Radiography/Projection Geometry/ hand
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
define radiography
conventional technique/process of using x-rays to produce a static, 2D image of internal structures of the body (radiograph; plain or projection view)
define imagining chain
components that contribute to radiographic image formation and display
what are components of the imaging chain
x-ray source: produces x-ray
image receptor: receives/detects data
image display device (for digital imaging): shows the radiograph/image
the path of radiation (x-ray beam) must include…
anatomy of interest, and receptor
radiographic image is essentially a map of…
beam attenuation
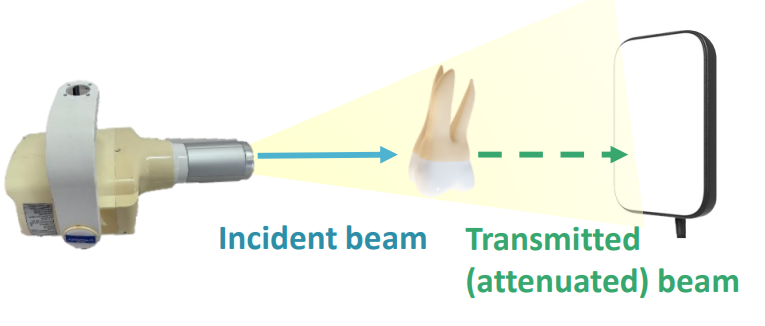
what is attenuation
reduction in x-ray beam intensity as it travels through the anatomy

the thicker and denser the structure, the more x-rays are absorbed and the ______ the beam is attenuated
more
key features of x-rays beams
consists of many x-ray photons
x-rays travel in straight lines
x-ray beam is divergent
incident beam is differentially attenuated by structures of different _______
densities
rank the following things in order of dec density: fat, air, dentin/cementum, metal, enamel, muscle, bone
metal > enamel > dentin/cementum > bone > muscle > fat > air
less attenuated structures = _____ (high/low) density
low
high attenuated structures = _______ (high/low) density
high
less attenuated structures have what appearance in radiograph formation
black: more intense transmitted beam- radiolucent
more attenuated structures have what appearance in radiograph formation
white: less intense transmitted beam- radiopaque
define density
degree of darkening or opacity of an exposed film or receptor
density depends on…
the number of x-ray photons absorbed by the receptor
in terms of density, the more x-ray photons (more intense transmitted beam)…
inc density → darker image
define contrast
range of densities on an image defined as the difference in densities between the light and dark regions
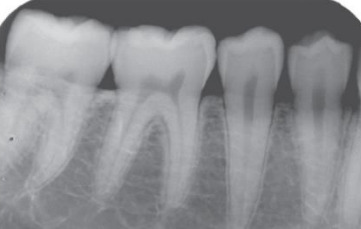
does this image have high or low contract
low
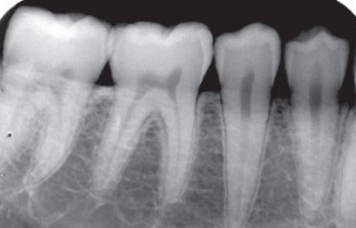
does this image have high or low contract
high
what are the two types of radiographs
intraoral and extraoral
what are the types of intraoral radiographs
PA, BWX, O
what are the types of extraoral radiographs
PANO, cephalometric and skull projections
reliability of an image in its representation of the…
true state of anatomy examined
what are the parameters of radiographic image quality (5)
image sharpness
spatial resolution
contrast resolution
magnification
distortion
image should have __________ magnification and distortion and ________ contrast and spatial resolution for the dx task
minimal; adequate
image sharpness and resolution are distinct but ___________ parameters
independent
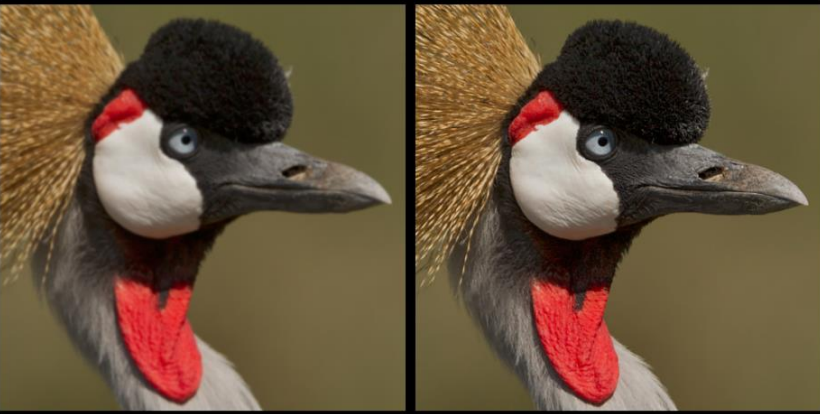

what does sharpness measure
how well a boundary between two areas of different radiodensity is revealed
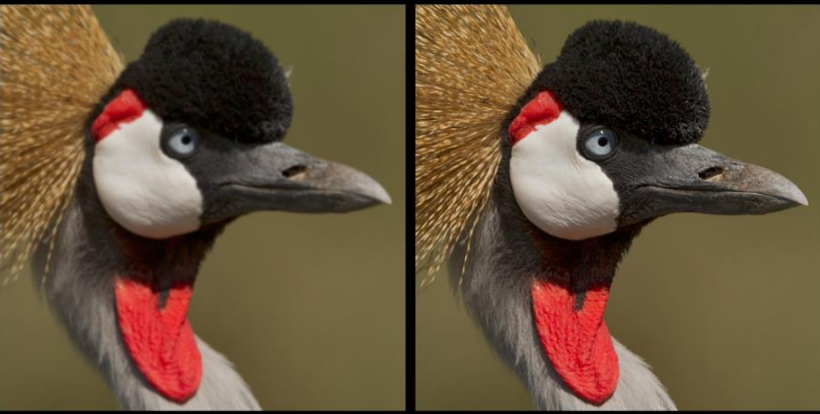

what does spatial resolution measure
how well an image reveals small objects that are close together
what is image size distortion
difference between object size on image an actual object size
what is magnification
inc of size of object on image compared to the actual size of object
what is magnification caused by
divergent paths of x-ray photons in a beam
what is image shape distortion
different in appearance of object shape on image compared to actual object shape
what is the image shape distortion a result of
unequal magnification of different parts of the same object
what are the principles of projection geometry
based on effects of focal spot size and relative positions of the object and image receptor on image clarity, magnification and distortion
when thinking of the principles of projection geometry, the focal spot should…
be as small as possible
when thinking of the principles of projection geometry, the source-receptor distance should…
be as long as possible
when thinking of the principles of projection geometry, the object-receptor distance should…
be as small as possible
when thinking of the principles of projection geometry, the receptor should be __________ (parallel/perpendicular) to the long axis of the object
parallel
when thinking of the principles of projection geometry, the central beam should be ____________ (parallel/perpendicular) to the object and receptor
perpendicular
what is a focal spot
the area on the target of the x-ray tube where x-rays are produced
x-rays originate from all points within…
the area of the focal spot
what is the focal spot range for dental PANOs and/or CT machines
0.4-0.8
a smaller focal point yields a _________ image
sharper
x-rays travel in what way
a straight line
x-rays produced at different points in the focal spot that pass through the same point on an object…
will NOT hit the same spot on the receptor causing blurring of object edges
what are the blurring edges of the object called that are caused by the x-ray being produced at different points in the focal spot
geometric unsharpness/penumbra/adumbration
a large focal spot creates…
wider zone of geometric unsharpness → loss of image sharpness
distances between the source and object and the object and recptor impact…
image sharpness and magnification
what should the source-object distance and the object-receptor distance be to get: reduced x-ray beam divergence, reduced geometric unsharpness, minimal image magnification
inc source-object distance and dec object-recptor distance
what is the magnification equation
SID= source to image (receptor) distance
SOD= source to object distance

intraoral radiographic image magnification is usually less than…
10%
magnification caused by an inc object-receptor can be minimized by inc…
the source to object distance
when does image shape distortion occur
when not all the parts of an object are at the same source-to-object and/or object-to-receptor distance
you can minimize shape distortion by…
aligning the object and image receptor parallel w each other
aligning the central ray perpendicular to both the object and image receptor
physical shape of an object may prevent optimal orientation, resulting in…
some shape distortion (max molar root divergence prevents placing all roots parallel- palatal root appears disproportionally longer)
what is foreshortening
radiographic image of object is shorter than the true object
what can cause foreshortening
the object is not parallel to the receptor
the central ray is perpendicular to receptor but not to the object
what is elongation
radiographic image of an object is longer than true object
what can cause elongation
object is not parallel to the receptor
central ray is perpendicular to the object but not the receptor
to maximize image sharpness… (3)
use a small focal spot as practical (determined by manufacture)
inc the source-object distance
minimize the object-receptor distance
define selection criteria
circumstances that suggest a need for dx imaging
imaging is needed/indicated when…
there is clinical evidence of abnormality that cannot be fully assessed by only a physical exam
there is a high probability of disease that is not clinically evident
before taking images, you should… (3)
know your dx objectives
determine which images will help achieve the goals
have justification for why you expose your pt to ionizing radiation
what are the three quality criteria for radiographs
record the complete area of interest in the image
have the least possible amount of distortion
have optimal density and contrast to facilitate interpretation
what is the backbone of dental dx imaging
intraoral radiographs
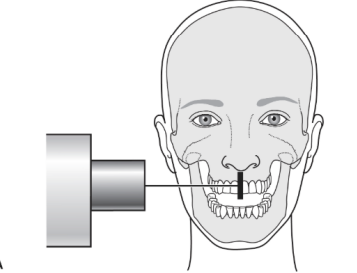
what is a periapical radiograph (PA)
projections show entire tooth length and surrounding peri-radicular bone
what are the two projection techniques of periapical x-rays, which is preferred?
paralleling and bisecting angle; parallel is preferred
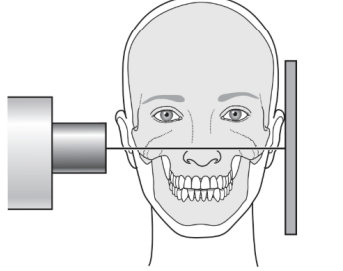
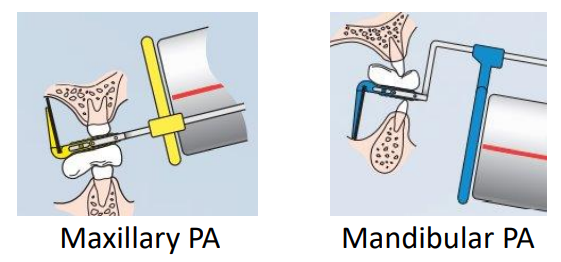
what is the paralleling technique (AKA right-angle, long-cone or extension cone technique)
position receptor parallel to the long axis of the tooth; use receptor holding instrument to hold receptor in place and guide ring to aid in cone alignment
to achieve the parallel technique, the receptor placement must be placed…
away from the teeth toward the midline
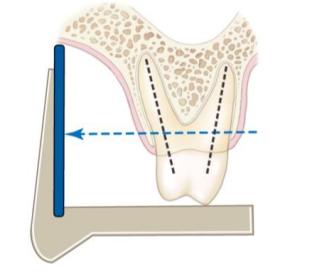
when trying to accomplish the parallel technique, there may be anatomical constraints such as…
shallow palate or vestibule, tori
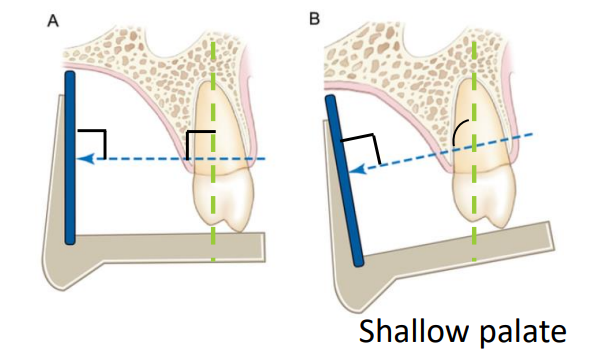
the use of the parallel technique has inc ________________ distance; what can be used to compensate for this inc distance
object-receptor; a long cone positioning indicating device (PID)
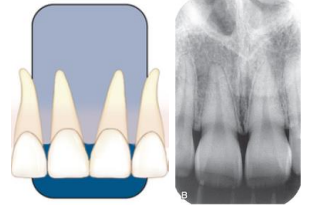
what is a bitewing radiograph (BWX)
projections show only the crowns of the teeth and adjacent alveolar crests
what is an occlusal radiograph
projections show an area of teeth and bone larger than PA images
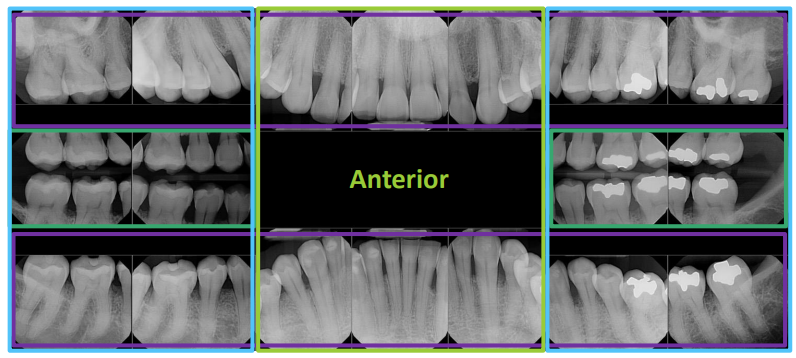
what is a full-mouth radiographic series (FMX)
includes a “survey” of the whole mouth intended to display the crowns and the roots of all teeth, PA areas, interproximal areas and alveolar bone (including edentulous areas); consists of PAs and BWXs; 18-20 images- 4 BWXs and 14-16 PAs
what are the types of x-ray sources
wall/ceiling mounted
hand-held
what is the difference w the operator in a wall/ceiling mounted vs hand-held x-ray source
wall/ceiling: exposure is made while operator is outside of the operatory
hand-held: operator is in the room holding the source wh
what is a position indicating device (PID)
attached to tubehead aperture to direct x-ray beam, usually an open-ended cylinder: “cone” or “aiming cylinder”
what is the job of the receptor
detects/records x-rays; only 1 active side that needs to face the source
what are the two types of receptors
film and digital
what are the two types of digital receptors
direct and indirect
what is the difference between direct vs indirect digital receptors
indirect receptors first convert X-rays to light, then to an electrical signal, while direct receptors convert X-rays directly into an electrical signal
is photostimulable phosphor plate (PSP) direct or an indirect digital receptor
indirect receptor
is solid state, direct digital sensor (CCD/CMOS, corded) a direct or indirect digital receptor
direct receptor
size 0 receptor
pediatric
size 1 receptor
pediatric, small mouth, narrow arch (anterior teeth)
size 2 receptor
most used; posterior teeth
size 4 receptor
occlusal
is the bisecting or the parallel technique used more
parallel
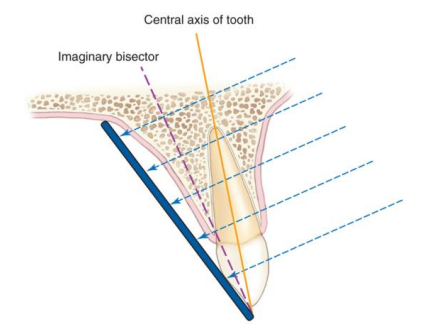
what is the bisecting technique generally
useful when parallel cannot be applies; receptor is placed as close to the tooth as possible and use your imagination to make a bisecting angle between the long axis of teeth and the long axis of the receptor, and align the x-ray tubehead to be positioned at a right angle to the bisecting line
what is vertical angulation
angle between the x-ray bean and line parallel to floor/occlusal plane
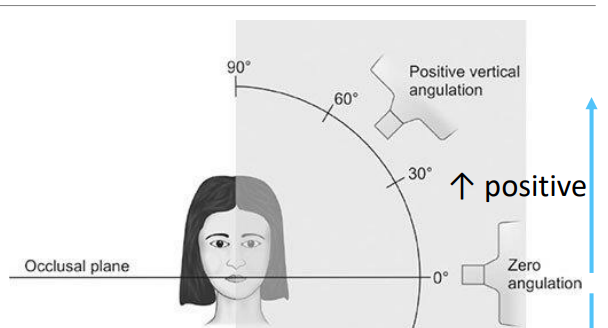
what does positive angulation mean
cone points downward
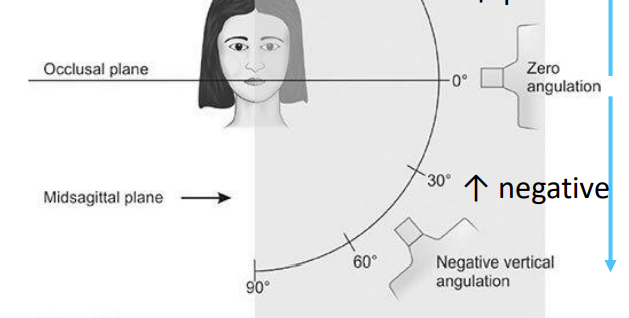
what is negative angulation
cone points upward
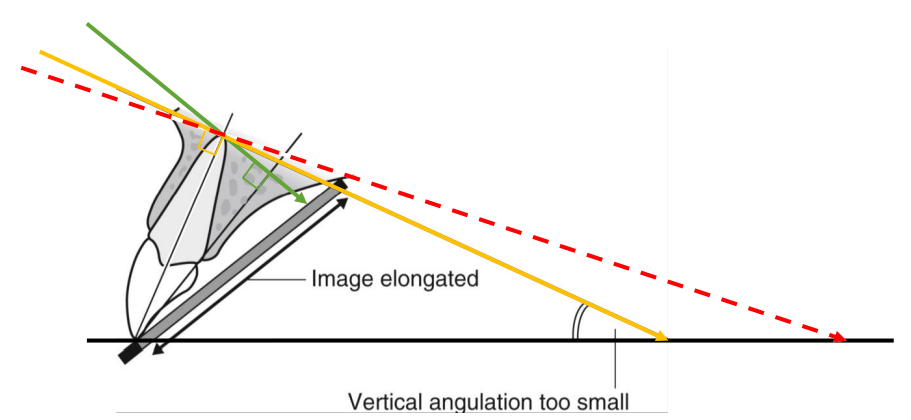
what is elongation, what is it caused by
vertical angle too small; under-anggulation
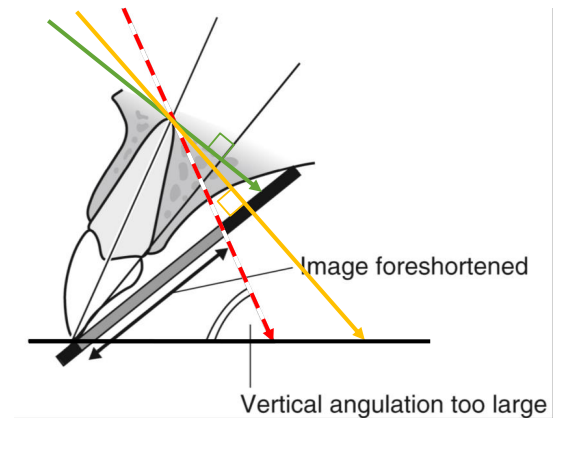
what is foreshortening, what is it caused by
vertical angle too large; over-angulation
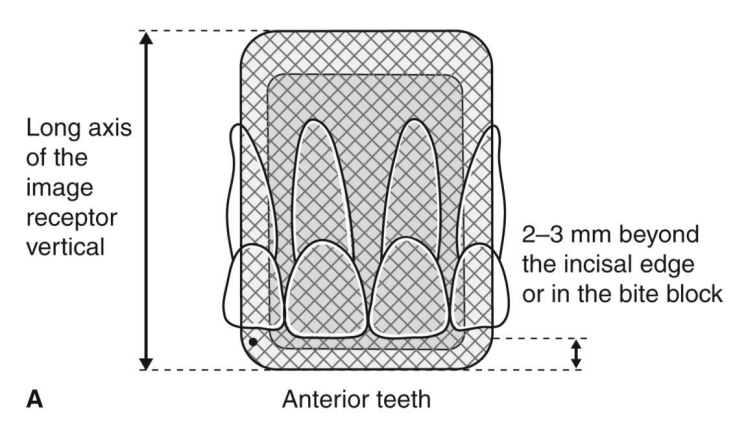
what is the PA orientation of an anterior tooth
long axis of the image receptor is vertical
what is the PA orientation in posterior teeth
long ais of the image receptor is horizontal
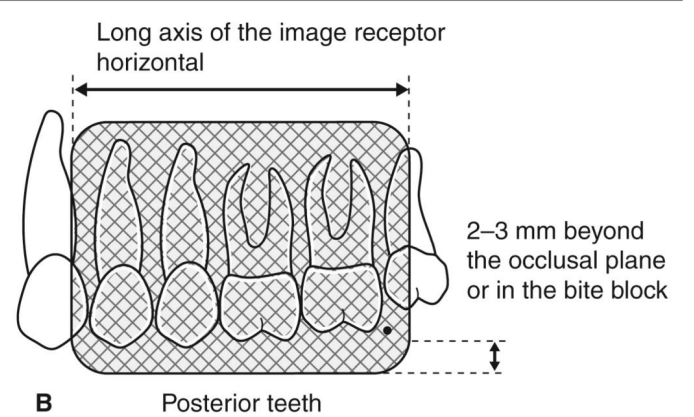
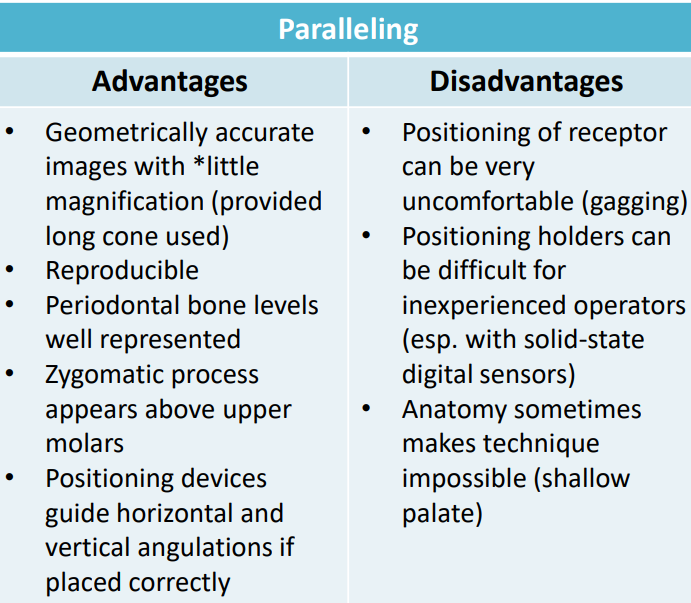
paralleling advantages and disadvantages
!