Unit 2 Part 1 APPsych Study Set
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
metacognition
thinking about our thinking
cognitive bias
systematic way of thinking that interferes with a person’s ability to draw rational and objective conclusions
skew perceptions, judgements, decision making, and problem solving
concepts
mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
can for hierarchies from concepts
prototypes
a mental image of the best example of a specific concept or category
schema
a mental representation of a set of connected ideas
framework for several related concept
influenced by our assumptions, stereotypes, and expectations
assimilation
allows us to make sense of new info/situations by relating it to our existing schemas
accommodation
occurs when we take in new information and then change the schema in order to incorporate that new information
executive functions
a set of cognitive processes that help us manage and coordinate our thoughts and actions and achieve goal-directed behavior
prefrontal cortex plays a key role in these processes
algorithms
specific set of step by step instructions for problem solving
heuristics
mental shortcut
faster but may lead to incorrect outcomes
ex: choosing a restaurant based on the waiting line or how filled up its parking lot is
representativeness heuristic
use to judge how closely something represents, or matches, our prototype for a given category
availability heuristic
estimates the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind, we presume such events are common
ex: car crashes vs. airplane crashes
confirmation bias
cognitive bias
tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or dismiss contradicting evidence
ignoring the red flags
mental set
tendency to approach decision-making in a particular way based on past experiences, habits, or previously successful strategies
can prevent us from exploring new approaches or alternative points of view
priming
unconscious, so we might not realize when something influences our decisions
involves exposing people to certain stimuli that unconsciously influence subsequent behavior or decisions
framing
a cognitive bias in which the way the information is worded influences how people perceive it and the decisions they make related to it
gambler’s fallacy
occurs when people believe that the outcomes of random events are influenced by previous outcomes, even when they are actually independent
ex: coin toss
sunk-cost fallacy
occurs when people continue investing resources into a project or endeavor because they have already invested significant resources, even when continuing to invest would not be rational based on the current circumstances
sunk costs should not effect our decision making
creativity
ability to produce novel and valuable ideas within any discipline
convergent thinking
in which a question has only one correct answer, limits creativity
divergent thinking
which is involved when a question or problem can have many possible responses, promotes creativity
functional fixedness
hinders creativity
cognitive bias that limits a person’s ability to see alternative uses for familiar objects or to think about problems in a novel way, they instead are fixated on the common use or function for that object
recall
must retrieve info learned earlier
fill-in-the-blank test
recognition
identification of previously learned items
multiple choice test
relearning
assesses the amount of time saved when learning material again
reviewing previously learned material
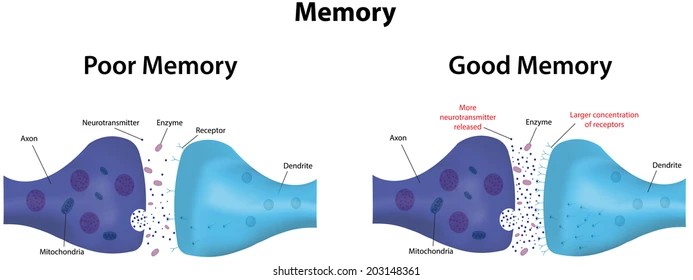
long-term potentiation
increased efficiency in neural firing which can result from repeated connections between neurons
encode
get info into our brain
store
retain encoded info over time
retrieve
later get the info back out of our brain
three stage multi-store model
sensory memory
short-term/working memory
long-term memory
sensory memory
immediate
very brief recording of info picked up by our sensory organs
short-term memory
temporarily holds a few select items in consciousness before it is either stored or forgotten
requires rehearsal and active maintenance
can hold 7 ± 2 pieces of info
long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system; includes knowledge, skills, experiences
iconic memory
eye-conic
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli
few tenths of a second long
echoic memory
echo/sound
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
if attention is elsewhere a sound or words can be recalled for 3-4 seconds
capacity
amount of information that the memory storage can hold
capacity of sensory memory is essentially unlimited
effortful processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
has to go from STM to LTM
automatic processing
this encoding does not require attention and conscious effort
can go straight from SM to LTM
automatic processing track
creates implicit memories
non-declarative, so well learned
classically conditioned associations among stimuli
effortful processing track
creates explicit memories
declarative memories, involve facts and experiences that one consciously know and declare
1st type of effortful processing ~ Semantic memories
facts and general knowledge
2nd type of effortful processing ~ Episodic memories
events in one’s own past
role of selective attention
information which is not novel or important enough to gain our attention may be lost or forgotten rather than transferred to STM
working memory
is like an active scratchpad for the STM as we consciously analyze new information received in our working memory, we retrieve relevant information from our LTM storage
subsystem of the central executive ~ phonological loop
briefly holds auditory information as you engage in active, conscious processing
subsystem of the central executive ~ visuospatial sketchpad
briefly holds information about an objects appearance and location in space as you engage in active, conscious processing
Maintenance rehearsal
info is repeated to keep it actively present in the working memory for a brief period, such as saying something over and over again
helps temporarily hold info
elaborative rehearsal
cognitive strategy
actively connect new info to existing knowledge in your LTM by creating meaningful associations, images, or stories, which help transfer info from STM to LTM
LTM holds…
both implicit and explicit memories and is essentially limitless
parallel processing
processing multiple aspects of a stimulus or a problem simultaneously
typical for implicit memories
Sequential processing
processing one aspect o a stimulus at a time
typical for explicit memories
shallow processing
focuses on superficial elements of words, such as sound or appearance
less durable memory
rehearsal, but memory won’t last long
structural encoding - shallow processing
based on physical appearance of a word
phonemic encoding - shallow processing
based on the sounds of the word
deep processing
involves semantic encoding, involving the meaning of the word
deep processing leads to better retention
chunking ~ semantic
organizing info into familiar, manageable units enables us to recall it more easily
mnemonics ~ semantic
memory aids
vivid imagery helps
method of loci
visualize a familiar location and mentally place items you want to remember in that space
hierarchies
organizing knowledge
broad concepts being divided and subdivided into narrower concepts and facts
distributed practice
retain info better when our encoding is distributed over time
spacing effect
the tendency for distributed study/practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study/practice aka cramming
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading info
memory consolidation
neural process of converting STM into LTM
can happen while awake or while sleeping
involves strengthening neural connections through long-term potentiation
method of loci
visualize a familiar location and mentally place items you want to remember in that space
hippocampus importance in memory
seems to act as a loading dock where the brain registers and temporarily holds info until it is transferred for storage elsewhere
case study of Henry Molaison (HM)
hippocampus was removed in hopes of reducing seizures
couldn’t form NEW LT explicit memories
could still perform cognitive tasks, working memory was functioning
could still learn new skills because procedural memory uses different part of brain
infantile amnesia
we have almost no conscious memory of our first 4 years
why:
hippocampus is 1 of the last brain structures to mature
we index much of our explicit memory w/ a command of language that young children do not yet possess
retrospective memory
refers to remembering experiences or info we learned in the past
prospective memory
pertains to our intended future actions; in other words, its concerned w/ remembering to do something in the future
ex: you need to text someone before you go out, perhaps you’d put your phone next to the door
priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of particular associations in memory
can influence our decision making w/out our awareness