Macromolecules (3.1-3.6)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
carbohydrate elements
CHO
carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharide
2 monosaccharides through dehydration synthesis create
disaccharide
monosaccharide examples
ends in -ose
sucrose, fructose, ribose
carbohydrate formula
Cx H2× Ox
carbohydrate function
short term energy
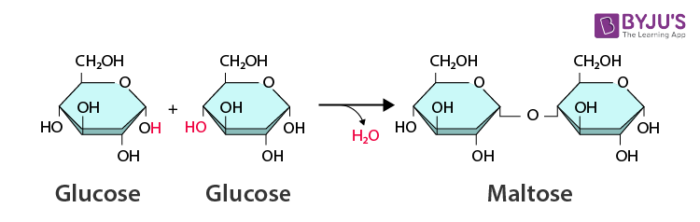
What process is this?
dehydration synthesis/condensation
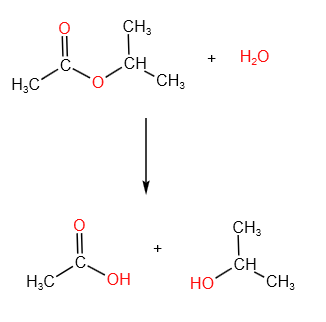
What process is this?
hydrolysis
condensation/dehydration
2 parts with a removed water to make 1 (+H2O)
hydrolysis
1 part broken by addition of water to make 2
polysaccharides
sugar; formed by carbon monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bond

starch
PLANTS: branches broken easily for energy storage, easily digested
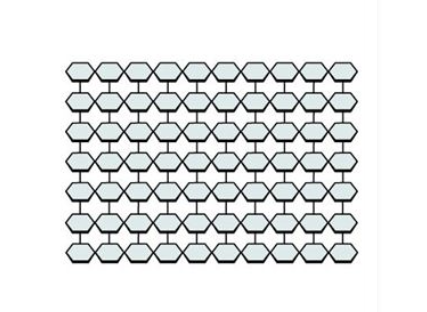
cellulose
PLANTS: humans cannot digest, compact structure, helps diet through excretion

glycogen
ANIMALS: stored energy, made in liver and muscle cells, release when blood sugar’s low, carb
chitin
FUNGI: exoskeleton, bugs/insects, shrimp
lipid elements
CHO
lipid monomers
fatty acids and glycerol
lipid (triglyceride) function
long term energy, insulation, protect organs
saturated fatty acid
solid at room temperature, more unhealthy
unsaturated fatty acid
liquid at room temperature, more healthy, C=C bond resulting in bent shape
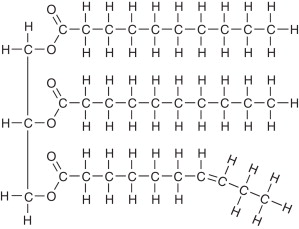
triglyceride composition
made up of 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol through dehydration
phospholipid
in bilayer, found near cell membrane, regulate in and out, amphipathic
phospholipid head
hydrophilic overall, contains glycerol and phosphate group (hydrophilic)
phospholipid tails
two hydrophobic (non polar) tails (fatty acids), with 1 having a kink.
steroids
lipid chemical messengers
steroid polarity
non polar because you don’t want it to dissolve in the bloodstream which is mostly water
protein elements
CHONS
enzymes
protein that speeds chemical reactions (ends in -ASE)
antibodies
hydrophilic proteins that fight diseases
membrane transport proteins
g-protein and tyrosine kinase (receptor proteins)
hormones
lipid (nonpolar) that’s a signaling molecule
myosin/actin
protein used in muscle contraction
protein monomer
amino acid
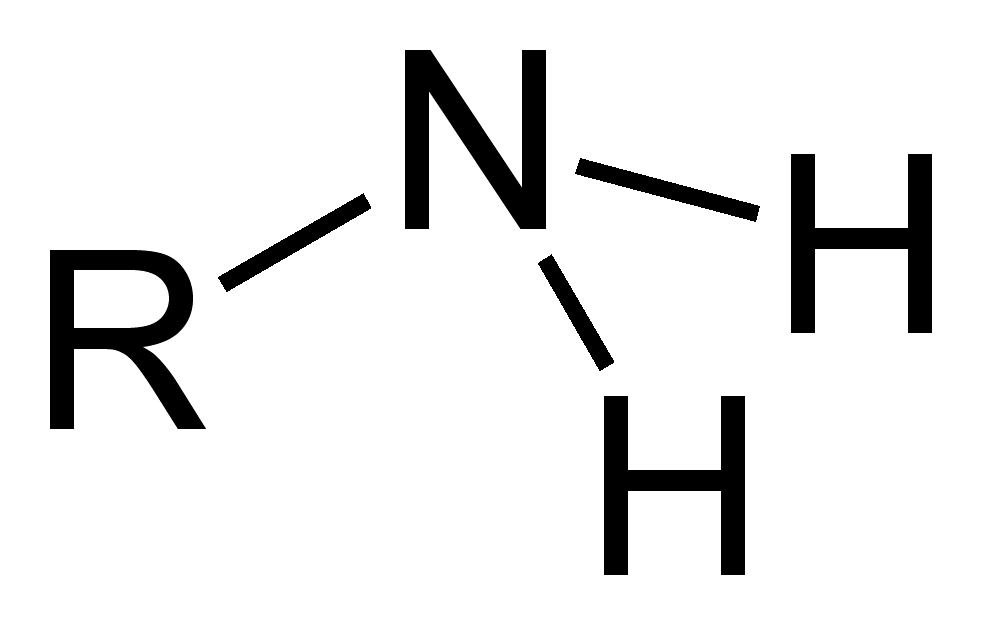
what’s this?
amino group (-NH2)
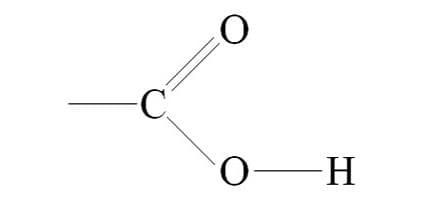
what’s this?
carboxyl group (-C=O)
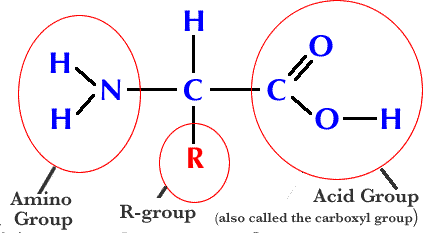
what’s the H above the C represent?
amino acid
bond between proteins
peptide bond (covalent)
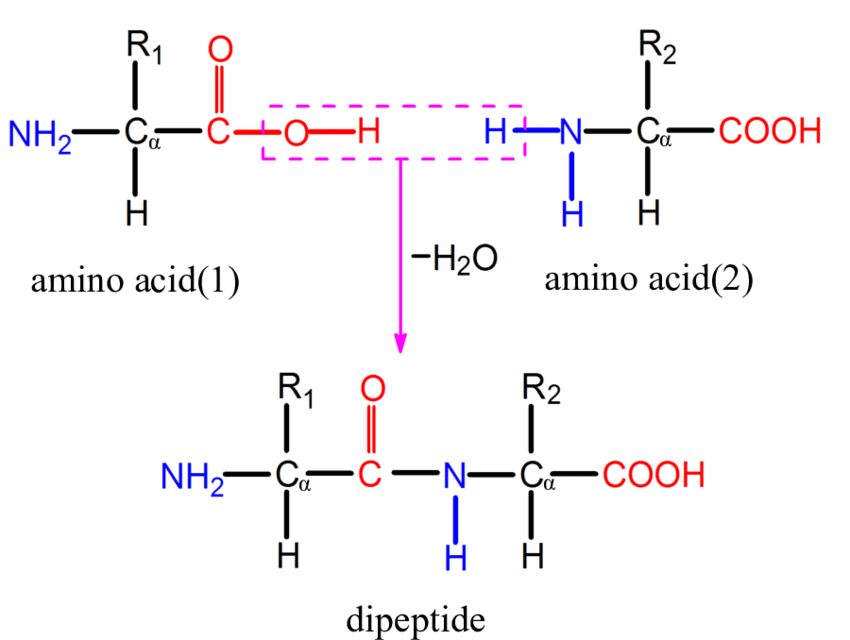
dehydration synthesis example
amino acid + amino acid - H2O = dipeptide +H2O
protein structure includes:
primary 1, secondary 2 (alpha helix and beta pleated sheet), tertiary 3, quaternary 4
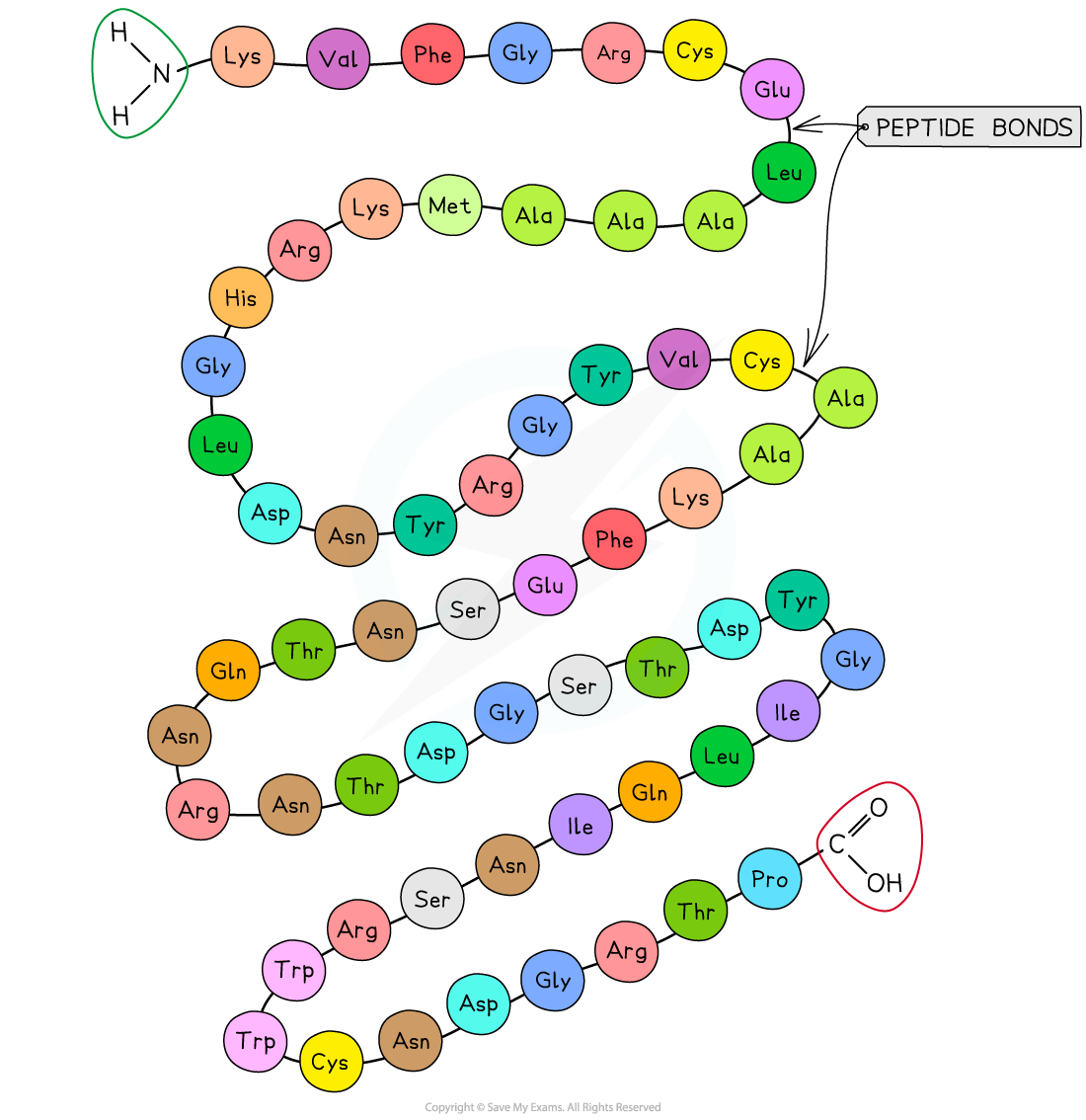
identify
primary 1
primary 1 shape
chain of amino acids released from ribosome
primary 1 bonds
peptide bonds
primary 1 example
insulin
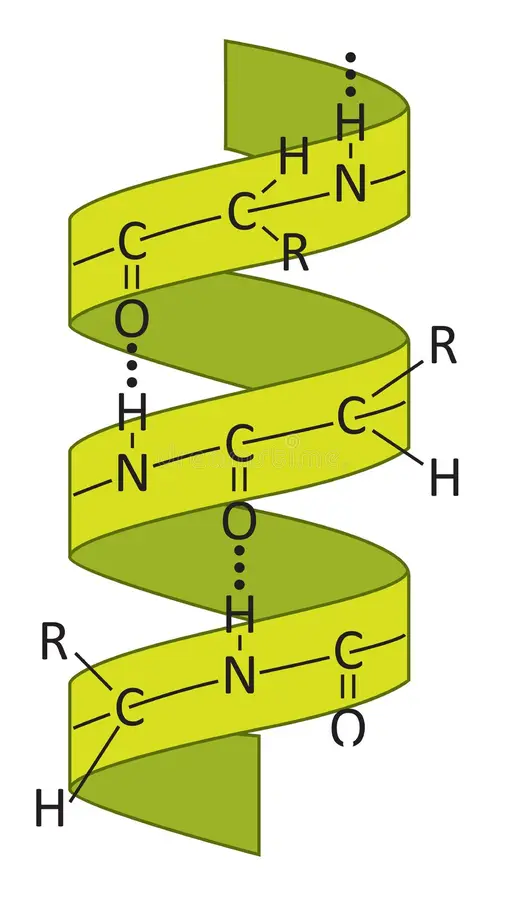
identify
secondary 2 alpha helix
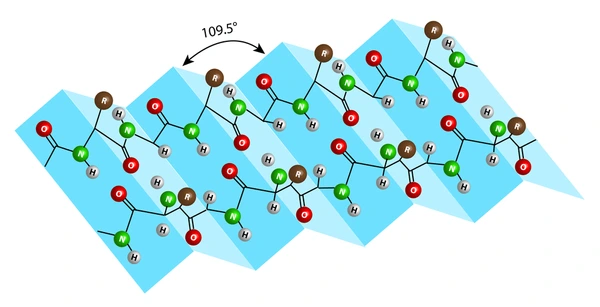
identify
secondary 2 beta pleated sheet
secondary 2 bonds
weak hydrogen bonds
secondary 2 example
fibroin
secondary composition
multiple amino acid chains (primary 1s)
tertiary 3 composition
primary, secondary alpha and beta
tertiary 3
interaction between r groups, polypeptide folds on itself
tertiary 3 bonds
vander waals, ionic bonds, h-bonds, disulfide bridge (S-S)
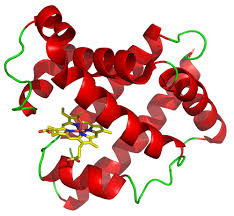
identify
tertiary 3
quaternary 4 composition
2 or more tertiary structures bonded together
quaternary bonds
vander waals, ionic bonds, H-bonds, disulfide bonds
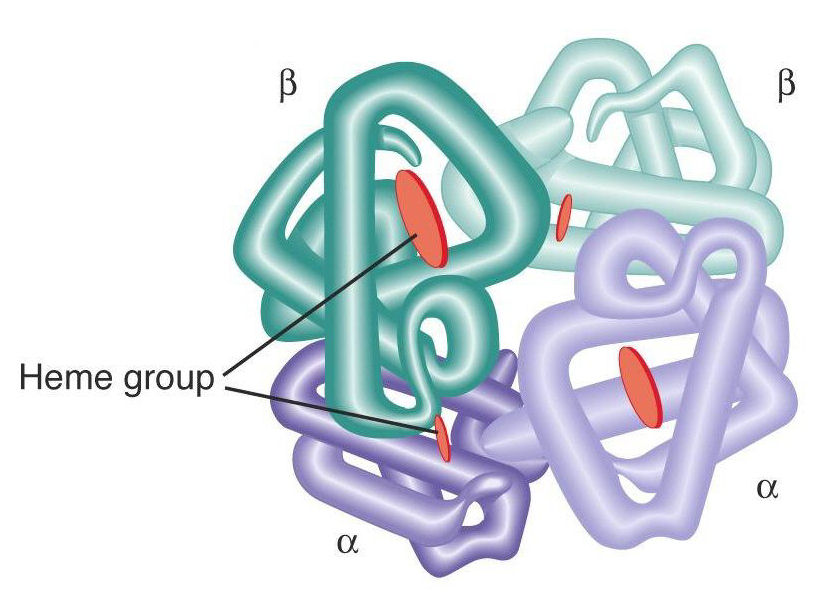
identify
quaternary 4
nucleic acid (monomer) elements
CHONP
DNA
nucleic acid that instructs protein construction and stores genetic info
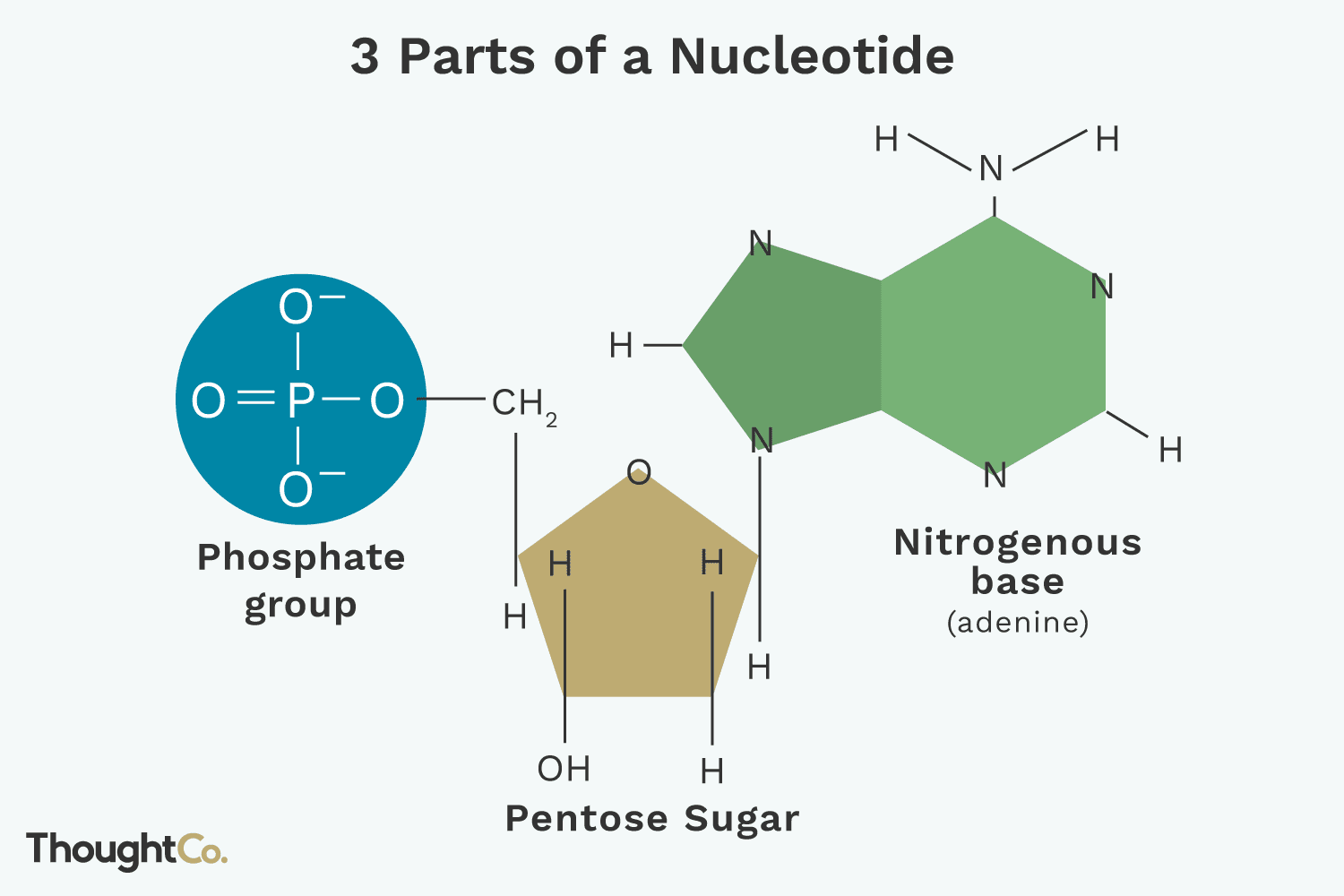
nucleotide composition
phosphate, sugar, base
RNA
nucleic acid, messenger to make proteins
DNA
double stranded
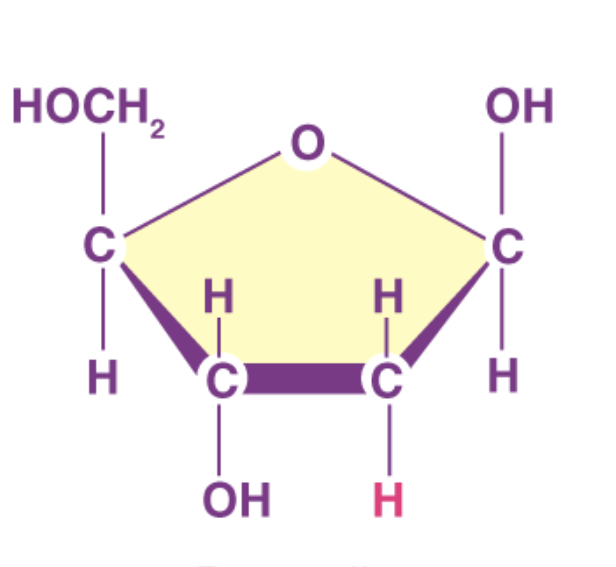
what sugar is this
deoxyribose
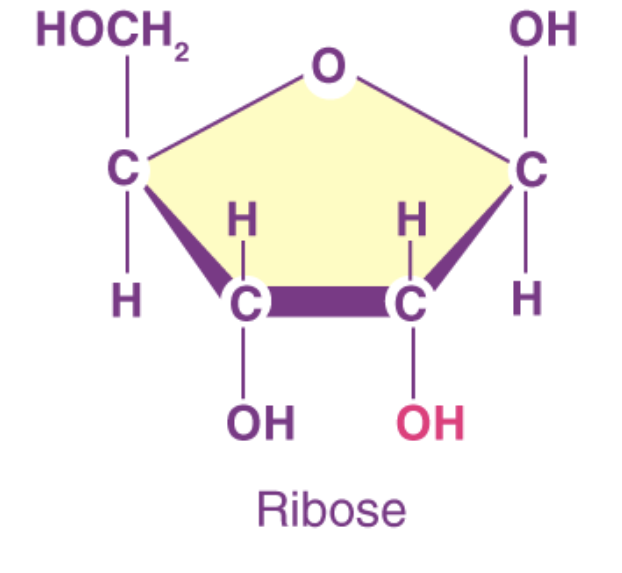
what sugar is this
ribose
quaternary example
hemoglobin
temperature, pH, concentration of salt can lead to what
denaturation
carbs found in
muscles
lipids found in
fatty tissue
proteins found in
muscles, organs, skin, and skeleton
nucleic acids found in
mitochondria, chloroplasts