Ventricular System and Blood Supply
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
what is the purpose of the ventricular system?
it is a network of cavities that produce and contain cerebrospinal fluid
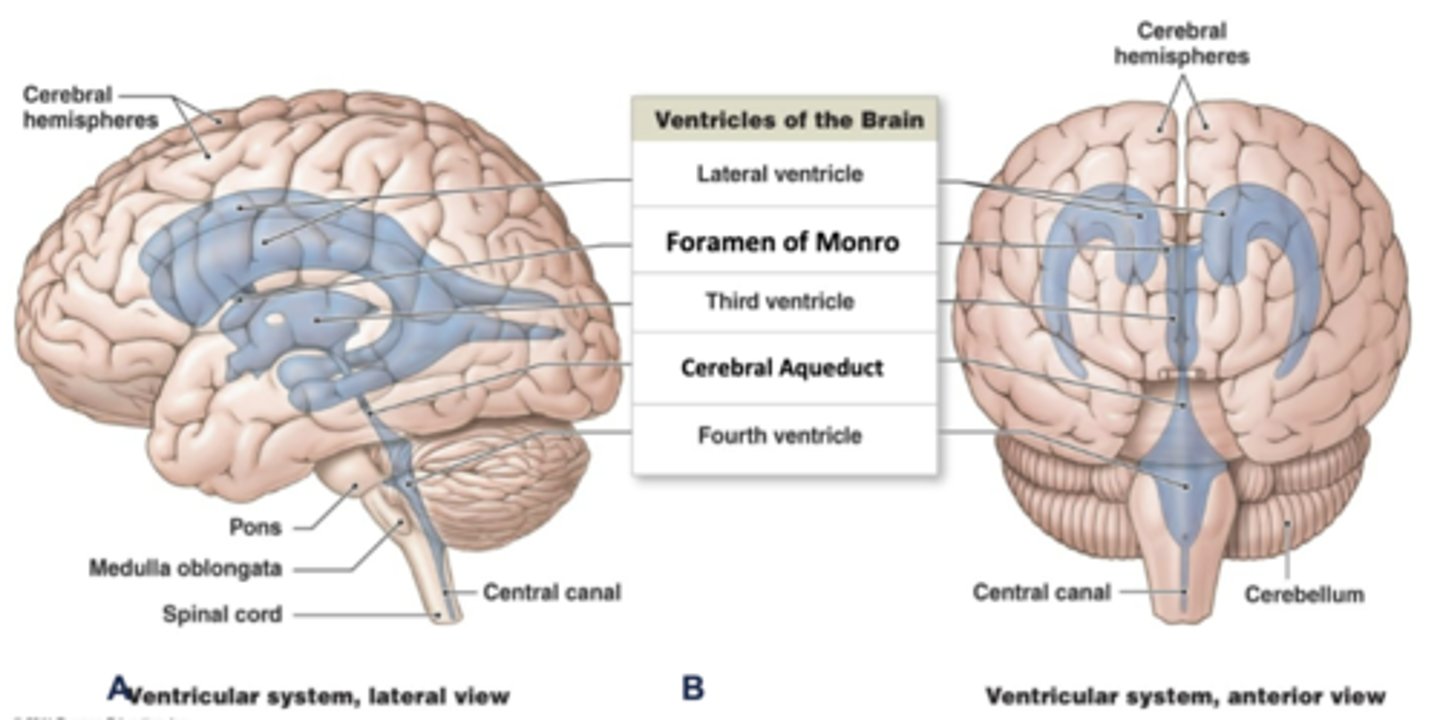
how many ventricles are there in the brain?
4
(2 lateral, 3rd, and 4th)
through what structure do the lateral ventricles transport cerebrospinal fluid to the 3rd ventricle?
foramen of monro
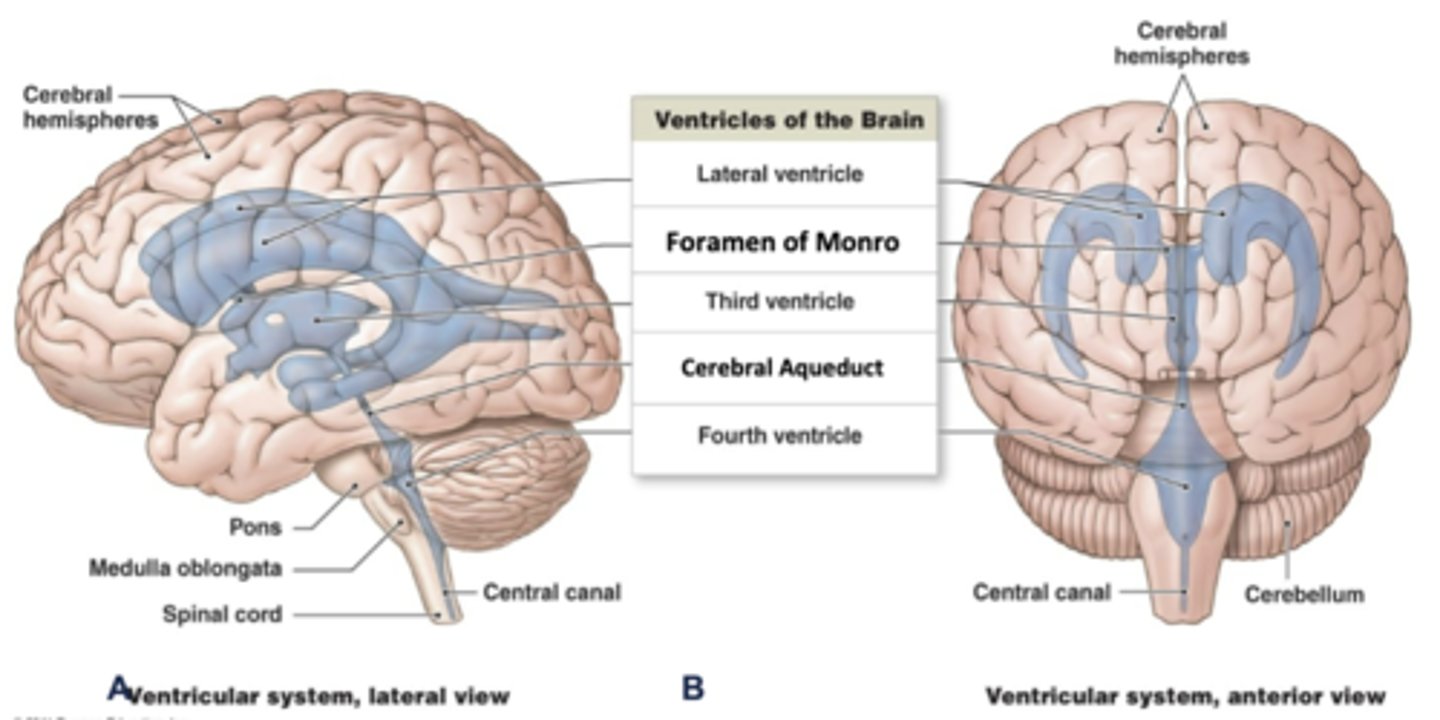
the lateral ventricles transport CSF to the ______ ventricle
3rd
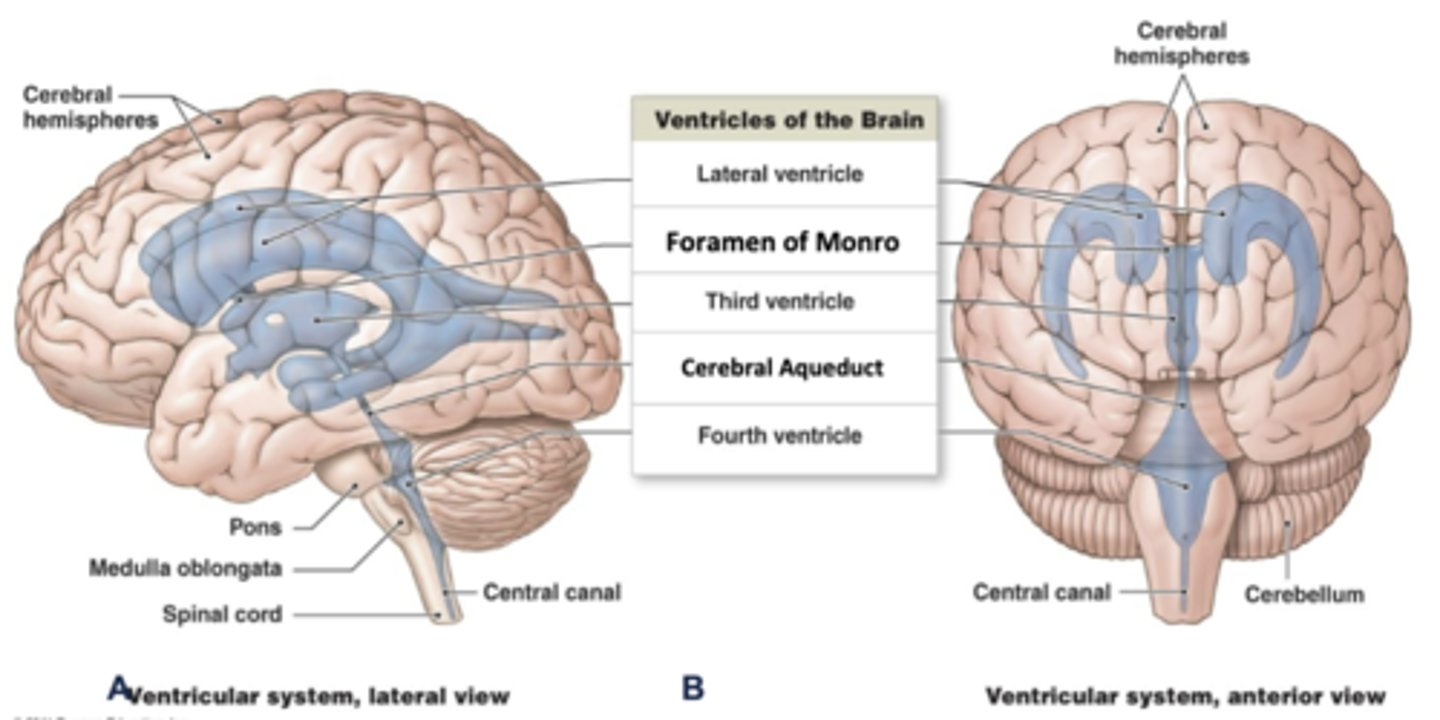
where are the 2 lateral ventricles located?
in the cerebral hemispheres (1 in each)
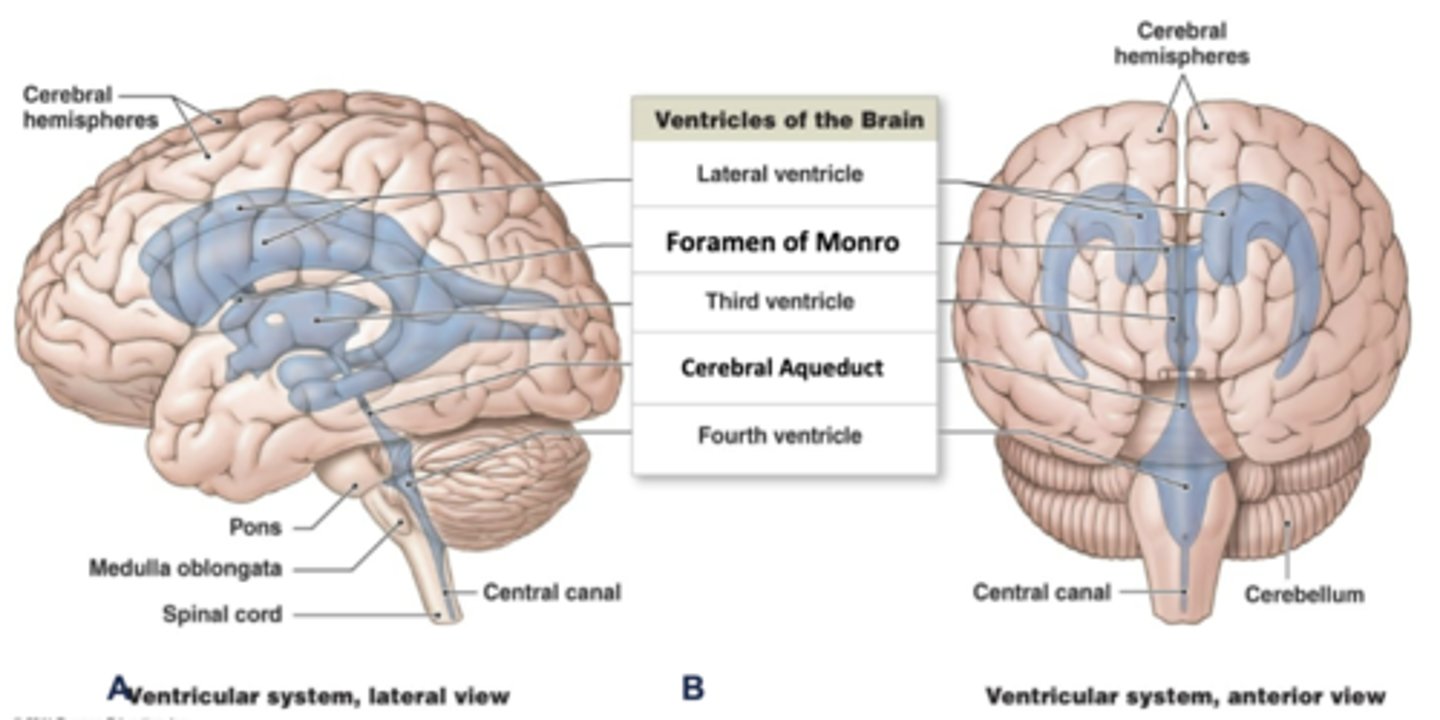
describe the shape of the lateral ventricles:
the have a "C" shape with 3 horns (anterior, posterior, inferior)
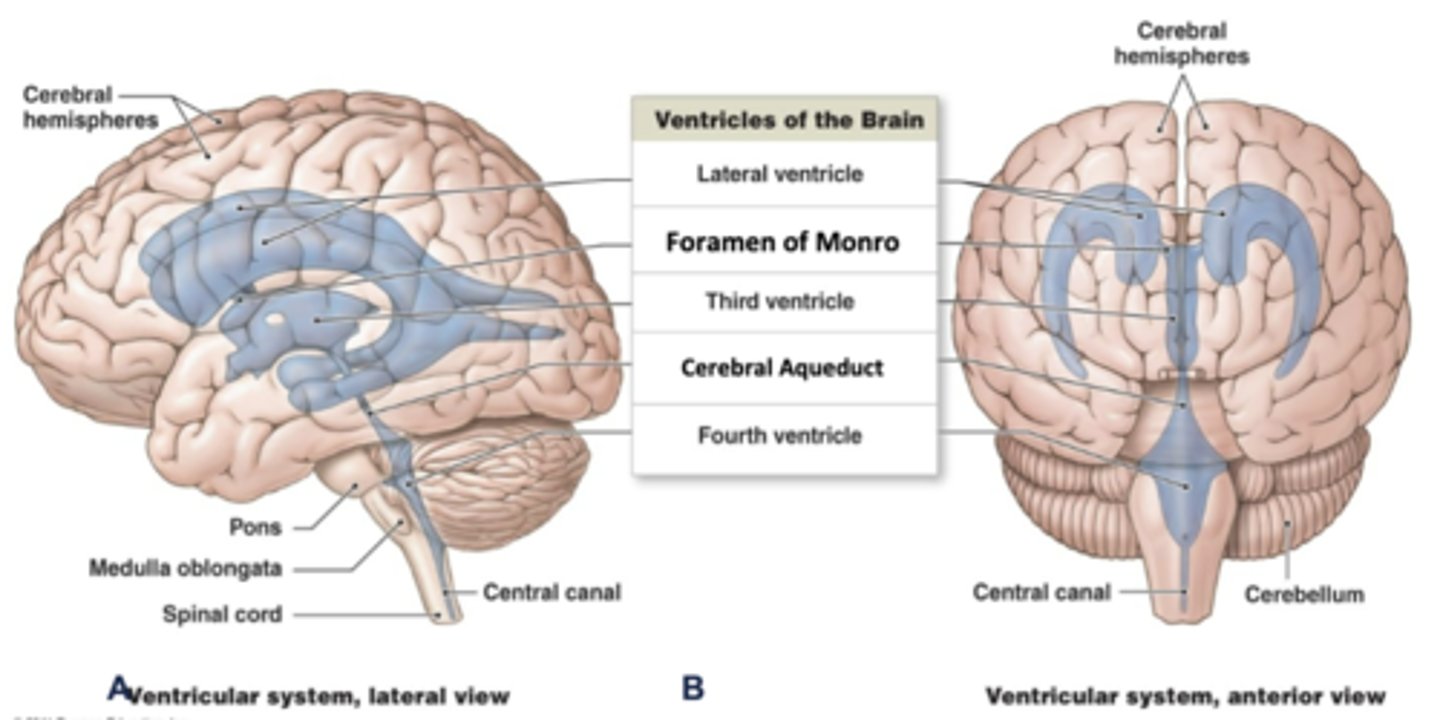
where is the 3rd ventricle located?
diencephalon
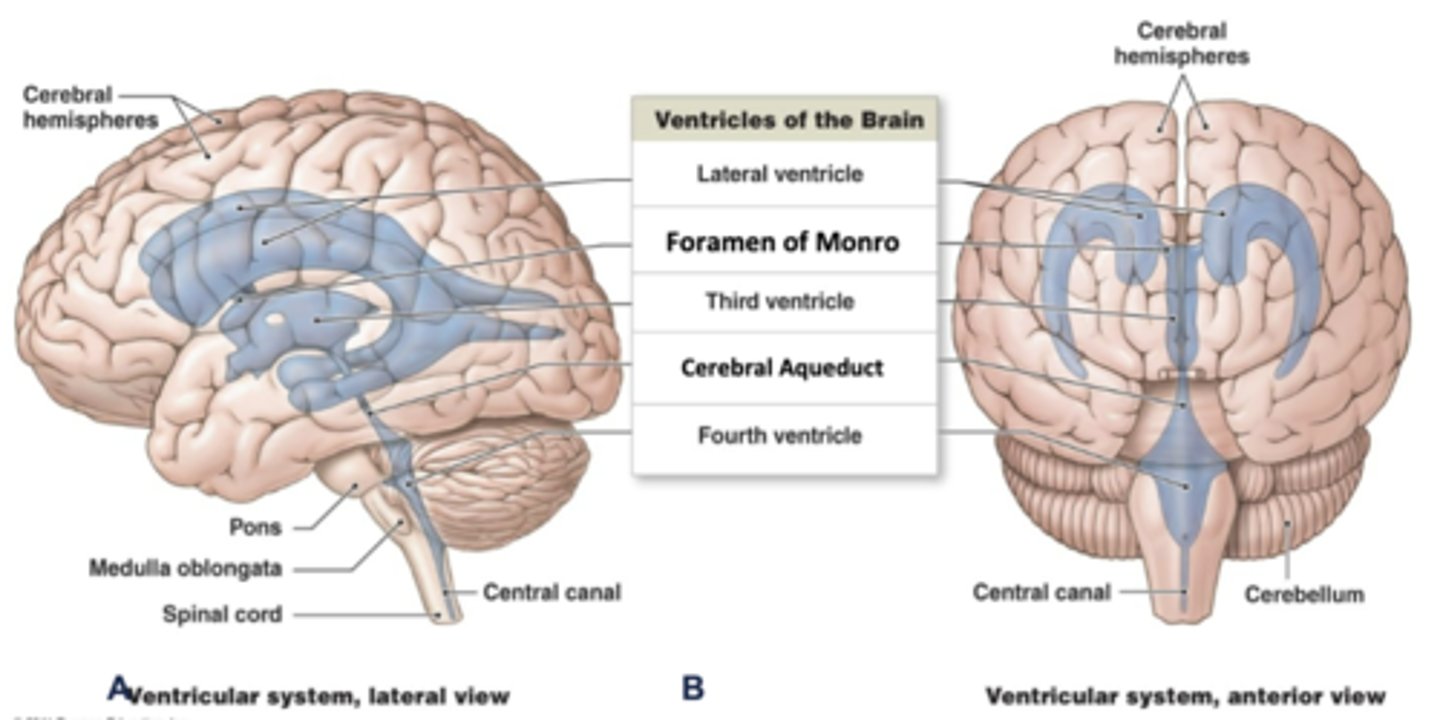
through what structure does the 3rd ventricle transport cerebrospinal fluid to the 4th ventricle?
cerebral aqueduct
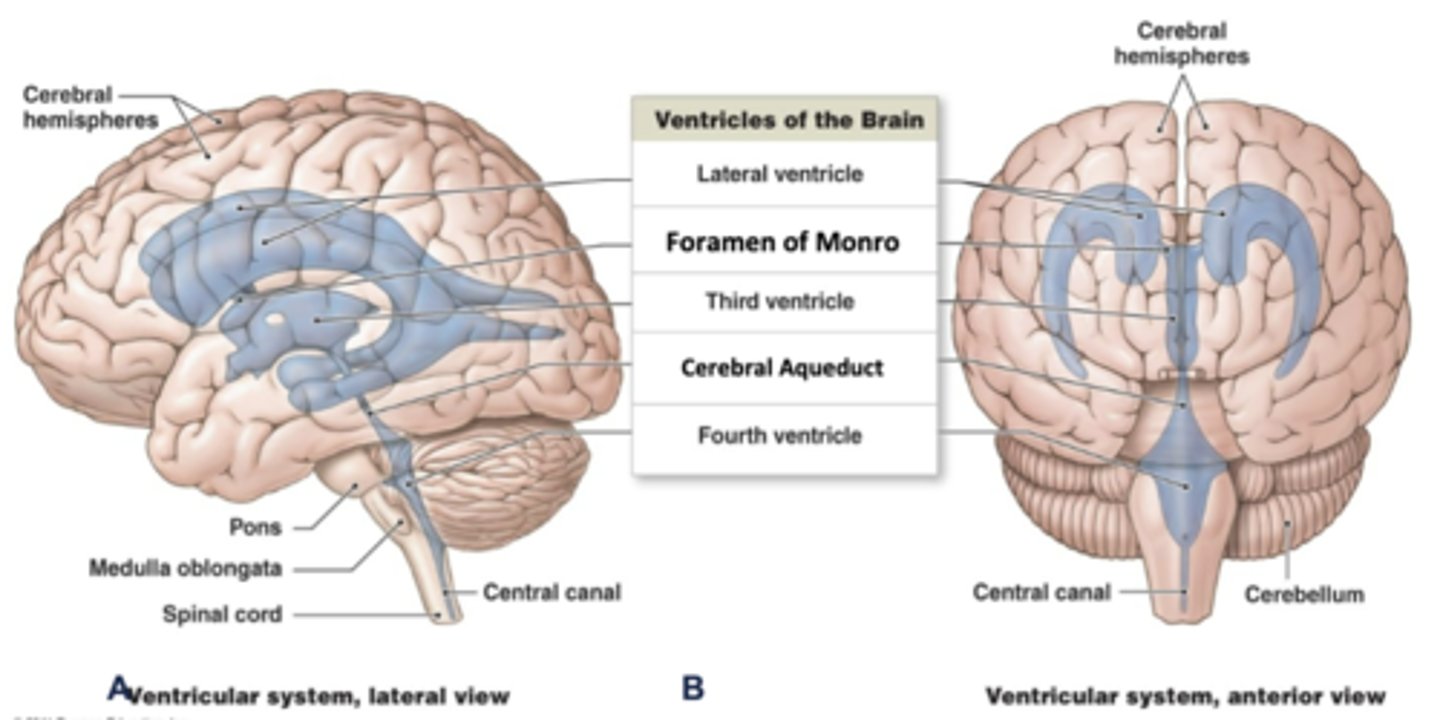
where is the cerebral aqueduct located?
midbrain
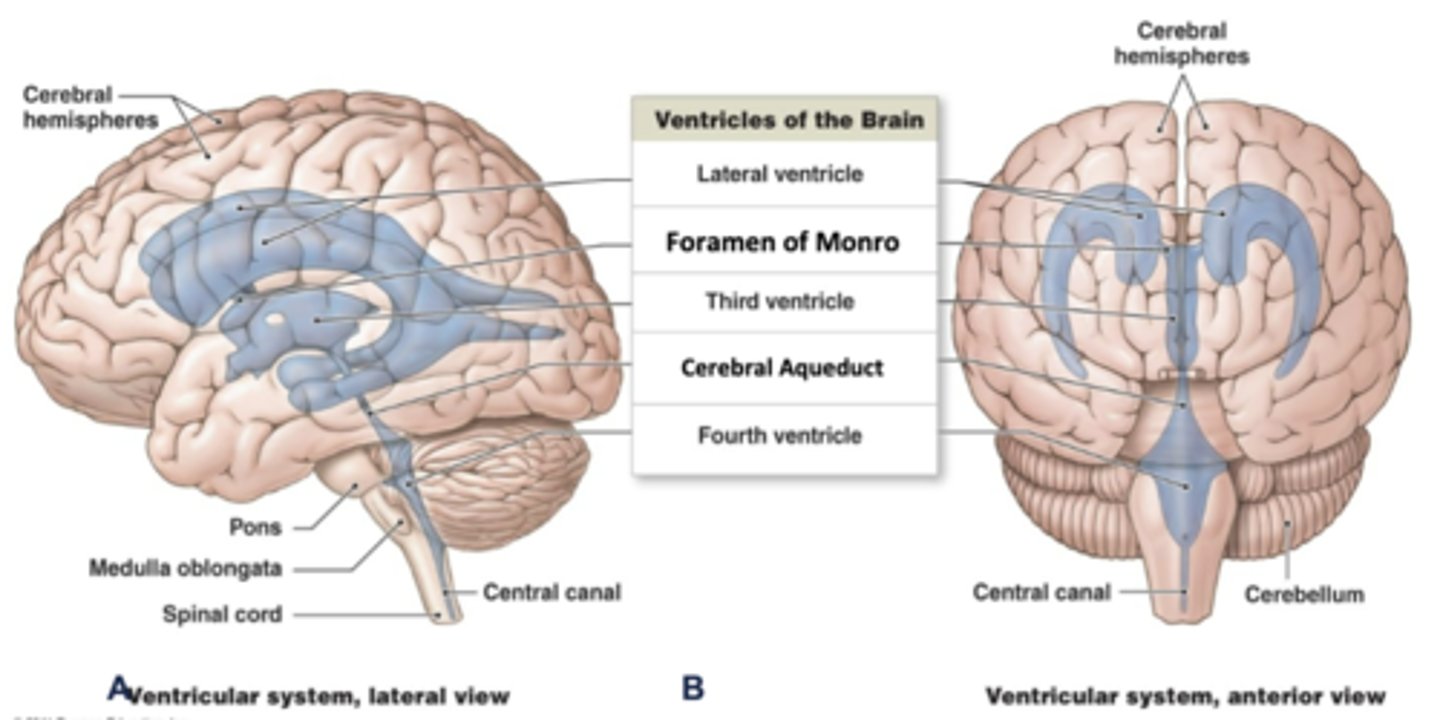
where is the 4th ventricle located?
pons/medulla
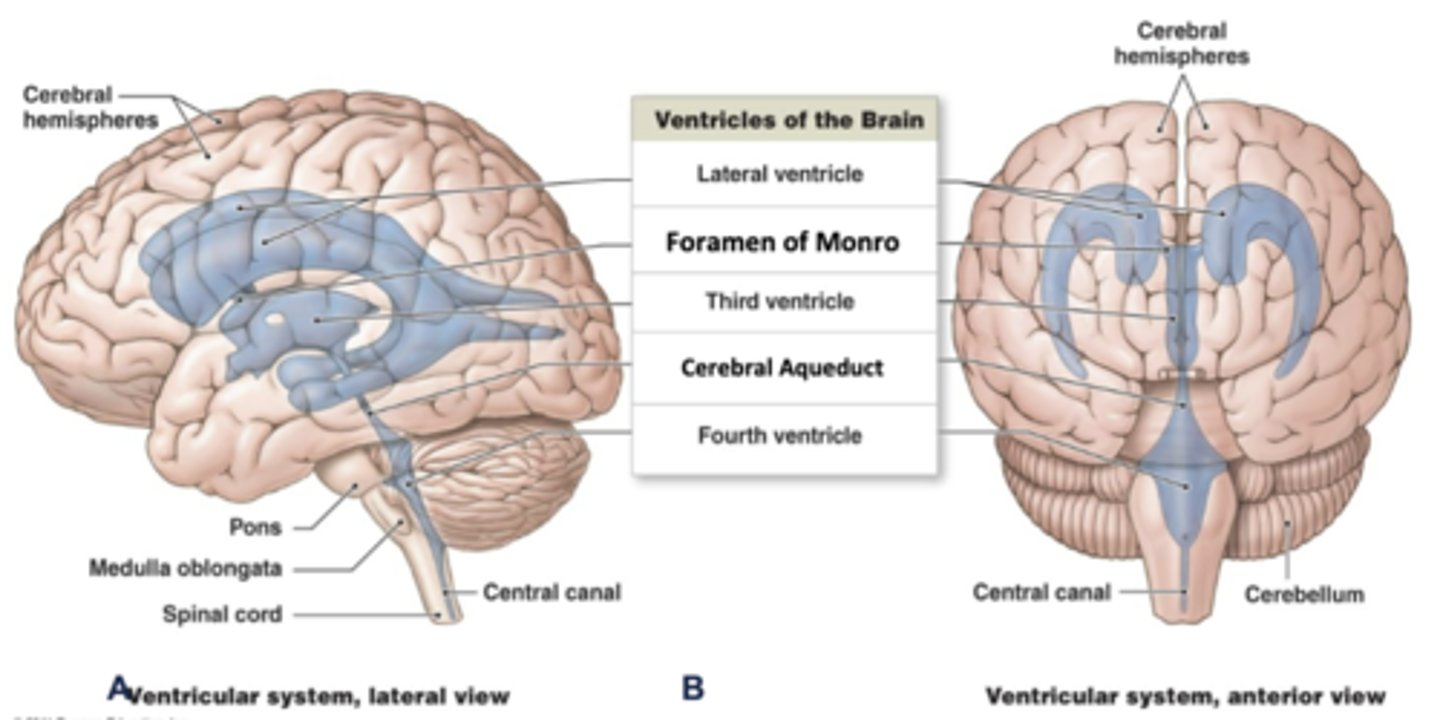
what is the continuation of the ventricular system into the spinal cord called?
the central canal
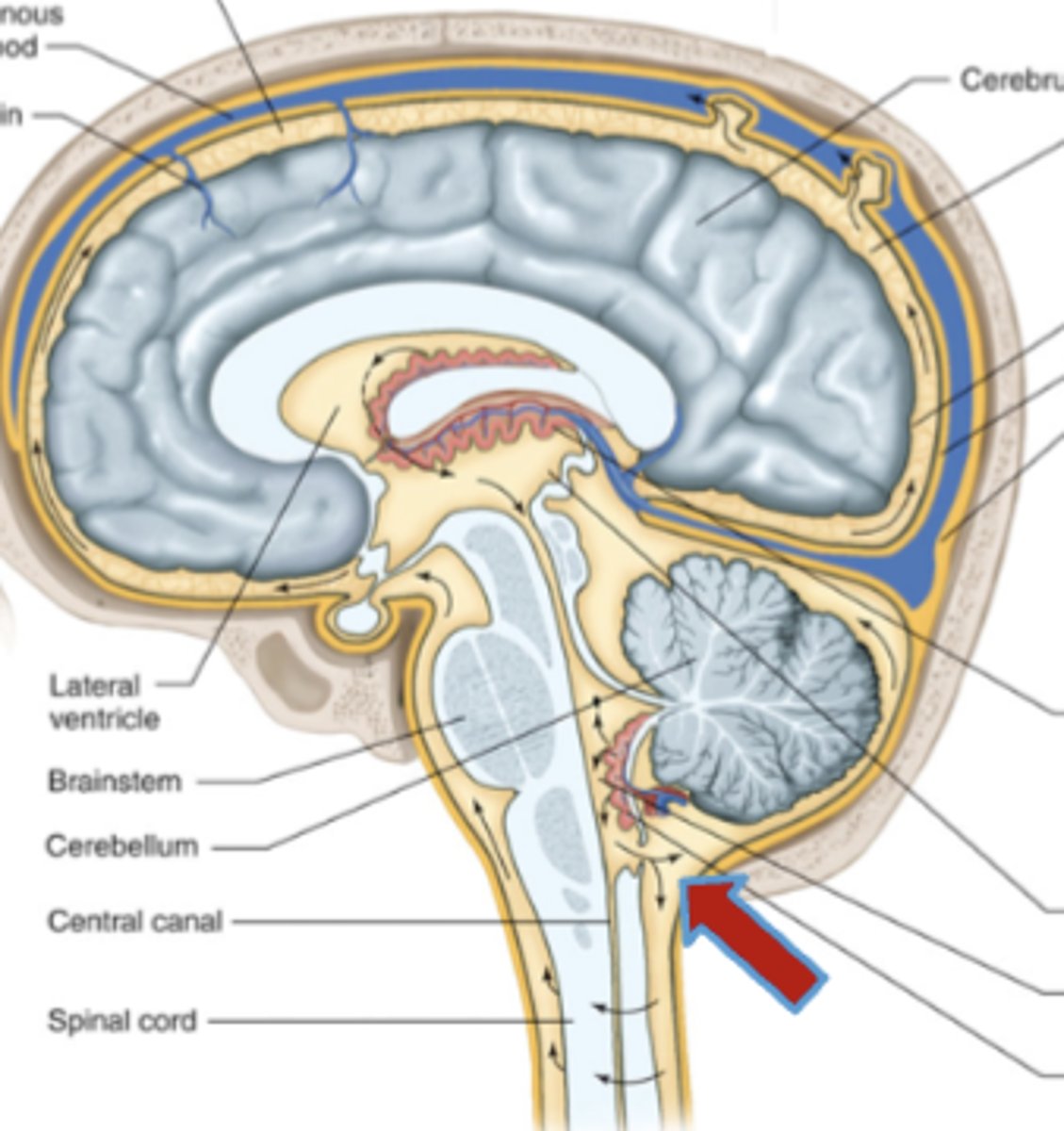
what structure specifically makes cerebrospinal fluid?
specialized ependymal cells in the choroid plexus (located in each ventricle)
CSF flows through the ventricular system and drains into what structure/space?
via holes in the 4th ventricle, it drains into the subarachnoid space
what are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid?
1. acts as a "shock absorber" to protect CNS from traumatic injury
2. provides nutrients to the CNS tissues
describe the pathway of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain:
lateral ventricles --> foramen of monro --> 3rd ventricle --> cerebral aqueduct --> 4th ventricle --> central canal of spinal cord
once external to the brain, how does cerebrospinal fluid get reabsorbed?
gets reabsorbed into venous blood at arachnoid granulations into cerebral sinuses
where is the subarachnoid space located?
in between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater
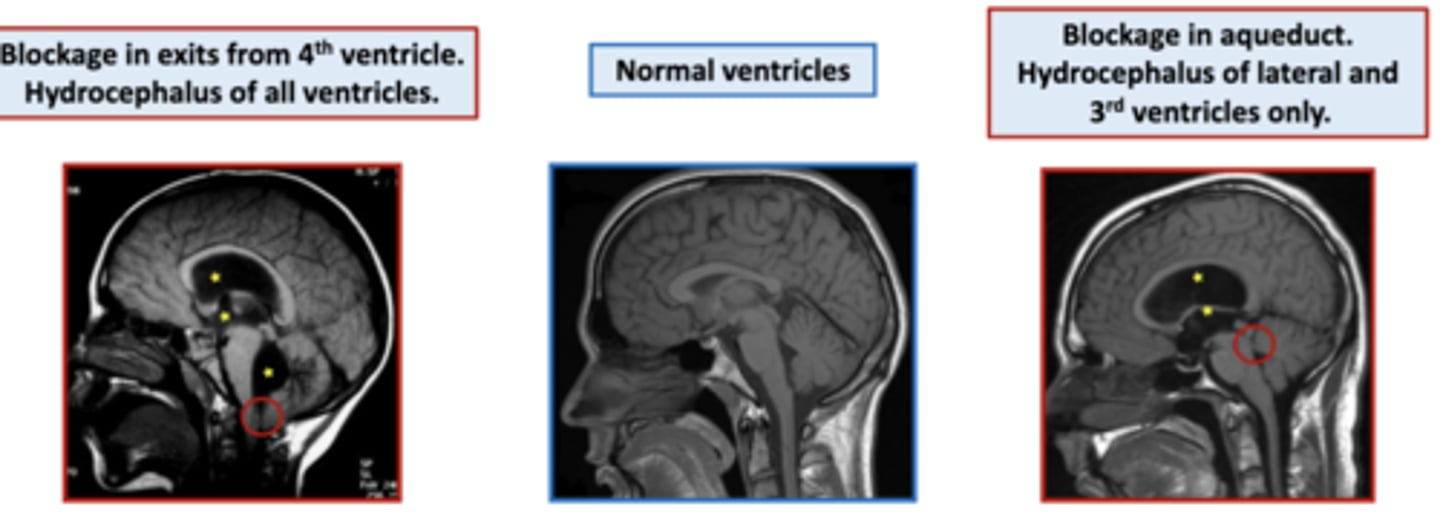
what is hydrocephalus?
increased CSF in the ventricles and/or the subarachnoid space due to blockage of CSF flow
wherever the blockage is, there will be increased CSF in the ventricles superior to it
what arteries supply the anterior circulation to the brain?
internal carotid arteries
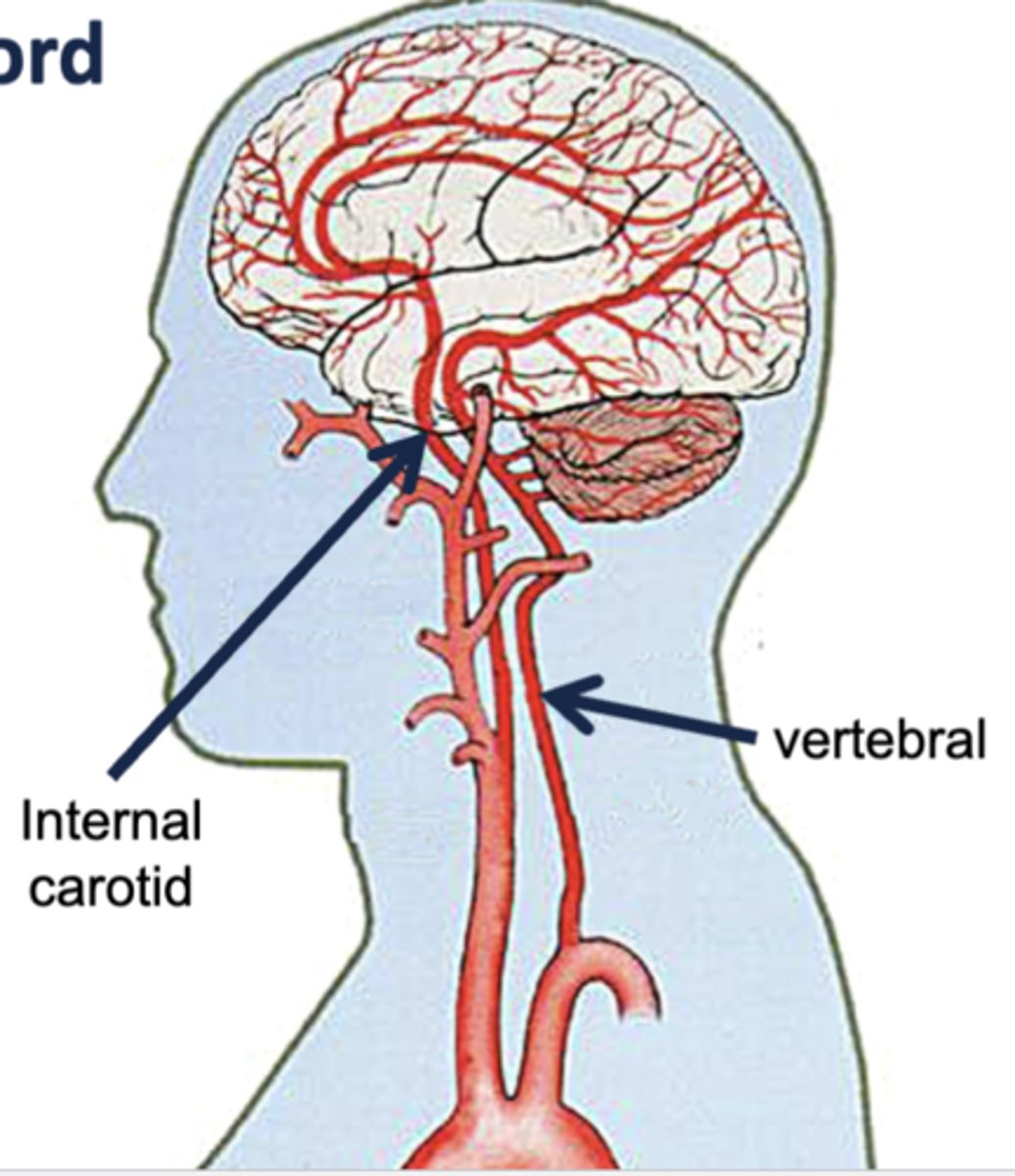
what arteries supply the posterior circulation to the brain?
vertebral arteries
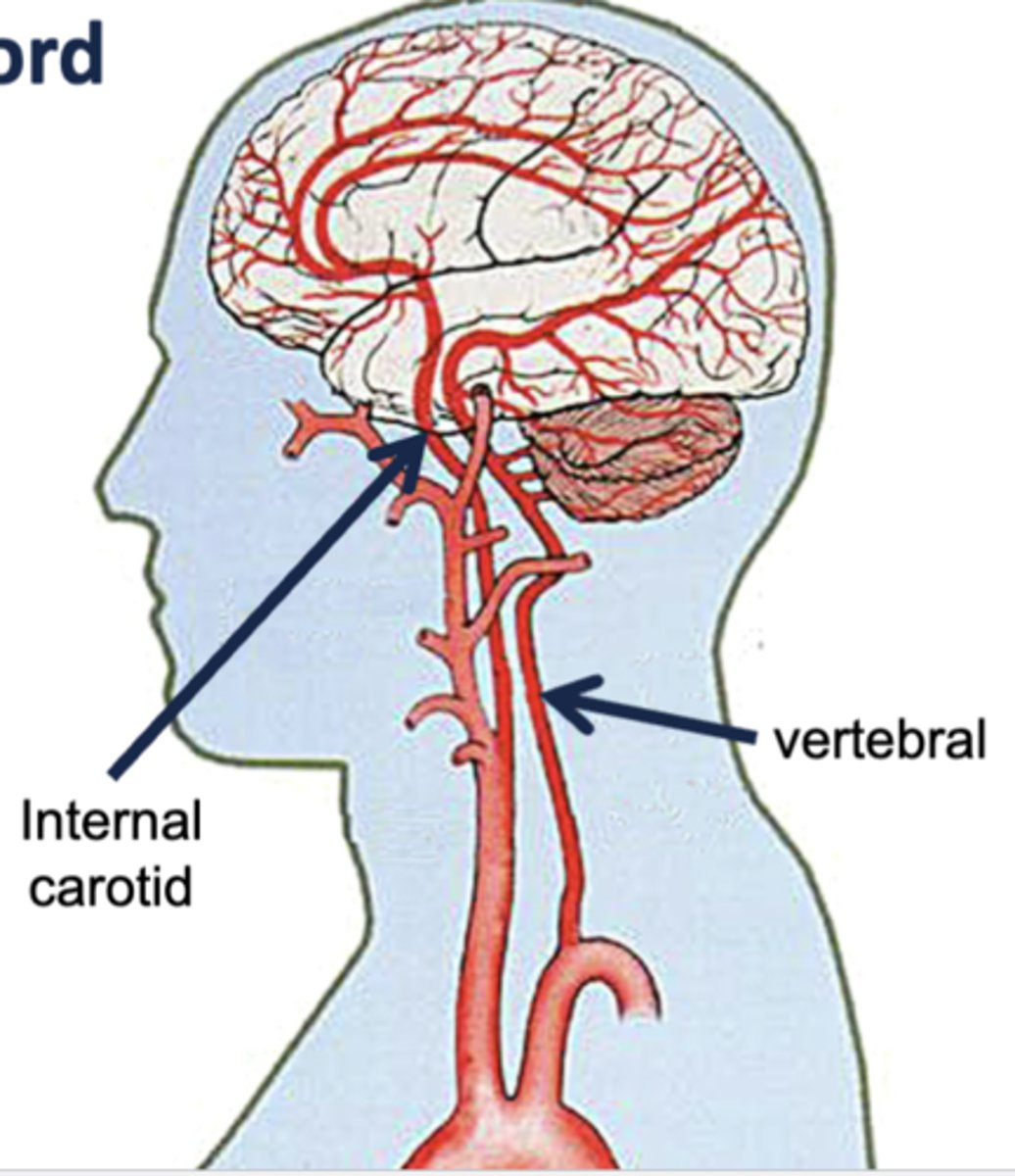
describe the internal carotid arteries, in terms of where they branch from and travel to in the brain:
branches from common carotid artery and enters the skull through the carotid canal in the temporal bone
supplies the anterior parts of the cerebrum
describe the vertebral arteries, in terms of where they branch from and travel to in the brain:
branches from subclavian artery, travels through the vertebral column, and enters the skull through the foramen magnum
supplies posterior cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and spinal cord
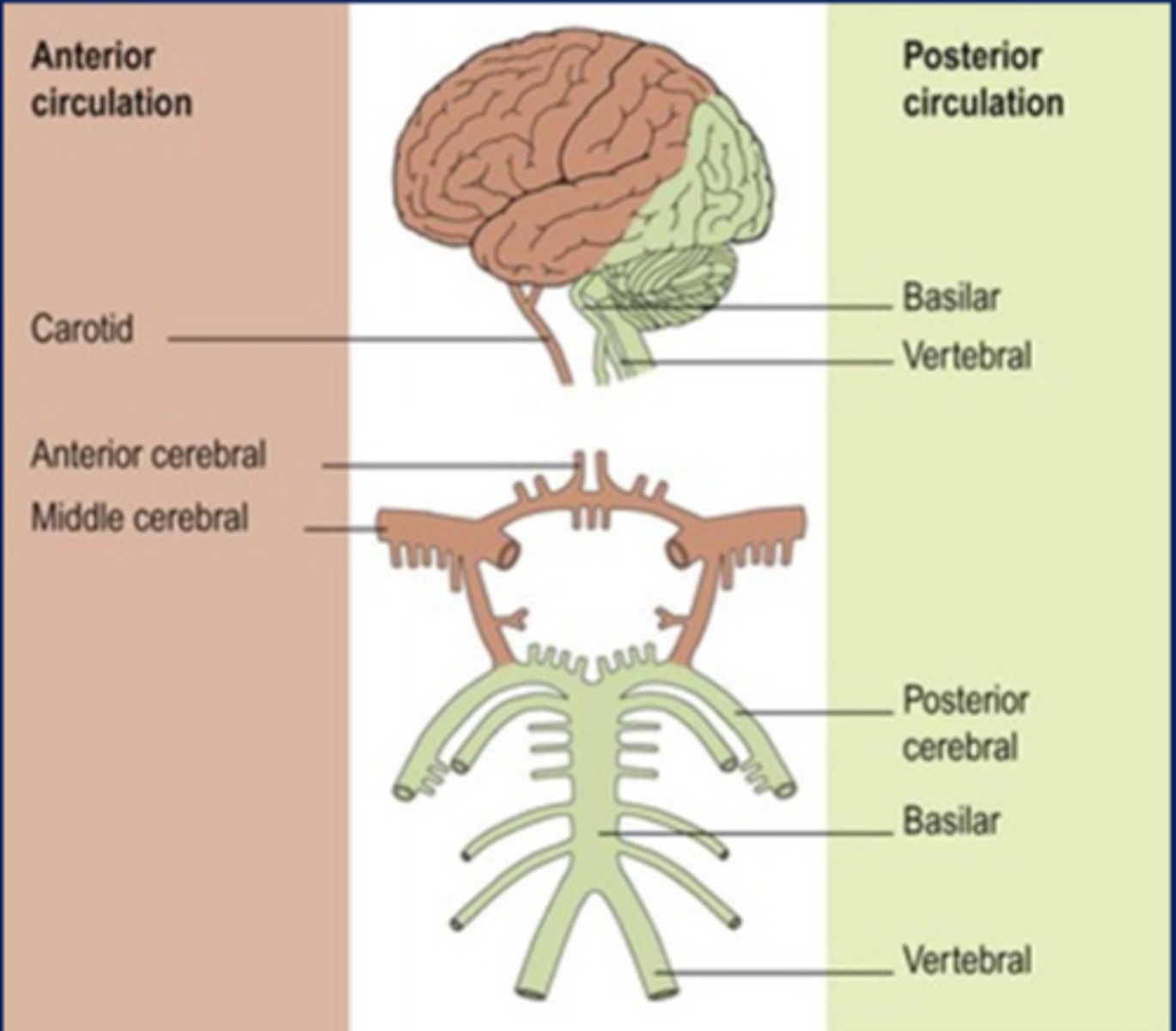
the 2 vertebral arteries come together to form the ________ artery
basilar artery
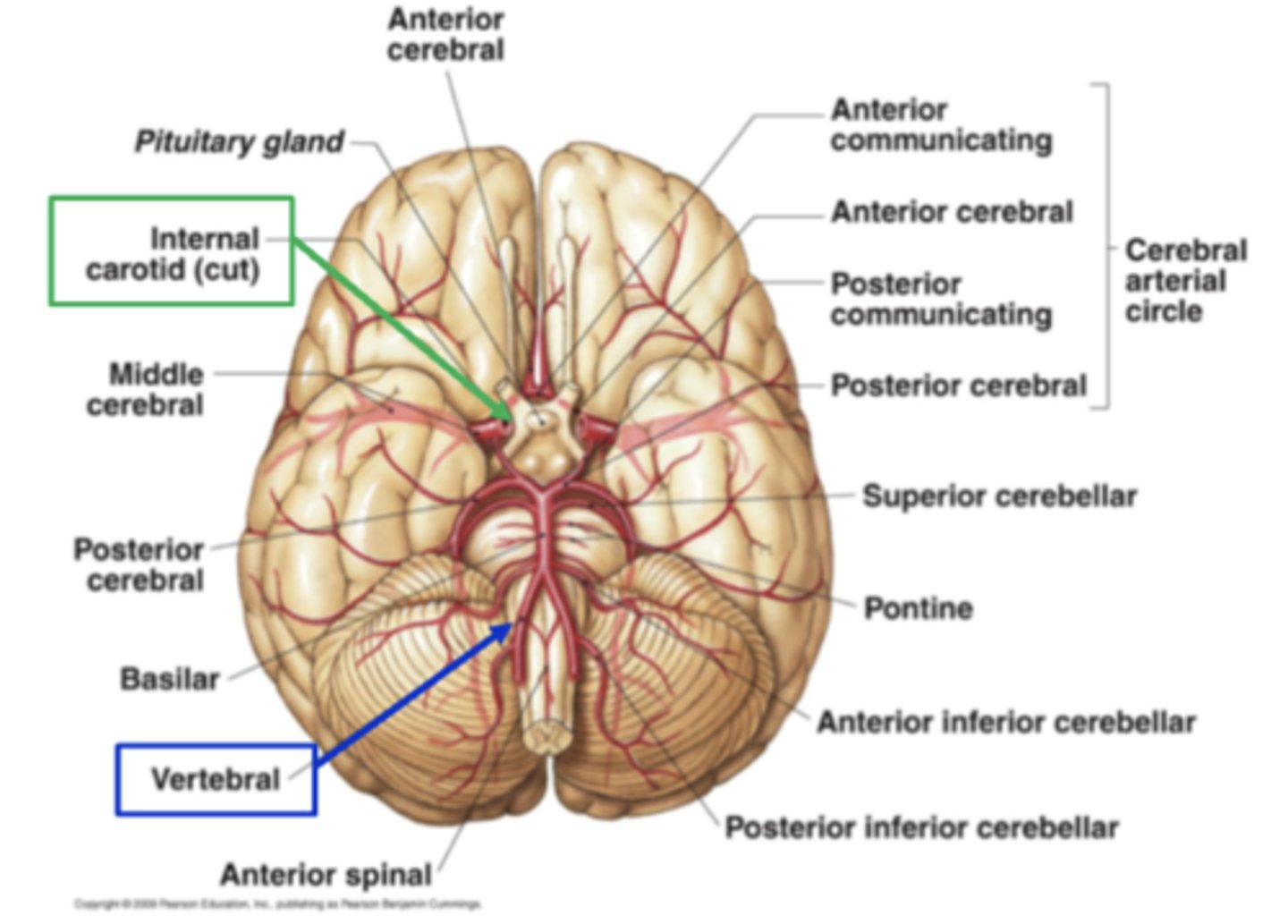
what is the main/terminal branch of the vertebral arteries?
posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)
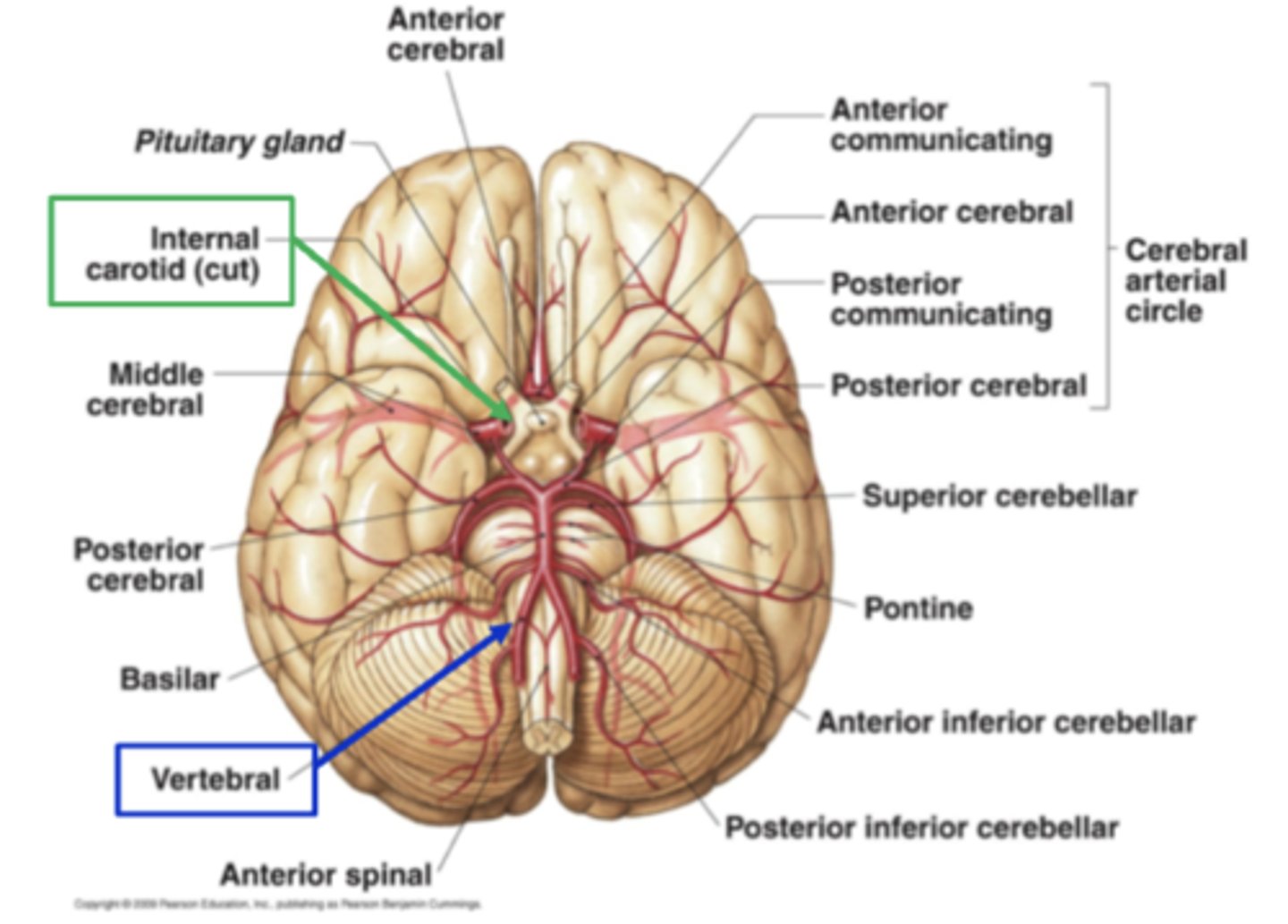
what are the 4 major branches of the internal carotid artery?
1. middle cerebral artery (MCA)
2. anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
3. anterior communicating artery
4. posterior communicating artery
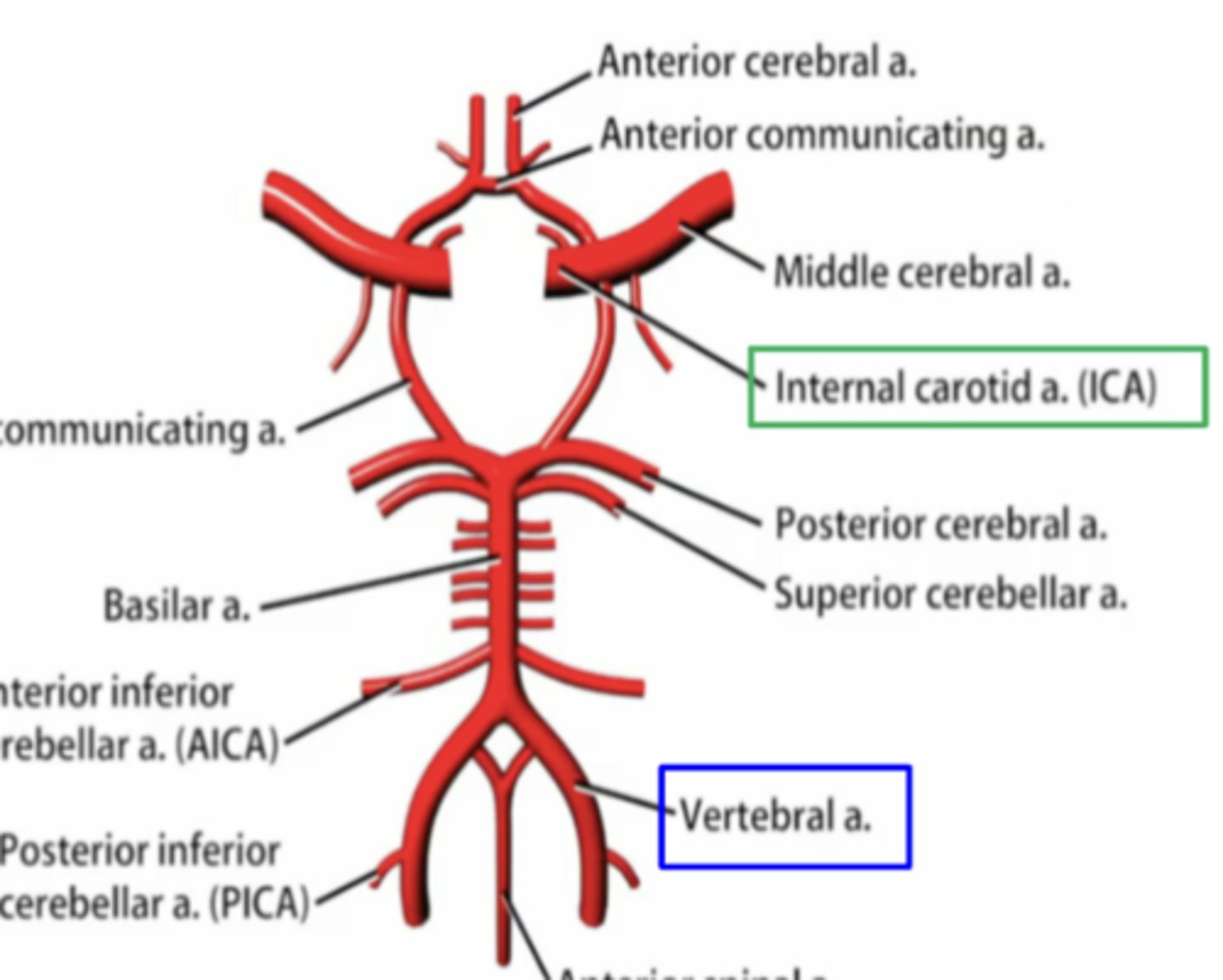
the anterior circulation includes blood supply to what major areas?
anterior parts of the brain
1. frontal lobes
2. temporal lobes
3. parietal lobes
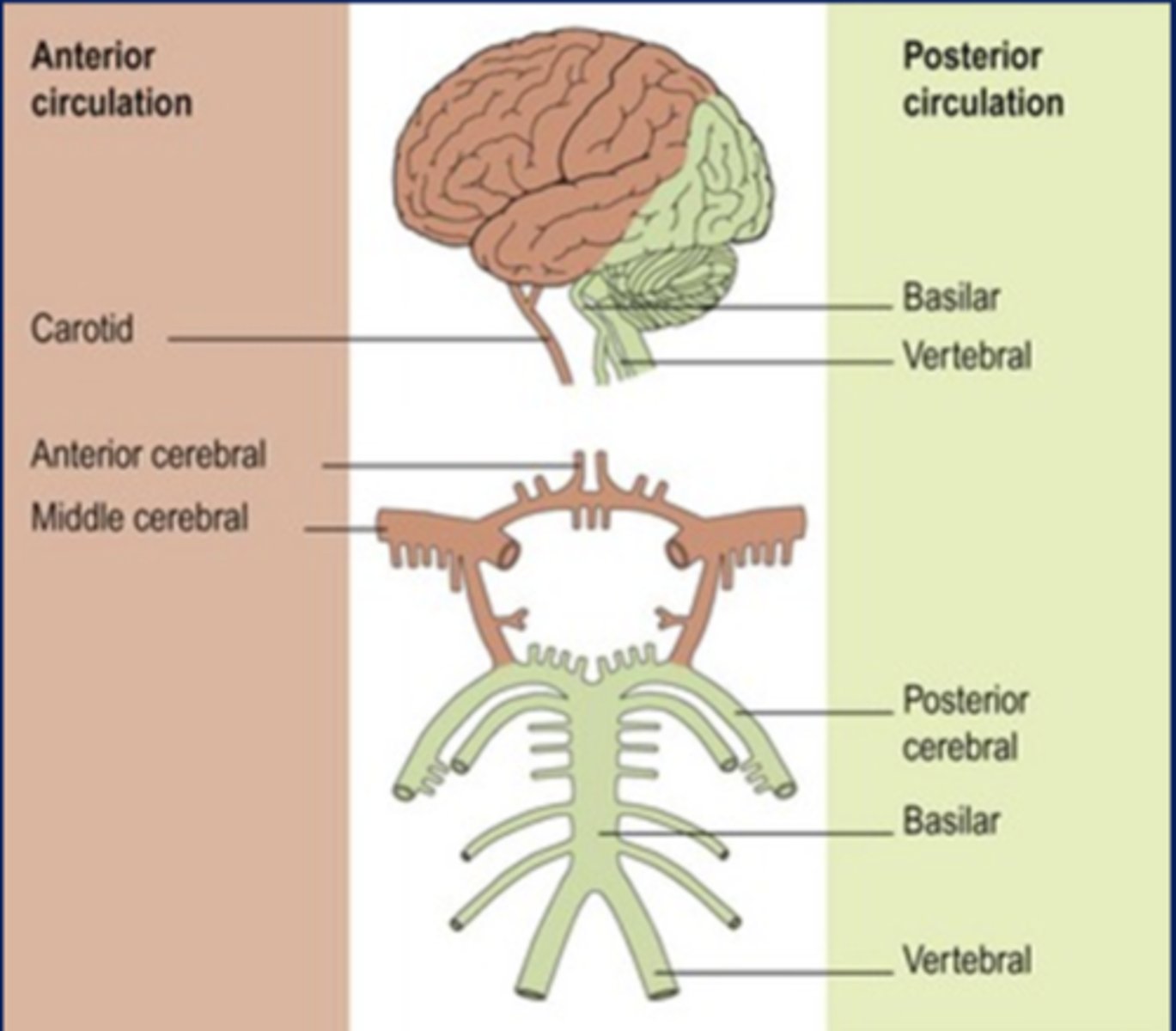
the posterior circulation includes blood supply to what major areas?
posterior parts of the brain
1. temporal lobes
2. occipital lobes
3. brainstem
4. cerebellum
5. spinal cord
the 3 branches of the vertebral artery give blood supply to what 3 structures?
1. medulla
2. spinal cord
3. cerebellum
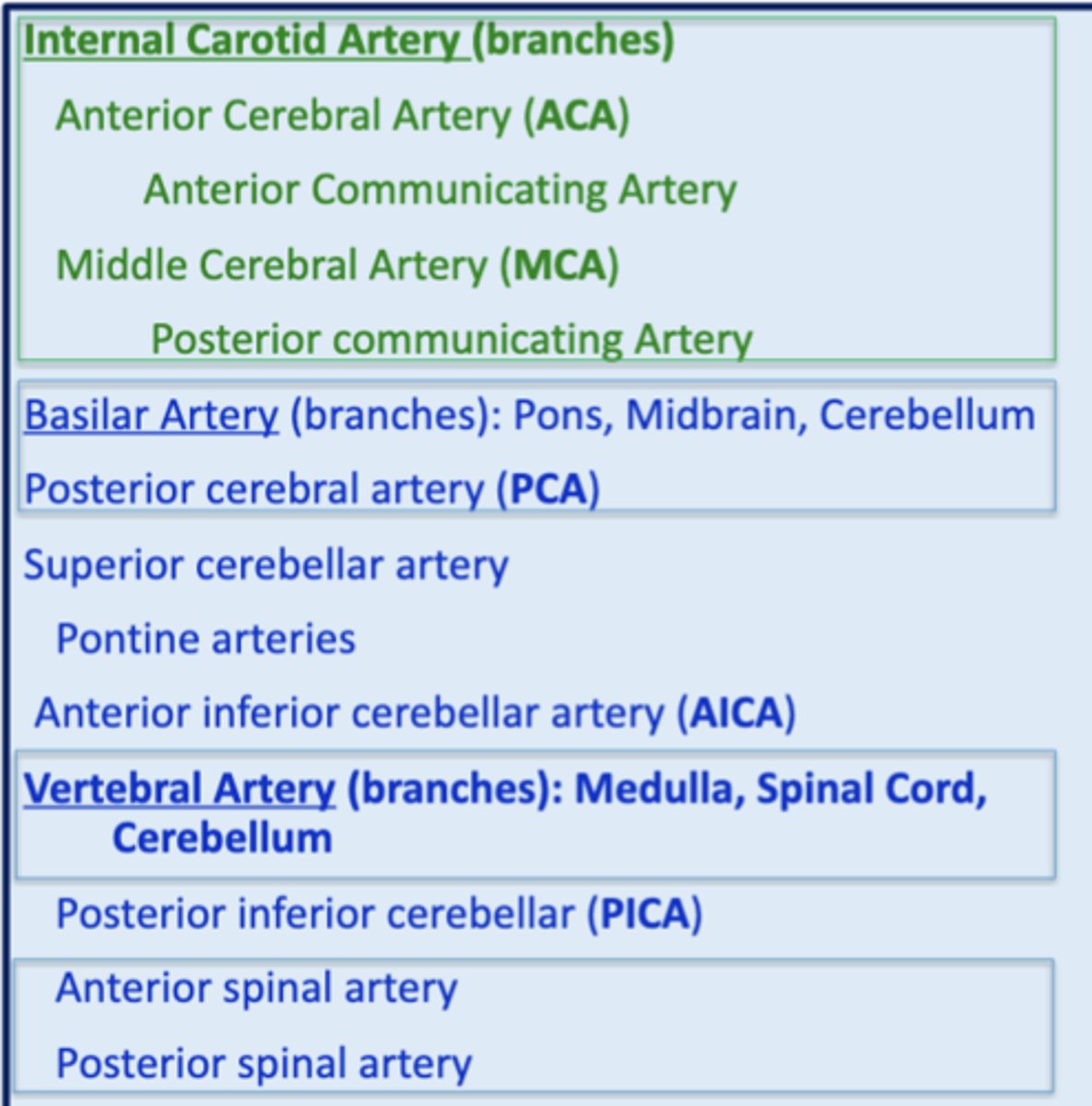
what branches of the vertebral artery give blood supply to the spinal cord?
1. anterior spinal artery
2. posterior spinal artery
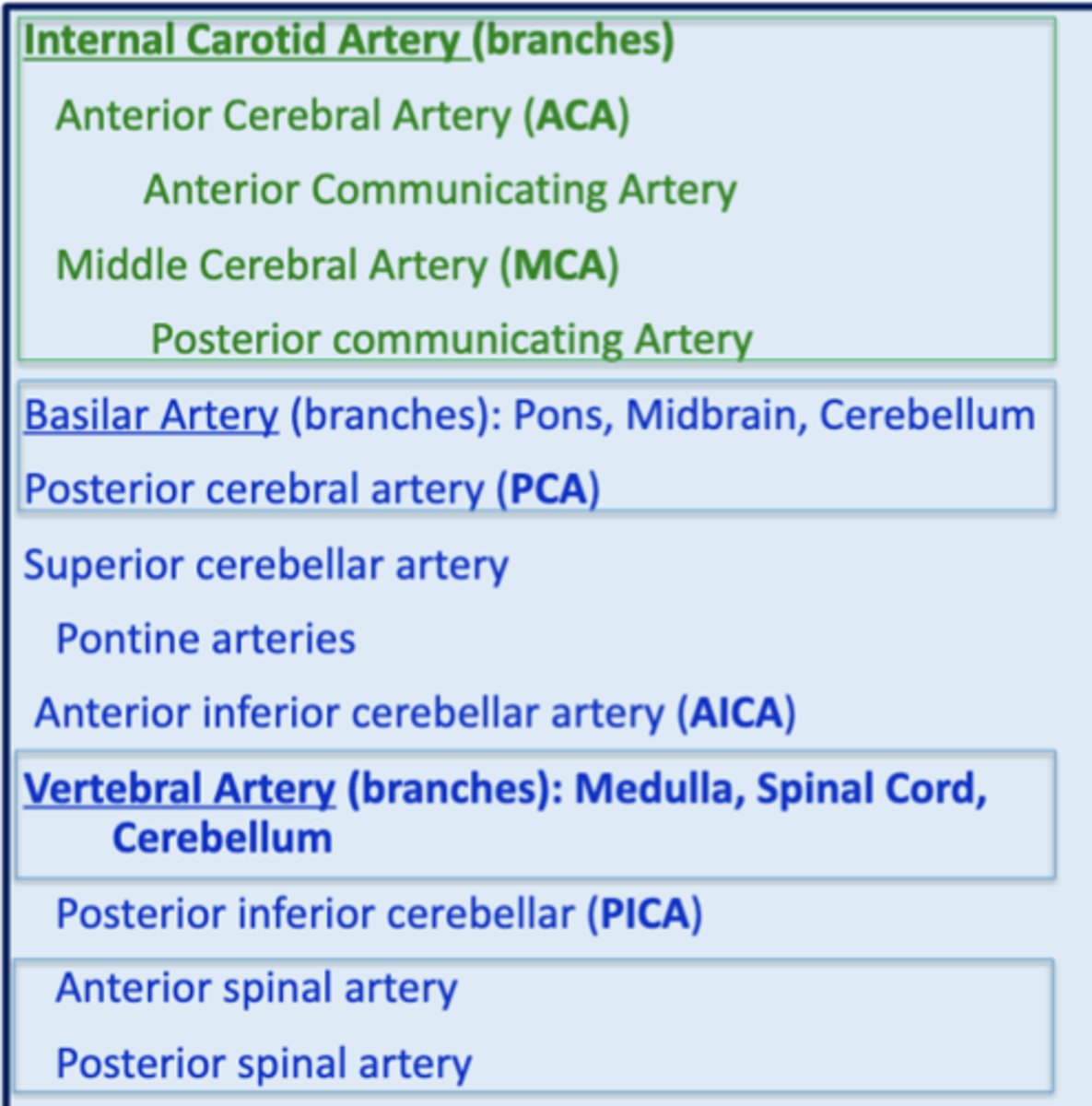
the branches of the basilar artery give blood supply to what 3 structures?
1. pons
2. midbrain
3. cerebellum
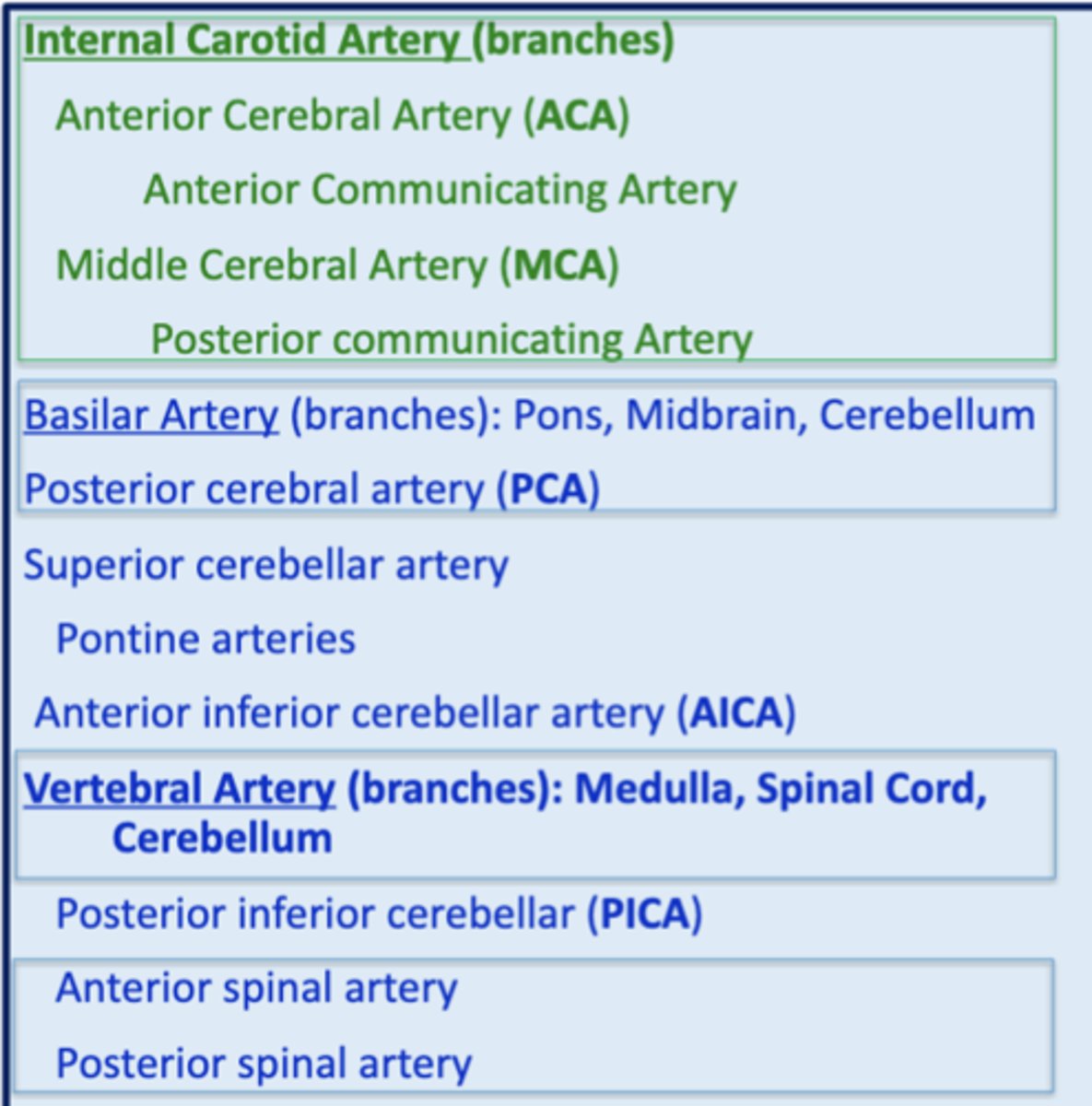
what is the circle of willis? where is it located?
a circle of anastomoses found where the anterior circulation meets the posterior circulation
it is located at the level of the diencephalon
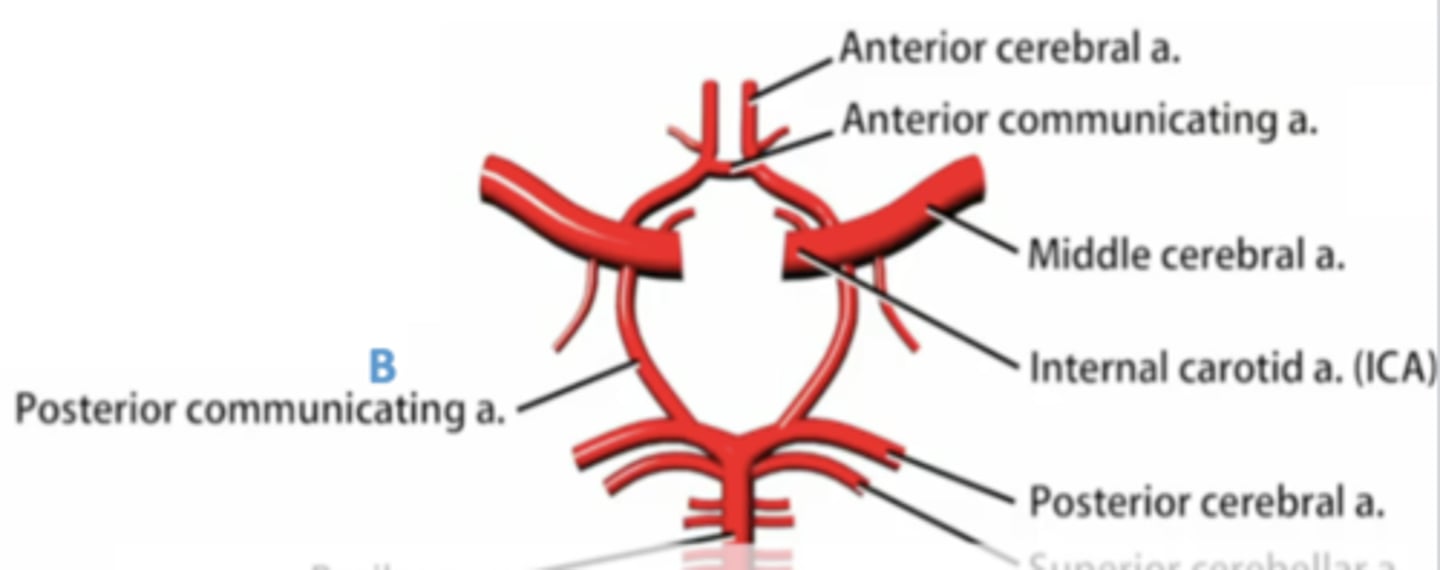
what arteries composed the circle of willis?
1. posterior cerebral arteries
2. posterior communicating arteries
3. internal carotid arteries
4. middle cerebral arteries
5. anterior communicating artery (only 1 of these)
6. anterior cerebral arteries
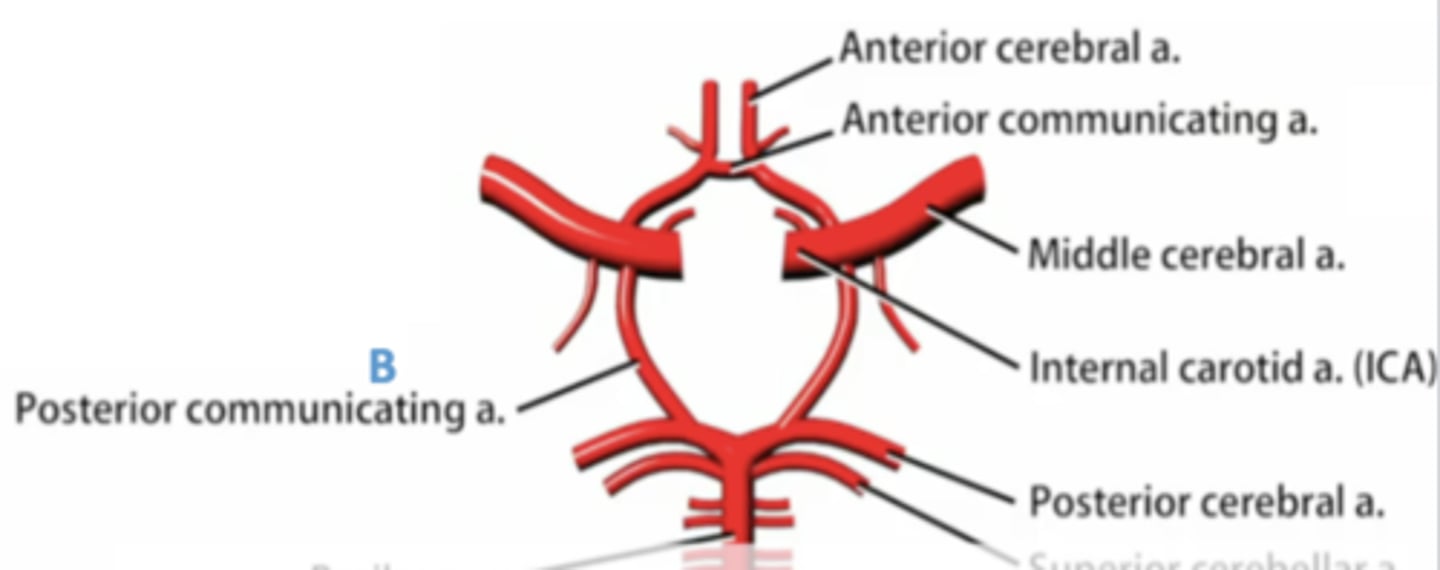
the circle of willis supplies blood to what major structure(s)?
cerebral hemispheres
what are the 3 main arteries that supply blood to the cerebral hemispheres?
1. anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
2. middle cerebral artery (MCA)
3. posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
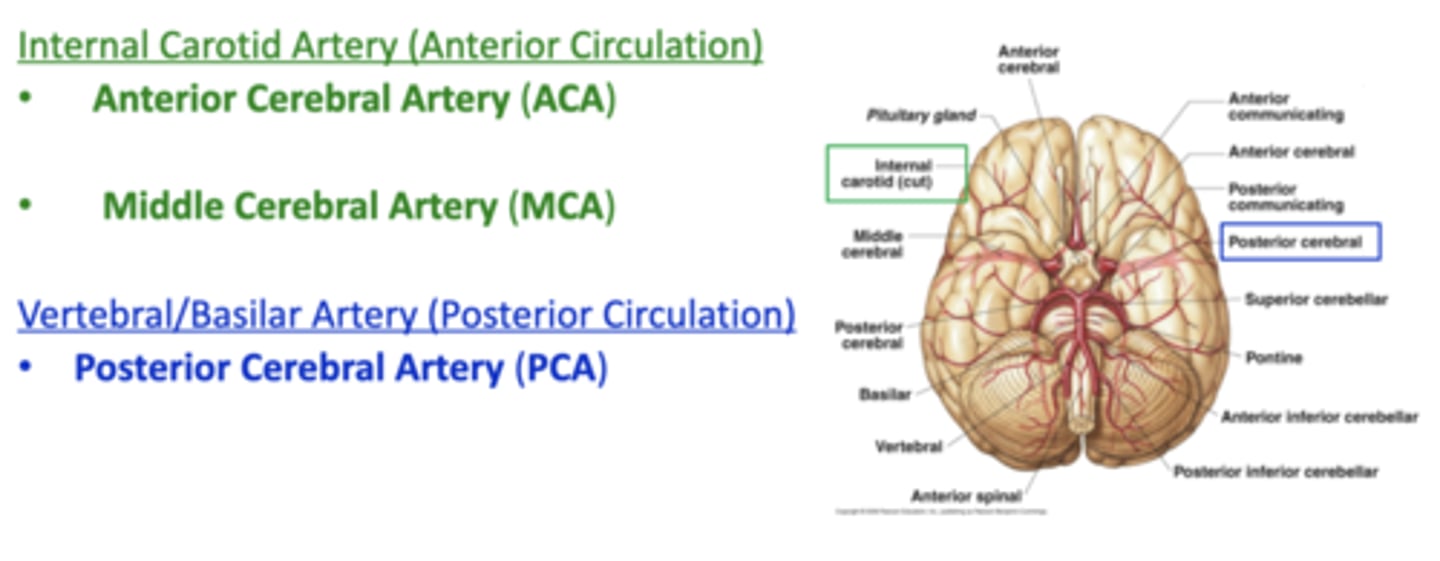
where does the anterior cerebral artery travel/where is it located?
lies in the longitudinal fissure on the medial surface of each hemisphere
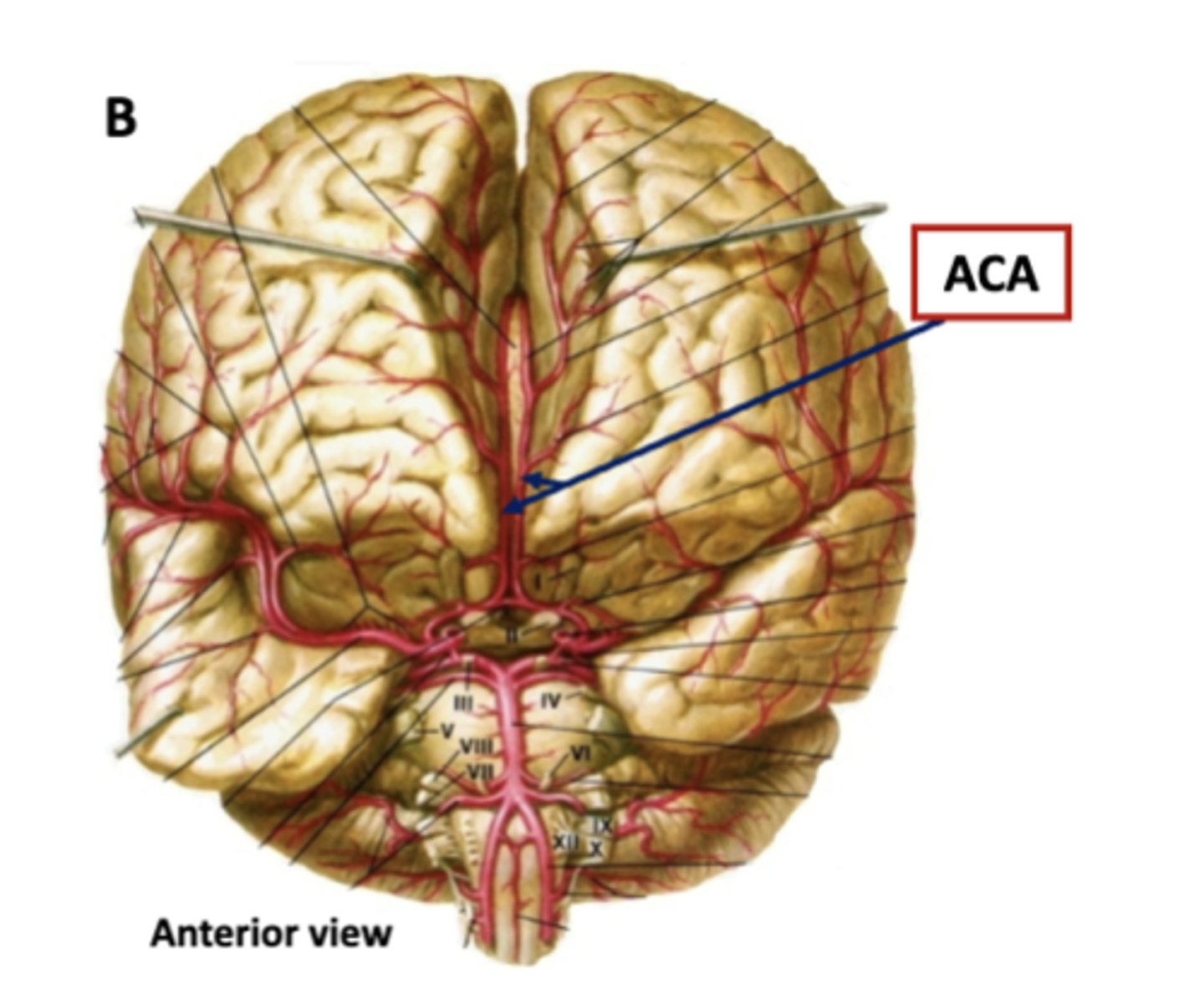
what parts of the brain does the anterior cerebral artery supply?
medial parts of the frontal and parietal lobes
this also means that it supplies the primary motor and primary somatosensory cortex for the lower limbs
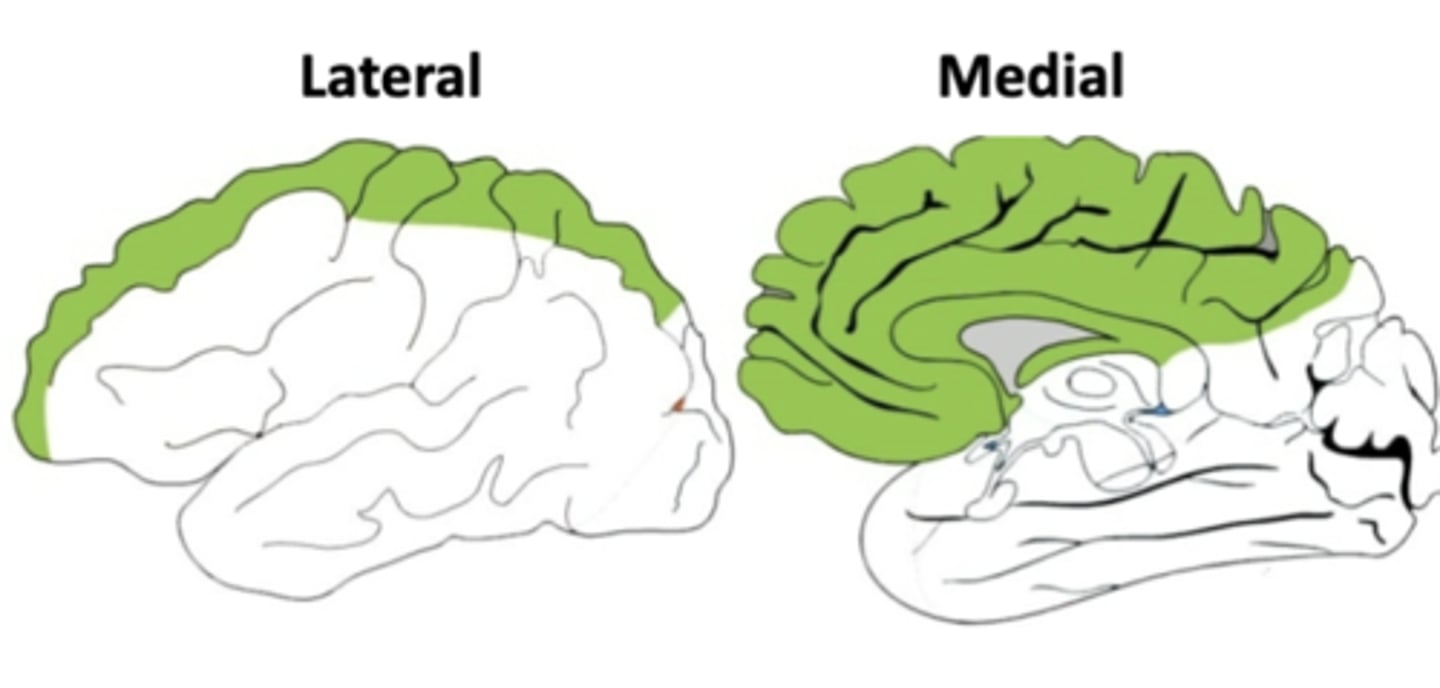
the anterior cerebral artery supplies blood to the primary somatosensory and primary motor cortices for the (upper/lower) limbs
lower
it is located medially on each hemisphere
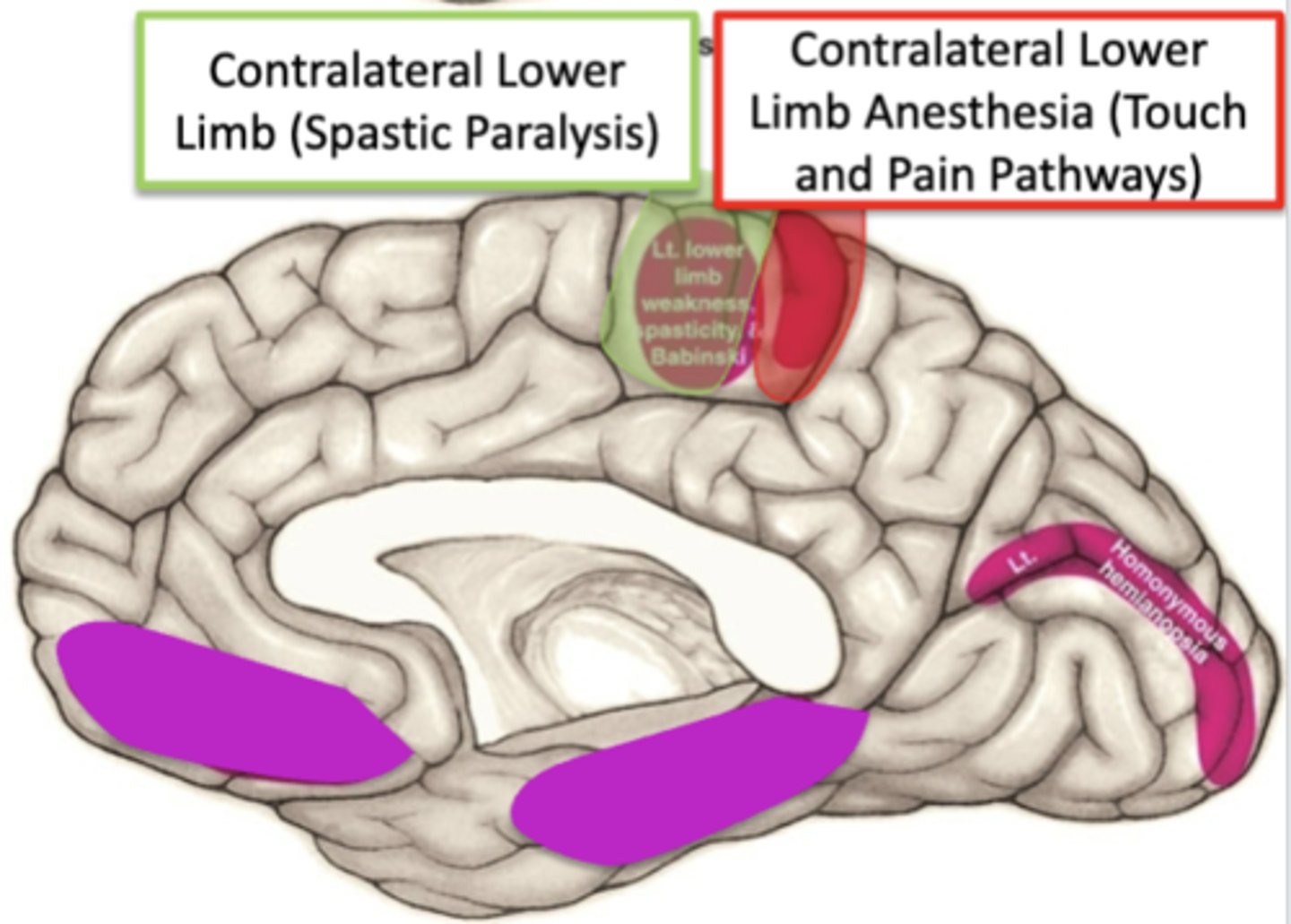
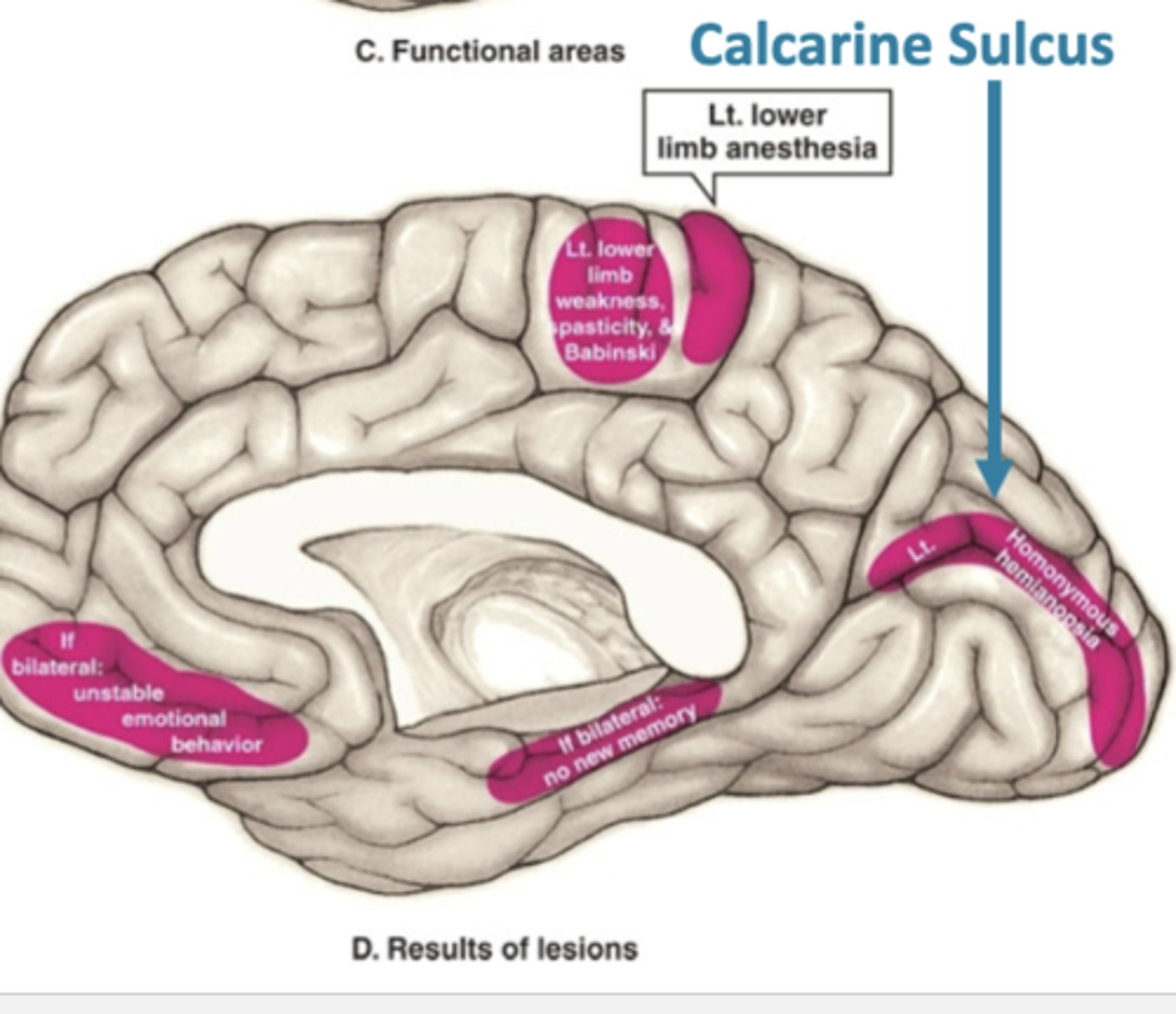
loss of blood supply to the primary motor cortex from the anterior cerebral artery would cause what?
spastic paralysis in the contralateral lower extremity (hyperreflexia, Babinski response, spasticity)
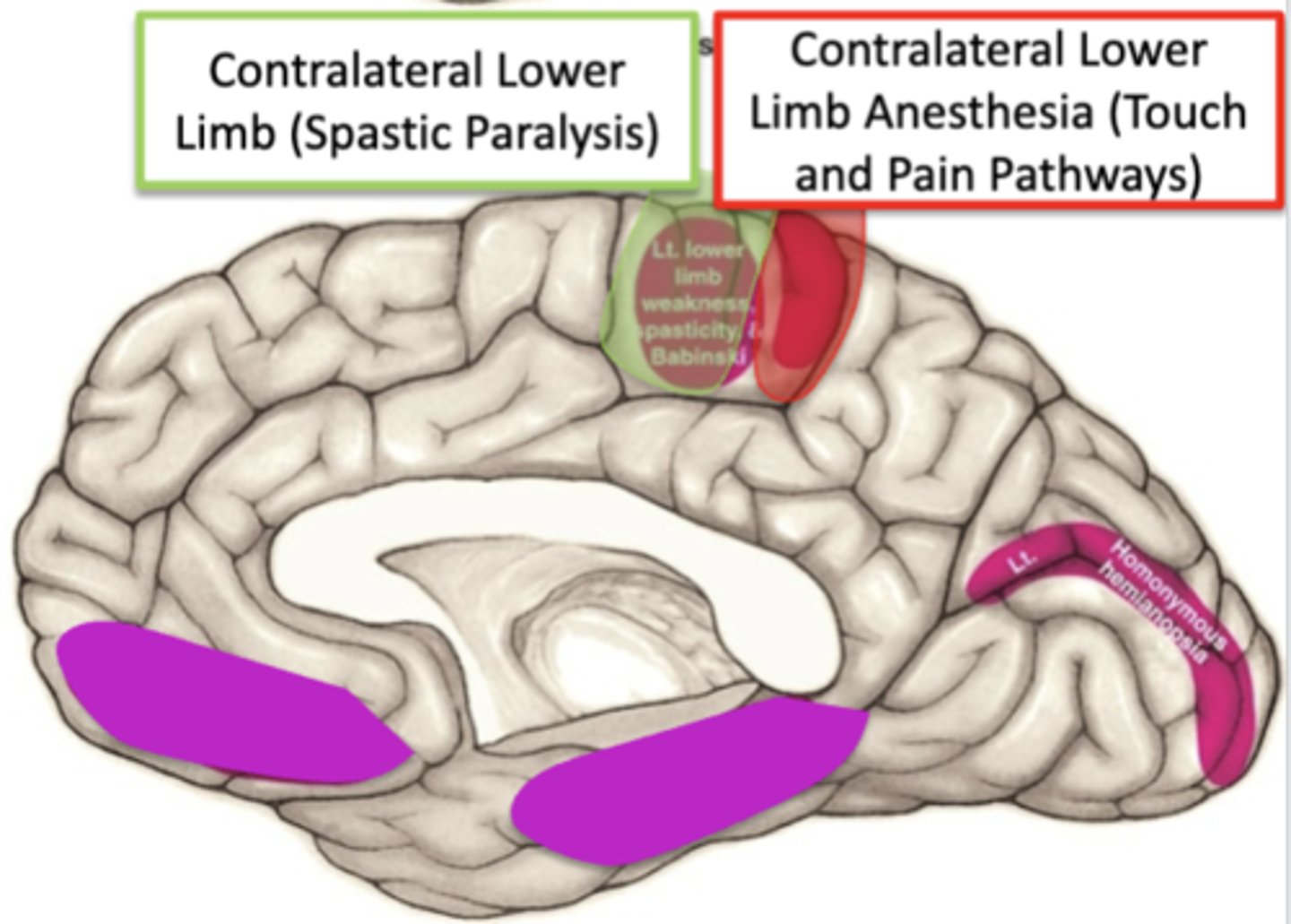
loss of blood supply to the primary somatosensory cortex from the anterior cerebral artery would cause what?
loss of all sensations in the contralateral lower extremity (pain, temp, touch)
where does the middle cerebral artery travel/where is it located?
lies in the lateral fissure between the frontal and temporal lobes
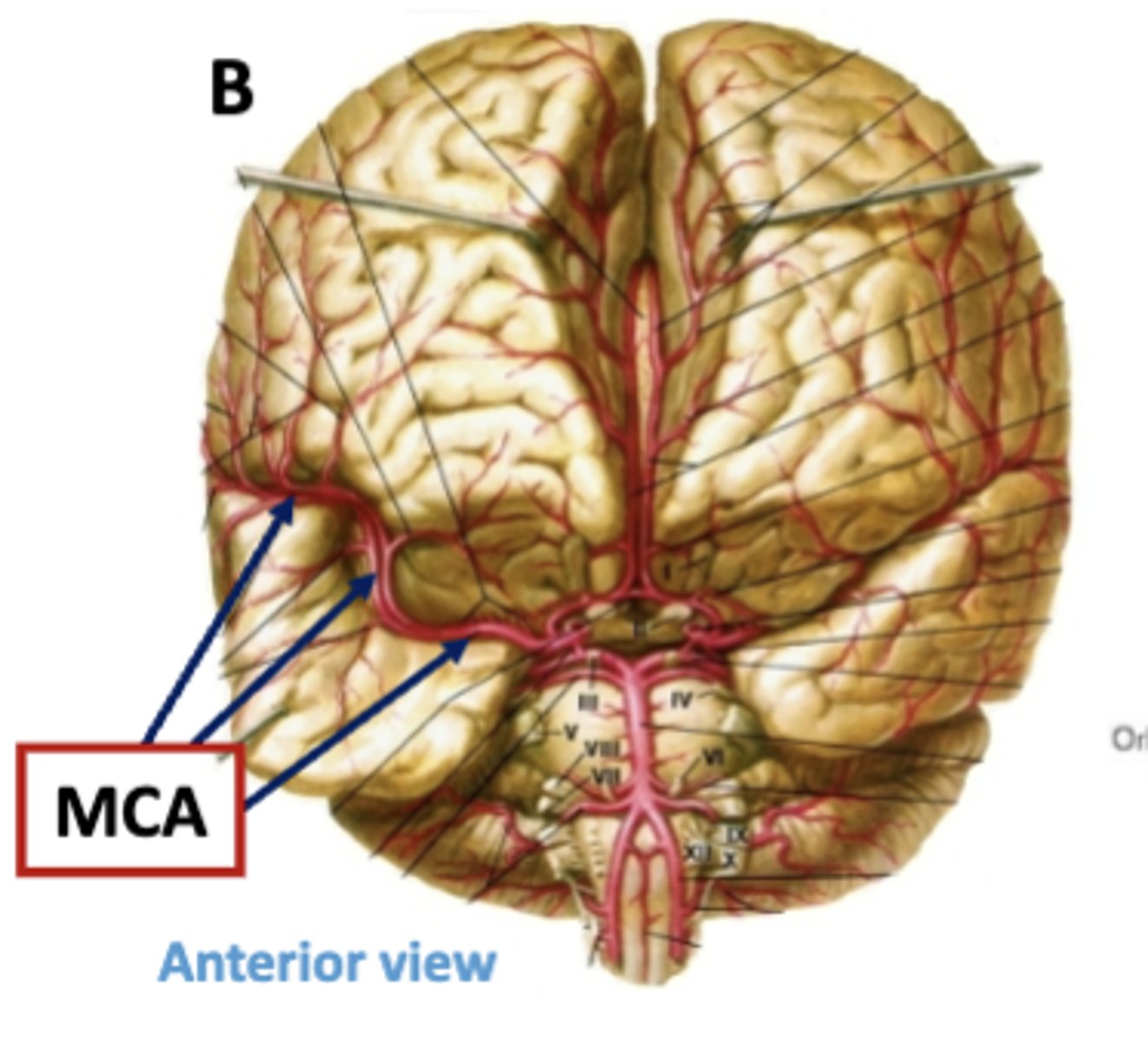
what parts of the brain does the middle cerebral artery supply?
lateral parts of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
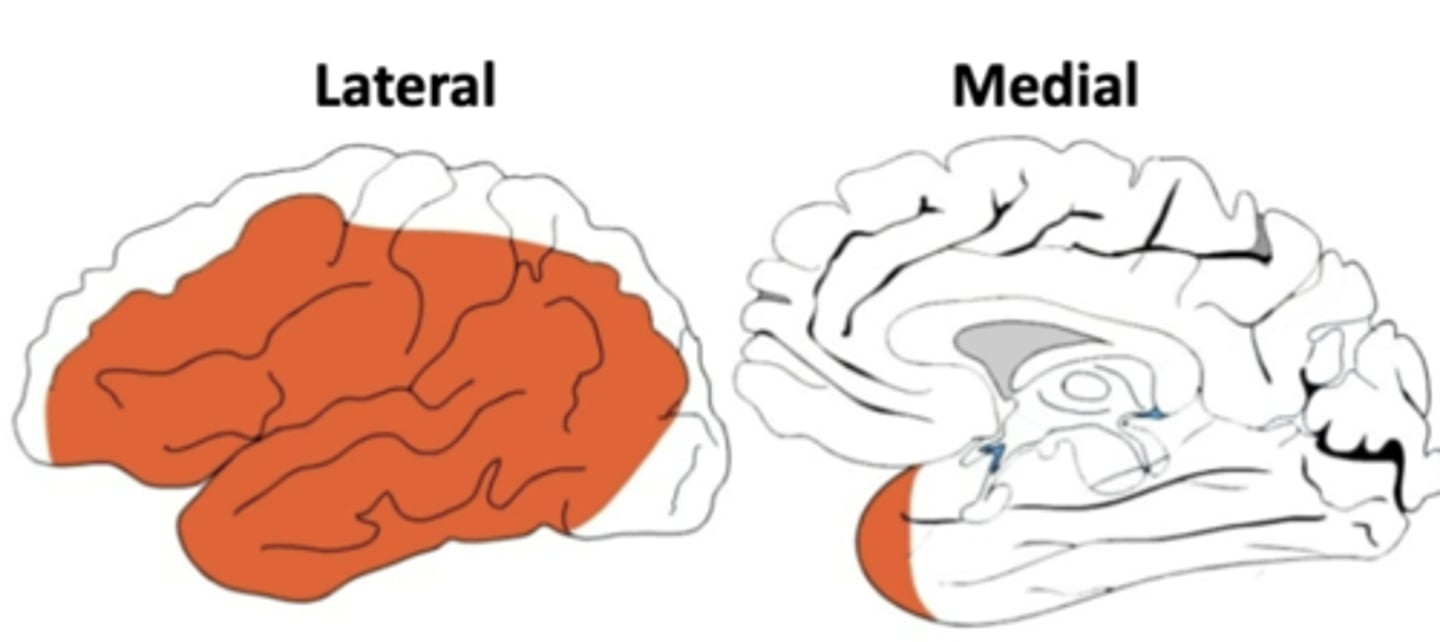
the middle cerebral artery supplies blood to the primary somatosensory and primary motor cortices for the (upper/lower) limbs
upper limbs AND the face
it supplies the lateral parts of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
loss of blood supply to the primary motor cortex from the middle cerebral artery would cause what?
spastic paralysis in the contralateral upper extremity (hyperreflexia, spasticity) and lower facial weakness
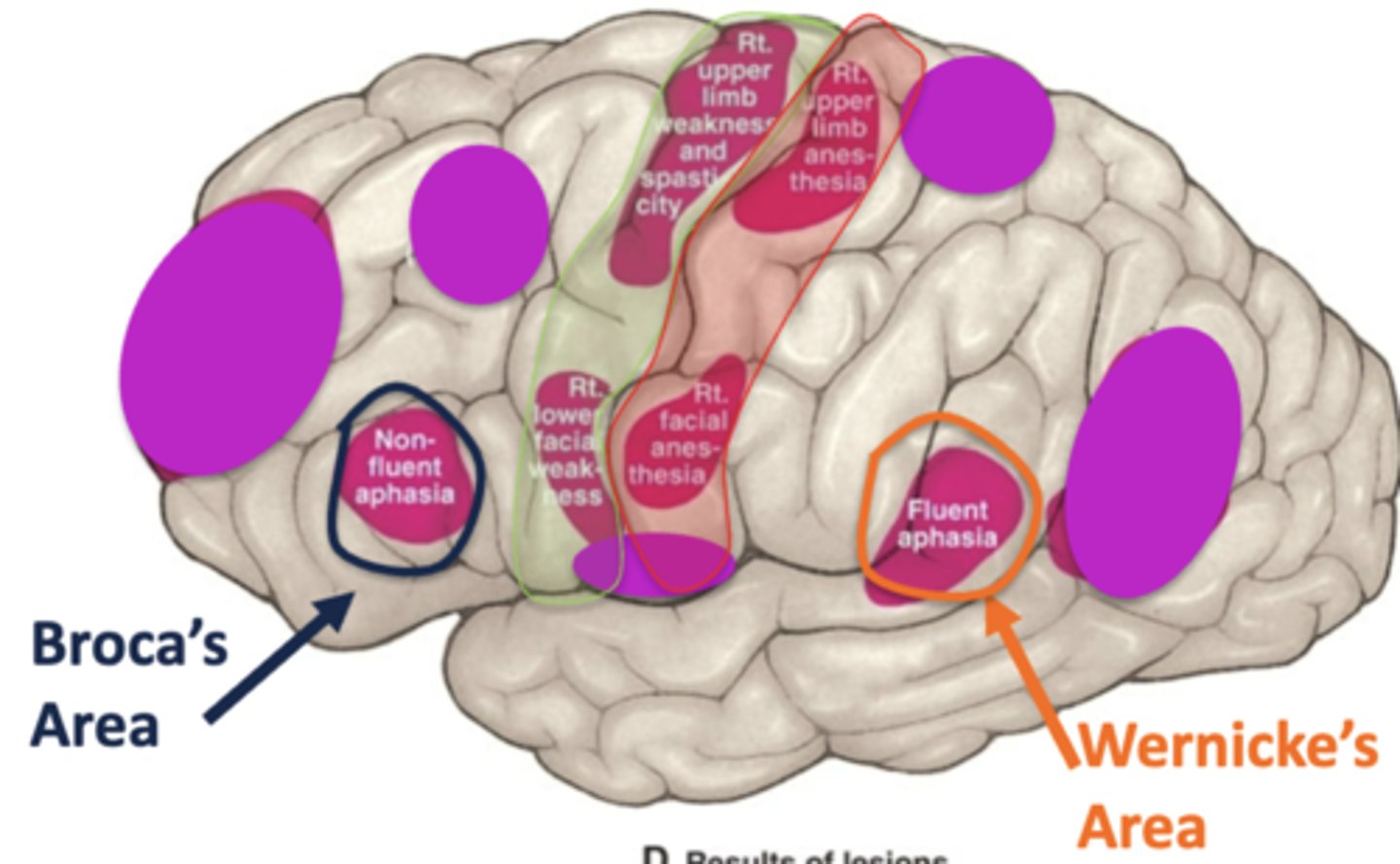
loss of blood supply to the primary somatosensory cortex from the middle cerebral artery would cause what?
loss of all sensations in the contralateral upper extremity and the face (pain, temp, touch)
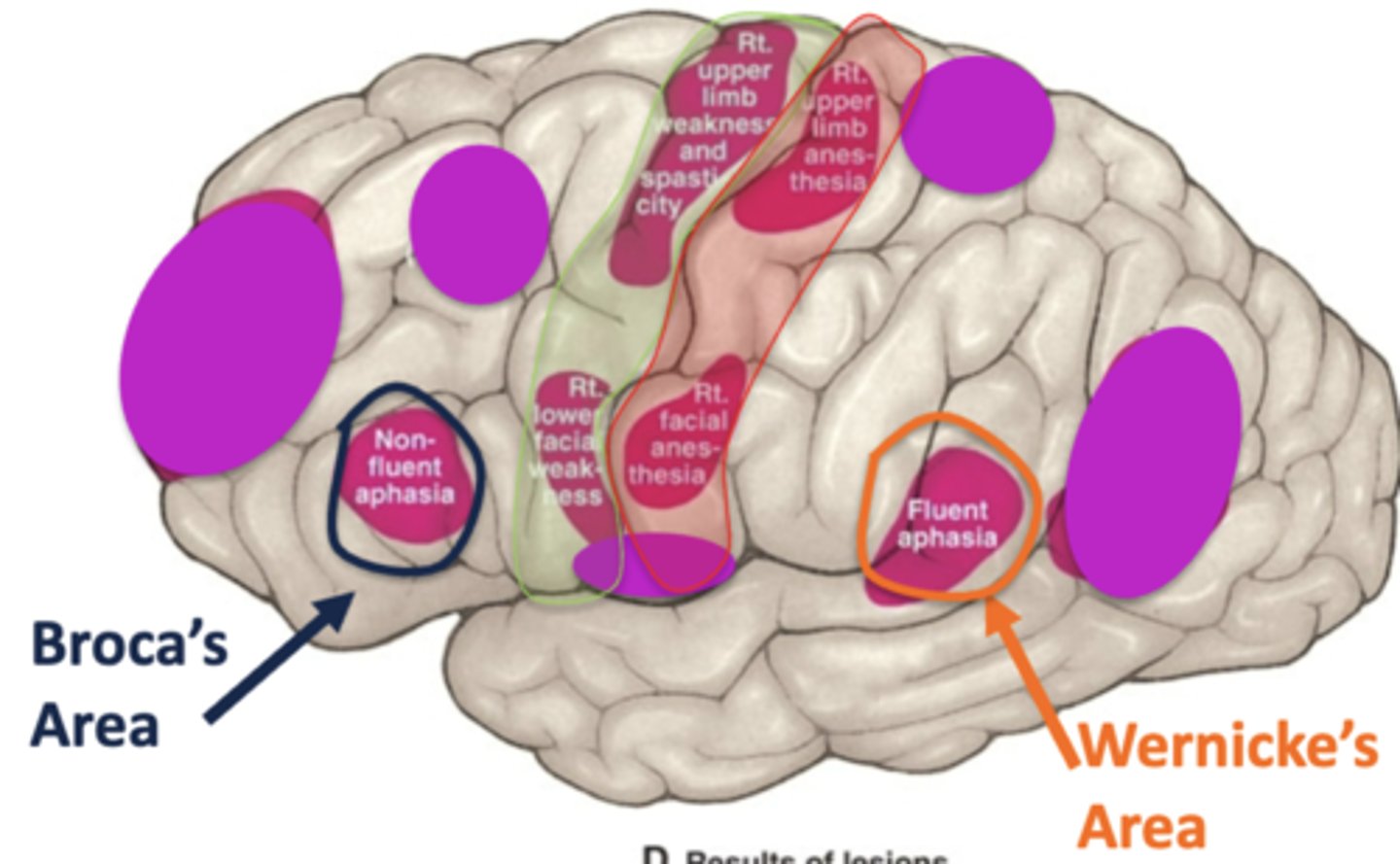
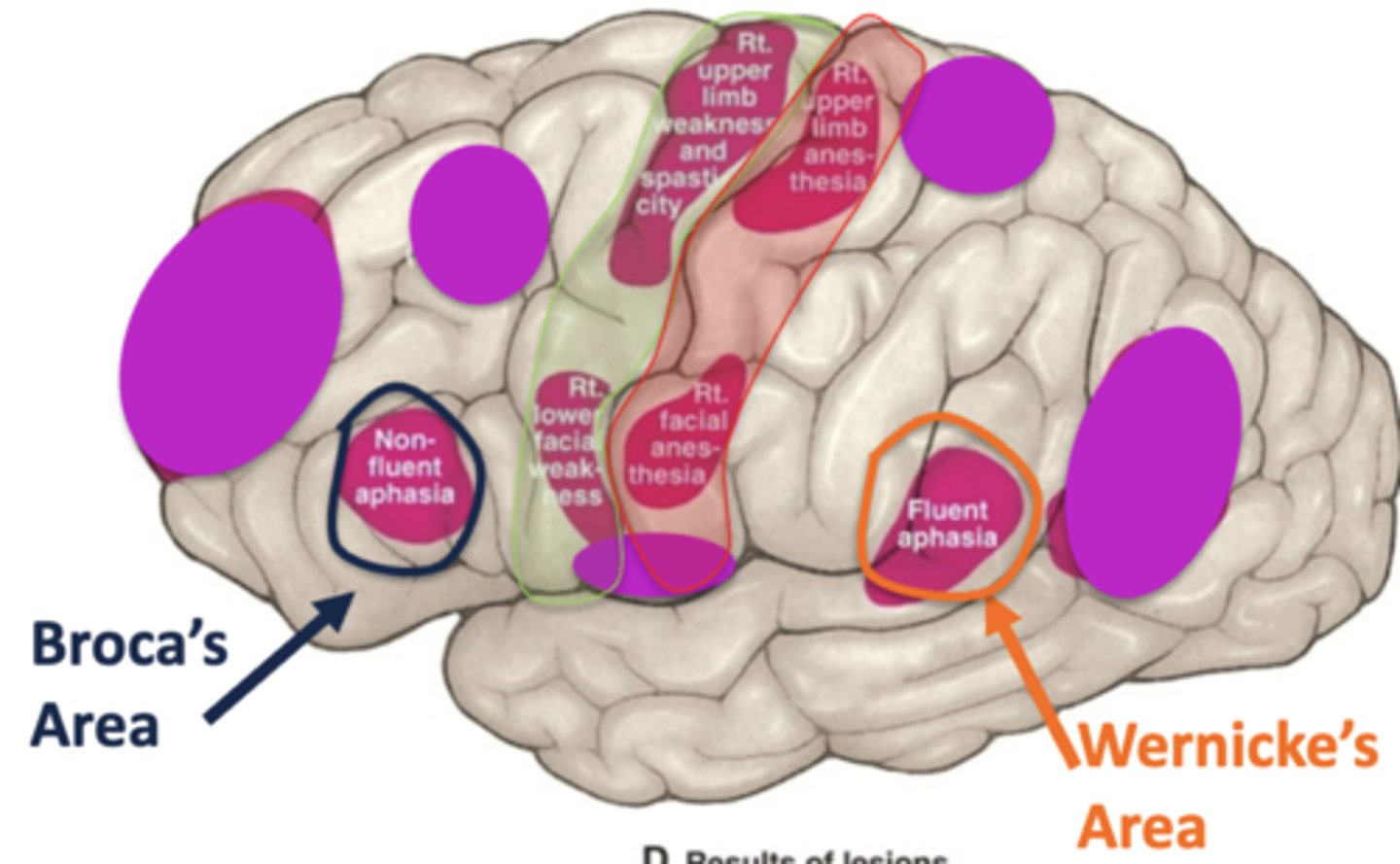
non-fluent aphasia could result in loss of blood supply from what artery and to what area?
loss of blood supply from the middle cerebral artery in the left cerebral hemisphere
this would mean there is a loss of blood supply to Broca's area
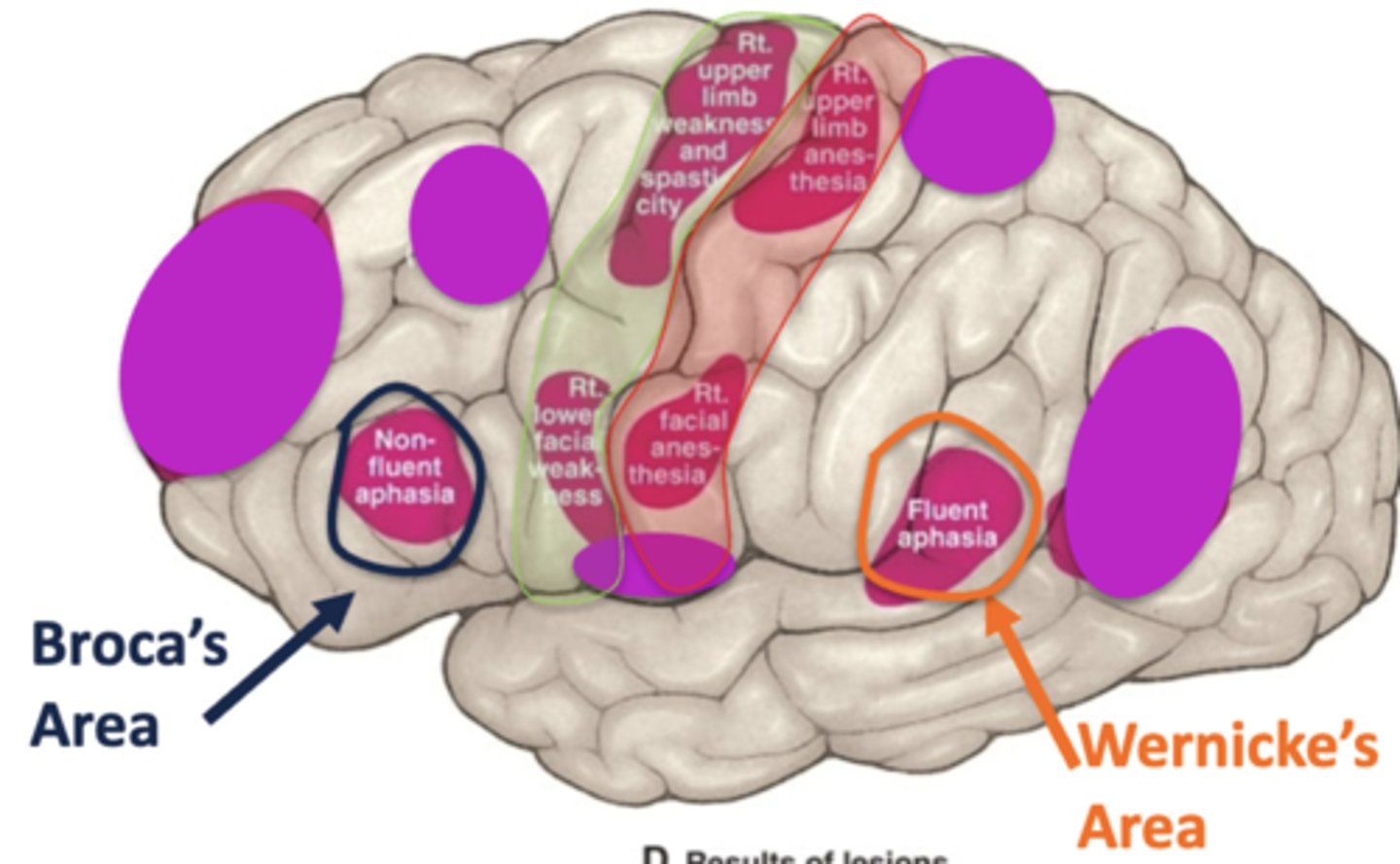
fluent aphasia could result in loss of blood supply from what artery and to what area?
loss of blood supply from the middle cerebral artery in the left cerebral hemisphere
this would mean there is a loss of blood supply to Wernicke's area
what is the blood supply to the internal capsule?
lenticulostriate arteries (deep penetrating arteries)
lenticulostriate arteries are branches off what other artery?
middle cerebral artery
what does the internal capsule contain?
1. descending motor tracts (corticospinal and corticobulbar)
2. ascending somatosensory tracts (all 4 spinal and cranial touch and pain pathways)
what can happen if you have damage to the internal capsule?
1. contralateral upper/lower extremity spastic paralysis
2. lower facial weakness
3. contralateral loss of all somatosensations to the face, upper and lower extremities
what is a common site for a typical stroke?
internal capsule
this means blood supply from the lenticulostriate arteries to the internal capsule is blocked
where does the posterior cerebral artery travel/where is it located?
on the inferior surface of the temporal lobe - it then spreads posteriorly and laterally
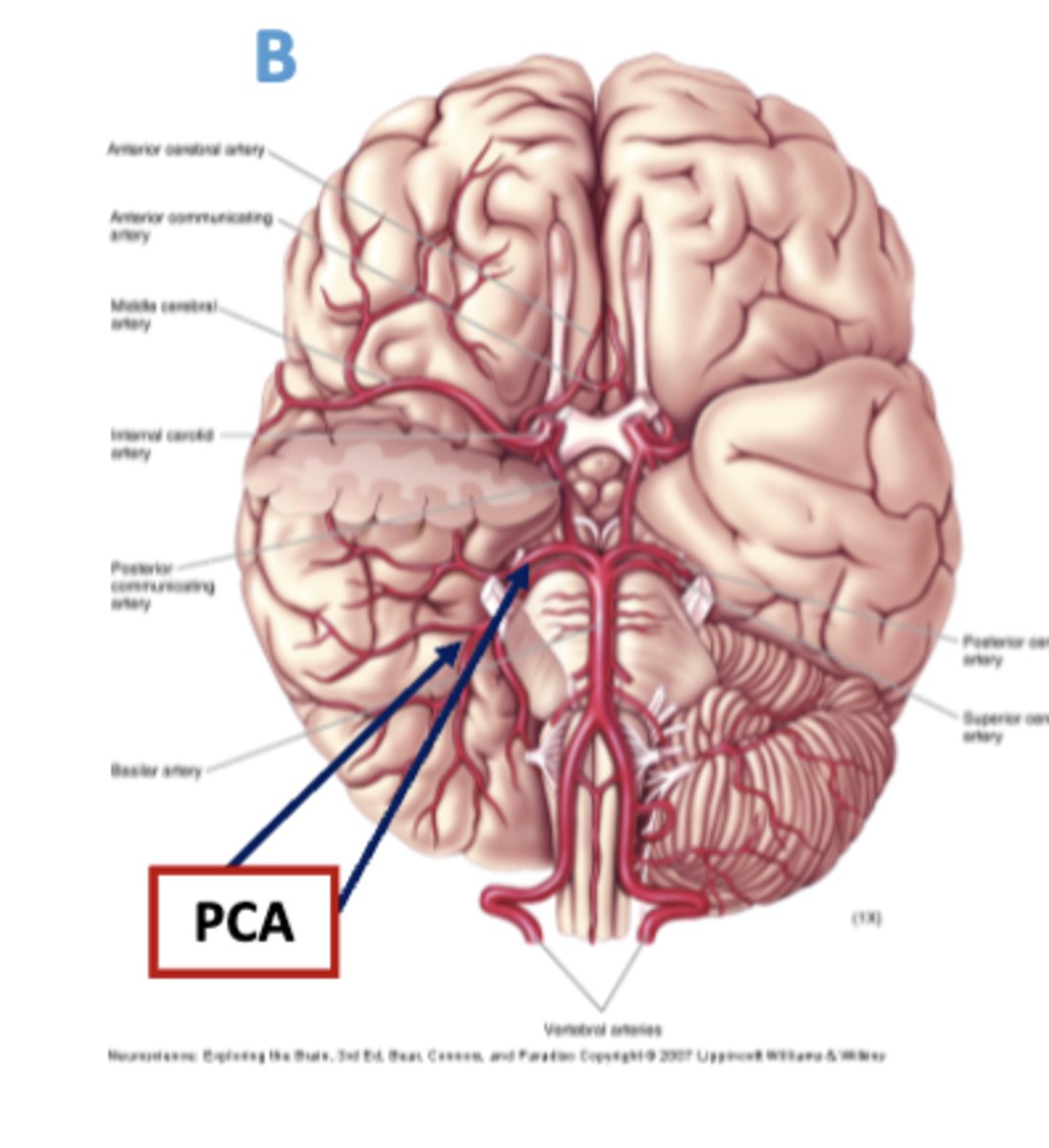
what parts of the brain does the posterior cerebral artery supply?
occipital lobe and part of the temporal lobes - primary visual cortex
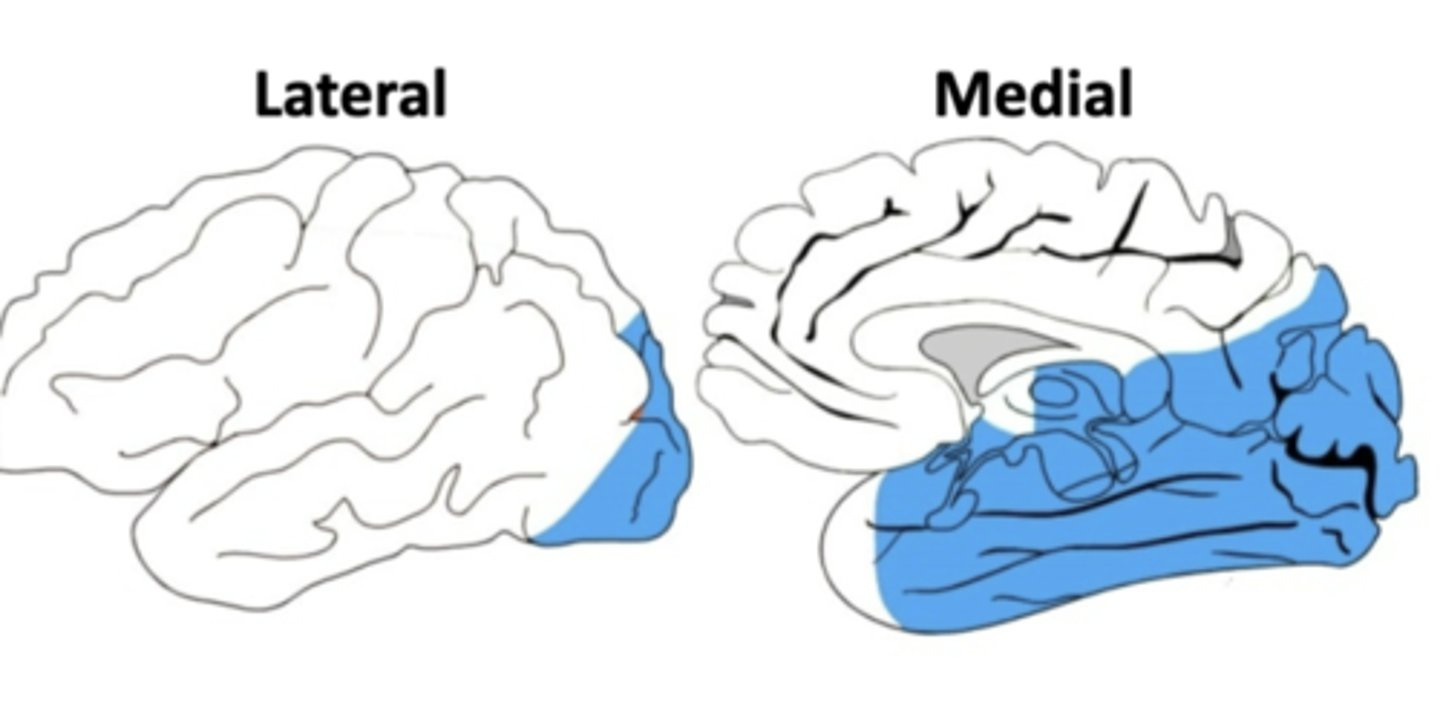
loss of blood supply to the primary visual cortex from the posterior cerebral artery would cause what?
contralateral homonymous hemianopsia (contralateral loss of the visual field in each eye)
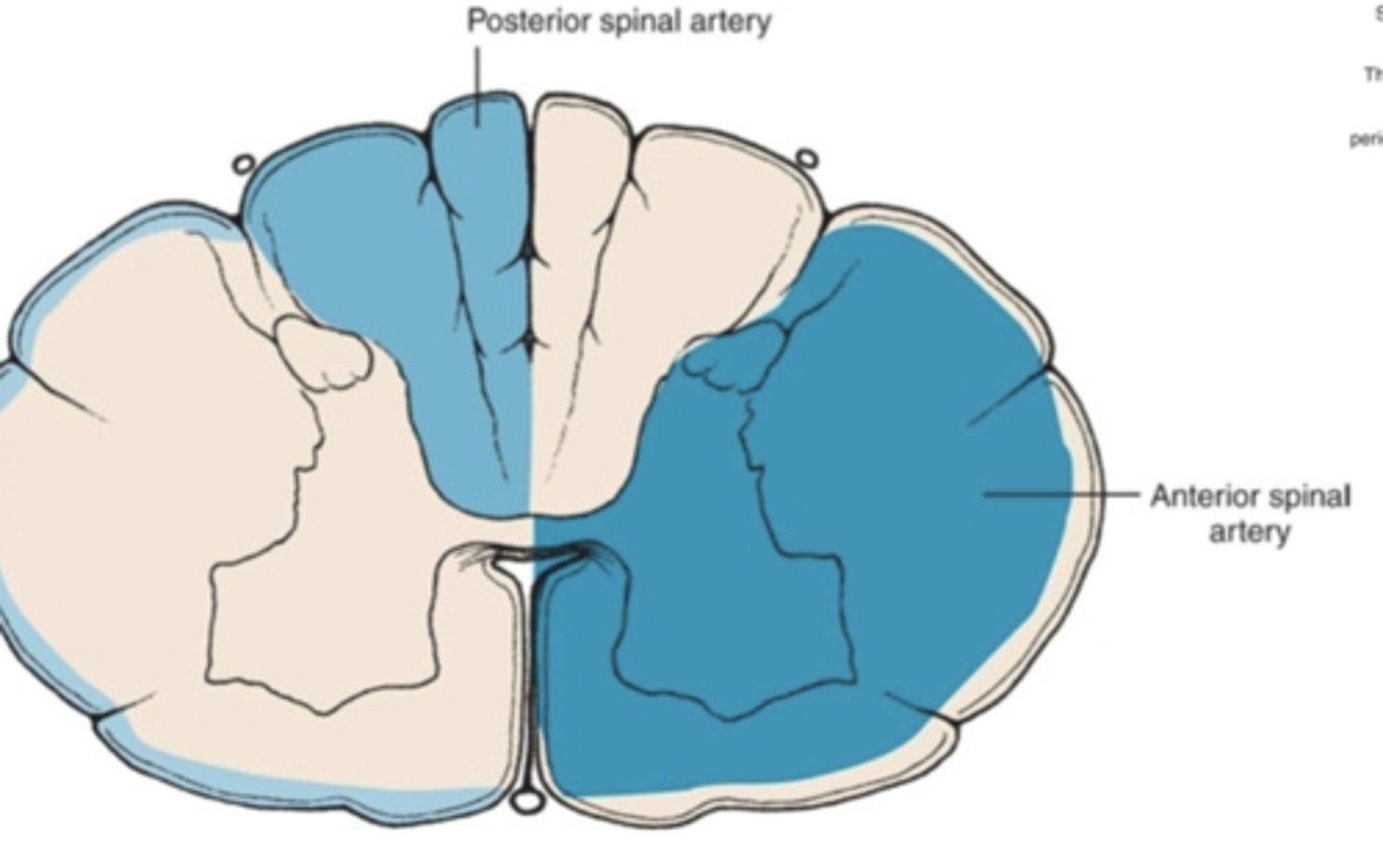
the posterior spinal arteries give blood supply to what part of the spinal cord?
posterior 1/3 of the spinal cord
(this will primarily be in the cervical part of the spinal cord)
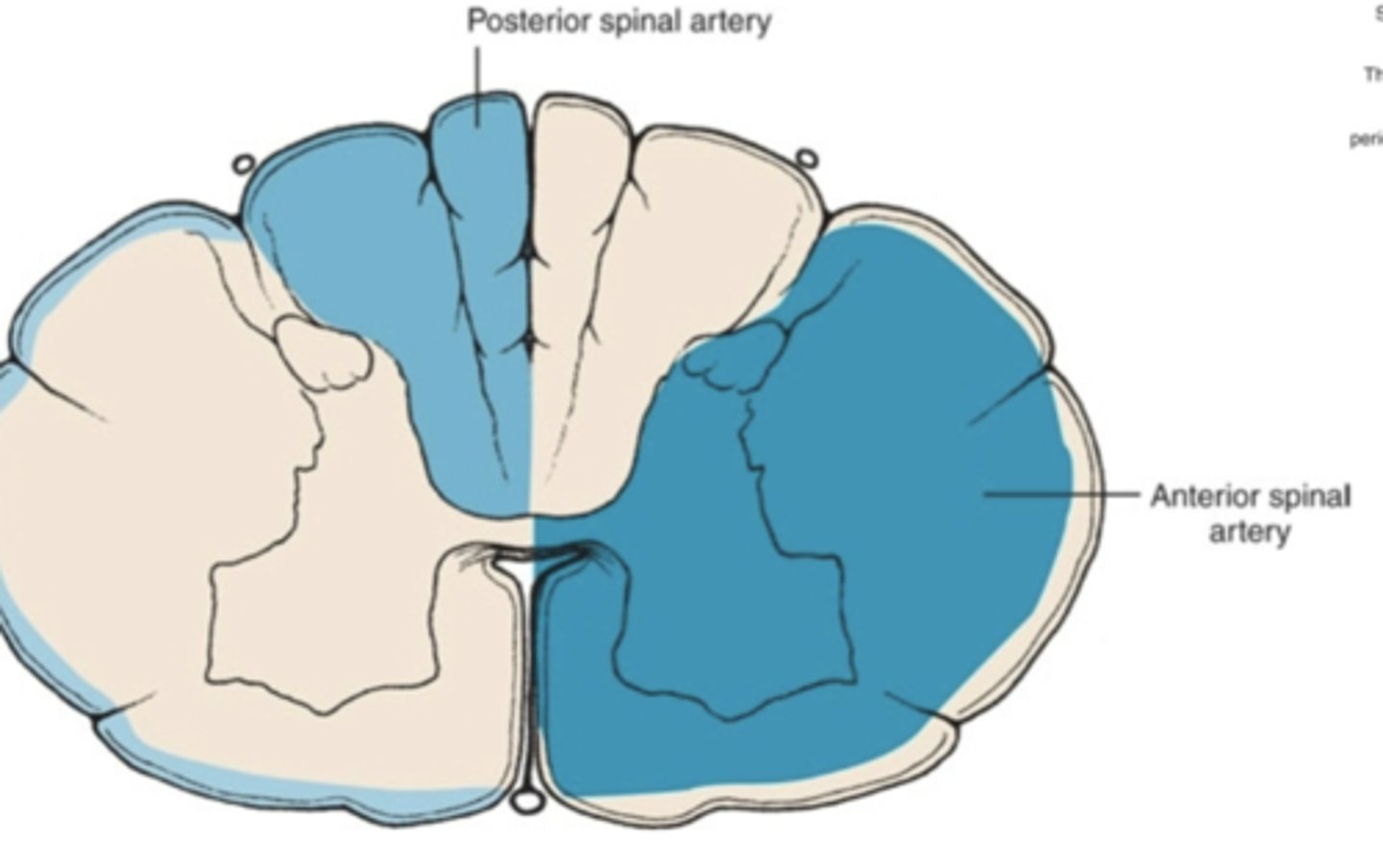
the anterior spinal artery gives blood supply to what part of the spinal cord?
anterior 2/3 of the spinal cord
(this will primarily be in the cervical part of the spinal cord)
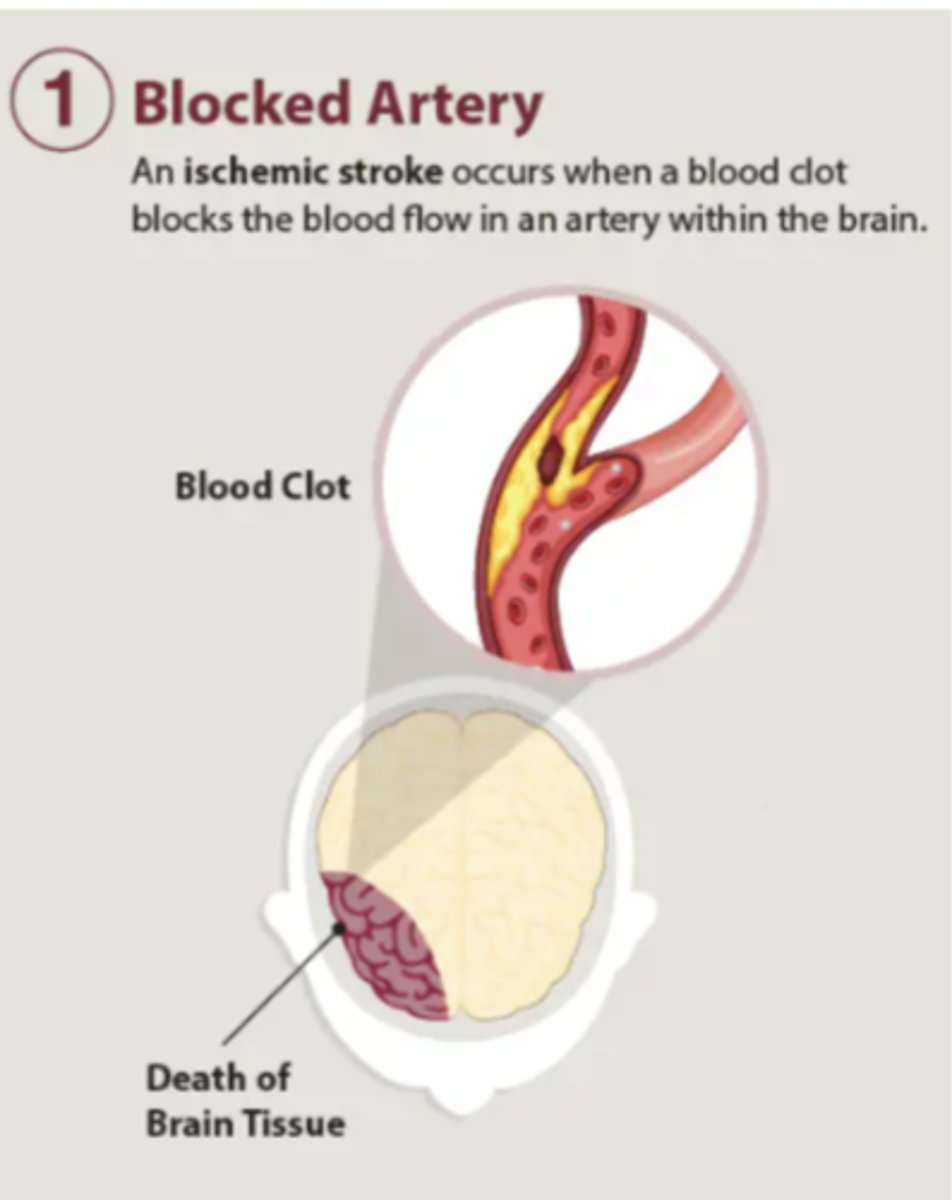
what is an ischemic stroke?
stroke caused by a blocked artery, most common after thrombus or atherosclerosis
85% of strokes
what is a hemorrhagic stroke?
stroke caused by rupture/leak of a weakened blood vessel; aneurysm
15% of strokes
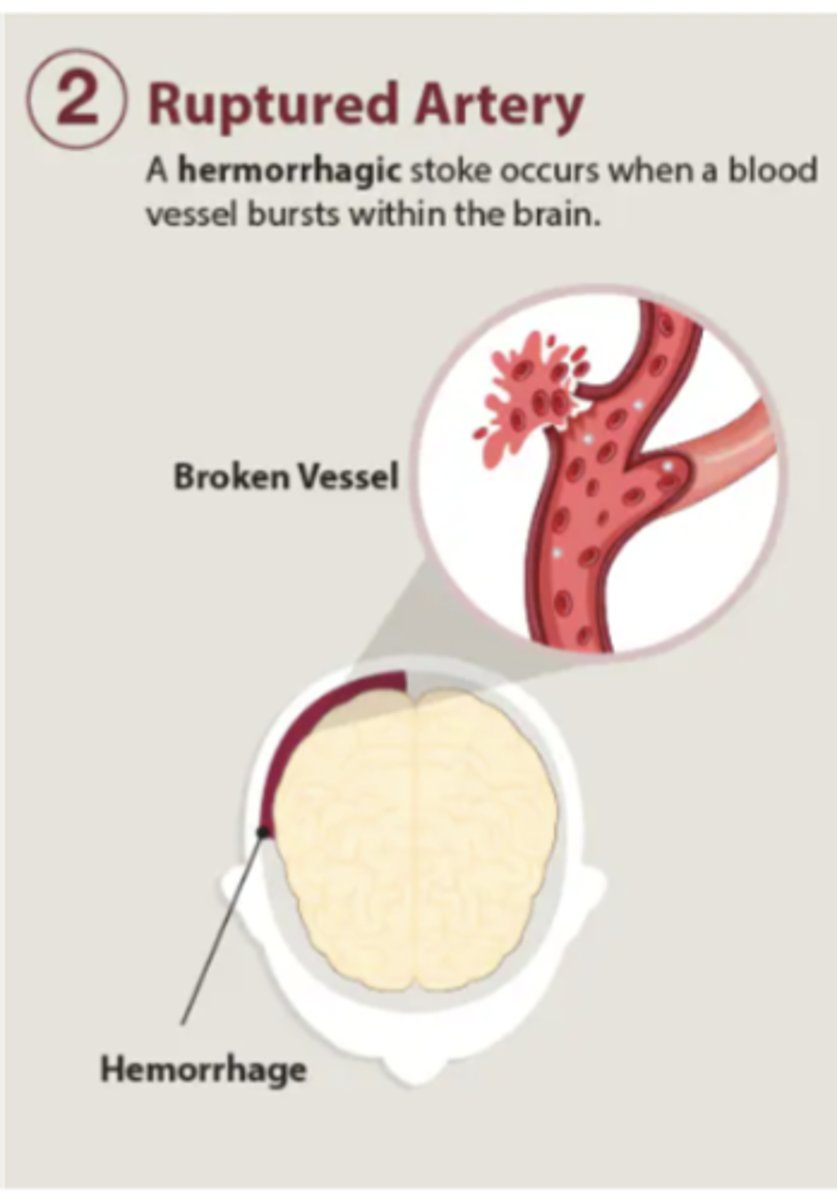
a hemorrhagic stroke can lead to a _______ in the brain
hematoma (blood filled space)
T/F: both ischemia or a hematoma in the blood can cause an infarct (brain damage)
true