River landscapes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Why are rivers important?
Supply and agriculture
Biodiversity and ecossytems
transportation and tourism
Cultural heritage
River emerge
the interaction of flowing water and a boundary (soil, rock, or ice) that can evolve in response to flow.
River main jobs
Moving water and Moving sediment
River move water

River move sediments

How are rivers organized?
Into networks to funnel water through the landscape.
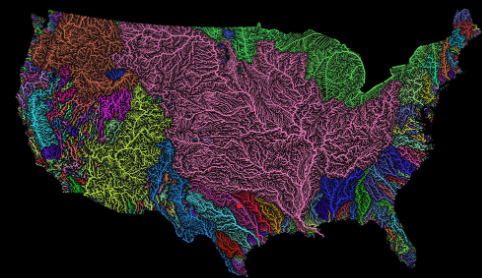
Drainage basin (or catchment, or watershed)
All of the area that contributes water to a downstream point.
Synthesizes the effects of local topography and geology.
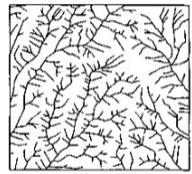
Drainage density
reflects the efficiency with which water moves through a landscape.
Low drainage density
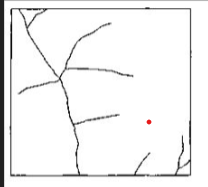
Medium drainage density

High drainage density
Drainage density equation
total stream lenth / drainage area
High drainage density are found where?
with little vegetation or very impermeable rocks and/or soils because infiltration and evaporation are low. All precipitation must move as surface water.
As drainage area increases—
so does the total volume of water or discharge, that the river must transport.
The shape of a river at a cross section—
reflects discharge
Cross section
elevation profile of a water from bank to bank (perpendicular to flow)
DIscharge (L³/T)
volumetric flux of water through a cross section
Velocity (L/T)
how fast the water is moving
Depth (L)
from water surface to bed
Width (L)
bank-to-bank distance
Discharge equation
Velocity x Depth x Width
Modes of sediment transport
Bedload
Suspended load
Dissolved load
Source
Where sediments is created and eroded
Transport
sediment moves through
Sink
where sediment is deposited
Weathering
the decomposition of rock into mobile sediment
Erosion
the movement of rock fragments (to rivers)
Source areas
generally steep mountain regions
Active tectonic uplift creating steep terrain
Course particles (cobbles and boulders)
Highest erosion rates because of rapid uplift
Bedrock rivers
backs and beds are made of solid rock

Abrasion-dominated systems

Plucking-dominated systems
