Acquired Macular Disease
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
AMD
angioid streaks
choroidal osteoma
fundus flavimaculatus
multifocal choroiditis
ocular histoplasmosis syndrome
optic disc drusen
ONH pits
pathological myopia
pattern dystrophies
photocoagulation
polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
sarcoidosis
serpiginous or geographic choroiditis
toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis
traumatic choroidal rupture
what are common ophthalmic conditions associated with macular neovascularization?
demographics
age
male vs female
race/ethnicity
what are ways to differentiate between the various causes of macular neovascularization?
angioid streaks
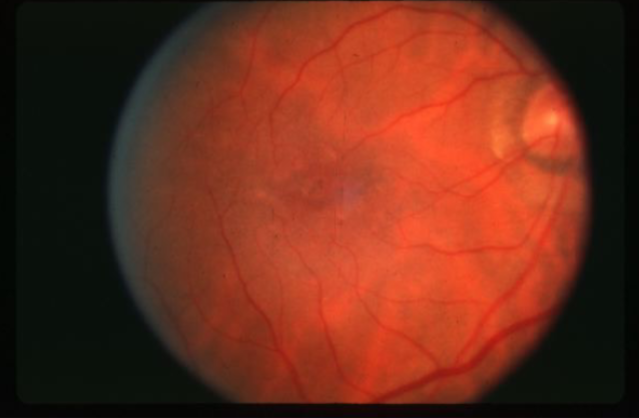
irregular, radiating, jagged, tapering line that extends from the peripapillary area into the peripheral fundus
results from changes in the collagenous & elastic portion of Bruch’s which renders it weak & predisposed to breaks
reddish orange to dark red or brown
CNVM can grow through into the sub-RPE or subretinal space in/near papillomacular region
may have significant underlying systemic disease
pseudoxanthoma elasticum
Ehler’s DanlosPaget’s
sickle cell
idiopathic
homocysteinuria
acromegaly
Marfan’s syndrome
what systemic conditions are angioid streaks associated with?
pathological myopia (myopic macular degeneration)
in myopes greater than -6.00D
slow progressive vision loss usually in 5th decade or later
clinical appearance:
scleral crescents
oblique nerve insertion
PPA
macular pigment mottling
posterior staphyloma
well circumscribed area of atrophy
lacquer cracks
risk of CNVM
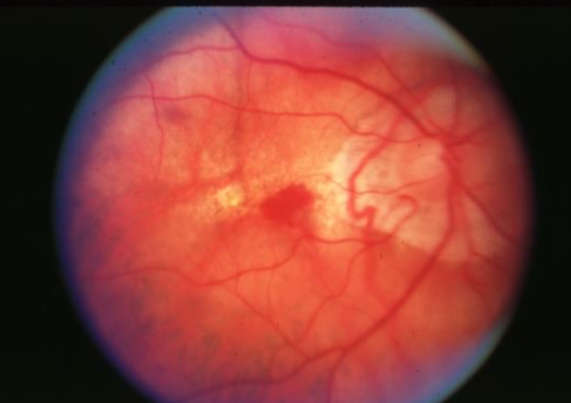
Fuch’s spot
Fuch’s spot
raised, circular pigmented lesion ~1/2 DD in size, consisting of localized ingrowth of fibrovascular tissue, associated w/ pathological myopia
lacquer cracks
spontaneous focal linear breaks in Bruch’s secondary to high or progressive/pathological myopia
may have associated small, subretinal hemorrhage unassociated w/ evidence of CNVM
felt to be caused by stretching of retina & choroid, pathological myopia
begins as thinning of choroid & RPE in macular area
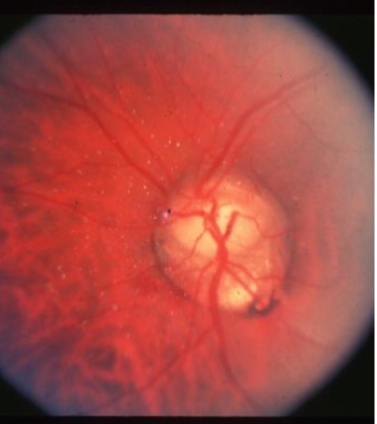
choroidal ruptures
contusion & rupture of the choroid & retina caused by high-velocity trauma, usually from blunt trauma to the globe, sclera may be visible w/in the break
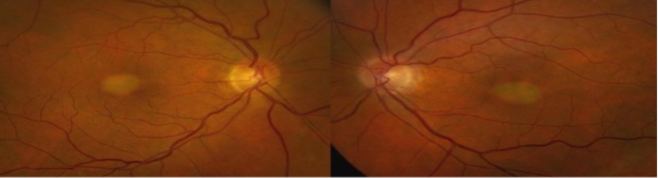
pattern macular dystrophy
adult onset
BILATERAL
autosomal dominant
typically begins midlife w/ visual disturbance
typically retain good vision in 1 eye until late adulthood
appearance:
deposits can range in color
patterns can vary widely & be asymmetric
good visual prognosis for all groups
rarely does CNVM develop
adult vitelliform pattern macular dystrophy
group of pattern macular dystrophies
can be asymmetrical
lesions can fade & pigment
butterfly shaped
group of pattern macular dystrophies
triradiate pattern
zone of depigmentation around deposits
multifocal pattern macular dystrophy
group of pattern macular dystrophies
yellow scattered flecks
normal choroidal fluorescence
better prognosis for vision
later onset than Stargardt’s
normal choroidal fluorescence
better prognosis
how do you differentiate between multifocal pattern simulating Stargardt’s macular dystrophy & Stargardt’s?
reticular pattern macular dystrophy
group of pattern macular dystrophies
fishnet pattern centered on fovea extending in all directions
better viewed w/ IVFA
can fade over time
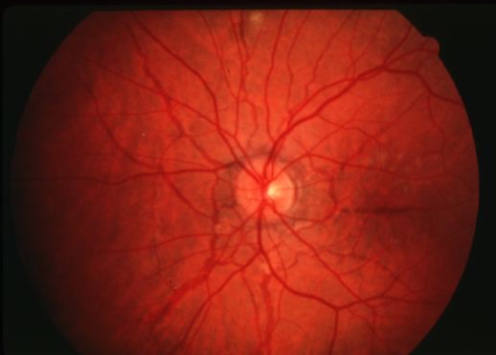
angioid streaks
angioid streaks
angioid streaks
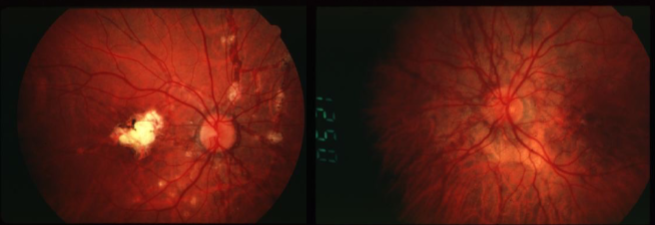
angioid streaks
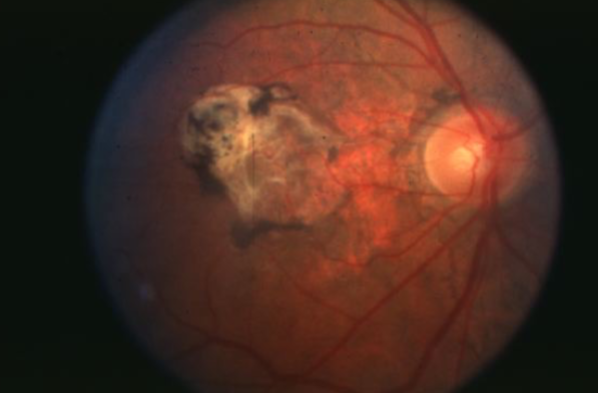
large CNVM & leaking
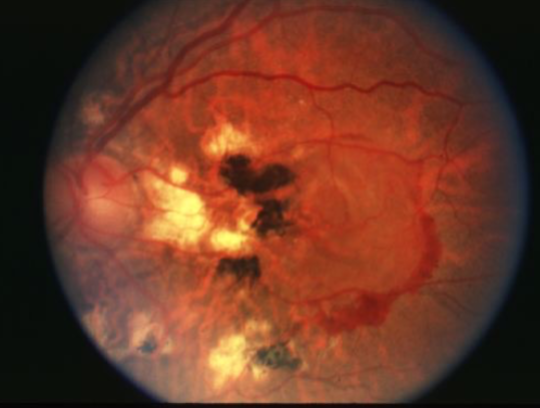
angioid streaks
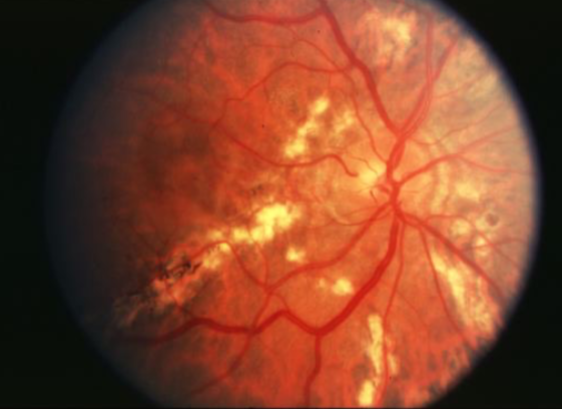
CNVM causing leaking of fluid
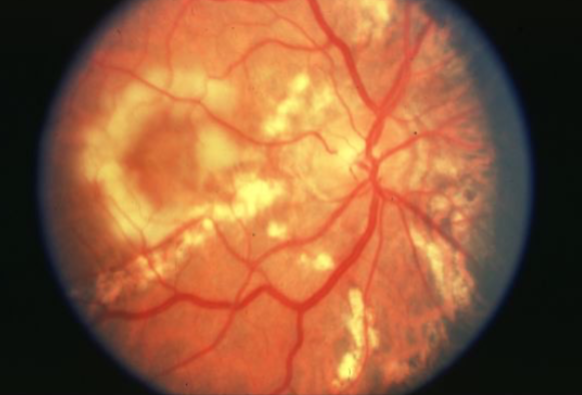
angioid streaks
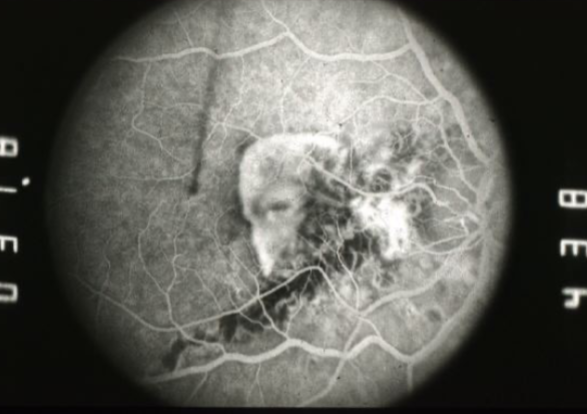
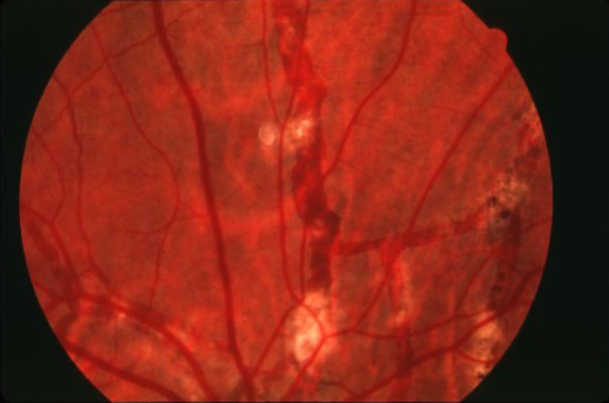
pigmented angioid streaks
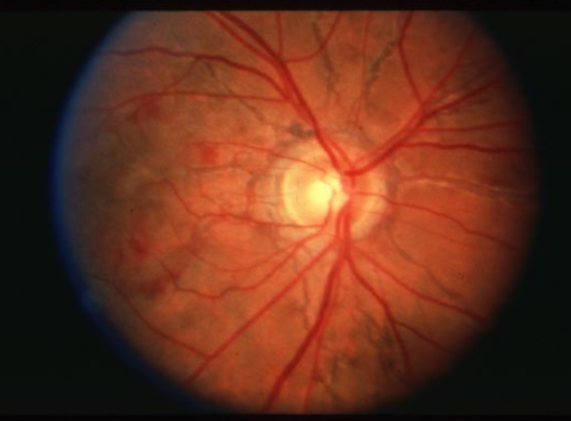
angioid streaks, CNV & subretinal hemorrhage associated
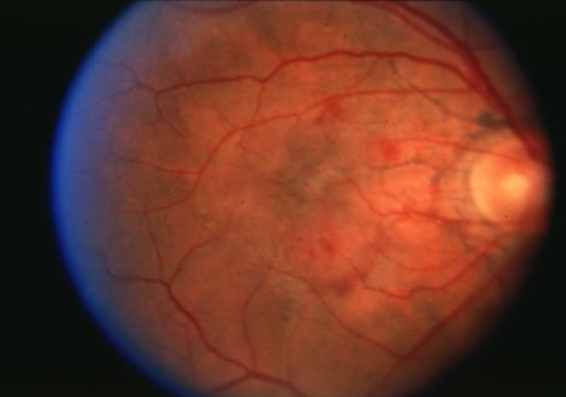
angioid streaks
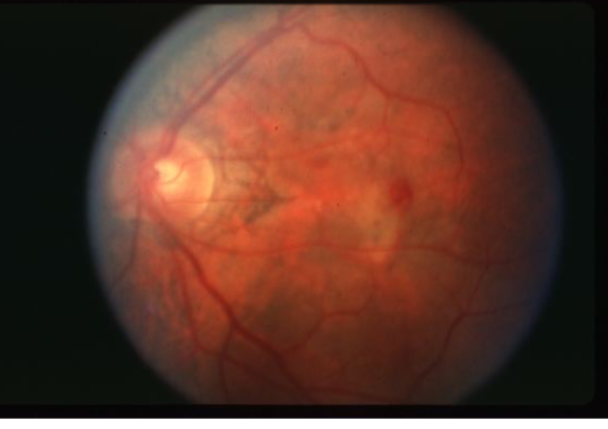
pathological myopia
lacquer cracks
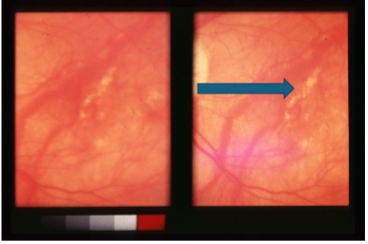
lacquer cracks
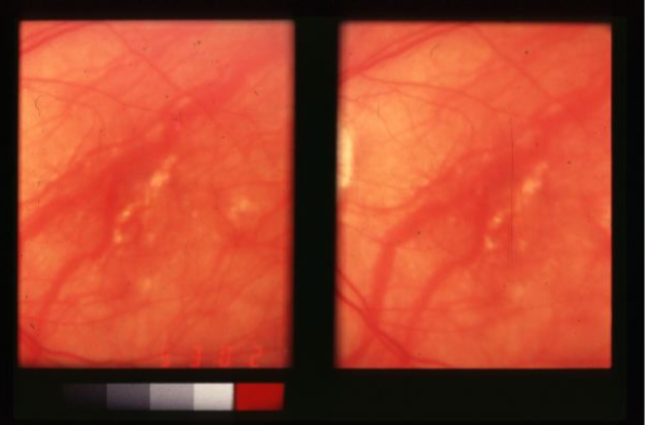
lacquer cracks
lacquer cracks & subretinal hemorrhage
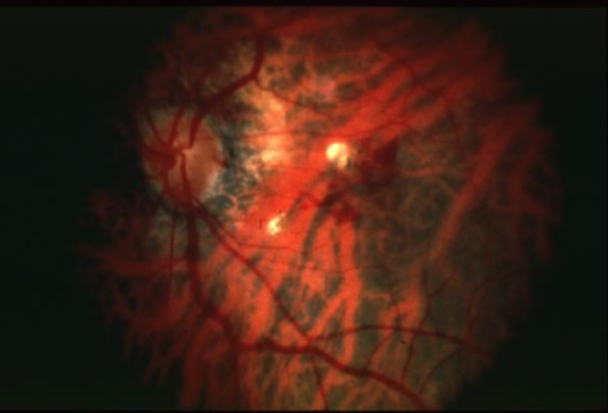
lacquer cracks
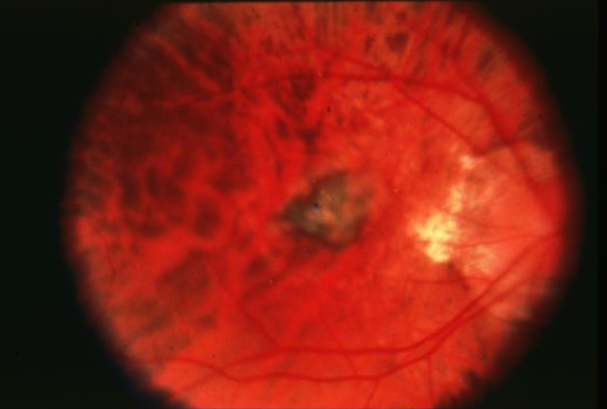
lacquer cracks

lacquer cracks
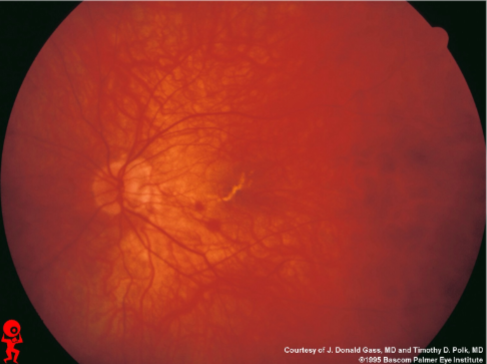
choroidal ruptures
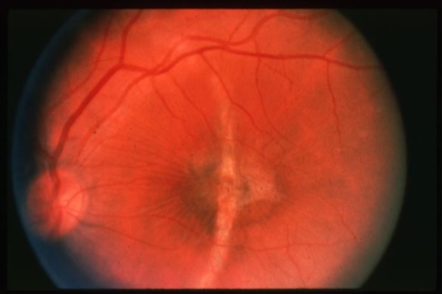
choroidal rupture & CNV
choroidal rupture
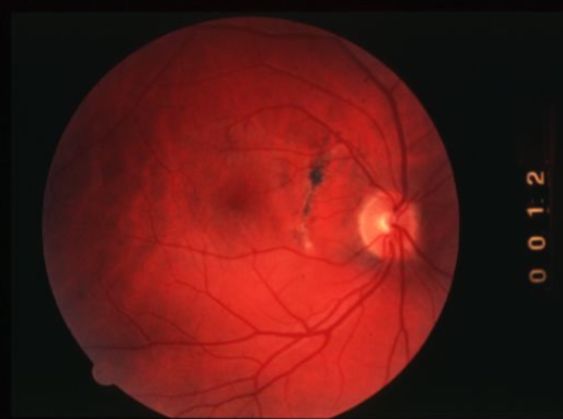
choroidal rupture
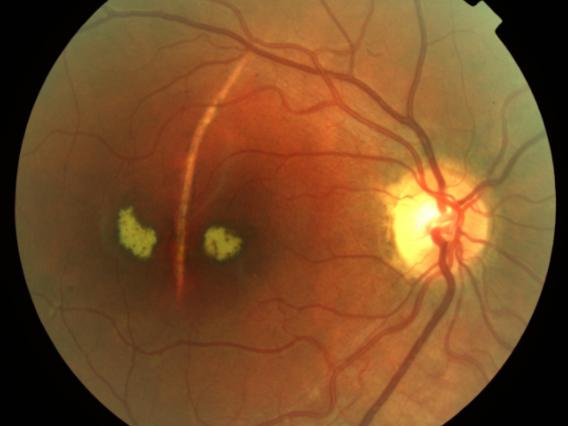
adult vitelliform pattern macular dystrophy
butterfly pattern macular dystrophy
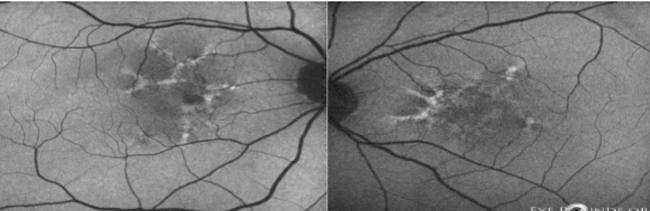
butterfly pattern macular dystrophy
butterfly pattern macular dystrophy
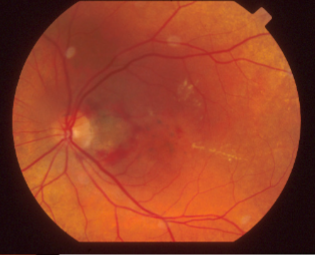
Stargardt’s like pattern dystrophy
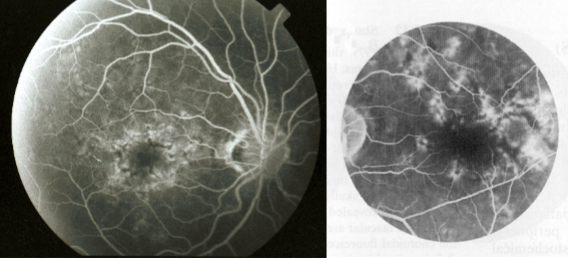
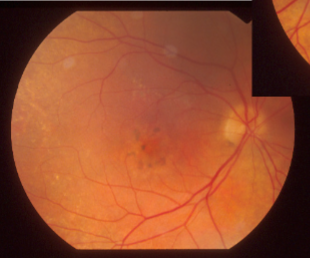
polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
idiopathic, primary disorder of inner choroidal vasculature
likely represents a form of CNV
inner choroidal vascular network w/ aneurysmal bulge
appearance:
visible orange, spheroid, polyp-like structure
multiple, recurrent serosanguineous detachments of the RPE & NS retina
usually bilateral
better visual prognosis
preponderance in heavily pigmented races
age of onset is much younger than in AMD
pachychoroid
attenuation of choriocapillaris overlying dilated choroidal veins
associated w/ progressive RPE dysfunction & neovascularization
thickened vessels that do not taper toward posterior pole, may be diffusely present or focal in nature
choriocapillaris thinning observed over thick vessels
greater than 300microns subfoveal
what constitutes a thick choroid?
Haller’s
in pachychoroid, the choroid is thick due to dilation of choroidal vessels in _____ layer
choroidal hyperpermeability → choriocapillaris attenuation, RPE complications, & neovascularization
what is the pathogenesis of pachychoroid?
idiopathic central serous chorioretinopathy (ICSC)
localized serous detachment of the retina in macular area
sloping margins
small RPE detachment
no blood or exudates
age of onset: mid 30s
range: 20-50yo
men > women
whites > non-whites
seen in type A personalities
relatively good prognosis (majority spontaneously recover in 4-8wks)
idiopathic but part of pachychoroid disease spectrum
what is the pathophysiology of ICSC?
unilateral, central vision loss or distortion or blur to moderate degree
VA may be near normal w/ a hyperopic shift (20/20 - 20/80)
micropsia
color vision complaints (blue-yellow)
decreased contrast sensitivity
poorer macular photostress recovery time
positive central scotoma or dark spot on Amsler testing
what are the signs/sx of ICSC?
3rd
if a pregnant pt has an ICSC, typically there is recovery in the ___ trimester
1/3 to 1/2
_______ of pts w/ ICSC have a recurrence
50
____% of pts that have an ICSC recurrence have it w/in the 1st year
10
__% of ICSC pts have a third episode
20
__% of ICSC pts become bilateral
5
less than __% of ICSC pts develop a CNVM
smoke stack
what is the characteristic appearance of ICSC on IVFA?
laser photocoagulation
what is the tx for ICSC?
RPE defect is >1/4 DD from foveal center &
greater than 4-6mo duration
pt has occupational considerations
turbid sub-retinal fluid
severe bouts of recurrence
bilateral cases w/ a defect in the fellow eye
when should laser tx be considered for ICSC?
no
can you tx ICSC w/ steroids?
aldosterone antagonist agents (spironolactone, eplerenone)
CAIs
tx of H. pylori (questionable)
what drugs can you use to manage ICSC?
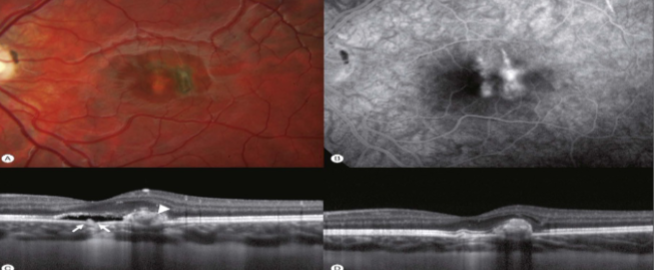
vitreal macular traction
traction on retinal surface & macular distortion
incomplete PVD
macular cysts
can progress to macular hole
central vision complaint
may spontaneously resolve/detach
vitrectomy indicated if persistent & symptomatic
idiopathic age-related macular hole
circular or oval depression in the central macula
varying in size
round, well-defined red area w/ surrounding gray halo of detached retinal elevation
50% have yellow nodular deposits at the level of the RPE (bread-crumb)
10-20% of pts have ERM
operculum structure often visible
age of onset: 6th-8th decade
females > males
blur/metamorphopsia when other eye is covered
mean VA: 20/200
+ Watzke sign
what are the signs/sx of idiopathic macular hole?
stage 1
idiopathic macular hole stage
loss of normal foveolar depression & FLR
localized contraction of prefoveal vitreous
yellow spot or ring may be apparent
no tx recommended at this stage
50% resolve spontaneously
stage 2
idiopathic macular hole stage
partial/early macular hole formation w/ a full thickness opening
stage 3
idiopathic macular hole stage
full development of macular hole
stage 4
idiopathic macular hole stage
macular hole & PVD
10
there is a ___% chance of bilaterality (usually w/in 2y) if PVD is not present in fellow eye
0
what is the chance of an idiopathic macular hole becoming bilateral if there is a PVD present in the other eye?
vitrectomy w/ fluid-gas exchange
what is the tx for an idiopathic macular hole?
polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
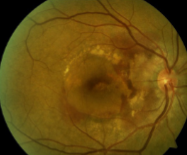
polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
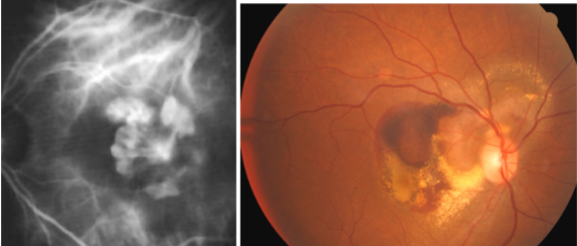
polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
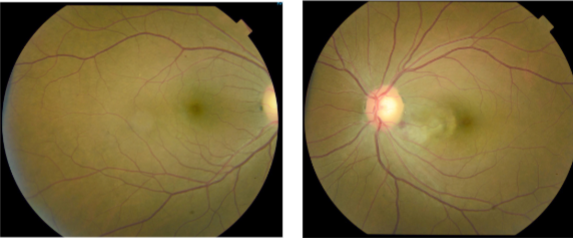
ICSC
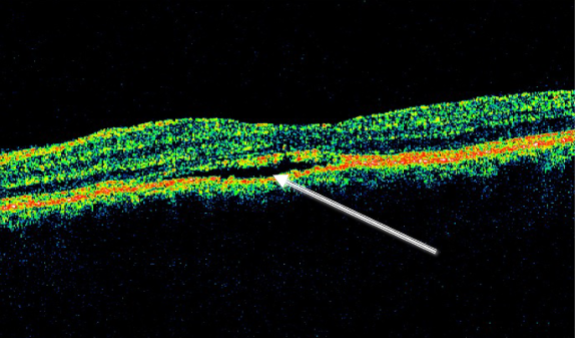
ICSC
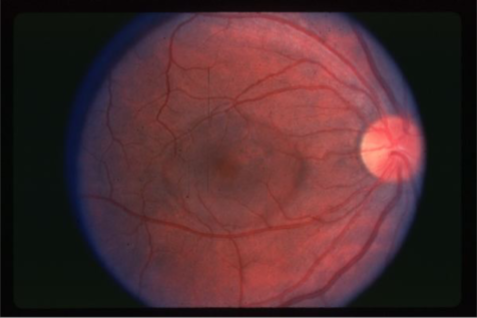
ICSC
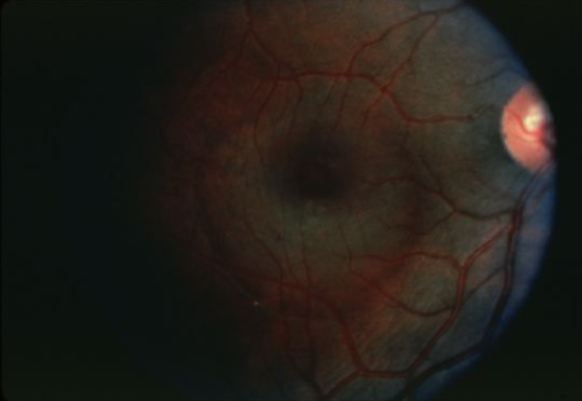
ICSC
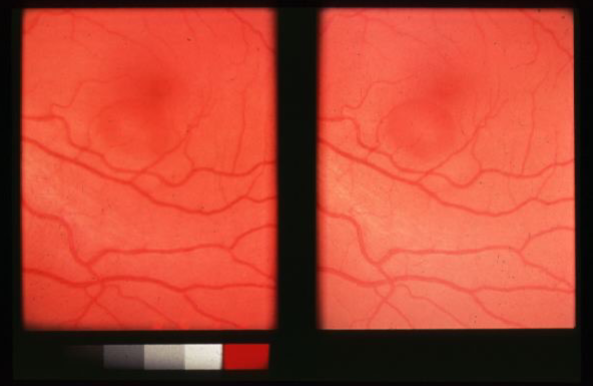
ICSC
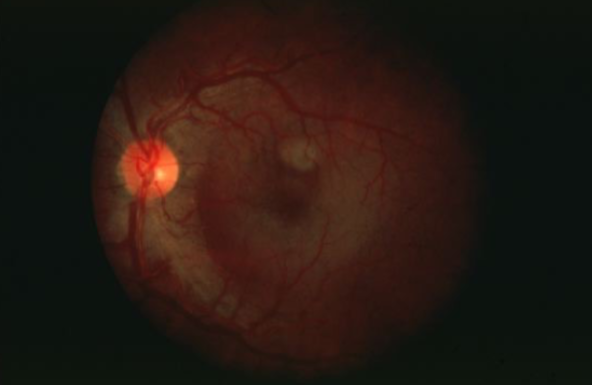
ICSC
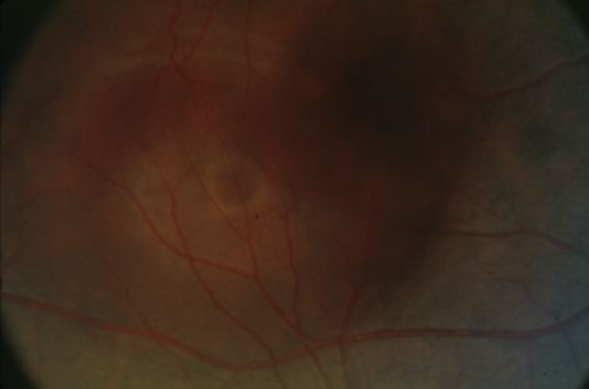
ICSC
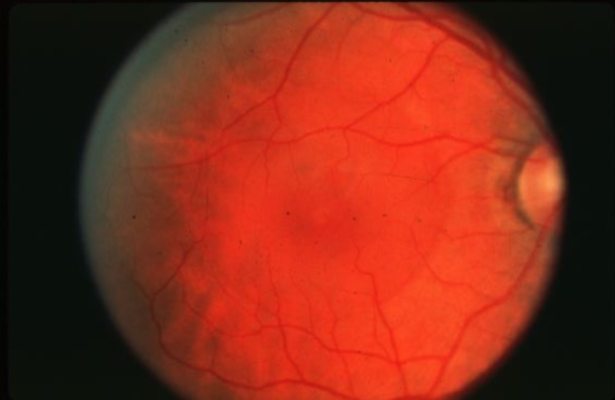
VMT
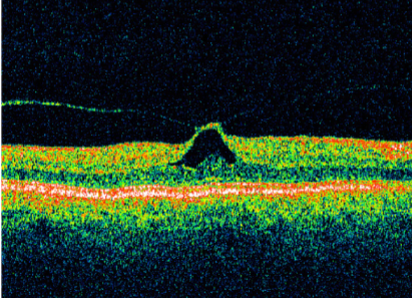
VMT

VMT
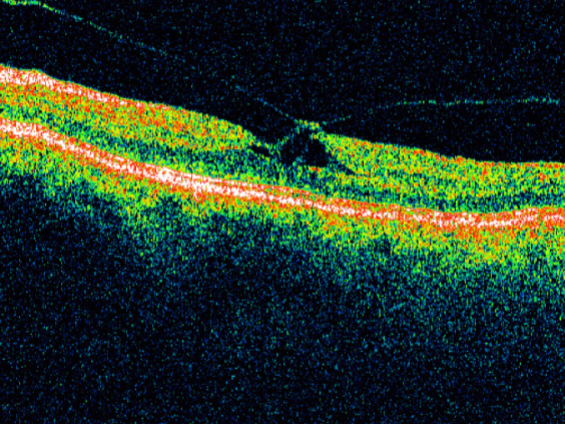
macular hole
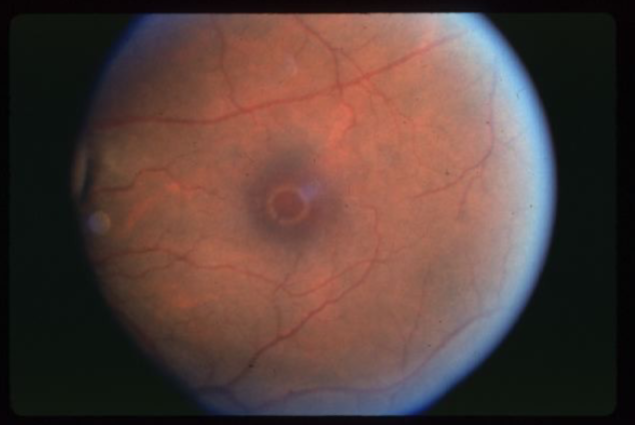
macular hole
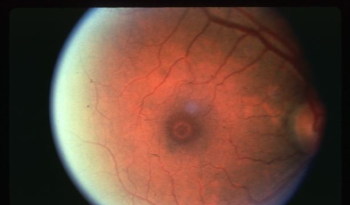
macular hole
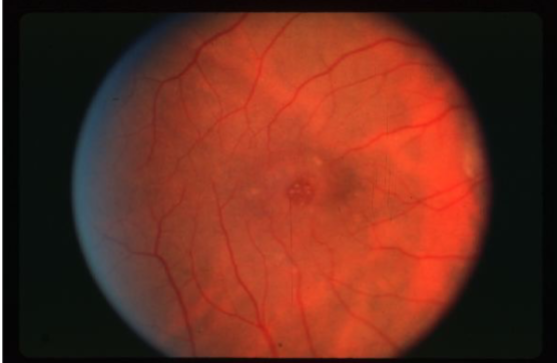
stage 1 macular hole
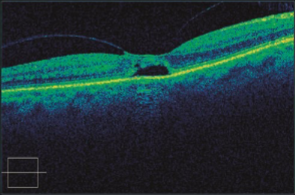
stage 1 macular hole
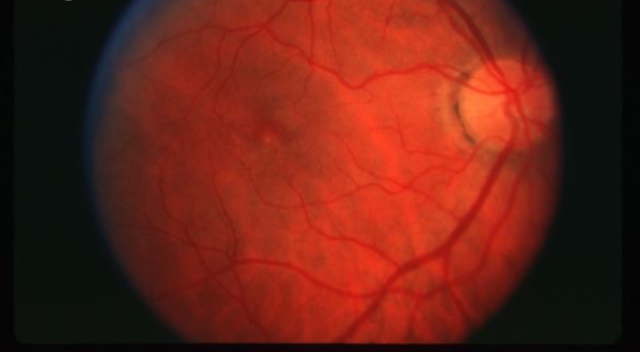
stage 2 macular hole
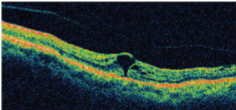
stage 2 macular hole
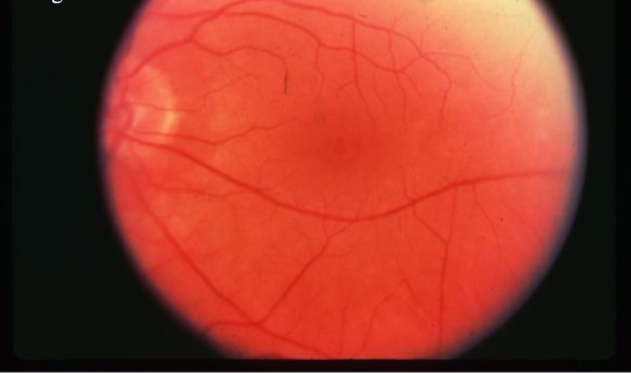
macular hole
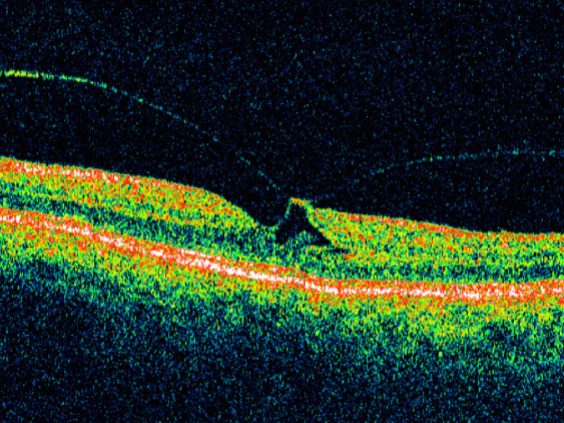
macular hole
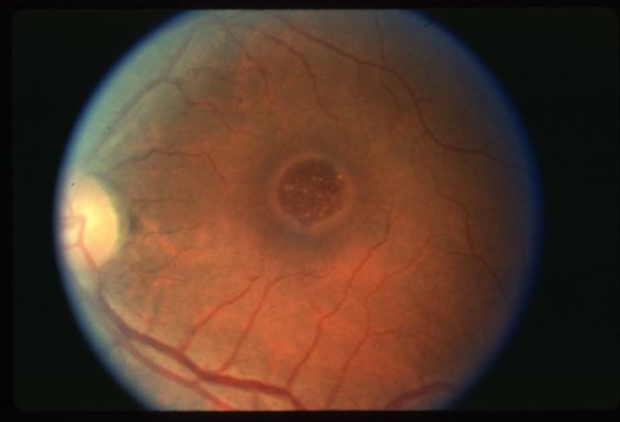
macular hole
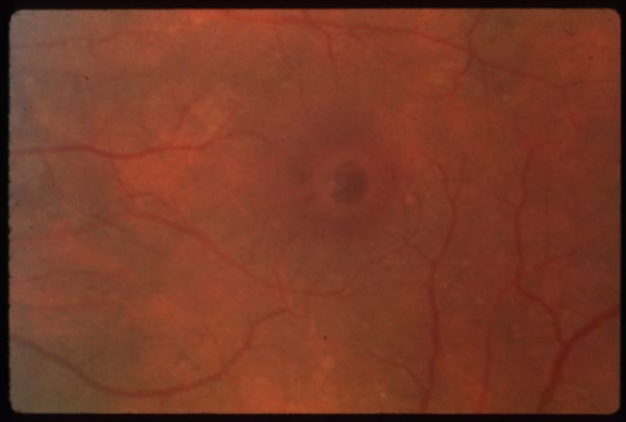
full thickness macular hole
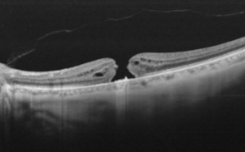
full thickness macular hole
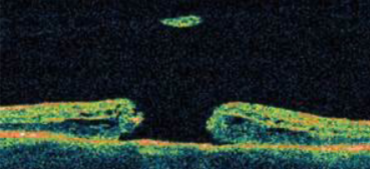
macular hole
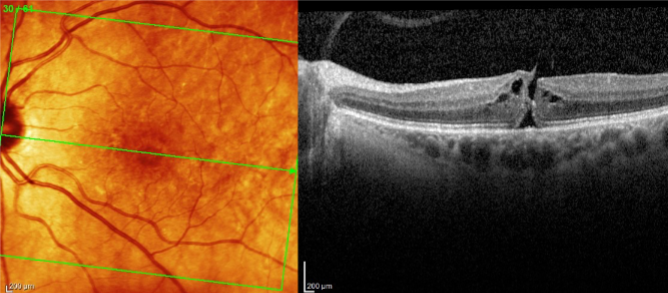
macular hole
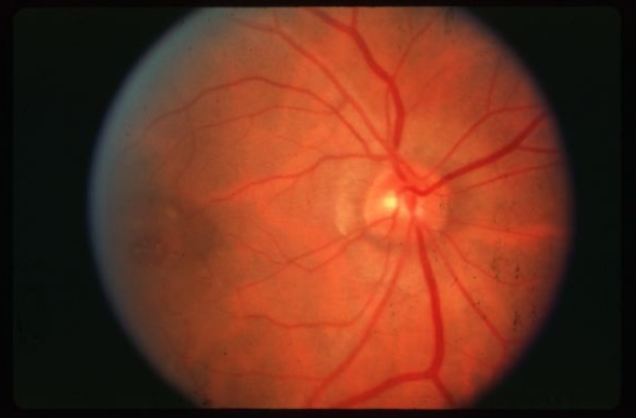
macular hole
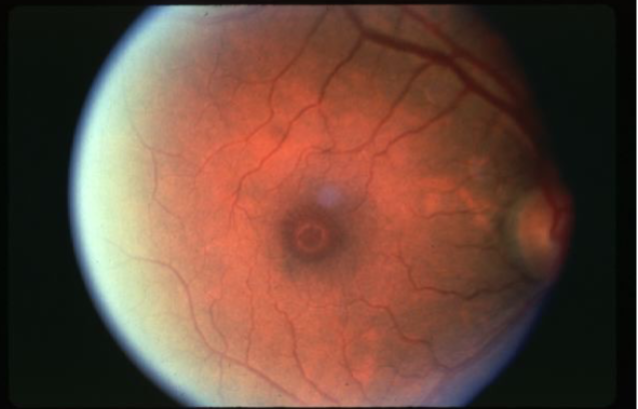
macular hole