AP PSYCH- SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Sensation
the process of our NS receiving information through out 5 known senses
Central NS
Transduction
process of stmuli being transformed into neural impulses in order to reach out NS, ex you see from your occipital lobes
Chemical senses
taste and smell
Electric senses
everything else besides taste and smell
Perception
interpreting information, much of it is objective, ex: “nice outfit”
Motion sickness
info sent to brain from eyes doesn't match up to signals sent to brain from inner ear and vestibular system.
Sensory Adaptation
getting used to something and becoming less sensitive to it over time
Habituation
behavioural process that is learned
Absolute threshold
the least amount of a stimulus that can be detected 50% of the time. ex eye chart, volume on TV, minimum amount of salt. From zero
Just Noticeable difference(JND)
the smallest adjustment /change that can be detected, noticing a change
Weber’s Law
change must be proportional to original stimulus to recognize a difference ex 50-100-200 the next will be 400 watt.,
Signal Detection Theory
we preserve/interpret a sensation/stimulus depending on expectations/setting. ex louid noice home alone vs in public
SCIPLRBGOTO
Sclera, Cornea, Iris, Pupil, Lens, Retina, Bipolar Cells, Ganglion cells, Optic nerve, Thalamus, Occipital lobe
Sclera
white part of eye
cornea
protective cover
iris
colored part of eye
Pupil
opening that admits light
Lens
focuses
Retina
sensory and visual receptors
Optic Nerve
sends signal to brain, there is a blind sport where signal is passed on
Thalamus
traffic controller
FOVEA
central section of retina, 7,000-30,000 cones(color) located there, sharpest vision but we have more rods(light/darkness)
Retinal Disparity
the difference between what your left and right eyes see
Convergence
object comes closer to our face, out eyes focus on and object to maintain binocular vision
Binocular vision
depth perception. using both eyes
monocular cues
little to no depth perception if using only one eye
visual cliff experiment
toddler, Plexi gass, cliff
Trichromatic theory
color is the result in visual sstem process color in pairs that inhibit/block each other, ex “after images” red, green, blue combine
How we hear: PETHASOCBOAT
Pinna, ear canal, tympanic membrane(eardrum), hammer/anvil/stirrup(HAS) oval window, Cochlea(snail/coil shaped, basilar membrane that contains organ of corti(hair cells), auditory nerve( in the temporal lobe),
How to remember ears
“PE TEACHER HAS OLD CORPSE BEHIND OUR AUDITORIUM TODAY”
Amplitude
height of sound waves(volume)
Frequency
speed(closeness) of sound waves impacts pitch and Timer(quality)
Conduction Deafness
physical(noise damage to hearing)
Sensorineural Deafness
nerve damage, birth
Vestribular
system responsible for balance and spatial orientation, using signals from the inner ear. ex driving a car
Kinesthetic
control of specific body parts. ex flick f a hand
Olfaction
sense of smell
Gustation
sense of taste
Big four tastes
Salty, sweet, Bitter, sour, umami/mog
Skin senses
sensory receptors send signals to the parietal lobe ex: cultures with touch and physical promixity
Placebo
non medicinal substance that is fake
False postive
Type I error, someone is healthy but tests positive. false alarm
False negative
Type II error, someone is unhealthy but tests as healthy.
Bottom up Processing
well thought out, in depth and takes time
Top Down processing
quick decision, not as through
feature detectors
our nervous system helps us pick out certain features that we know, usually visual ut not exclusive
Perceptual consistency
ability to recognize a familiar object in different settings, ex recognizing a teacher in public
Ambigous
images with more then one intepretation
Muller-Lyer Illusion
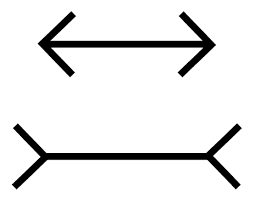
Context effect
the surrounding info helps interpret data, info your senses are taking in Ex A 13 C 1234
Figure
part of picture that grabs your attention
Ground
part of picture that does not grab your attencion
PHI Phenomenon
blinking lights, appearance of motion
Gestalt Psychology
visual perecption
Similarity
grouping similar objects together
Proximity
grouping close objects together
Contrunity
preferring continuous flow of a line/figure
Common fate
a group of objects moving with similar destination
Pragnaz
brain prefers simple
Closure
close a geometric figure, close incomplete circle
cocktail party effect
abilty to tune out attention to a single stimulus
stroop effect
a cognitive phenomenon where naming the color of the word interferes with reading the word itself, often due to conflicting meanings.
Broca’s area
where language is processed
Wernecke’s area
left temporal lobe, emotions of speech
Wharfs hypothesis
language impacts how we think
subliminal
below the absolute threshold for consciousness awareness
Gustav Fechner
pioneer in psychophysics who formulated laws measuring the relationship between stimuli and perception.
Priming
how a persons stimulus influences a persons response to another stimulus
accommodation
the process by which the eye changes its focus by adjusting the lens shape to see objects at varying distances.
Optic nerve
movies numeral impulse from eye to brain
Opponent-process theory
a theory in color vision that states colors are perceived in terms of opposing pairs: red-green, blue-yellow, and black-white.
David Hubel/ Torsten Wiesel
provedthat visual processing occurs in multiple stages in the brain and identified specific areas responsible for processing different aspects of vision.
Place theory
a theory that explains how we perceive pitch, stating that different pitches are perceived based on the location of activation on the basilar membrane within the cochlea.
frequency theory
a theory that suggests the perception of pitch is related to the frequency at which hair cells in the cochlea fire. This means that lower frequencies correspond to lower pitches, while higher frequencies correspond to higher pitches.
gate control theory
the spinal cord has a neurological gate that controls if pain signals reach the brain
Sensory interaction
brain blends senses, one may influence the toher
embodied cognition
how sensations to the body influence judgements