Reproduction (copy)
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction without the use of another organism
Sexual reproduction
Reproduction with the use of another organism
Negatives of asexual reproduction
Lack of genetic variation
Negatives of sexual reproduction
Requires a mate, takes longer to produce offspring
Example of asexual reproduction
Yeast
Example of sexual reproduction
Animals
Male gamate in a plant
Pollen grains
Female gamate in a plant
Eggs or ova
What is a gamate?
Sex cell
Pollination
Male gamates are transferred to the female gamates
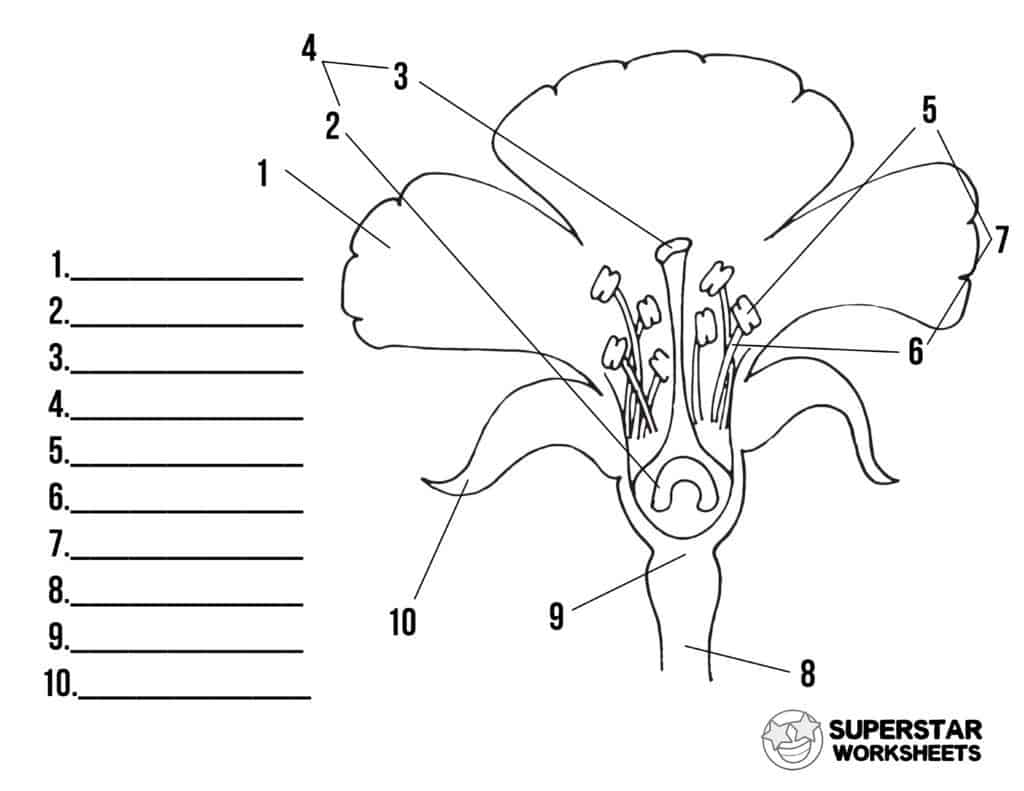
What is 1 and its function?
Petal, to encourage fertilisation
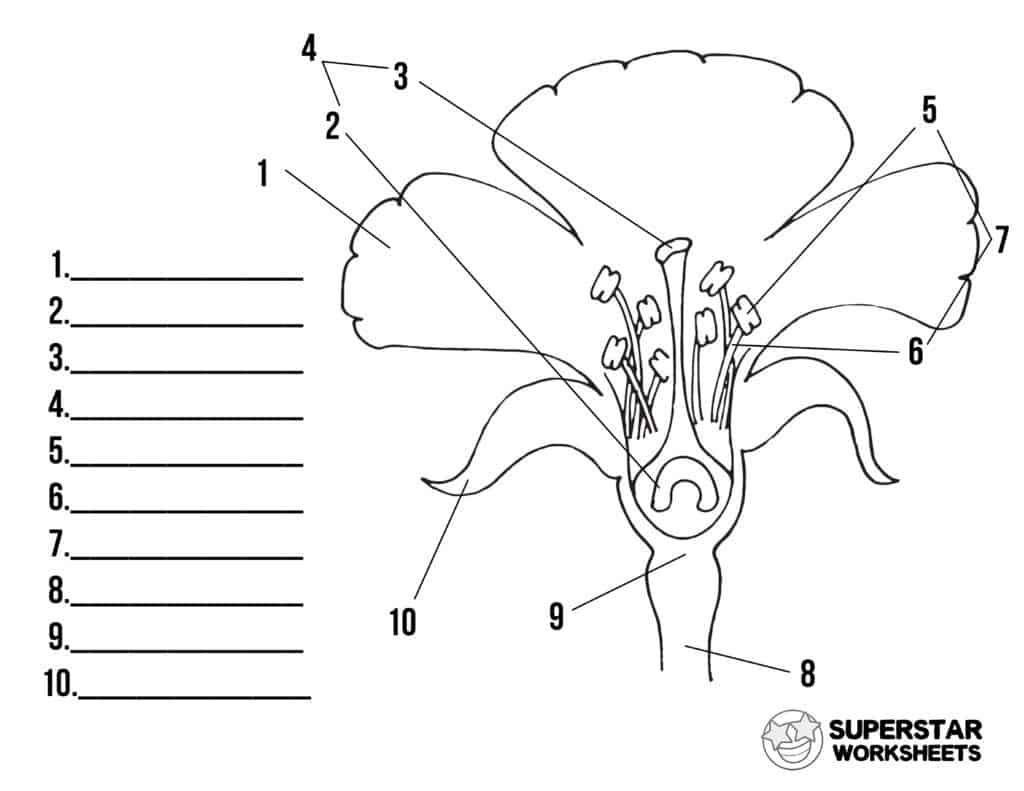
What is 2 and its function?
Ovary, stores the ovum
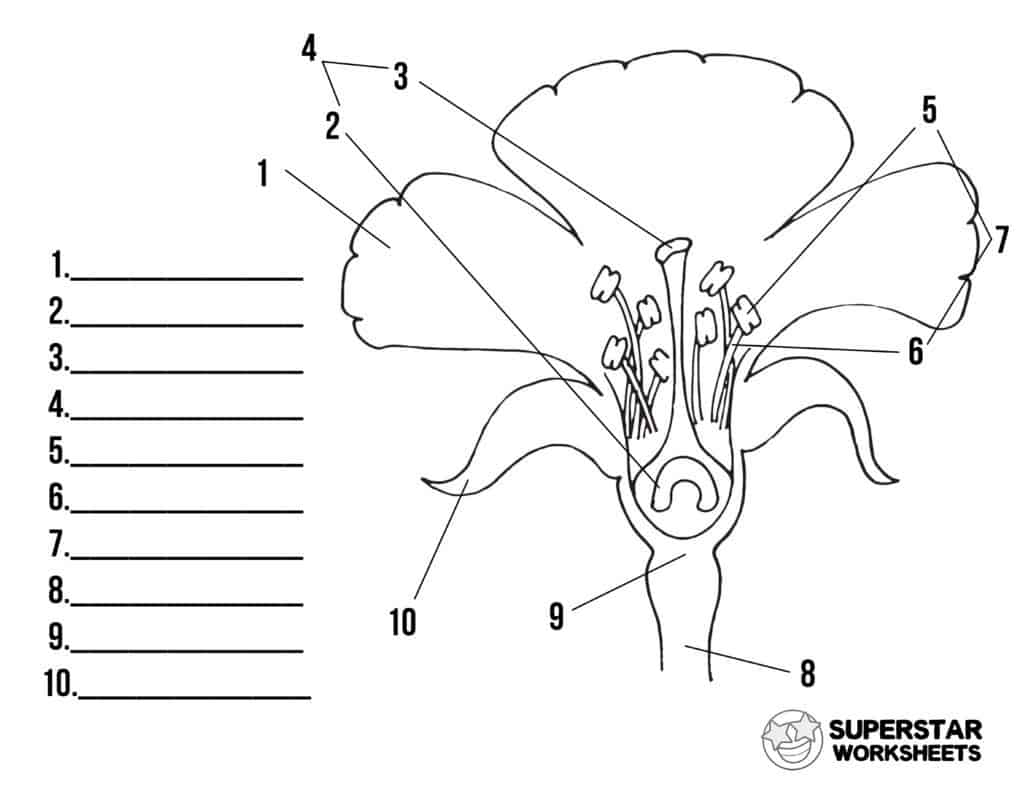
What is 3 and its function?
Stigma, sticky, receives the pollen grain
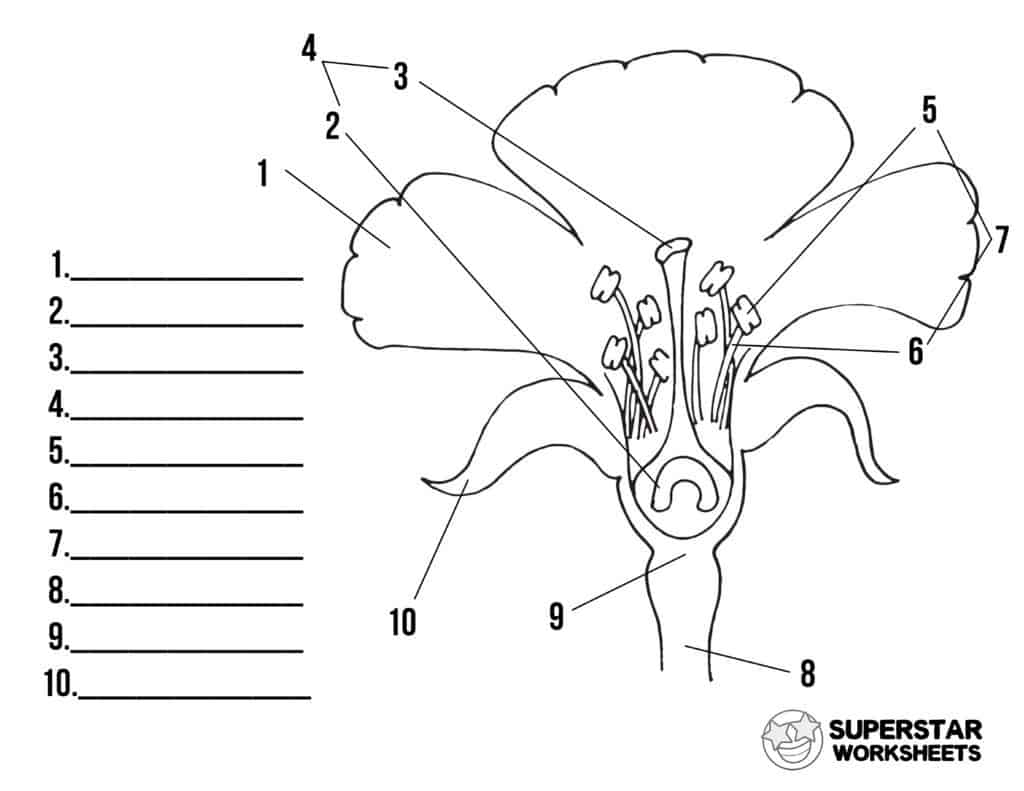
What is 5 and its function?
Anther, produces pollen grain
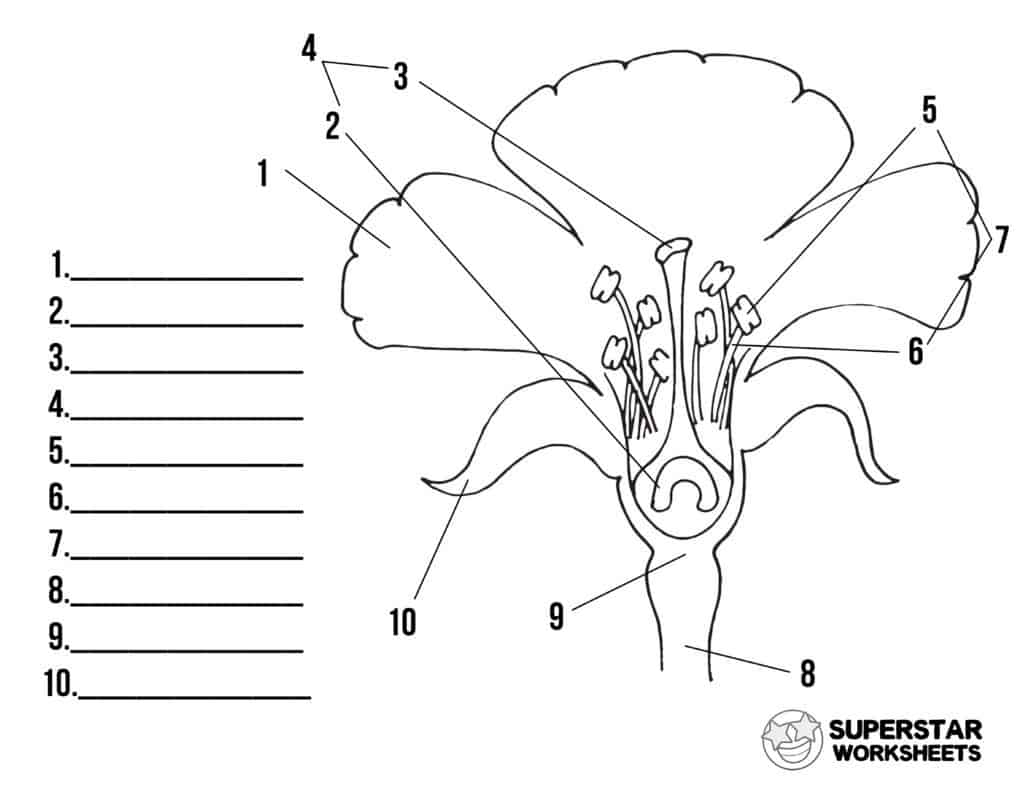
What is 6 and its function?
Filament, holds the anther
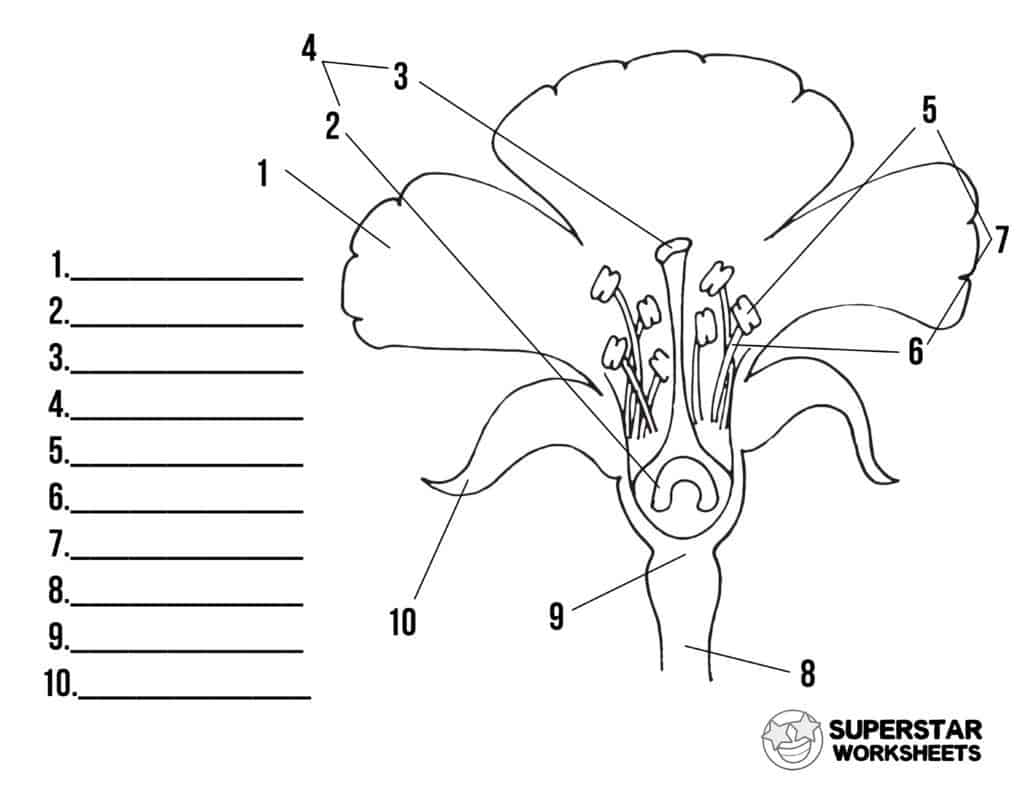
What is 8 and its function?
Stalk, hold up the flower
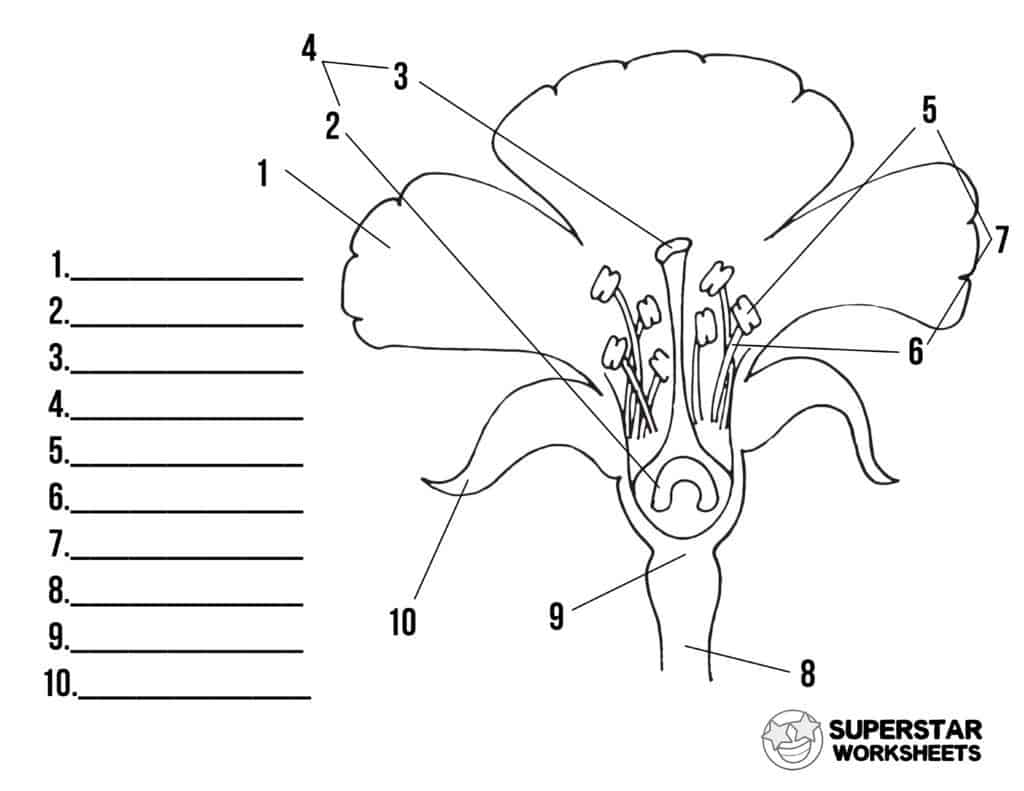
What is 9 and its function?
Receptacle, supports the flower
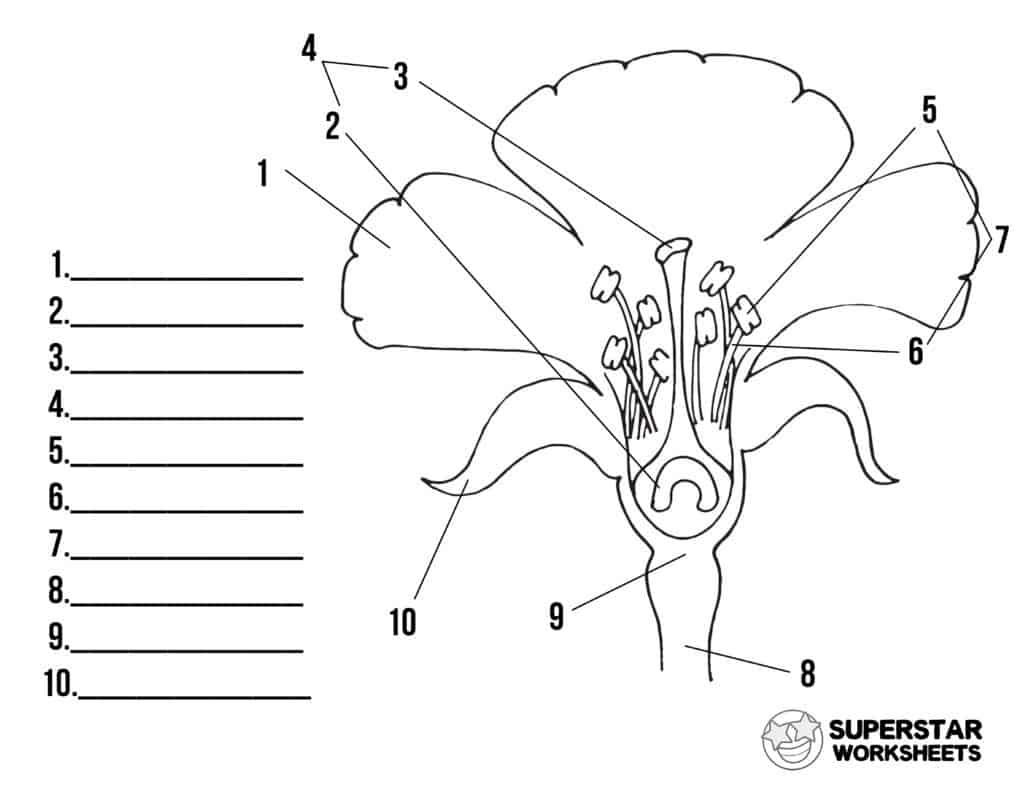
What is 10 and its function?
Speal, leaf like, protects the flower until it opens.
Characteristics of an insect pollinated plant
Large vibrant petals
Scent
Nectaries
Stamen inside the flower
Pistal inside the flower
Stigma is a long tube
Lots of pollen
Characteristics of a wind pollinated plant
Few, small, dull petals
No scent
No nactaries
Stamen outside the flower
Pistal inside the flower
Feathery stigma
Little pollen
Plant fertilisation
Pollen gran sticks to stigma (pollination)
Pollentube germinates from the pollen grain, down the style and enters the ovule via the micropyle
Pollen nucleus (male gamate) moves down the pollen tube
Pollen nucleus fuses with the egg cell in the ovule and forms a zygote (fertiliastion)
Germination
When seeds start to grow
Conditions for germination
Warm temp (for enzymes)
Water
Oxygen
Variables for germination practical
Independent - water, temp, oxygen
Dependent - germination (growth)
Control - type of seed, size of seed, amount of seeds
Runners
Natural method of cloning. Fast growing stems, clones of parent. No genetic variation
Cuttings
Artificial method of cloning. Cuttings then planted. No genetic variation
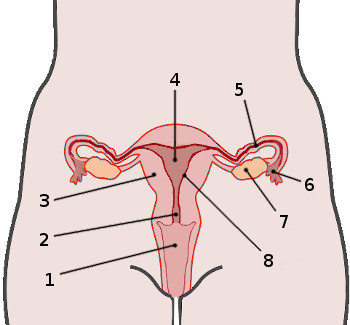
What is 1?
Vagina
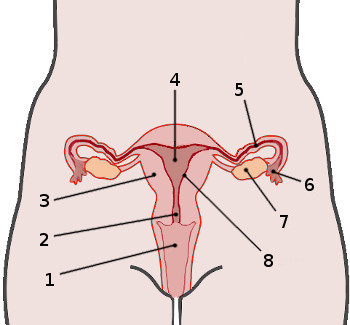
What is 2?
Cervix
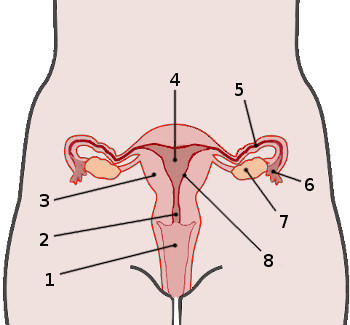
What is 4?
Uterus
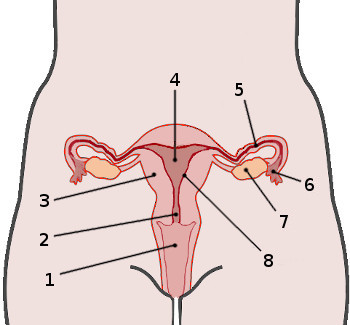
What is 5?
Fallopian tube
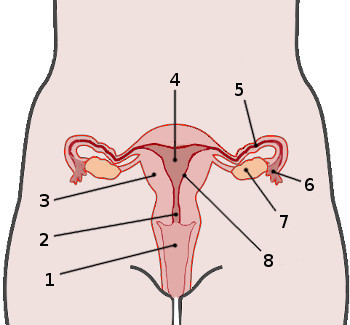
What is 7?
Ovaries
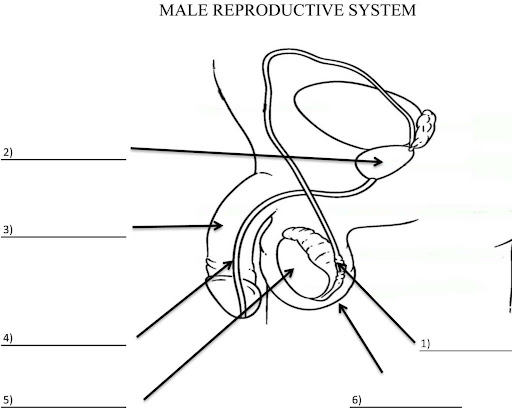
What is 2?
Prostate gland
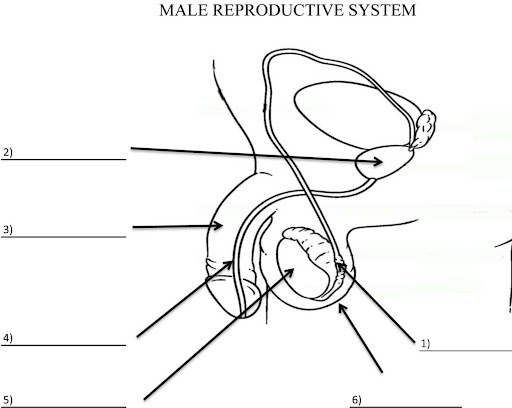
What is 3?
Penis
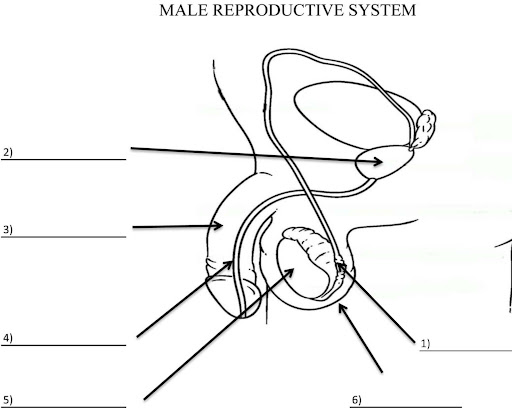
What is 4?
Ureathra
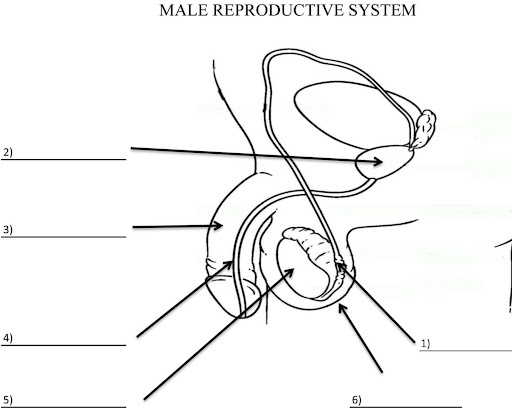
What is 5?
Testis
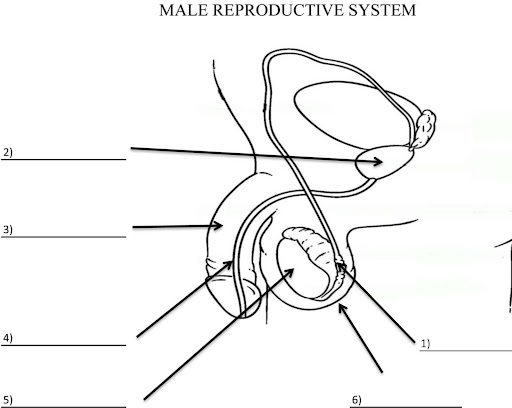
What is 6?
Scrotum
Where does the sperm cell fuse with the egg cell (fertilization)?
Fallopian tubes
Where is testosterone produced?
The testes
Where is oestrogen and progesterone produces?
The ovaries
What happens once a zygote is formed (humans?)
Divides multiple times to develop a ball of cell embryo which moves to uterus where it will implanted
What is foetus?
Emryo after 3 months
How long does it take for the placenta to develop?
3 months
What is the placenta?
Allow foetus to obtain oxygen + nutrience from the mother’s blood and removes waste products (CO2 and Urea), secrets progesterone
What is the amniotic fluid?
Protects the foetus from sudden movements and bumps and temp change
What does oestrogen do to women?
Pubic hair
Hips widen
Development of breasts
Ovum release and start of periods
What does testosterone do to men?
Facial and body hair
Muscles develop
Penis and testicles enlarge
Sperm production
Deepening of voice