1.2.1 Primary Storage (Memory)
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Why do computers have primary storage (memory)?
To provide fast access to data, instructions, and software currently in use by the CPU.
Main memory (sometimes called ________ ________) refers to storage locations that are directly _________ by the _________.
primary storage, accessible, processor
Main memory offers very ____ read/write speeds but is typically much _______ capacity than ________ _________ devices.
fast, lower, secondary storage
What does primary storage usually consist of?
RAM and ROM.
What does it mean for memory to be volatile?
Its contents are lost when the computer loses power.
What does it mean for memory to be non-volatile?
Its contents are not lost when the computer loses power.
What is stored in the Random Access Memory (RAM)?
It holds all of the data and instructions that are currently being processed.
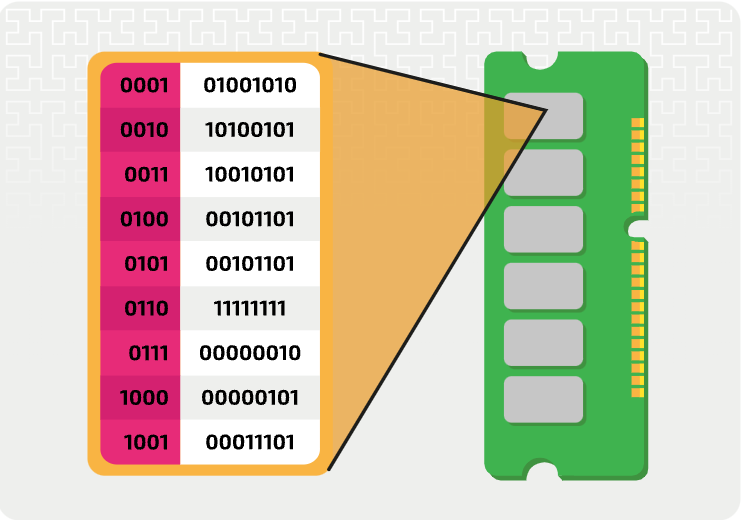
What are the characteristics of Random Access Memory (RAM)?
It is volatile
You can read and write to it
It is quicker to access than secondary storage
It has the largest capacity of all main memory
In order for any program to be executed, it must first be loaded into the RAM from secondary storage. Why is this the case?
This is because RAM has quicker read and write speeds than secondary storage devices.
The processor will fetch __________ (and any necessary ____) from the ____ directly before __________ and _________ them.
instructions, data, RAM, decoding, executing
Within the RAM, the memory is split up into separate __________, each of which is given a unique _______ ________. The __________ will use these addresses to access the data stored in ____.
locations, memory address, processor, RAM
Why is RAM called ‘random access’ memory?
Any of the locations in RAM can be accessed in the same amount of time, unlike other storage devices where a sensor (such as a read/write head) needs to be moved into place. Any location can be accessed "at random" with no impact on speed.
Is the Random Access Memory (RAM) volatile or non-volatile?
Volatile.
Any data that needs to be stored ____________ must be moved out of RAM before a computer is _________ ___.
permanently, switched off
Although the capacity of RAM is typically ______ than secondary storage devices, it is often the ________ capacity form of main memory.
lower, highest
What is stored in the Read-Only Memory (ROM)?
The boot sequence (BIOS) for a computer.
What are the characteristics of ROM?
It is non-volatile
It is written by the computer manufacturer
Usually stores the BIOS
Smaller capacity than RAM
True or False: the ROM’s contents can be modified during normal operation.
False.
The contents of ROM are set by the ___________ _____________ and, as the name implies, your computer usually only _____ from ROM.
computer manufacturer, reads
The BIOS (______ _______ _______ ______) stored on ___ is a very _______ sequence of instructions that checks that the ____ components of the computer system (___, fundamental _____/_____ devices, _______ storage) are connected and responding correctly.
Basic Input Output System, ROM, limited, core, RAM, input, output, secondary
Which of these components do you think the BIOS checks first?
The screen
Is the Read-Only Memory (ROM) volatile or non-volatile?
Non-volatile.
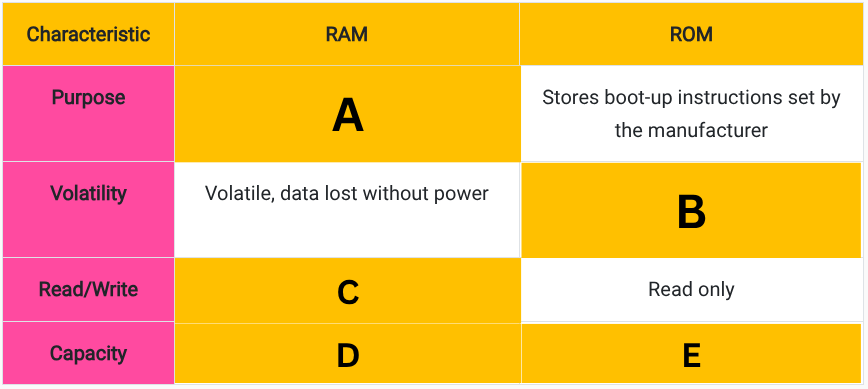
Fill in the blanks in this table comparing RAM and ROM. (A)
Stores data and instructions during processing.
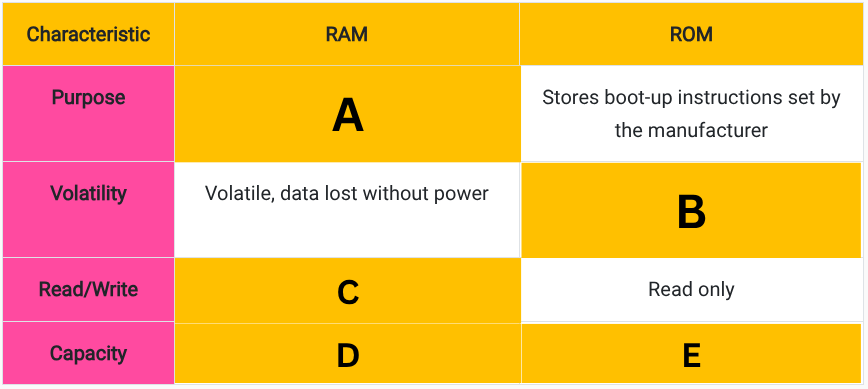
Fill in the blanks in this table comparing RAM and ROM. (B)
Non-volatile, data remains after power is switched off
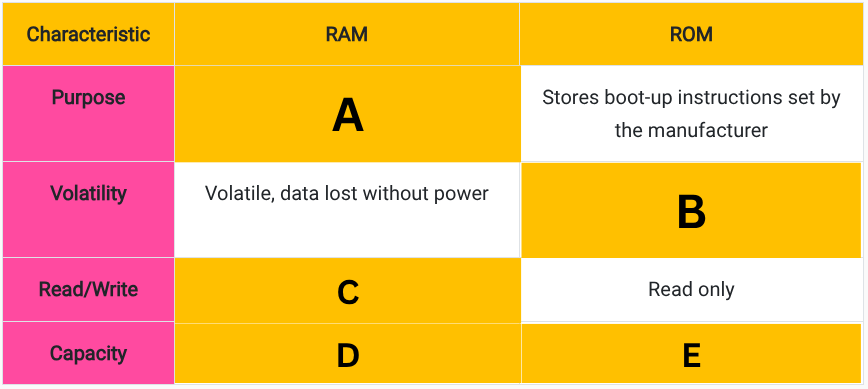
Fill in the blanks in this table comparing RAM and ROM. (C)
Read and write
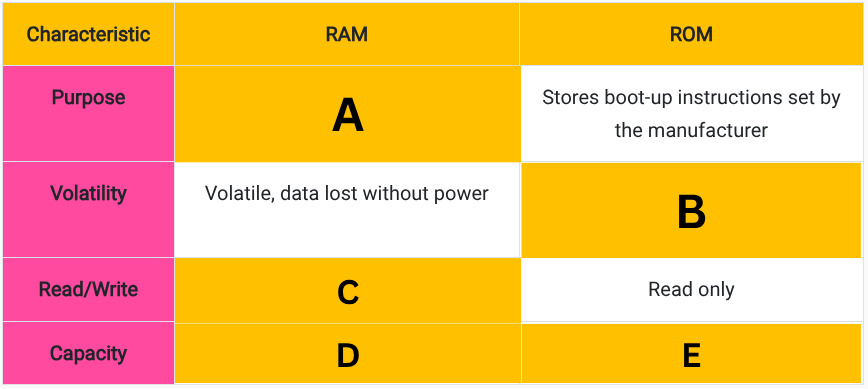
Fill in the blanks in this table comparing RAM and ROM. (D)
Usually several gigabytes
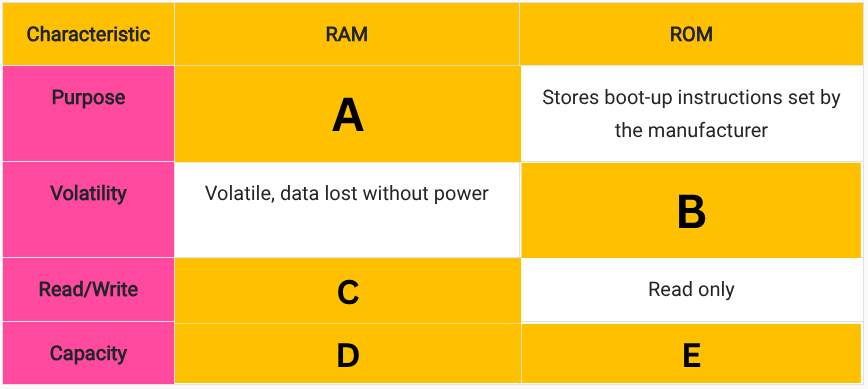
Fill in the blanks in this table comparing RAM and ROM. (E)
A few megabytes in size
Virtual memory is a way a computer system can compensate for a shortage of ___.
RAM
Running applications with high main memory requirements on systems with ________ main memory will lead to issues as applications ______ with each other for access to ___.
minimal, compete, RAM
Why might virtual memory be needed in a system?
When a computer’s RAM is full and there are still more programs or data that need to be loaded.
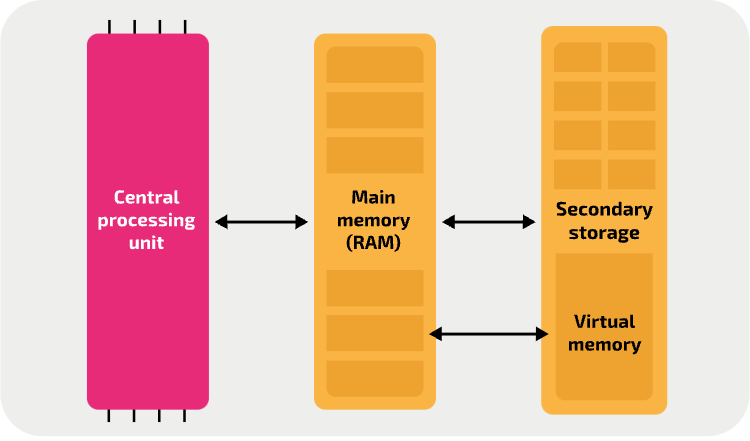
To reduce the likelihood of a slowdown in performance, computer systems allocate a portion of _________ _______ as virtual memory. This process allocates a portion of the ___ / ___ for storage of applications and files that are ________ open.
secondary storage, HDD, SSD, currently
How does virtual memory work?
The system uses part of the secondary storage (such as a hard drive or SSD) as if it were extra RAM.
When a system requires _______ ________, the operating system creates a set of ________ addresses (RAM is separated into a set of _________ addresses).
virtual memory, virtual, physical
Data moved to virtual memory is stored as _____. When the processor (___) is ready to accept instructions from the files in _______ _______, it moves the page files into ___, allocating a _________ address to the data.
pages, CPU, virtual memory, RAM, physical
When page files are moved from ______ to ____ memory, other data is moved from RAM to either ________ ________ or back to the ____________ _________.
virtual, real, virtual memory, secondary storage
Virtual memory shouldn't be confused with ________ _______ — a term used to refer to secondary storage located away from the computer, such as cloud storage and other network storage services.
virtual storage
Both HDDs and ___s are used for virtual memory. SSDs have an advantage over ___s in that access speed is closer to that of ___. However, a system that uses SSDs regularly for ______ _______ reduces the _______ of the SSDs, as a result of their ______ read/write lifecycle.
SSD, HDD, RAM, virtual memory, lifespan, finite
What is stored in the cache?
Frequently used data/instructions.
What is another type of memory designed to make access to frequently used data much faster?
Cache memory
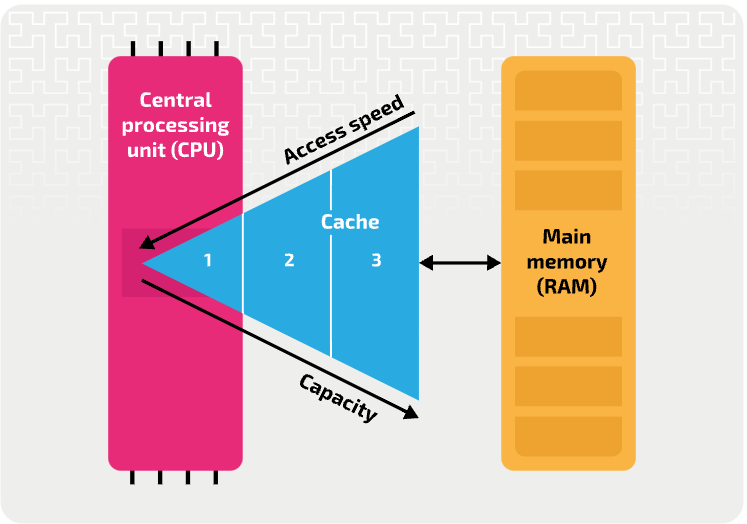
Cache site between the _________ and ___.
processor, RAM
The closer the cache is to the CPU, the _______ it can ____ and write data, but the ____ it can store.
faster, read, less
The level one cache is usually a part of the __________ itself. This cache has the ________ capacity, but the ________ access speed.
processor, lowest. quickest
In some processors, the level two cache might be built into the _________ along with level one. Level two is slightly _______ to read, but has a _______ capacity than level one.
processor, slower, higher
The level three cache might be the ________ at reading and writing, but it is still roughly twice as fast as ___.
slowest, RAM
Onboard the CPU there are very small memory devices called ________. Registers provide faster access than both the ___ and ______, but are only able to hold a few _____ at most.
registers, RAM, cache, bytes
What are two categories that registers are split into?
General purpose and dedicated (special purpose)
General purpose registers are used to temporarily store values generated by ___________, if they need to be used again in the ____ instruction.
instructions, next
Dedicated registers serve a specific purpose in the ______-________-______ cycle.
fetch, decode, execute
A car has a ‘Follow Me’ system that uses a cruise control feature to allow the car to follow the car in front of it. It will keep the same speed and distance without the driver’s intervention. The cruise control system is an example of an embedded system. The car’s system has Read Only Memory (ROM) and Random Access Memory (RAM). State two items that will be stored in the ROM for the ‘Follow Me’ system.
Startup instructions and operating system
A car has a ‘Follow Me’ system that uses a cruise control feature to allow the car to follow the car in front of it. It will keep the same speed and distance without the driver’s intervention. The cruise control system is an example of an embedded system. The car’s system has Read Only Memory (ROM) and Random Access Memory (RAM). The RAM will store currently running data and instructions. State three items of data that will be stored in the RAM for the ‘Follow Me’ system.
The current speed of the car in front, the distance between the two cars, current speed of the car.
A car has a ‘Follow Me’ system that uses a cruise control feature to allow the car to follow the car in front of it. It will keep the same speed and distance without the driver’s intervention. The cruise control system is an example of an embedded system. The car’s system has Read Only Memory (ROM) and Random Access Memory (RAM). Explain why the ‘Follow Me’ system does not need virtual memory.
There is no secondary storage to use as virtual memory. There are no memory intensive tasks.
An artist has a computer that they use to create images. Their computer has both hardware and software. The hardware includes primary and secondary storage. Explain why a computer needs both primary and secondary storage.
Primary storage is needed to store active instructions that the processor needs to access.
Secondary storage is used to store data permanently.
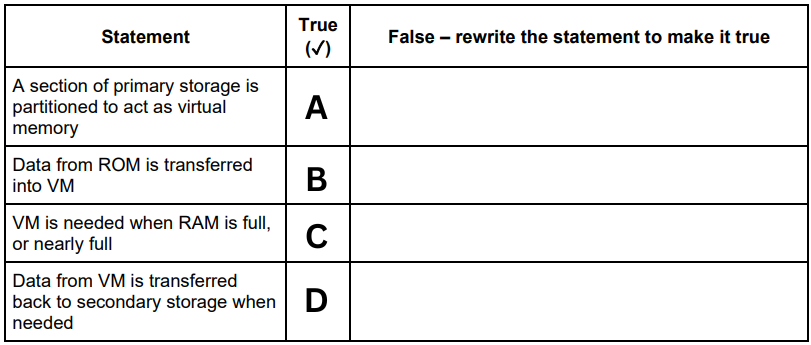
A computer has Virtual Memory (VM). The table has four statements about VM. Not all of the statements are correct. Re-write any statement that is incorrect in the False column by changing the statement to make it true. (A)
False - A section of secondary storage is partitioned to act as virtual memory
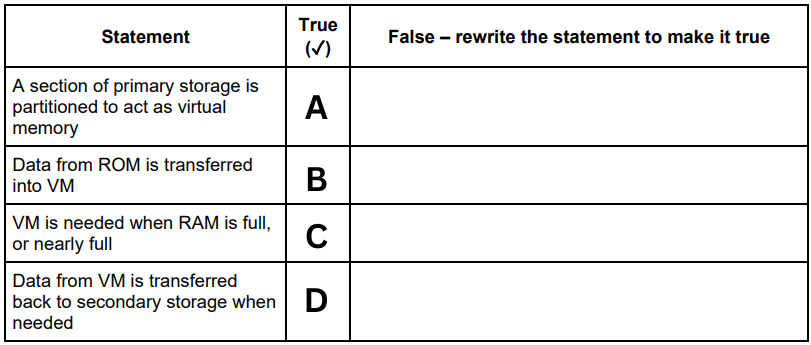
A computer has Virtual Memory (VM). The table has four statements about VM. Not all of the statements are correct. Re-write any statement that is incorrect in the False column by changing the statement to make it true. (B)
False - Data from RAM is transferred into VM
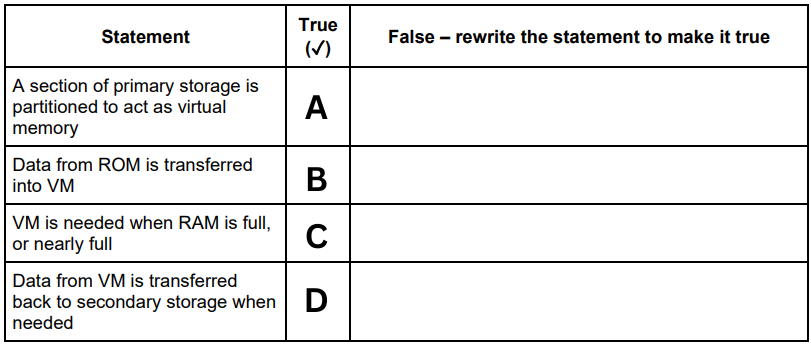
A computer has Virtual Memory (VM). The table has four statements about VM. Not all of the statements are correct. Re-write any statement that is incorrect in the False column by changing the statement to make it true. (C)
True
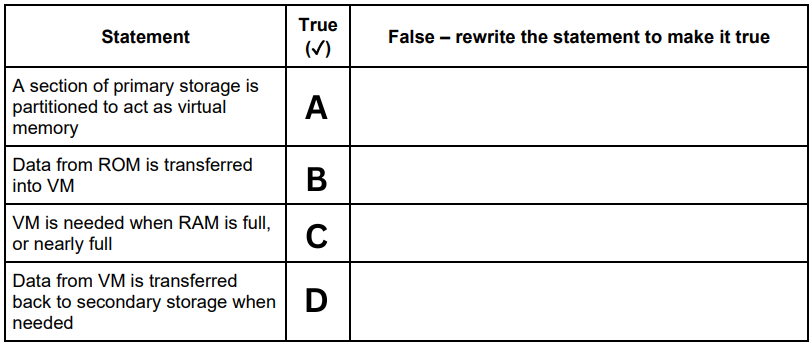
A computer has Virtual Memory (VM). The table has four statements about VM. Not all of the statements are correct. Re-write any statement that is incorrect in the False column by changing the statement to make it true. (D)
False - Data from VM is transferred back to RAM when needed
A smart television allows the user to search the Internet and watch videos online. A smart television has both RAM and ROM. State the difference between RAM and ROM.
RAM is volatile, ROM is non-volatile
Give two examples of data that a smart television could store in RAM.
Current TV program being watched and current volume.
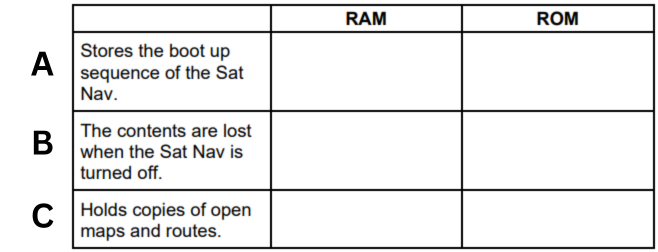
A satellite navigation system (Sat Nav) uses RAM and ROM. State whether each of the statements is true for the RAM or ROM in a Sat Nav. (A)
ROM
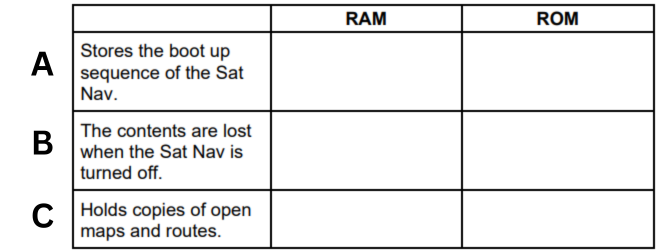
A satellite navigation system (Sat Nav) uses RAM and ROM. State whether each of the statements is true for the RAM or ROM in a Sat Nav. (B)
RAM
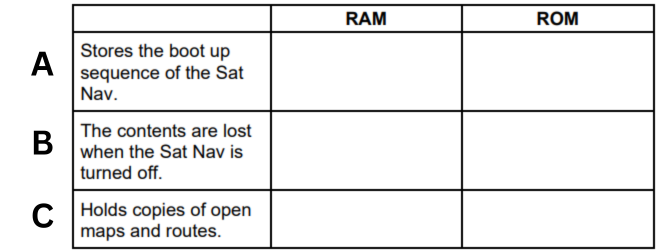
A satellite navigation system (Sat Nav) uses RAM and ROM. State whether each of the statements is true for the RAM or ROM in a Sat Nav. (C)
RAM