chair
Moon
luna or Selene
Silver
Themes
Faith and Morality: exploring the importance of faith and moral choices
Courage and friendship: facing challenges that test their bravery to save Prince Rillain
Good vs evil: The struggle between the characters and the wicked witch
What is the planet, God, metal and characteristics of The Horse and His Boy
Mercury
Hermes
quicksilver or mercury
themes
exploration of identity, freedom, and cultural differences
Identity and destiny with Shasta who is actually prince Cor
courage and personal growth
What is the planet, God, metal and characteristics of The Magician’s Nephew
Venus
Hesperus
Copper
themes
Bravery and loyalty:
Digory following Polly into the unknown when she was tricked by Uncle Andrew
Impulsive and stubborn:
When Digory acts on impulse and rings the bell awakening Jadis (white Witch)
Growth and Maturity
Digory changes from a self-centered boy into a boy that’s thoughtful and responsible even when confronting the consequences of his actions
What is the planet, God, metal and characteristics of The Last Battle
Saturn
Father time
lead
Themes
Faith and belief - trusting in Aslan and discerning truth from deception
Redemption and judgement: the consequences for evil actions and reward for heaven for faith
illusion vs reality: the false Aslan and the apparition of tash
myth became fact
the story of Jesus Christ represents myth becomes fact
Lewis's conversion and realization from atheism to Christianity
Myth is a reflection of truth and serve as a bridge between abstract truth and concrete realities
Even though myths may not be truth themselves
Myths are essential for understanding the human experience across cultures and time periods
Addison’s walk talk with Tolkien
A discussion between C.S. Lewis, J.R.R Tolkien, and Hugo Dyson discussed myth, metaphor, and the intersection of storytelling and truth
Tolkien argued that myths reflect fragments of the ultimate truth and that the natural world was not enough to express ultimate truth about humanity, morality and the cosmos
Plato
Plato's allegory of the cave like in the underground city in the silver chair
Plato proposed that the material world is a shadow or copy of a higher reality
Digory remarks “It’s all in Plato, all in Plato,” signifying that the progression from our world → Narnia → New Narnia reflects Plato’s distinction between appearances and true reality
Looking at/along the beam for Contemplation
External:
the observer is outside the phenomenon examining it from a distance
Experience along a beam:
standing aside, one sees the beam itself, the dust, how the light enters but does not experience what the light illuminates
The beam becomes an object of observation